💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
文献来源:

目的:
压缩传感是一种用于在不影响图像质量的情况下加速磁共振成像 (MRI) 采集的技术。虽然它已被证明在心脏电影等动态成像程序中特别有用,但很少有作者将其应用于功能性磁共振成像 (fMRI)。本研究的目的是检查基于现有先验图像的先验图像约束压缩感知(PICCS)算法是否能够比其他利用时间冗余的策略更好地改善fMRI中的统计图。
方法:
PICCS 与时空总变异 (TTV) 和 k-t FASTER 进行了比较,因为它们已经在其他 MRI 应用中分别表现出高性能和稳健性,例如心脏电影 MRI 和静息态 fMRI。PICCS的先前图像是所有欠采样数据的平均值。PICCS和TTV均使用拆分Bregman公式求解。K-t FASTER算法依靠矩阵补全来重构欠采样的k空间。使用两个具有高信噪比和低信噪比 (SNR) 的数据集(BOLD 对比度)评估了这三种算法,这些数据集是在 7 T 临床前 MRI 扫描仪中采集的,并以不同的速率(即加速因子)进行回顾性欠采样。作者通过受试者工作特征曲线和统计图的目视检查,评估了BOLD检测的灵敏度/特异性。
结果:
在高信噪比研究中,PICCS的性能与最先进的算法TTV和k-t FASTER相似,并在ROI时提供一致的BOLD信号。在低信噪比和高加速因子的场景中,PICCS仍然提供一致的图谱和比TTV更高的灵敏度/特异性,而k-t FASTER未能提供显著的图谱。
结论:
