39. 组合总和
candidates 的所有元素互不相同,且不会有 0
和组合问题的差异:
- 树的下一层还可以选本节点的数(一个元素可以重复多次选),但不能选之前的树(防止组合重复)
- 用组合的和限制深度
易错点:
递归是 backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i),不是 backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i + 1),因为可重复选。
也不是 backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], startIndex);
剪枝:
先排序,如果进入下一层递归会导致 target < 0,那么就没必要进入下一层递归了。
同时由于已排序,所以下一层递归的兄弟节点也不用遍历了。
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum(int[] candidates, int target) {
Arrays.sort(candidates); // 先排序
backtrack(candidates, target, 0);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int startIndex) {
if (target < 0) {
return;
}
if (target == 0) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (target - candidates[i] < 0) { // 剪枝
return;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
backtrack(candidates, target - candidates[i], i);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
40. 组合总和 II
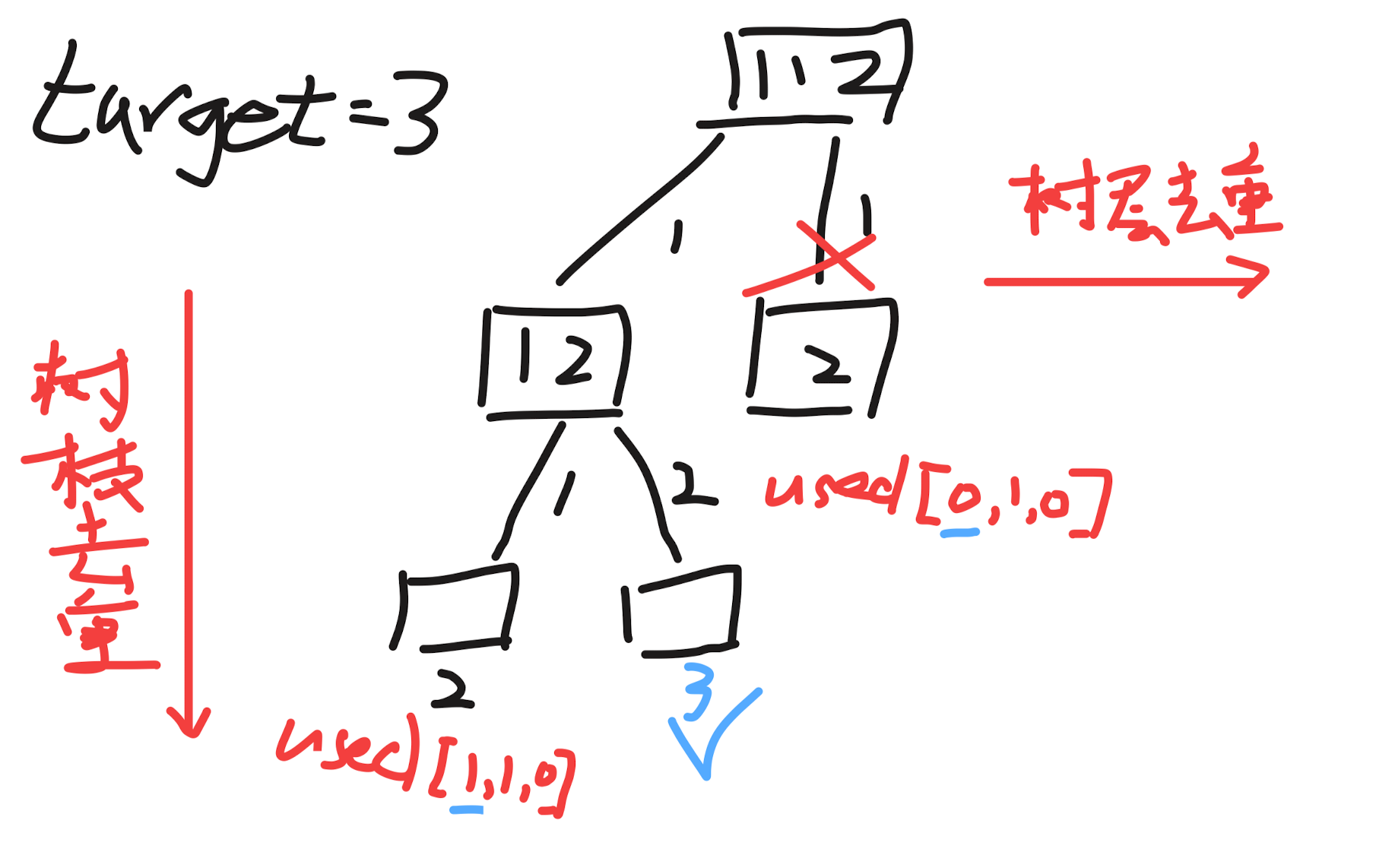
boolean[] used:
used[i - 1] = true是树枝重used[i - 1] = false是树层重
要进行树层去重,不用树枝去重
去重条件:和前一位元素相等,但前一位未被使用过(说明是树层去重)
用一个 used 数组表示是否使用过
class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> combinationSum2(int[] candidates, int target) {
int n = candidates.length;
boolean[] used = new boolean[n];
Arrays.sort(candidates); // 先排序!
