
大家好,欢迎阅读这份《智能体(AI+Agent)开发指南》!
在大模型和智能体快速发展的今天,很多朋友希望学习如何从零开始搭建一个属于自己的智能体。本教程的特点是 完全基于国产大模型与火山推理引擎实现,不用翻墙即可上手,非常适合国内开发者快速实践。
通过循序渐进的讲解,你将学会从 环境配置、基础构建、进阶功能到实际案例 的完整流程,逐步掌握智能体开发的核心技能。无论你是初学者还是有经验的工程师,相信这份教程都能为你带来启发。
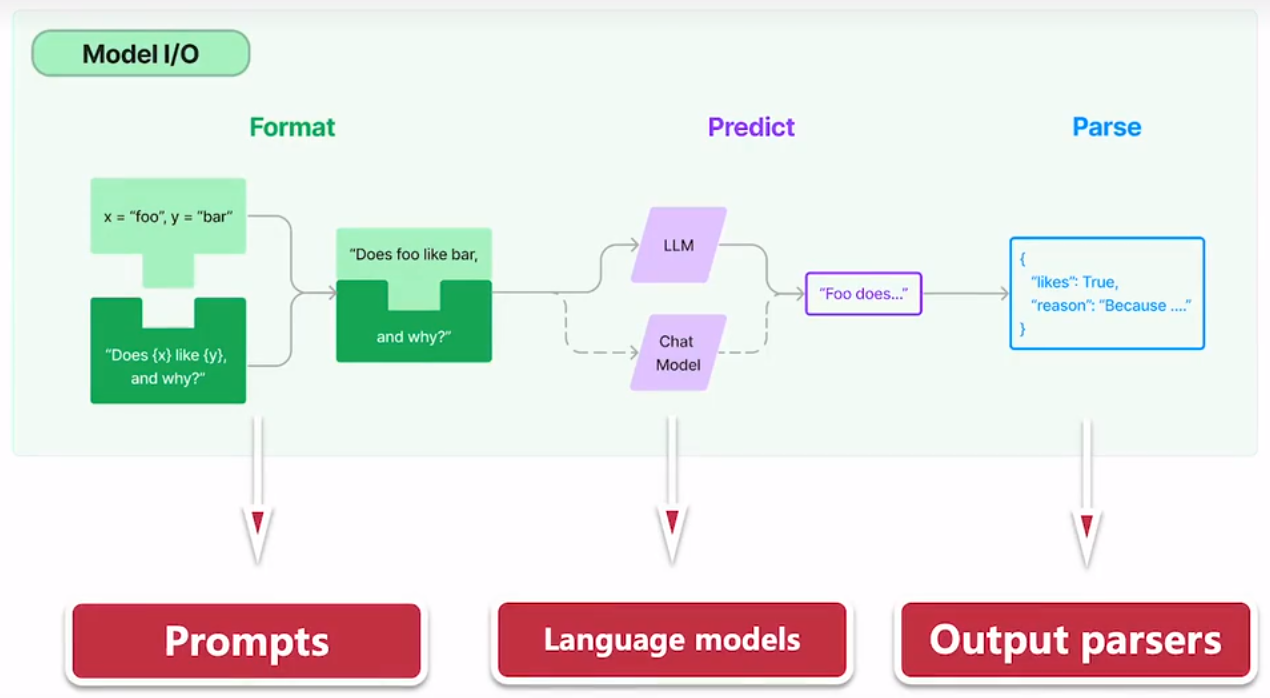
参考:
https://python.langchain.com/docs/introduction/
https://github.com/liaokongVFX/LangChain-Chinese-Getting-Started-Guide
一. 大模型流式输出
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
# 配置智谱AI的模型服务
base_url = 'https://open.bigmodel.cn/api/paas/v4'
api_key = 'your_API_key'
model_name = 'glm-4.5'
def zhipu_chain_streaming_demo():
"""使用智谱AI的链式流式输出演示"""
# 创建支持流式输出的 LLM
streaming_llm = ChatOpenAI(
model=model_name,
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
streaming=True,
temperature=0.8,
max_tokens=800
)
print("\n=== 智谱AI 链式流式输出演示 ===")
print("使用 ChatPromptTemplate 和链式调用:")
print("-" * 60)
# 创建提示模板
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template(
"你是一个专业的AI分析师,请用中文回答以下问题:{question}"
)
# 创建可运行序列
chain = prompt | streaming_llm
# 测试问题
test_questions = [
"中国大模型行业在2025年将面临哪些机遇和挑战?",
"请分析一下大语言模型在教育领域的应用前景",
"写一段关于未来科技发展的短文"
]
for i, question in enumerate(test_questions, 1):
print(f"\n问题 {i}: {question}")
print("回答:")
try:
# 使用流式输出
for chunk in chain.stream({"question": question}):
if hasattr(chunk, 'content'):
print(chunk.content, end='', flush=True)
print("\n" + "="*60)
except Exception as e:
print(f"流式输出错误: {e}")
print("使用普通输出...")
