1. Run a few randomly-generated problems with just two jobs and
two queues; compute the MLFQ execution trace for each. Make
your life easier by limiting the length of each job and turning off
I/Os.
运行一些随机产生的问题(?):两个job,两个队列,限制每个job的长度,不进行io,计算mlfq的运行轨迹
andy@LAPTOP-B6LCN2OM:~/HW-MLFQ$ ./mlfq.py -j 2 -n 2 -m 5 -M 0 -c
Here is the list of inputs:
OPTIONS jobs 2
OPTIONS queues 2
OPTIONS allotments for queue 1 is 1
OPTIONS quantum length for queue 1 is 10
OPTIONS allotments for queue 0 is 1
OPTIONS quantum length for queue 0 is 10
OPTIONS boost 0
OPTIONS ioTime 5
OPTIONS stayAfterIO False
OPTIONS iobump False
For each job, three defining characteristics are given:
startTime : at what time does the job enter the system
runTime : the total CPU time needed by the job to finish
ioFreq : every ioFreq time units, the job issues an I/O
(the I/O takes ioTime units to complete)
Job List:
Job 0: startTime 0 - runTime 4 - ioFreq 0
Job 1: startTime 0 - runTime 2 - ioFreq 0
Execution Trace:
[ time 0 ] JOB BEGINS by JOB 0
[ time 0 ] JOB BEGINS by JOB 1
[ time 0 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 1 [ TICKS 9 ALLOT 1 TIME 3 (of 4) ]
[ time 1 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 1 [ TICKS 8 ALLOT 1 TIME 2 (of 4) ]
[ time 2 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 1 [ TICKS 7 ALLOT 1 TIME 1 (of 4) ]
[ time 3 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 1 [ TICKS 6 ALLOT 1 TIME 0 (of 4) ]
[ time 4 ] FINISHED JOB 0
[ time 4 ] Run JOB 1 at PRIORITY 1 [ TICKS 9 ALLOT 1 TIME 1 (of 2) ]
[ time 5 ] Run JOB 1 at PRIORITY 1 [ TICKS 8 ALLOT 1 TIME 0 (of 2) ]
[ time 6 ] FINISHED JOB 1
Final statistics:
Job 0: startTime 0 - response 0 - turnaround 4
Job 1: startTime 0 - response 4 - turnaround 6
Avg 1: startTime n/a - response 2.00 - turnaround 5.002. How would you run the scheduler to reproduce each of the examples in the chapter?
如何使用这个模拟器复现书中的一些例子?
简单起见,这里选择的是书中第一个例子:
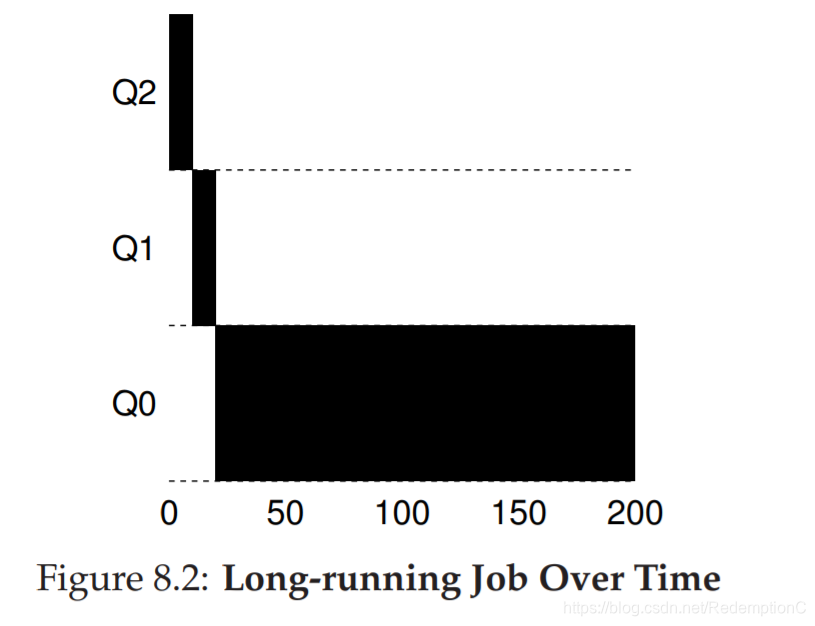
如图:一个job,三级队列,0时进入,耗时200(为了答案比较简单,这里设置运行时间为10),不进行io
其中-a选项规定了每个队列的分配时间为1,-q选项规定了每个队列的时间片大小为1
andy@LAPTOP-B6LCN2OM:~/HW-MLFQ$ ./mlfq.py -l 0,10,0 -c -a 1 -q 1
Here is the list of inputs:
OPTIONS jobs 1
OPTIONS queues 3
OPTIONS allotments for queue 2 is 1
OPTIONS quantum length for queue 2 is 1
OPTIONS allotments for queue 1 is 1
OPTIONS quantum length for queue 1 is 1
OPTIONS allotments for queue 0 is 1
OPTIONS quantum length for queue 0 is 1
OPTIONS boost 0
OPTIONS ioTime 5
OPTIONS stayAfterIO False
OPTIONS iobump False
For each job, three defining characteristics are given:
startTime : at what time does the job enter the system
runTime : the total CPU time needed by the job to finish
ioFreq : every ioFreq time units, the job issues an I/O
(the I/O takes ioTime units to complete)
Job List:
Job 0: startTime 0 - runTime 10 - ioFreq 0
Execution Trace:
[ time 0 ] JOB BEGINS by JOB 0
[ time 0 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 2 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 9 (of 10) ]
[ time 1 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 1 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 8 (of 10) ]
[ time 2 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 7 (of 10) ]
[ time 3 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 6 (of 10) ]
[ time 4 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 5 (of 10) ]
[ time 5 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 4 (of 10) ]
[ time 6 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 3 (of 10) ]
[ time 7 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 2 (of 10) ]
[ time 8 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 1 (of 10) ]
[ time 9 ] Run JOB 0 at PRIORITY 0 [ TICKS 0 ALLOT 1 TIME 0 (of 10) ]
[ time 10 ] FINISHED JOB 0
Final statistics:
Job 0: startTime 0 




 本文探讨了如何使用模拟器来实现和分析多级反馈队列(MLFQ)调度器。通过调整参数,模拟RR调度器,以及研究如何通过特定工作负载使一个任务在特定时间内获得99%的CPU资源。还讨论了如何保证长时间运行的任务至少获得5%的CPU,并分析了在不同I/O处理策略下对队列的影响。
本文探讨了如何使用模拟器来实现和分析多级反馈队列(MLFQ)调度器。通过调整参数,模拟RR调度器,以及研究如何通过特定工作负载使一个任务在特定时间内获得99%的CPU资源。还讨论了如何保证长时间运行的任务至少获得5%的CPU,并分析了在不同I/O处理策略下对队列的影响。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1220
1220

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