backtrack(candidates, target, 0, 0, used);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(int[] candidates, int target, int sum, int startIndex, boolean[] used) {
if (sum > target) {
return;
}
if (sum == target) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < candidates.length; i++) {
if (i > 0 && candidates[i] == candidates[i - 1] && used[i - 1] == false) { // 去重
continue;
}
path.add(candidates[i]);
used[i] = true;
backtrack(candidates, target, sum + candidates[i], i + 1, used);
used[i] = false;
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
131. 分割回文串
子串就是 [startIndex, i],左闭右闭区间。
回文:palindrome
class Solution {
List<String> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<String>> result = new ArrayList<>();
public List<List<String>> partition(String s) {
backtrack(s, 0);
return result;
}
public void backtrack(String s, int startIndex) {
if (startIndex == s.length()) {
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return; // 注意这里要 return,否则代码逻辑正确,但可能在 lc 多线程测评机制下错误。
}
for (int i = startIndex; i < s.length(); i++) {
String subStr = s.substring(startIndex, i + 1); // Java subString 是左闭右开
if (isPalindrome(subStr)) { // 左闭右闭区间
path.add(subStr);
} else {
continue;
}
backtrack(s, i + 1);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
public boolean isPalindrome(String str) {
int left = 0;
int right = str.length() - 1;
for (; left < right; left++, right--) {
if (str.charAt(left) != str.charAt(right)) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
优化:判断是否是回文子串时,用动态规划或记忆化搜索。见官方题解。
额外发现:如果忘记 return,虽然逻辑上正确,不会进入 for 循环。但是 leetcode 评测失败。
为什么在 LeetCode 上会错
LeetCode 的评测环境有几点差异:
- 多线程 / 多用例复用机制
- LeetCode 的后端执行器可能在不同用例之间复用同一个
Solution实例(即同一个对象),而不是每次都重新 new。- 如果你没写
return,那意味着回溯结束后仍可能继续往下执行某些语句(例如 for 循环之后的逻辑、栈帧未清理完全),- 当评测机在快速切换到下一个用例时,
path或result里的数据还没被完全清理,会出现交叉污染。- LeetCode 的输入数据验证非常严格
- 当递归逻辑没有明确的
return,有些 JVM 优化器或 LeetCode 的在线执行器会提前优化或延迟清理局部变量栈;- 这可能导致在特定输入(比如空字符串
""或只有一个字符"a")时,result.add()被调用多次或被漏掉。- JVM 优化差异(解释器 vs JIT 编译器)
- 本地 IDEA 默认使用 JIT(即时编译优化),递归返回条件在字节码层面被优化;
- LeetCode 运行环境更接近“解释执行”,不会进行相同的优化;
- 导致无
return时的控制流略有不同。
回溯法总结
三部曲
- 函数参数返回值
- 确定终止条件
- 单层搜索逻辑
backtrack(..., startIndex):
for 循环内部递归时,如果不能重复选自己,就是 backtrack(..., i + 1);如果可以,就是 backtrack(..., i)





















 739
739

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








