一、二叉排序树:又称二叉查找树,当它不为空时,具有以下性质:
1)若他的左子树不为空,则左子树上所有结点的值均小于其根值。
2)若他的右子树不为空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于其根值。
3)他的左右子树也均为二叉排序树。
二、二叉排序树的插入和创建:
插入算法的基本思想
- 递归查找空位置:从根节点开始,比较插入值与当前节点值的大小:
- 若插入值 < 当前节点值 → 递归插入到左子树
- 若插入值 > 当前节点值 → 递归插入到右子树
- 找到空位置创建新节点:当递归到空节点时,在此处创建新节点并返回。
二叉排序树的创建:将结点一个个插入。
参考代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TNode{
int val;
TNode* lc;
TNode* rc;
TNode(int v):val(v),lc(NULL),rc(NULL){} //左右孩子
};
TNode* Insert(TNode*root,int value){ //插入函数
if(!root) //找到空结点则插入
root=new TNode(value);
else{ //递归
if(value<root->val)
root->lc=Insert(root->lc,value);
else
root->rc=Insert(root->rc,value);
}
return root;
}
void InOrder(TNode* root){ //中序遍历
if(root==NULL)
return ;
else{
InOrder(root->lc);
cout<<root->val<<" ";
InOrder(root->rc);
}
}
int main(){
TNode* root=NULL;
int n,i; //n:结点个数
int value;
cin>>n;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>value;
root=Insert(root,value); //构建二叉排序树
}
InOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
int t;
cin>>t; //插入t个数值
while(t--){
cin>>value;
root=Insert(root,value);
InOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
运行结果:
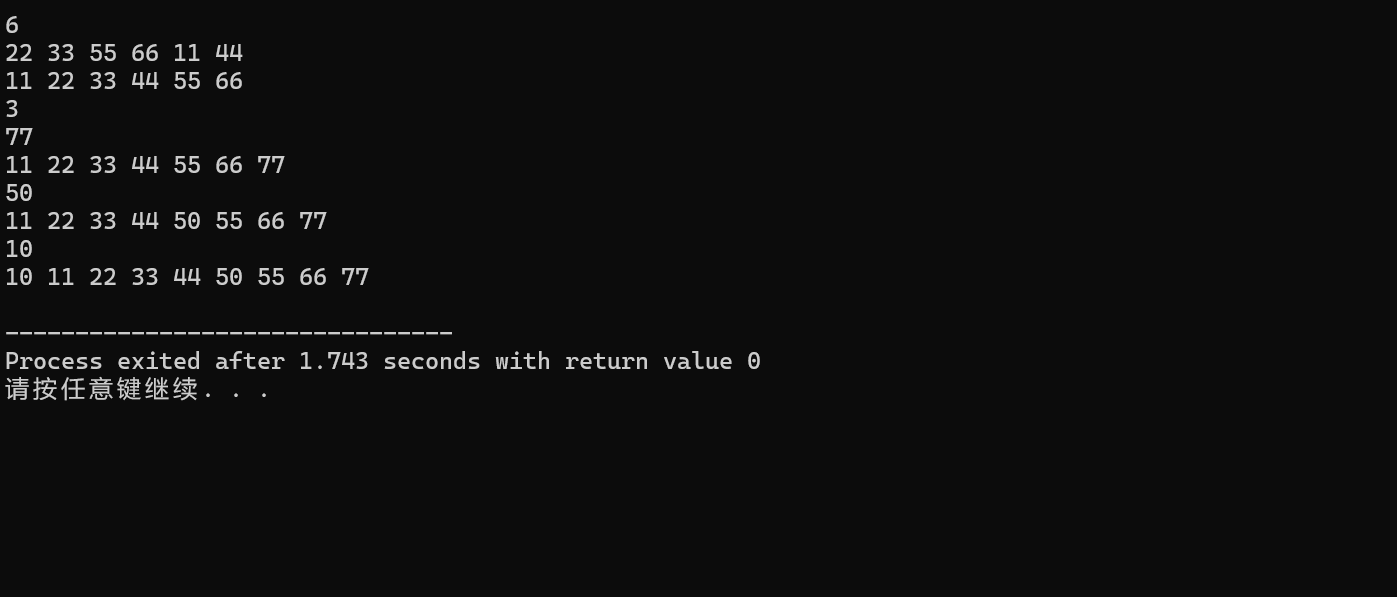
由此可知二叉排序树中序遍历的结果是升序的。
三、二叉排序树的查找算法:基本思想和插入算法类似
参考代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TNode{
int val;
TNode* lc;
TNode* rc;
TNode(int v):val(v),lc(NULL),rc(NULL){} //左右孩子
};
TNode* Insert(TNode*root,int value){ //插入函数
if(!root) //找到空结点则插入
root=new TNode(value);
else{ //递归
if(value<root->val)
root->lc=Insert(root->lc,value);
else
root->rc=Insert(root->rc,value);
}
return root;
}
bool Search(TNode* root,int& count,int key) { //查找算法
count++; //每查找一次count+1
if(!root) //结点为空在查找失败
return false;
else if(root->val==key)
return true;
else{ //递归
if(key<root->val){
return Search(root->lc,count,key);
}
else{
return Search(root->rc,count,key);
}
}
}
int main(){
TNode* root=NULL;
int n,i; //n:结点个数
int value;
cin>>n;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>value;
root=Insert(root,value); //构建二叉排序树
}
int t;
cin>>t; //查找次数
while(t--){
int key;
int count=0;
cin>>key;