response = chain.invoke({"question": question})
print(response.content)
print("\n" + "="*60)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行链式流式输出演示
zhipu_chain_streaming_demo()
二. 用国产大模型实现文本向量化
模型地址:https://console.volcengine.com/ark/region:ark+cn-beijing/openManagement?EMBEDDING=%7B%7D&LLM=%7B%7D&OpenAuthorizeModal=false&OpenTokenDrawer=false&tab=Embedding
import requests
import json
import numpy as np
# 配置火山引擎API
base_url = 'https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3'
api_key = 'your_API_key'
model_name = 'doubao-embedding-text-240715' # 使用您提供的模型名称
def get_text_embeddings(texts):
"""
获取文本的向量表示
参数: texts - 文本列表
返回: 向量列表
"""
# 设置请求头
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': f'Bearer {api_key}'
}
# 准备请求数据
data = {
"encoding_format": "float",
"input": texts,
"model": model_name
}
try:
# 发送POST请求
response = requests.post(
f"{base_url}/embeddings",
headers=headers,
json=data,
timeout=30
)
# 检查响应状态
if response.status_code == 200:
result = response.json()
# 提取向量数据
embeddings = []
for item in result['data']:
embeddings.append(item['embedding'])
return embeddings
else:
print(f"请求失败: {response.status_code}")
print(f"错误信息: {response.text}")
return None
except Exception as e:
print(f"请求异常: {e}")
return None
def calculate_similarity(vec1, vec2):
"""
计算两个向量的余弦相似度
参数: vec1, vec2 - 两个向量
返回: 相似度值 (0-1之间,越接近1越相似)
"""
# 计算余弦相似度
dot_product = np.dot(vec1, vec2)
norm1 = np.linalg.norm(vec1)
norm2 = np.linalg.norm(vec2)
if norm1 > 0 and norm2 > 0:
similarity = dot_product / (norm1 * norm2)
return similarity
else:
return 0.0
def main():
"""主函数 - 演示文本向量化功能"""
# 测试文本 - 参考您的curl命令
test_texts = [
"天很蓝",
"海很深",
"人工智能很强大",
"机器学习很有趣"
]
# 获取文本向量
embeddings = get_text_embeddings(test_texts)
import pdb; pdb.set_trace()
if embeddings:
# 计算第一个文本与其他文本的相似度
first_text = test_texts[0]
first_vector = embeddings[0]
print(f"\n以 '{first_text}' 为基准,计算与其他文本的相似度:")
for i in range(1, len(test_texts)):
similarity = calculate_similarity(first_vector, embeddings[i])
print(f" '{first_text}' vs '{test_texts[i]}': {similarity:.4f}")
# 找到最相似的文本
similarities = []
for i in range(1, len(test_texts)):
similarity = calculate_similarity(first_vector, embeddings[i])
similarities.append((i, similarity))
most_similar_idx, most_similar_score = max(similarities, key=lambda x: x[1])
print(f"\n与 '{first_text}' 最相似的文本是: '{test_texts[most_similar_idx]}' (相似度: {most_similar_score:.4f})")
else:
print("❌ 向量生成失败")
print("\n可能的原因:")
print("1. API密钥不正确")
print("2. 模型名称不存在")
print("3. 网络连接问题")
print("4. 账户权限不足")
def simple_example():
"""简单示例 - 只处理两个文本"""
texts = ["天很蓝", "海很深"]
# 获取向量
embeddings = get_text_embeddings(texts)
if embeddings:
# 计算相似度
similarity = calculate_similarity(embeddings[0], embeddings[1])
print(f"\n两个文本的相似度: {similarity:.4f}")
else:
print("❌ 向量生成失败")
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 运行完整演示
main()
# 运行简单示例
# simple_example()
三. 多个chain的组合使用
