模型信息:
模型地址-huggingface:https://huggingface.co/Qwen/Qwen3-8B-AWQ
模型地址-modelscope:https://www.modelscope.cn/models/Qwen/Qwen3-8B-AWQ
Qwen3-8B 具有以下特性:
-
类型:因果语言模型
-
训练阶段:预训练和后训练
-
参数数量:82 亿
-
非嵌入参数数量:69.5 亿
-
层数:36
-
注意力头数(GQA):Q 为 32,KV 为 8
-
上下文长度:原生 32,768 和 使用 YaRN 时 131,072 个 token。
-
量化:AWQ 4 位
量化前模型大小16G+,量化后模型大小6G
离线推理
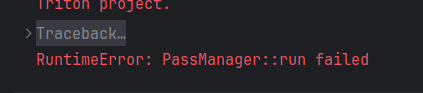
使用官方给的代码,模型加载正常,但是推理时generate会报错如下图,参照某篇博客的内容对模型加载和推理模块都进行了调整(现找不到那篇博客了,在此表示感谢),可以正常运行。
- 模型加载
# qwen_vllm.py
# 模型加载
from transformers import AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
DEFAULT_CKPT_PATH = "/home/emma/.cache/modelscope/hub/models/Qwen/Qwen3-8B-AWQ"
# Initialize the tokenizer
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(DEFAULT_CKPT_PATH) # 替换成本地路径
# Input the model name or path. Can be GPTQ or AWQ models.
llm = LLM(
model=DEFAULT_CKPT_PATH,
max_model_len=2048, # 最大上下文长度:8192
max_num_seqs=1, # 最大并发序列数:256
quantization="awq",
enforce_eager=True,
dtype="auto",
# block_size=16
gpu_memory_utilization=0.6, # 默认0.9
# max_num_seqs=64
) # 替换成本地路径- 模型推理
# 模型推理
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
# Pass the default decoding hyperparameters of Qwen2-7B-Instruct
# max_tokens is for the maximum length for generation.
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.7, top_p=0.8, repetition_penalty=1.05, max_tokens=512)
# # =================== 单个推理 ====================
# # Prepare your prompts
# prompt = "---\n请判断上面这段文本属于哪些标签,[现场音乐会,滑雪,爬山,美食之旅,水族馆游览,随上随下巴士,蹦极,博物馆体验,观赏熊猫,艺术课程,摩托艇,骑骆驼],并输出命中的标签列表,如果没有命中,则输出'无',不要输出解释信息"
# text = "使用地址:广州青深民谣现场珠影店 广东省广州市海珠区赤岗街道广州大道南173号温馨提示:演出为有座演出;最下方有道理指引图;学生票需出示学生证;VIP票数量有限,先抢先得。"
# messages = [
# {"role": "system", "content": "You are a helpful assistant."},
# {"role": "user", "content": text + prompt}
# ]
# text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
# messages,
# tokenize=False,
# add_generation_prompt=True
# )
#
# # generate outputs
# outputs = llm.generate([text], sampling_params)
# # =================== 单个推理 ====================
# # # =================== batch推理 ====================
# Prepare your prompts
texts = ["使用地址:广州青深民谣现场珠影店 广东省广州市海珠区赤岗街道广州大道南173号温馨提示:演出为有座演出;最下方有道理指引图;学生票需出示学生证;VIP票数量有限,先抢先得。", "专业的初级滑雪练习场,适合初学者及儿童,激情雪圈,单人滑,双人滑,三人滑,不限次数!雪圈运送机助你轻松戏雪! 不含自费项目:滑雪押金200元,滑雪服(衣服+库组)30元/套,滑雪专用手套10元/副,更衣箱10元/个,头盔30元/个,雪镜30元/个,护臂30元/个", "骆驼牧场参观,免费骑骆驼", "🔺【客人自行进入游玩,向导和车辆在外等候】🐼熊猫谷不仅是大熊猫回归自然的桥梁,也是圈养大熊猫走向野外进行自我繁衍的可行性研究基地。目前,熊猫谷拥有完善的大熊猫适应性生态兽舍、半野化过渡训练区和小熊猫生态放养区,常驻有10余只大熊猫和20余只小熊猫"]
texts = ["使用地址:广州青深民谣现场珠影店 广东省广州市海珠区赤岗街道广州大道南173号温馨提示:演出为有座演出;最下方有道理指引图;学生票需出示学生证;VIP票数量有限,先抢先得。"]
prompt = "---\n请判断上面这段文本属于哪些标签,[现场音乐会,滑雪,爬山,美食之旅,水族馆游览,随上随下巴士,蹦极,博物馆体验,观赏熊猫,艺术课程,摩托艇,骑骆驼],并输出命中的标签列表,如果没有命中,则输出'无',不要输出解释信息"
messages = []
for text in texts:
message = [
{"role": "system", "content": "你是一个文本分类模型"},
{"role": "user", "content": text + prompt + "/think"} # "/no_think"
# 通过用户输入在思考模式和非思考模式之间切换,提供了一种软开关机制,允许用户在 enable_thinking=True 时动态控制模型的行为。具体来说,您可以在用户提示或系统消息中添加 /think 和 /no_think 来逐回合切换模型的思考模式。模型将在多轮对话中遵循最近的指令。
]
messages.append(message)
text = tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True,
enable_thinking=True # True is the default value for enable_thinking
)
# generate outputs
outputs = llm.generate(text, sampling_params)
