203. 移除链表元素
重点:
设置哑节点 dummyHead,以便统一对要移除元素是否是头节点的操作
易错点:
最后要返回 dummyHead.next 而不是 head,因为 head 有可能已经被删除
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode dummyHead = new ListNode();
dummyHead.next = head;
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
while (cur.next != null) {
if (cur.next.val == val) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
} else {
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return dummyHead.next;
}
}
// TODO: 递归方法
707. 设计链表
重点:
- 再创建一个
ListNode类很有必要,MyLinkedList只添加成员变量size和dummyHead - 要找到第 n 个节点,则必须使第 n 个节点为
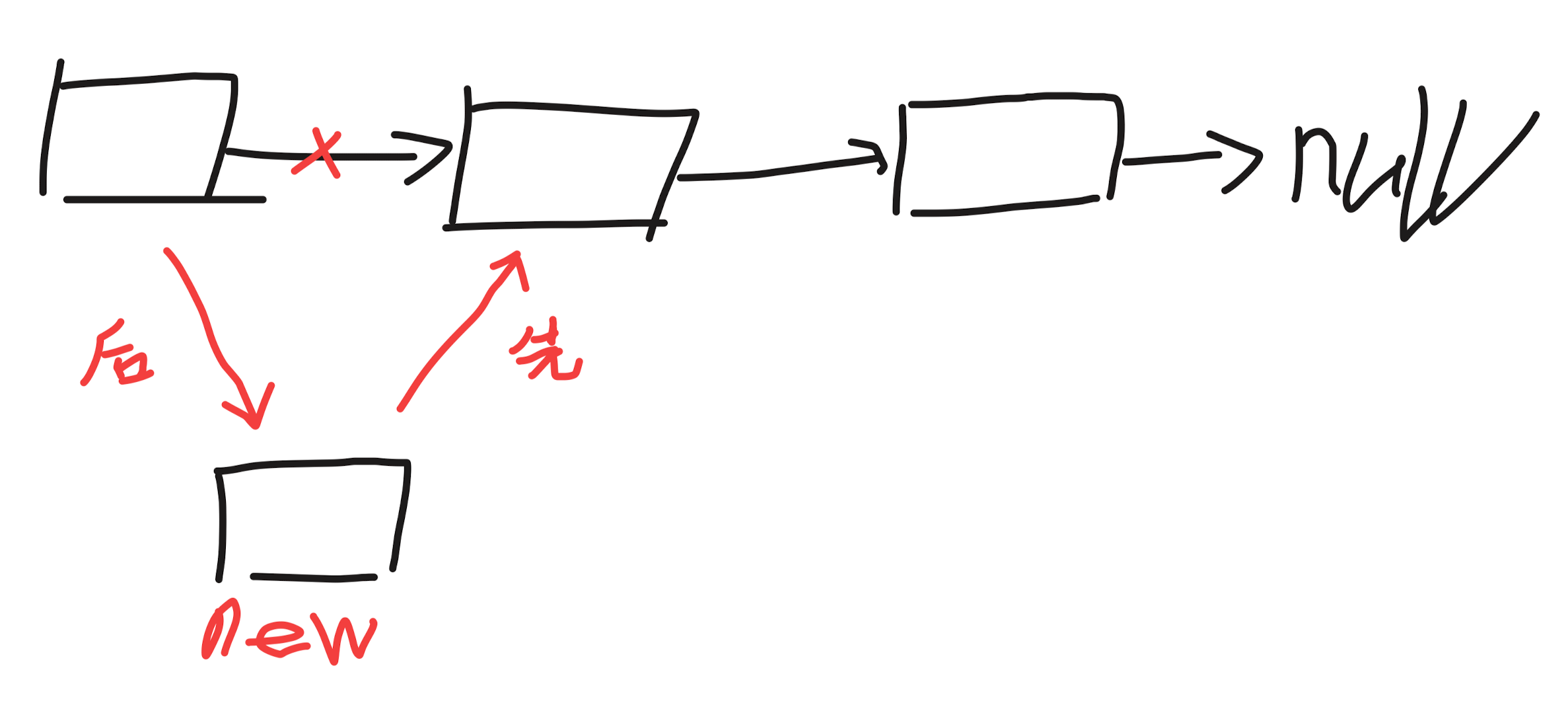
cur.next,也就是使cur指向第 n - 1 个节点 - 增加节点时,先修改右边的,再修改左边的。可以省去创建一个临时变量保存,如图:
易错点:
- 每次增加或删除节点后,
size也要同步增或减 addAtIndex的index范围是0 ~ size(size相当于在末尾添加)
deleteAtIndex的index范围是0 ~ size - 1
class MyLinkedList {
class ListNode {
public int val;
public ListNode next;
public ListNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) {
this.val = val;
this.next = next;
}
}
int size;
ListNode dummyHead;
public MyLinkedList() {
dummyHead = new ListNode(0);
}
public int get(int index) {
if (index >= size || index < 0) {
return -1;
}
int n = index;
ListNode cur = dummyHead.next;
for (; n > 0; n--) {
cur = cur.next;
}
return cur.val;
}
public void addAtHead(int val) {
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = dummyHead.next;
dummyHead.next = newNode;
size++;
}
public void addAtTail(int val) {
addAtIndex(size, val);
}
public void addAtIndex(int index, int val) {
int n = index;
if (n < 0 || n > size) {
return;
}
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
for (; n > 0; n--) {
cur = cur.next;
}
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(val);
newNode.next = cur.next;
cur.next = newNode;
size++;
}
public void deleteAtIndex(int index) {
int n = index;
if (n < 0 || n >= size) {
return;
}
ListNode cur = dummyHead;