作者对利用fMRI中时间冗余的三种重建(PICCS、TTV和k-t FASTER)进行了比较。在嘈杂场景中,基于先验的算法 PICCS 比 TTV 和 k-t FASTER 更好地保留了 BOLD 激活和灵敏度/特异性。PICCS 算法可能达到 ×8 的加速因子,并且仍然在 ROI 中提供粗体对比度,曲线下面积超过 0.99。
📚2 运行结果
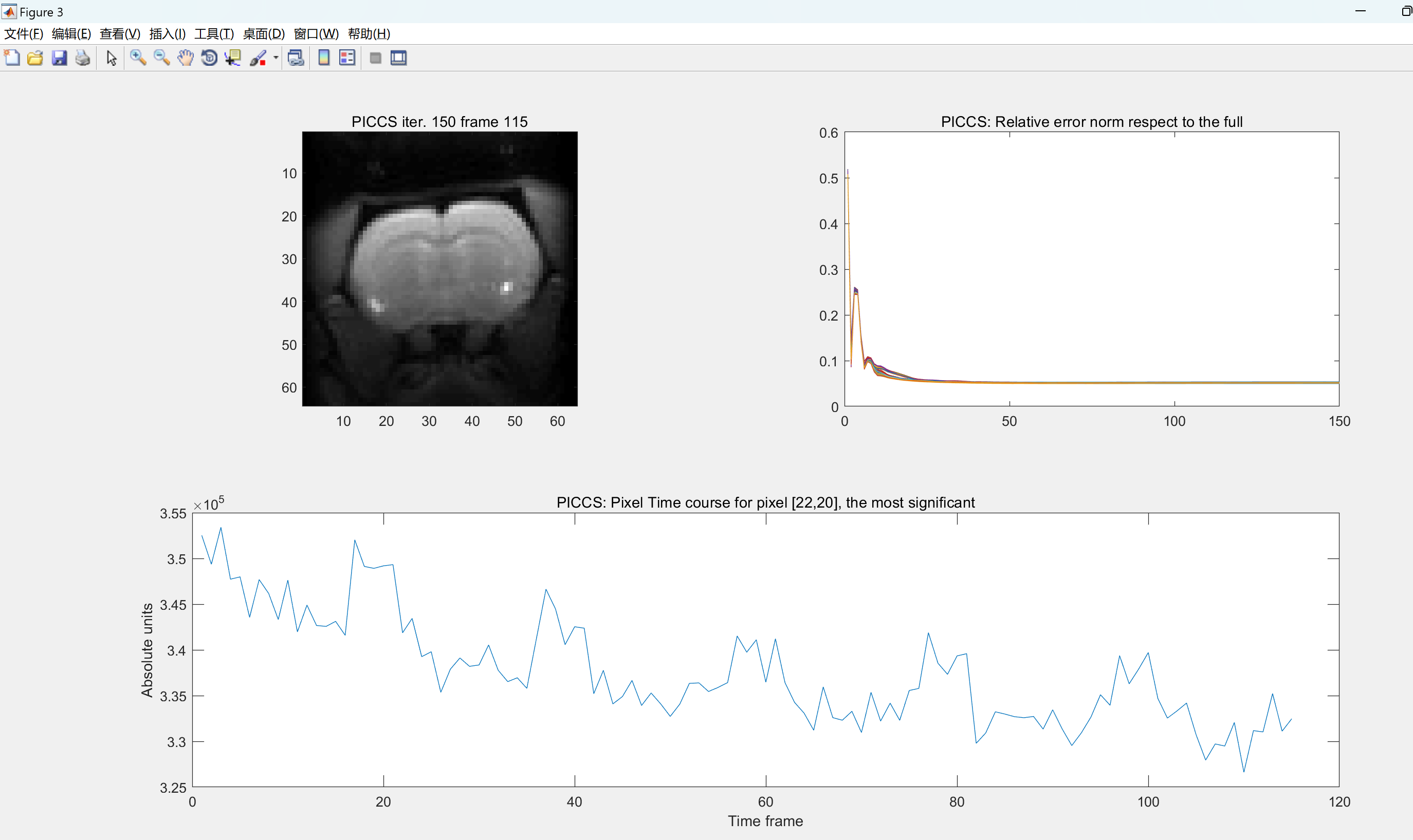
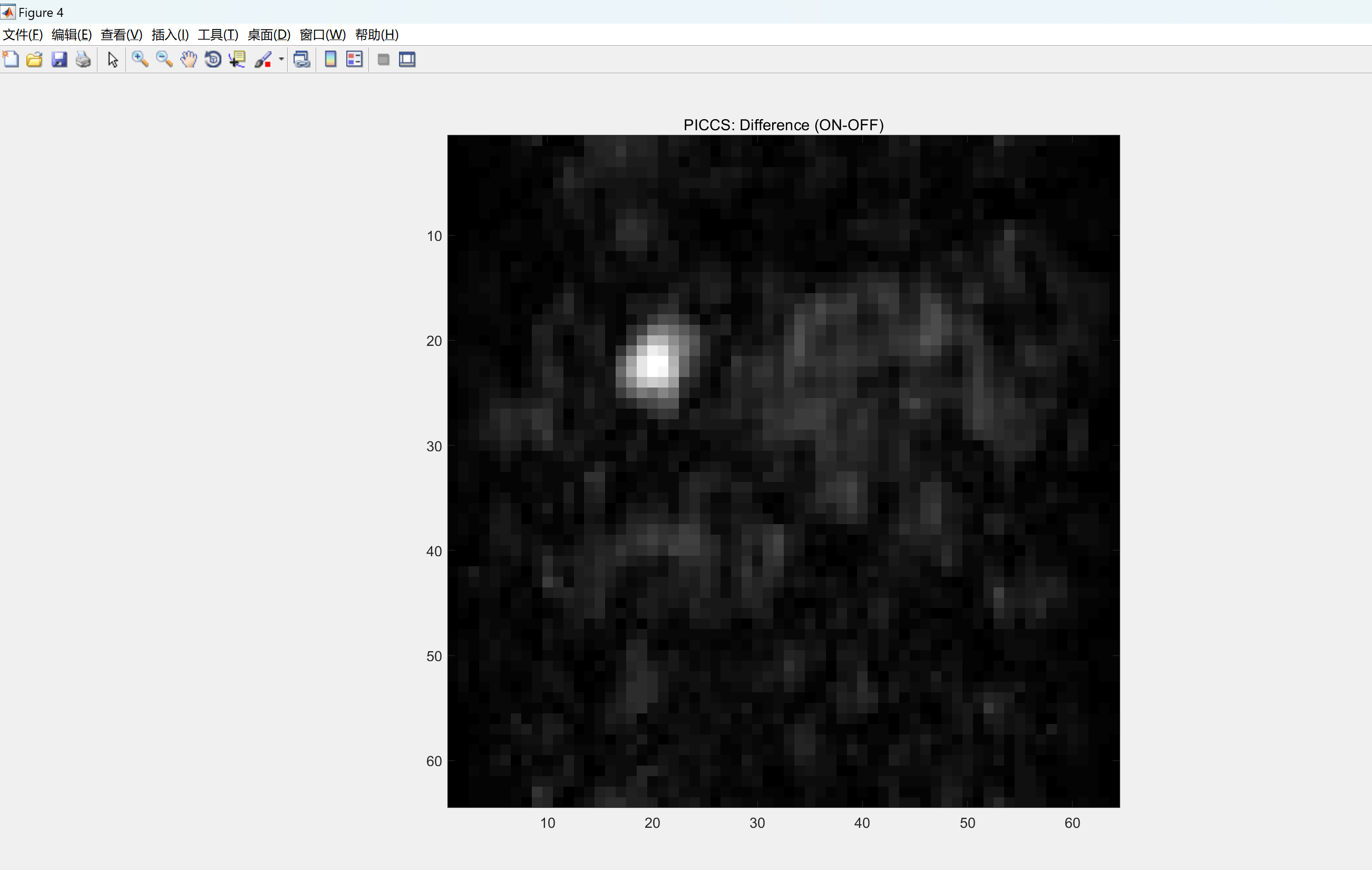
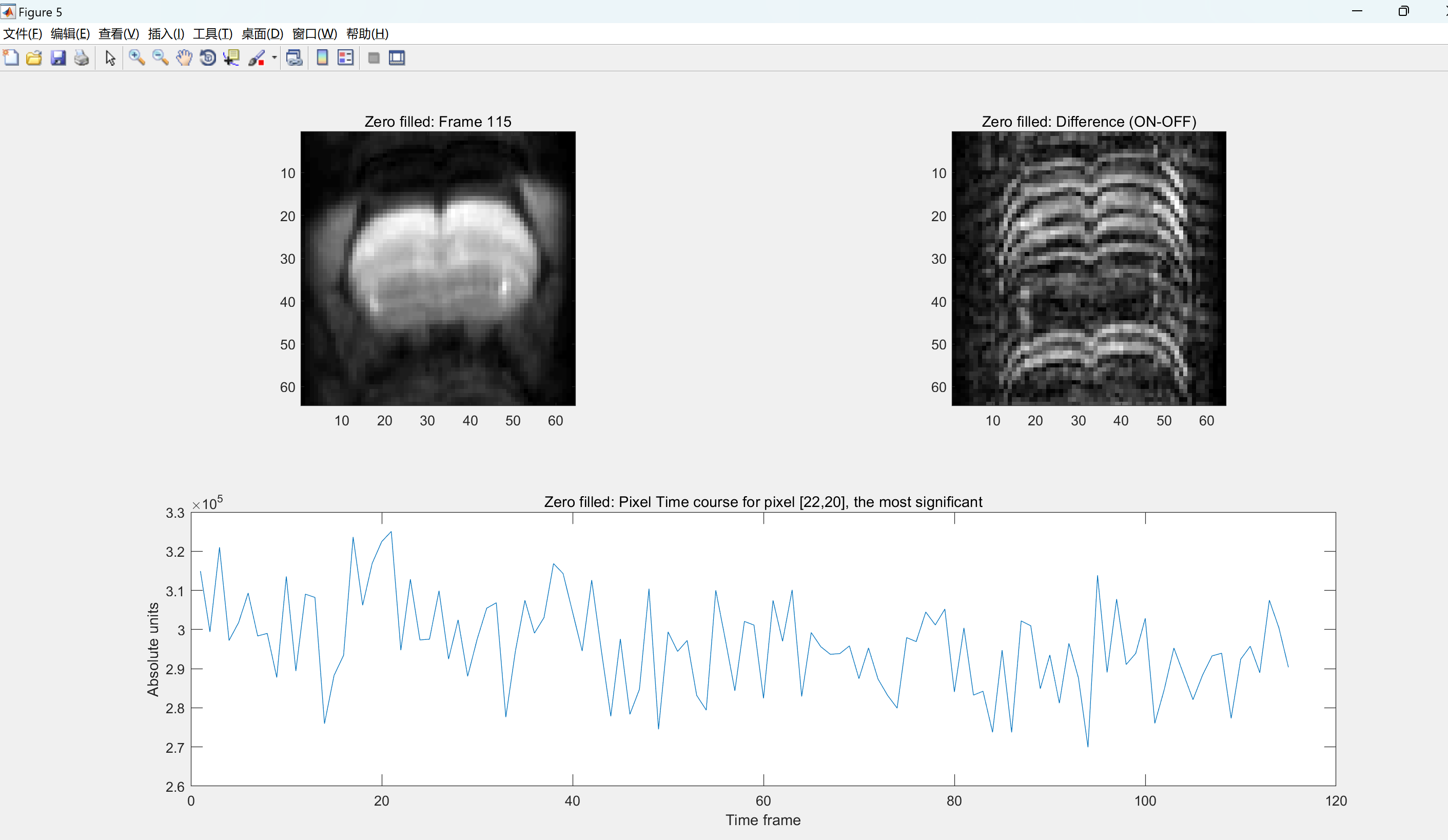 部分代码:
部分代码:
% Simulate data
data0 = fft2(image0);
%==========================================================================
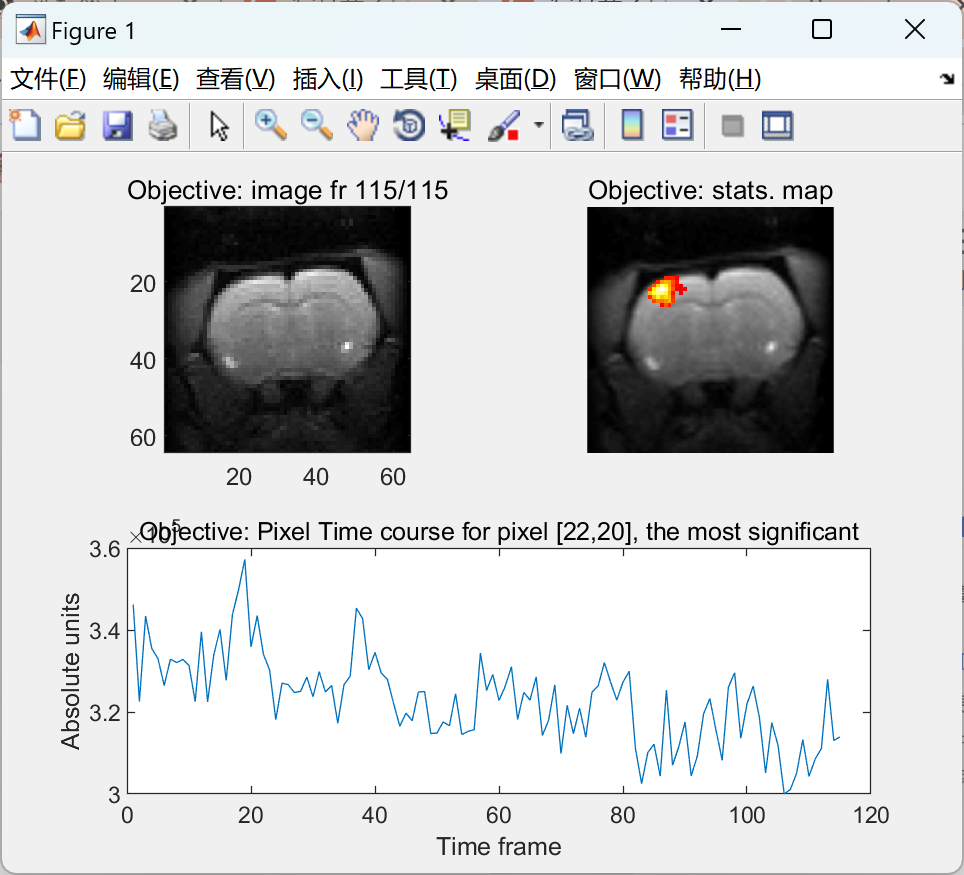
% DISPLAY FULL DATASET, highest activation pixel is [22,20]
%==========================================================================
% Here we display the thresholded statistical map obtained from the
% original fully sampled dataset analyzed with: https://github.com/HGGM-LIM/fmrat