# # # =================== batch推理 ====================
# Print the outputs.
for output in outputs:
prompt = output.prompt
# generated_text = output.outputs[0].text
output_ids = output.outputs[0].token_ids
# parsing thinking content
try:
# rindex finding 151668 (</think>)
index = len(output_ids) - output_ids[::-1].index(151668)
except ValueError:
index = 0
thinking_content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[:index], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
content = tokenizer.decode(output_ids[index:], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
print(f"prompt:{prompt!r}")
print(f"thinking content: {thinking_content!r}")
print("content:", content)
# print(f"Prompt: {prompt!r}, Generated text: {generated_text!r}")- GPU使用情况分析:
gpu_memory_utilization参数说明:
vllm会预先分配显存,默认值是0.9,与batch size无关。
gpu_memory_utilization设置越大,可占用显存越大,就有更多显存可用于 KV 缓存,推理速度也会越快。在显存足够的情况下,gpu_memory_utilization可以设置为0.95。
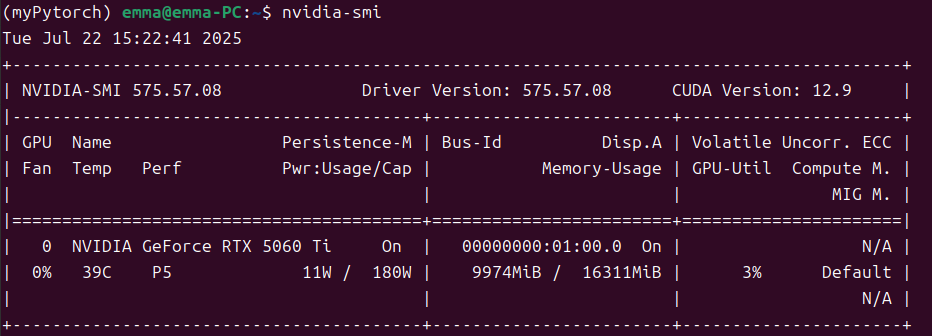
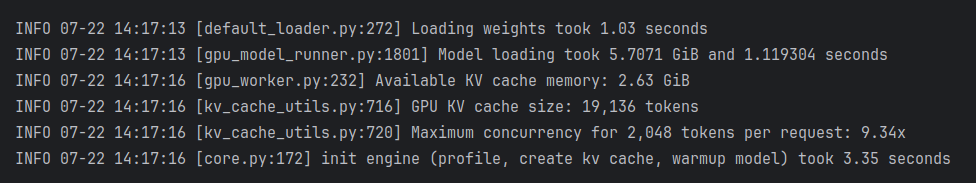
gpu_memory_utilization=0.6时的GPU占用情况:
gpu_memory_utilization=0.8时的GPU占用情况:
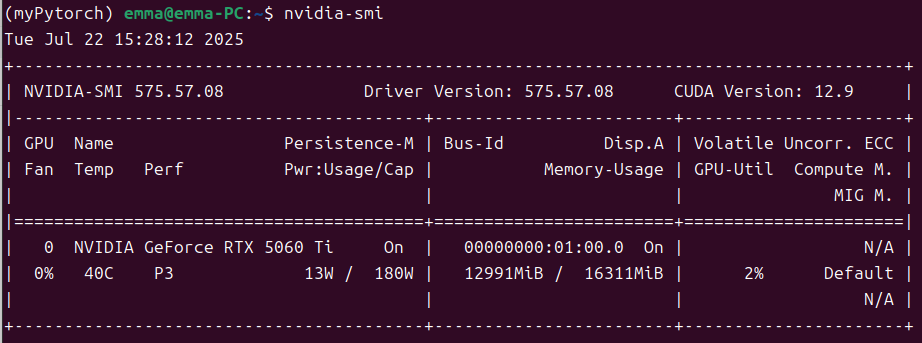
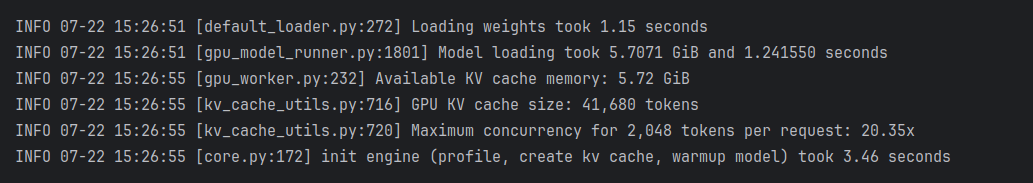