for (; n > 0; n--) {
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = cur.next.next;
size--;
}
}
206. 反转链表
思路:双指针。cur 指向 head,pre 指向 null,同时用一个临时变量 temp 保存 cur.next。最终 cur 指向 null,返回 pre 即可。
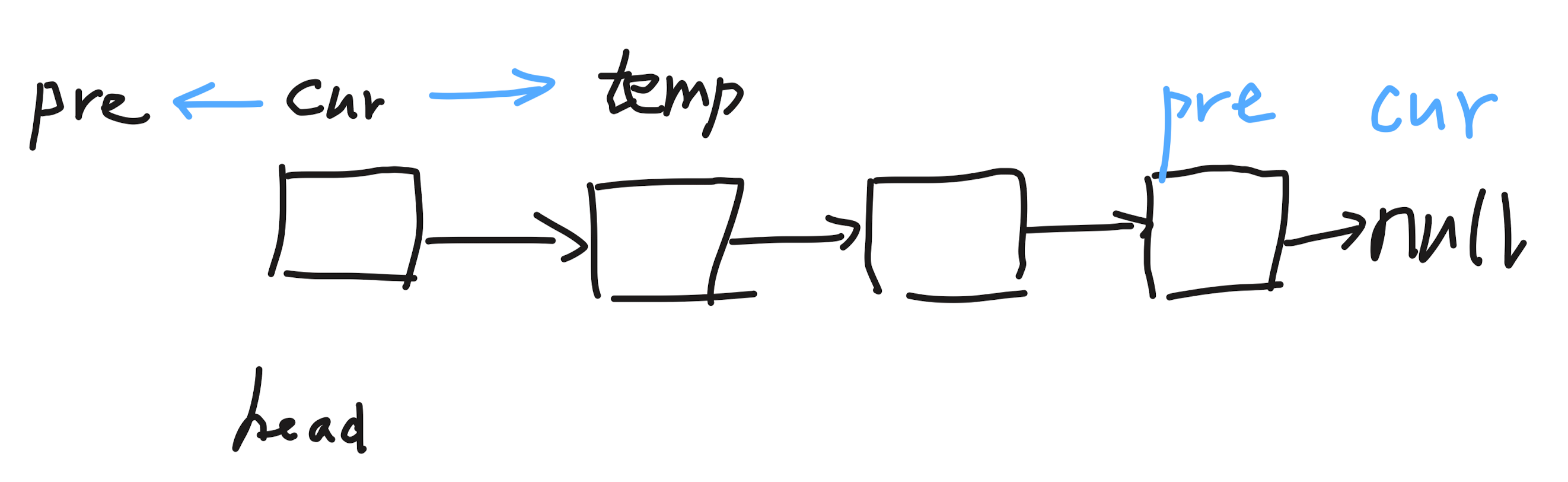
双指针:
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head;
ListNode pre = null;
for (; cur != null;) {
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = temp;
}
return pre;
}
}
代码随想录递归写法:
其实就是对照着迭代法改的
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(head, null);
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode cur, ListNode pre) {
if (cur == null) {
return pre;
}
ListNode temp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
return reverse(temp, cur);
}
}
// TODO 官解递归写法:
有点云里雾里
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
// 如果当前节点为空或者只有一个节点,直接返回该节点(递归终止条件)
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
// 递归调用,将当前节点的下一个节点作为新的头节点
ListNode newHead = reverseList(head.next);
// 将当前节点的下一个节点指向当前节点(反转指针方向)
head.next.next = head;
// 将当前节点的 next 指向 null(防止形成环)
head.next = null;
// 返回新头节点
return newHead;
}
递归过程示例
以链表 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4 -> 5 为例:
reverseList(1)调用reverseList(2)reverseList(2)调用reverseList(3)reverseList(3)调用reverseList(4)reverseList(4)调用reverseList(5)reverseList(5)返回5(因为5.next == null)
然后开始回溯:
reverseList(4)中,4.next.next = 4→5 -> 4,然后4.next = null→5 -> 4reverseList(3)中,3.next.next = 3→5 -> 4 -> 3,然后3.next = null→5 -> 4 -> 3reverseList(2)中,2.next.next = 2→5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2,然后2.next = null→5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2reverseList(1)中,1.next.next = 1→5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1,然后1.next = null→5 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2 -> 1
最终返回 5。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








