1、二叉树创建:
使用递归的思想,先创建头结点,然后再调用创建二叉树的函数创建左右子树。
存储结构:
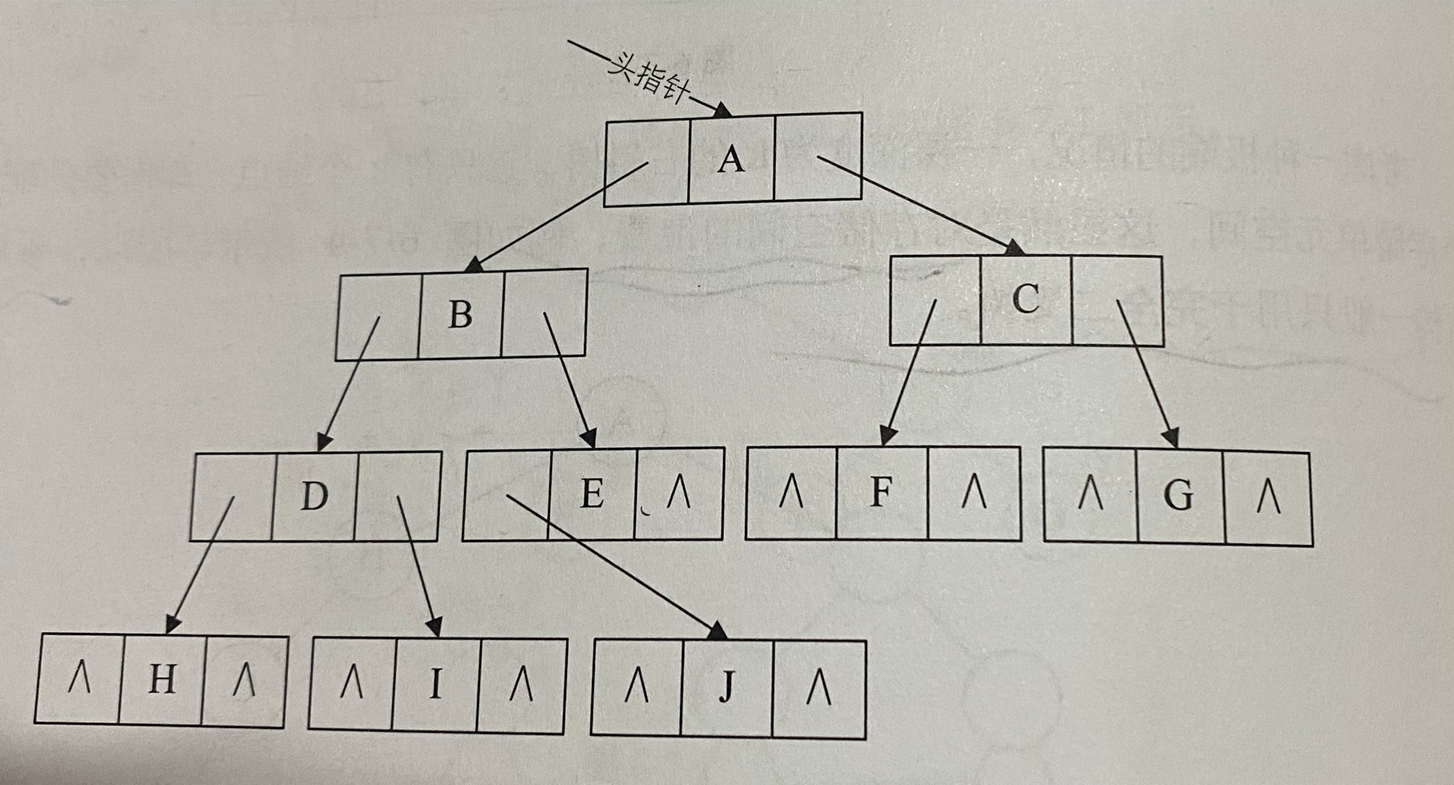
2、遍历:
1)前序遍历:
- 顺序:根节点→左子树→右子树
- 实现:递归或栈模拟,先访问根节点,再递归遍历左右子树
2)中序遍历:
- 顺序:左子树→根节点→右子树
- 实现:递归或栈模拟,中序遍历二叉搜索树可得有序序列。
3) 后序遍历:
- 顺序:左子树→右子树→根节点
- 实现:递归或栈模拟,常用于释放树节点内存(后序释放避免悬空指针)。
4) 层次遍历:
- 顺序:按层从上到下、从左到右访问节点
- 实现:队列辅助,根节点入队,每次出队时访问并将子节点入队,直至队列为空。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct TNode{ //二叉树结点
char cc;
TNode*lc;
TNode*rc;
};
TNode* CreatT(string& str){ //根据输入的字符串str 创建二叉树
if(str.empty())
return NULL;
else if(str[0]=='0'){
str.erase(str.begin()); //若字符为'0’则为空结点,删除首元素并返回空指针
return NULL;
}
else{
TNode*root=new TNode;
root->cc=str[0];
str.erase(str.begin()); //删去首元素,使用递归构建当前结点的左右子树
root->lc=CreatT(str);