模型文件本身6G左右,从上图可以看出Model loading用了5.7G,比模型本身更小,应该是因为VLLM采用了显存技术优化,大幅减少了冗余占用。
- 模型输出
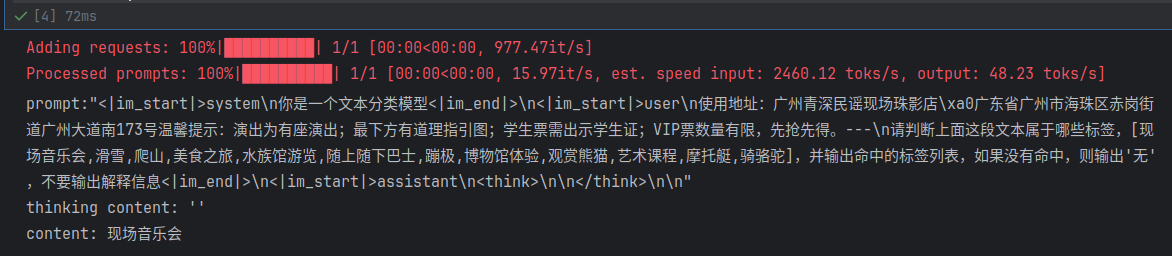
非思考模式输出(单条70ms左右)
思考模式输出(单条4s左右)
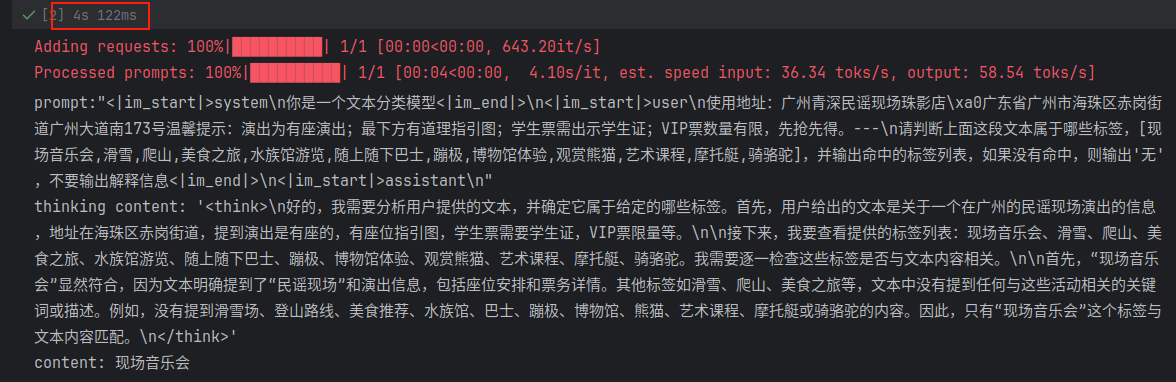
NOTE:
为了 API 兼容性,当 enable_thinking=True 时,无论用户是否使 /think 或 /no_think,模型总是会输出一个被 <think>...</think> 包裹的块。但是,如果禁用了思考,这个块中的内容可能是空的。 当 enable_thinking=False 时,软开关无效。无论用户输入了任何 /think 或 /no_think 标签,模型都不会生成思考内容,也不会包含 <think>...</think> 块。
高级用法:通过用户输入在思考模式和非思考模式之间切换
我们提供了一种软开关机制,允许用户在 enable_thinking=True 时动态控制模型的行为。具体来说,您可以在用户提示或系统消息中添加 /think 和 /no_think 来逐回合切换模型的思考模式。模型将在多轮对话中遵循最近的指令。
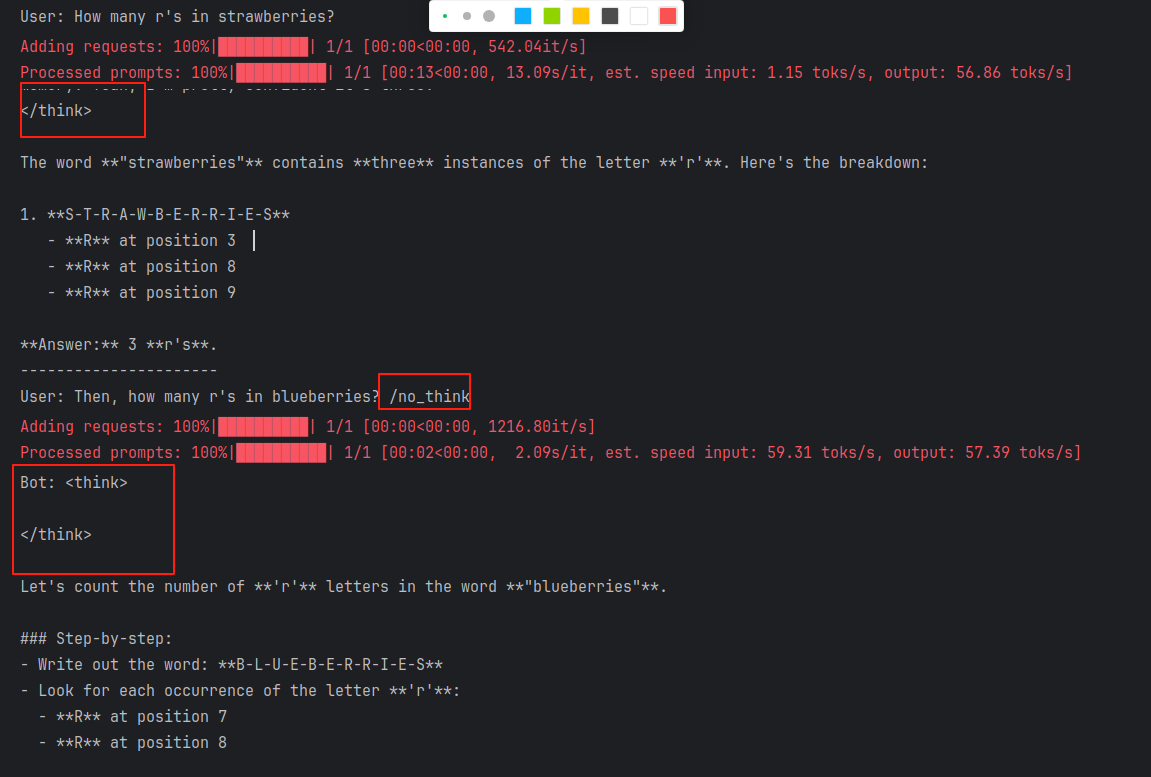
以下是一个多轮对话的例子:
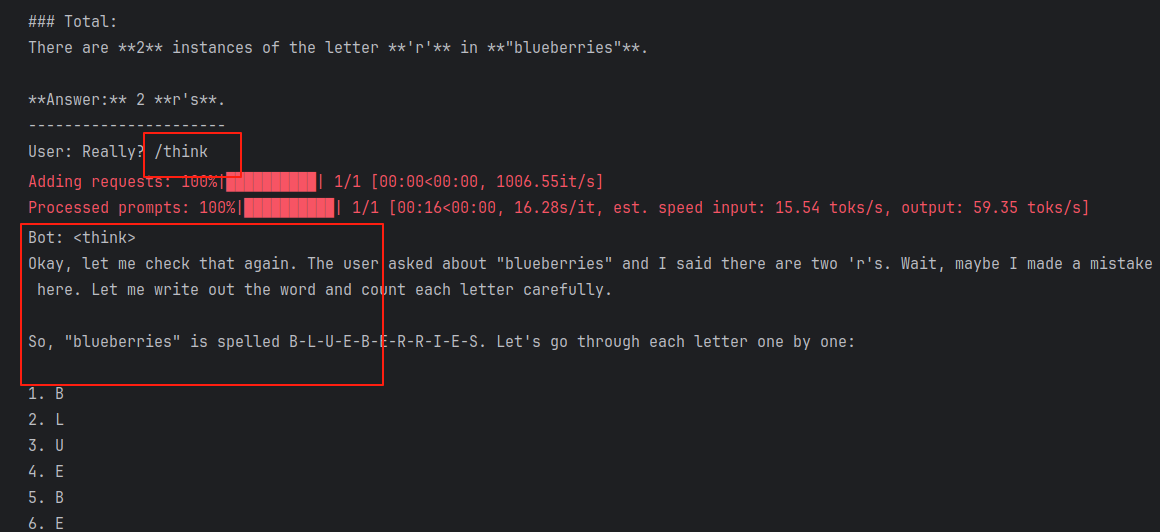
从后面的输出结果可以看出,/think 和 /no_think 起到了作用,在思考模式和非思考模式之间进行了切换。
from modelscope import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
from vllm import LLM, SamplingParams
class QwenChatbot:
def __init__(self, model_name="/home/emma/.cache/modelscope/hub/models/Qwen/Qwen3-8B-AWQ"):
self.tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(model_name)
# self.model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
# Input the model name or path. Can be GPTQ or AWQ models.
self.model = LLM(