if(Search(root,count,key)){
cout<<count; //查找成功则输出查找次数
}
else{
cout<<"false";
}
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
在处理大量数据时使用递归可能会导致栈溢出,也可以使用以下代码:
bool Search(TNode* root, int& count, int key) {
TNode* current = root;
while (current) {
count++;
if (key == current->val)
return true;
else if (key < current->val)
current = current->lc; //这里运用了迭代的思想
else
current = current->rc;
}
return false;
}
四、二叉树的删除算法:
删除结点有以下三种情况:
1)叶子结点
2)仅有左子树或右子树
3)有左子树和右子树
对于第三种情况,可以通过找到其左子树中最大的结点或者右子树中最小的结点来代替它
这里我们找左前驱结点:先找根结点的左结点,然后不停地寻找该节点的右节点直到右侧尽头,此时的结点就是左前驱结点(左子树中最大的结点),将该点的值赋给要删除的根结点,再将该点以情况二的方法进行删除
参考代码:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
struct TNode{
int val;
TNode* lc;
TNode* rc;
TNode(int v=0):val(v),lc(NULL),rc(NULL){} //左右孩子
};
TNode* Insert(TNode*root,int value){ //插入函数
if(!root) //找到空结点则插入
root=new TNode(value);
else{ //递归
if(value<root->val)
root->lc=Insert(root->lc,value);
else
root->rc=Insert(root->rc,value);
}
return root;
}
bool Delete(TNode* &root){ //这里需要用引用传参
TNode* p,*s;
if(!root->lc){ //只有右子树
p=root;
root=root->rc;
delete p;
}
else if(!root->rc){ //只有左子树
p=root;
root=root->lc;
delete p;
}
else{
p=root;
s=p->lc;
while(s->rc){
p=s;
s=s->rc;
} //通过循环找到root的直接前驱
if(p!=root){
root->val=s->val;
p->rc=s->lc;
delete s;
}
else{
root->val=s->val;
p->lc=s->lc;
delete s;
}
}
return true;
}
bool DeleteBST(TNode* &root,int key){
if(!root)
return false;
else if(root->val==key)
return Delete(root);
else{
if(key>root->val){
return DeleteBST(root->rc,key);
}
else{
return DeleteBST(root->lc,key);
}
}
}
void InOrder(TNode* root){ //中序遍历
if(root==NULL)
return ;
else{
InOrder(root->lc);
cout<<root->val<<" ";
InOrder(root->rc);
}
}
int main(){
TNode* root=NULL;
int n,i; //n:结点个数
int value;
cin>>n;
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
cin>>value;
root=Insert(root,value); //构建二叉排序树
}
InOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
int t;
cin>>t; //删除的次数
while(t--){
int key;
cin>>key;
DeleteBST(root,key);
InOrder(root);
cout<<endl;
}
return 0;
}




















 3141
3141

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








