1 storage
我们主要关注的是disk-oriented DBMS,即DB是存在disk上的
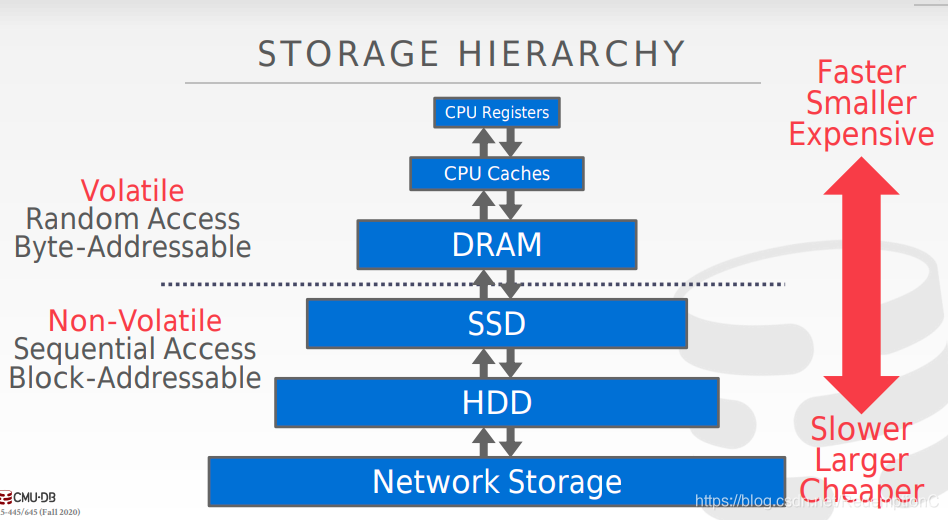
Volatile:
- 断电就 失去保存的内容
- 支持高速随机存取,byte-addressable
- 我们统称为memory
Non-Volatile:
- 不需要通电也能保存数据
- block/page addressable
- 对顺序存取支持更好
- 统称为disk,一般本课不会去区分SSD和HDD
当前还有一种正在研发并流行的存储介质,persistent memory,具有上述两者的优点,快并且persistent,本课不介绍这个
因为DB保存在disk上,所以DBMS需要负责数据在disk和memory间传送
我们主要专注于减小来自disk的时延,而不是关注与寄存器和cache的优化,因为disk带来的latency明显大得多:
If reading data from the L1 cache reference took half a second, reading from an SSD would take 1.7 days, and reading from an HDD would take 16.5 weeks.
2. Disk-Oriented DBMS Overview
DB全在disk上,并且以page的形式组织,第一页是directory page
(是吗?)
为了操作db,DBMS必须将数据读进内存。buffer pool负责管理数据在disk和memory之间的移动
DBMS还有一个execution engine来执行query,execution engine会向buffer pool要某一个page,buffer pool负责将该page带入内存,给execution engine一个指向该page的指针,buffer pool manager则会保证当engine处理该部分内存时,该page一直在那
(buffer pool和buffer pool manager是不是一回事?)
3. DBMS vs OS
OS is not your friend
TODO
4. File Storage
most basic form,DBMS将DB作为一个文件保存在disk上,有时候会使用file hierarchy,有时候则是单个文件,比如sqlite
OS不知道DB文件代表什么,因为是以特定格式编码的
DBMS的storage manager负责管理DB文件,它将文件表示为一系列的page,它还跟踪读出来和写入的数据,以及这些page还有多少free space





 本文深入探讨了磁盘导向的数据库管理系统(Disk-Oriented DBMS),重点在于如何减少从磁盘获取数据的延迟。讨论了数据库在内存和磁盘间的传输、页面布局、页管理以及不同类型的页面,包括槽页和日志结构。同时,提到了DBMS相对于操作系统的作用,以及数据文件的存储方式。
本文深入探讨了磁盘导向的数据库管理系统(Disk-Oriented DBMS),重点在于如何减少从磁盘获取数据的延迟。讨论了数据库在内存和磁盘间的传输、页面布局、页管理以及不同类型的页面,包括槽页和日志结构。同时,提到了DBMS相对于操作系统的作用,以及数据文件的存储方式。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 913
913

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