root->rc=CreatT(str);
return root;
}
}
void preOrder(TNode*root,string&ss){ //前序遍历,使用ss来存储遍历结果
if(root){
ss+=root->cc;
preOrder(root->lc,ss); //根->左->右
preOrder(root->rc,ss);
}
}
void inOrder(TNode*root,string&ss){ //中序遍历,使用ss来存储遍历结果
if(root){
inOrder(root->lc,ss);
ss+=root->cc; //左->根->右
inOrder(root->rc,ss);
}
}
void posOrder(TNode*root,string&ss){ //后序遍历,使用ss来存储遍历结果
if(root){
posOrder(root->lc,ss);
posOrder(root->rc,ss); //左->右->根
ss+=root->cc;
}
}
void leverOrder(TNode*root,string&ss){ //层次遍历,使用ss来存储遍历结果
if (root) {
queue<TNode*>q; //使用队列来进行分层
q.push(root); //先将首结点压入队列
while(!q.empty()){
TNode*current=q.front(); //取队列中最前面的结点并将其子节点压入
q.pop();
if(current->lc)
q.push(current->lc);
if(current->rc)
q.push(current->rc);
ss+=current->cc;
}
}
}
void destroyTree(TNode* root) { //释放空间
if(root == NULL) return;
destroyTree(root->lc);
destroyTree(root->rc); //递归思想
delete root;
}
int main(){
int t;
cin>>t;
while(t--){
string result;
cin>>result;
TNode*tt=CreatT(result);
string pres;
preOrder(tt,pres);
string ins;
inOrder(tt,ins);
string poss;
posOrder(tt,poss);
string levs;
leverOrder(tt,levs);
cout<<pres<<endl;
cout<<ins<<endl;
cout<<poss<<endl;
cout<<levs<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
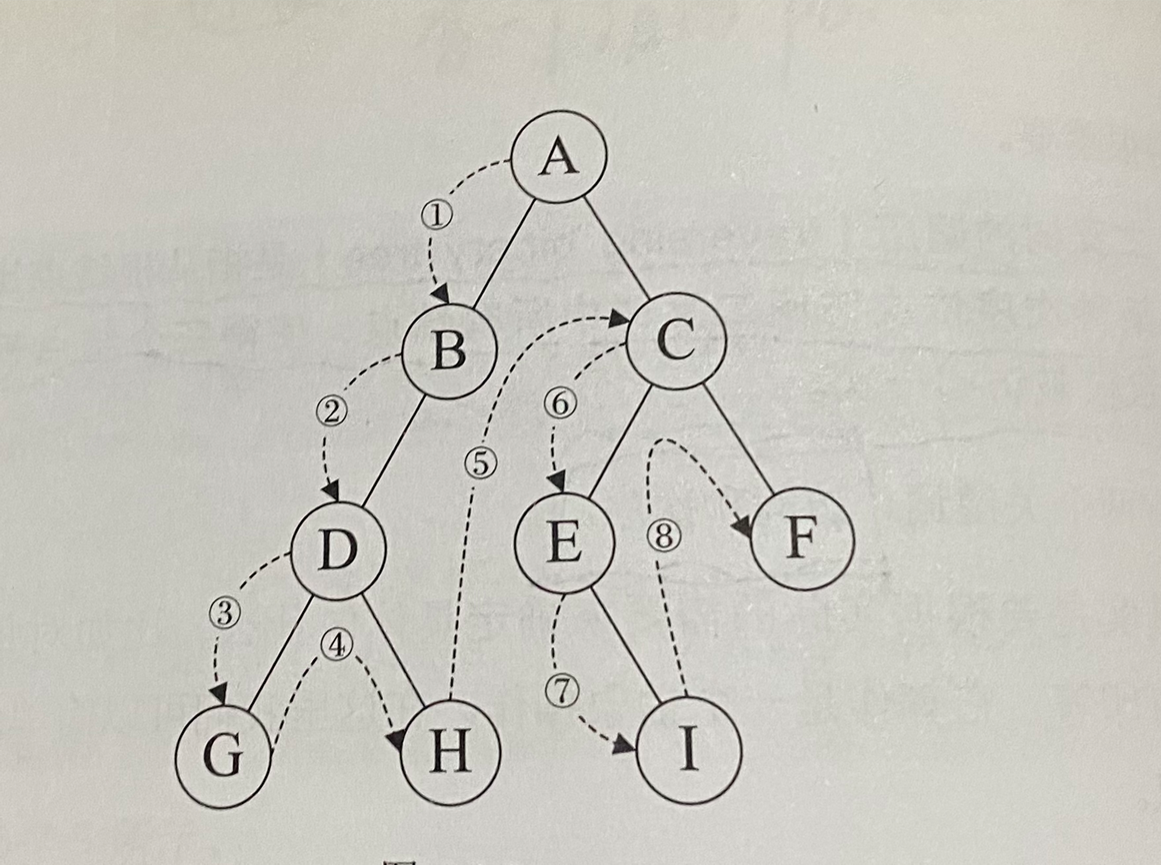
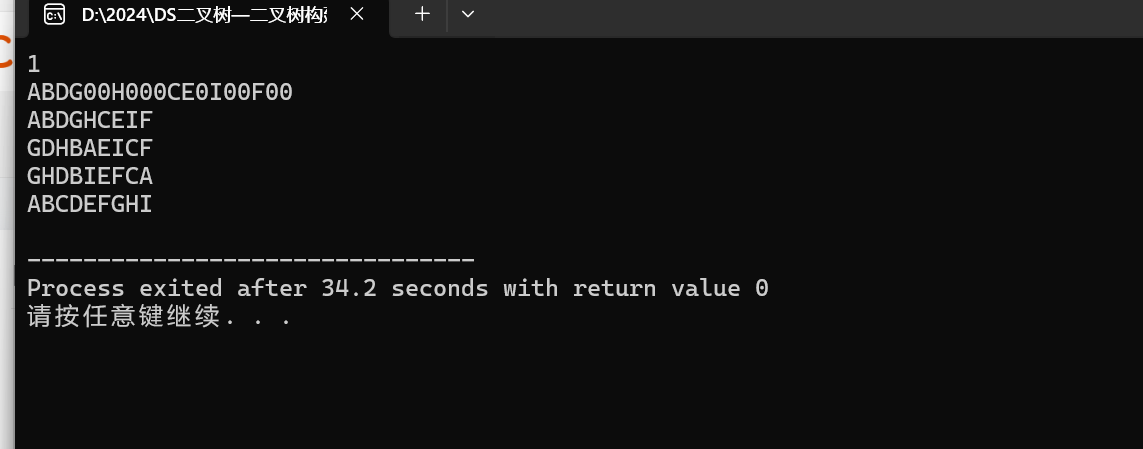
案例示范:构建下面的树并输出结果:




















 631
631

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