% As well as the fully sampled 115 frames in the simulated fMRI series and
% the time course of the pixel [22,20], which yielded the highest statistical
% t value.
% Display the statistical map
close('all');
scrs = get(0,'ScreenSize');
h1 = figure; set(h1,'Position',[30,scrs(4)/2,scrs(3)/3,scrs(4)*0.8/2]);
subplot(2,2,2); imshow('map_full_p_0_01_k_12.tif'); title('Objective: stats. map');
% Display the time frames
subplot(2,2,1);
for i=1:115
figure(h1);
imagesc(abs(image0(:,:,i))); title(['Objective: image fr ' num2str(i) '/115']);
colormap gray; axis image; drawnow;
pause(0.05);
end
% Display the time course of the highest activation pixel
tcourse=subplot(2,2,3:4); plot(squeeze(image0(22,20,:))); title(tcourse,'Objective: Pixel Time course for pixel [22,20], the most significant')
ylabel(tcourse,'Absolute units'),xlabel(tcourse,'Time frame');
%==========================================================================
% UNDERSAMPLE DATASET, choose an undersampling rate (1/acc. factor)
%==========================================================================
% sp = [ ...
% 0.05;... % 5% of lines
% 0.1; ... % 10% of lines
% 0.125;... % 12.5% of lines
% 0.15;... % 15% of lines
% 0.175;... % 17.5% of lines
% 0.2; ... % 20% of lines
% 0.3; ... % 30% of lines
% 0.4; ... % 40% of lines
% 0.5; ... % 50% of lines
% 0.6; ... % 60% of lines
% 0.7; ... % 70% of lines
% 0.8; ... % 80% of lines
% 0.9 ... % 90% of lines
% ];
% The following are parameters required to generate the pdf at these
