利用pcl中的kdtree可以做到搜索关键点某半径邻域内的区域.
主要步骤
1.读入点云数据
2.设置kdtree
3.设置关键点和邻域半径
4.执行搜索函数
附上代码
#include <iostream>
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include <pcl/io/pcd_io.h>
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include <pcl/kdtree/kdtree_flann.h>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
typedef pcl::PointXYZI PointType;
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
if(argc != 3)
{
cerr<<"输入参数数量不对!"<<endl;
exit(1);
}
string input_filename = argv[1];
string output_filename = argv[2];
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
std::string format = input_filename.substr(input_filename.length()-4, 4);
//std::cout<<"pointcloud format:"<<format<<std::endl;
if(format == ".ply")
{
if(pcl::io::loadPLYFile(input_filename, *cloud)==-1)
{
PCL_ERROR("error! \n");
exit(1);
}
}
else if(pcl::io::loadPCDFile(input_filename, *cloud)==-1)
{
PCL_ERROR("error! \n");
exit(1);
}
//创建kdtree 结构
pcl::KdTreeFLANN<PointType> kdtree;
//传入点云
kdtree.setInputCloud(cloud);
pcl::PointCloud<PointType>::Ptr source_key_Neigh(new pcl::PointCloud<PointType>());
//设置关键点
PointType searchPoint;
searchPoint.x = 0;
searchPoint.y = 0;
searchPoint.z = 0;
// 创建两个向量,分别存放近邻的索引值、近邻的中心距
std::vector<int> pointIdxRadiusSearch;
std::vector<float> pointRadiusSquaredDistance;
// 指定随机半径
//float radius = 256.0f * rand () / (RAND_MAX + 1.0f);
float radius = 15;
std::cout << "Neighbors within radius search at (" << searchPoint.x
<< " " << searchPoint.y
<< " " << searchPoint.z
<< ") with radius=" << radius << std::endl;
// kdtree.radiusSearch (searchPoint, radius, pointIdxRadiusSearch, pointRadiusSquaredDistance)
if ( kdtree.radiusSearch (searchPoint, radius, pointIdxRadiusSearch, pointRadiusSquaredDistance) > 0 )
{
cout<<"最近邻点数: "<<pointIdxRadiusSearch.size ()<<endl;
for (size_t i = 0; i < pointIdxRadiusSearch.size (); ++i)
{
// std::cout << cloud->points[ pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].x
// << " " << cloud->points[ pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].y
// << " " << cloud->points[ pointIdxRadiusSearch[i] ].z
// << " (squared distance: " << pointRadiusSquaredDistance[i] << ")" << std::endl;
source_key_Neigh->push_back(cloud->points[pointIdxRadiusSearch[i]]);
}
pcl::io::savePCDFile(output_filename, *source_key_Neigh);
}
else
cout<<"找不到最近点"<<endl;
cout<<"end"<<endl;
return 0;
}
CMakeLists.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 2.8)
project(search_pc_neighbourhood)
set(CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS} -std=c++11")
# pcl
find_package( PCL 1.7 REQUIRED)
include_directories( ${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS} )
add_definitions( ${PCL_DEFINITIONS} )
#LINK_DIRECTORIES(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS}$)
list(REMOVE_ITEM PCL_LIBRARIES "vtkproj4")
add_executable(main "main.cpp")
target_link_libraries(main ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
效果展示
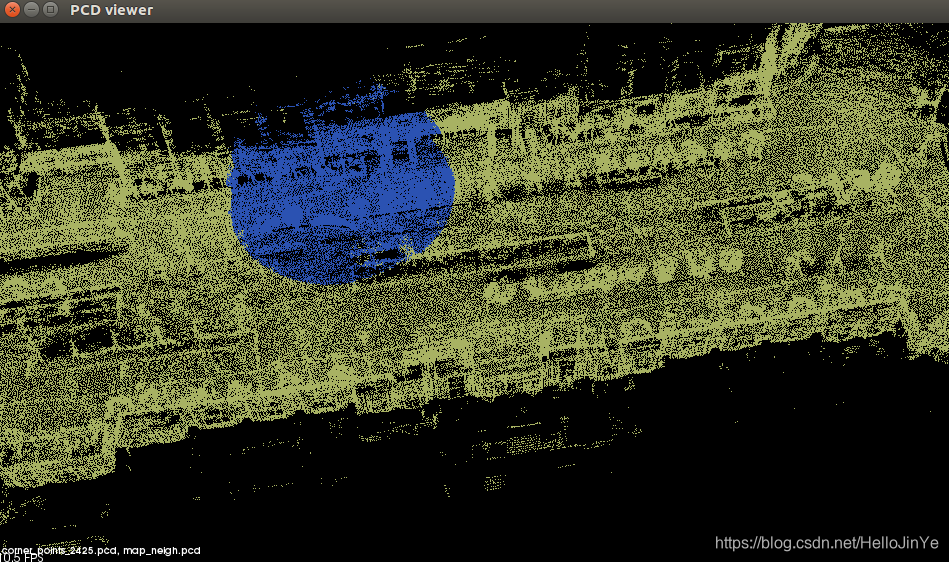
 PCL KdTree邻域搜索
PCL KdTree邻域搜索





 本文介绍如何使用PCL库中的KdTree进行点云数据的关键点邻域搜索,通过设定关键点和邻域半径,实现对点云中特定区域的筛选,并提供了完整的代码示例。
本文介绍如何使用PCL库中的KdTree进行点云数据的关键点邻域搜索,通过设定关键点和邻域半径,实现对点云中特定区域的筛选,并提供了完整的代码示例。
















 368
368