model=model_name,
max_model_len=2048, # 最大上下文长度:8192
max_num_seqs=1, # 最大并发序列数:256
quantization="awq",
enforce_eager=True,
dtype="auto",
# block_size=16
gpu_memory_utilization=0.7, # 默认0.9
# max_num_seqs=64
) # 替换成本地路径
self.history = []
def generate_response(self, user_input):
sampling_params = SamplingParams(temperature=0.7, top_p=0.8, repetition_penalty=1.05, max_tokens=2048)
messages = self.history + [{"role": "user", "content": user_input}]
text = self.tokenizer.apply_chat_template(
messages,
tokenize=False,
add_generation_prompt=True
)
# inputs = self.tokenizer(text, return_tensors="pt")
# response_ids = self.model.generate(**inputs, max_new_tokens=4096)[0][len(inputs.input_ids[0]):].tolist() # 32768
# response = self.tokenizer.decode(response_ids, skip_special_tokens=True)
# generate outputs
output = self.model.generate([text], sampling_params)[0]
output_ids = output.outputs[0].token_ids
# parsing thinking content
# try:
# # rindex finding 151668 (</think>)
# index = len(output_ids) - output_ids[::-1].index(151668)
# except ValueError:
# index = 0
# response = self.tokenizer.decode(output_ids[index:], skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
response = self.tokenizer.decode(output_ids, skip_special_tokens=True).strip("\n")
# Update history
self.history.append({"role": "user", "content": user_input})
self.history.append({"role": "assistant", "content": response})
return response
# Example Usage
if __name__ == "__main__":
chatbot = QwenChatbot()
# First input (without /think or /no_think tags, thinking mode is enabled by default)
user_input_1 = "How many r's in strawberries?"
print(f"User: {user_input_1}")
response_1 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_1)
print(f"Bot: {response_1}")
print("----------------------")
# Second input with /no_think
user_input_2 = "Then, how many r's in blueberries? /no_think"
print(f"User: {user_input_2}")
response_2 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_2)
print(f"Bot: {response_2}")
print("----------------------")
# Third input with /think
user_input_3 = "Really? /think"
print(f"User: {user_input_3}")
response_3 = chatbot.generate_response(user_input_3)
print(f"Bot: {response_3}")输出结果:





















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