% undersampling rates above:
% Ps = [17,10,8,8,7.5,5,3,2,2,2,2,2,2]; % Decay
% N = size(image0,1); % #phase enc lines
% radius = [2/N ,3/N, 3.3/N, 3.7/N, 4.1/N, ... % Central radius
% 4.5/N,7/N,7/N,7/N,7/N,7/N,7/N,7/N];
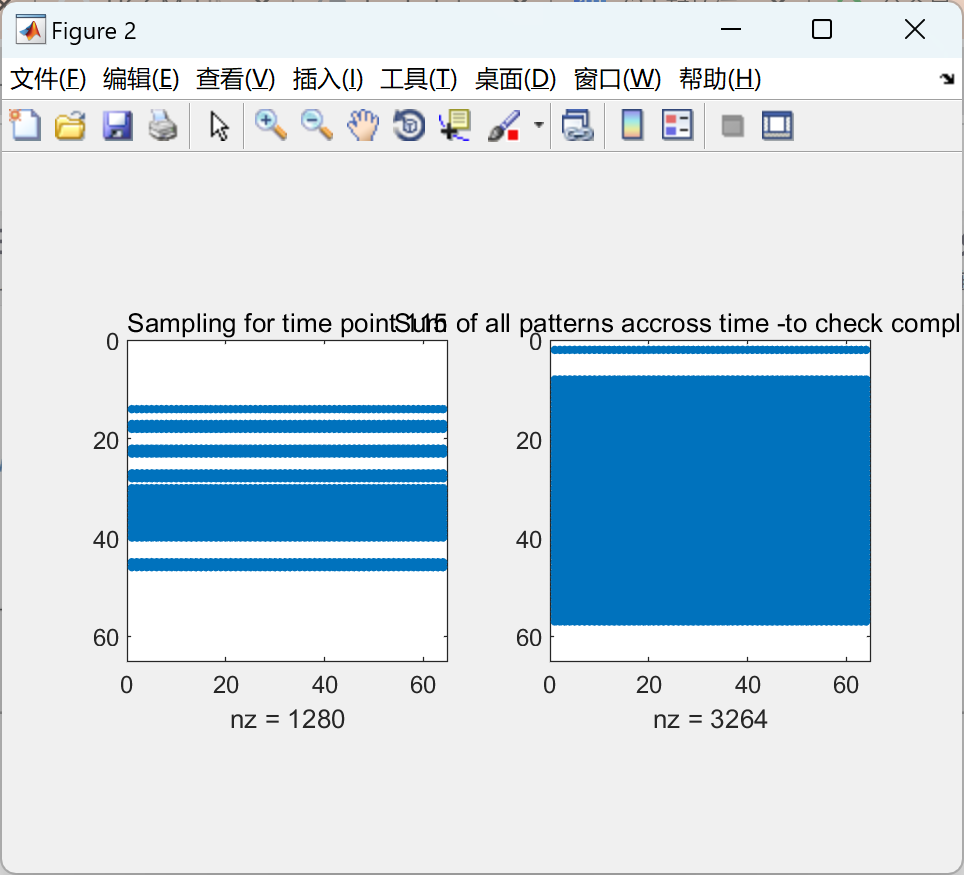
% To display the generated patterns for the 115 time frames
h2 = figure;
set(h2,'Position',[30+scrs(3)/3,scrs(4)/2,scrs(3)/3,scrs(4)/2*0.8]);
rname = 'central_dense';
% Choose an undersampling rate (acc. factor)
sp = 0.3;
Ps = 3;
radius = 7/size(image0,1);
% Create an undersampling for each time frame and display them
dims = size(image0);
RAll = genRAll(dims,sp,Ps,radius,pwd,rname,h2);
fprintf('Generated RAll %s\t for sparsity: %s \r\n',rname, num2str(sp));
% Display the sum of the undersamplings along time to check the kspace completion
RAll_visu = fftshift(RAll);
figure(h2),subplot(1,2,2),
spy(squeeze(sum(RAll_visu,3))), 100*nnz(squeeze(sum(RAll_visu,3)))/size(image0,1)
title('Sum of all patterns accross time -to check completion-');
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。





 本文探讨了压缩感知在功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)中的应用,比较了基于先验图像的PICCS算法与TTV和k-tFASTER在不同信噪比条件下的性能。结果显示,在低信噪比下,PICCS在保留BOLD激活和灵敏度/特异性方面优于其他两种方法。
本文探讨了压缩感知在功能性磁共振成像(fMRI)中的应用,比较了基于先验图像的PICCS算法与TTV和k-tFASTER在不同信噪比条件下的性能。结果显示,在低信噪比下,PICCS在保留BOLD激活和灵敏度/特异性方面优于其他两种方法。


















 507
507

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