"""
多个chain的组合使用
1. 生成产品介绍
2. 生成总结
3. 组合两个步骤
4. 执行链
5. 打印结果
"""
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
base_url = "https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3"
api_key = "your_API_key"
model_name = "doubao-1-5-pro-32k-250115"
llm = ChatOpenAI(
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
model_name=model_name,
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=1024,
timeout=30,
max_retries=3,
)
# 第一个提示模板:生成产品介绍
prompt1 = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["product"],
template="给{product}写一个产品介绍,500字左右",
)
# 第二个提示模板:生成总结
prompt2 = PromptTemplate(
input_variables=["description"],
template="请你根据{description},写一个总结,总结不超过100字",
)
# 使用现代LangChain语法创建链
def create_description(inputs):
"""第一步:生成产品介绍"""
result = (prompt1 | llm).invoke(inputs)
return {"description": result.content}
def create_summary(inputs):
"""第二步:生成总结"""
result = (prompt2 | llm).invoke(inputs)
return {"summary": result.content}
# 组合两个步骤
def main_chain(inputs):
"""主链:先生成描述,再生成总结"""
# 第一步:生成产品介绍
description_result = create_description(inputs)
# 第二步:基于描述生成总结
summary_result = create_summary(description_result)
# 返回完整结果
return {
"product": inputs["product"],
"description": description_result["description"],
"summary": summary_result["summary"]
}
# 执行链
result = main_chain({"product": "小米10s"})
print("=== 产品介绍 ===")
print(result["description"])
print("\n=== 总结 ===")
print(result["summary"])
效果:

四. 爬取网页并结构化输出
"""
爬取网页并输出JSON数据
"""
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import PromptTemplate
from langchain.chains import LLMChain
import requests
base_url = "https://ark.cn-beijing.volces.com/api/v3"
api_key = "your_API_KEY"
model_name = "doubao-1-5-pro-32k-250115"
llm = ChatOpenAI(
base_url=base_url,
api_key=api_key,
model_name=model_name,
temperature=0.7,
max_tokens=1024,
timeout=30,
max_retries=3,
)
template = """在 >>> 和 <<< 之间是网页的返回的HTML内容。
网页是新浪财经A股上市公司的公司简介。
请抽取参数请求的信息。
>>> {requests_result} <<<
请使用如下的JSON格式返回数据
{{
"company_name":"a",
"company_english_name":"b",
"issue_price":"c",
"date_of_establishment":"d",
"registered_capital":"e",
"office_address":"f",
"Company_profile":"g"
}}
Extracted:"""
prompt = PromptTemplate(
template=template,
input_variables=["requests_result"],
)
# 使用简单的requests库
def fetch_webpage_content(url):
"""获取网页内容"""
try:
headers = {
'User-Agent': 'Mozilla/5.0 (Windows NT 10.0; Win64; x64) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/91.0.4472.124 Safari/537.36'
}
response = requests.get(url, headers=headers, timeout=10)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.text
except Exception as e:
return f"获取网页内容失败: {str(e)}"
# 主函数
def main():
"""主函数:爬取网页并分析数据"""
url = "https://vip.stock.finance.sina.com.cn/corp/go.php/vCI_CorpInfo/stockid/600519.phtml"
print("正在获取网页内容...")
# 获取网页内容
html_content = fetch_webpage_content(url)
if html_content.startswith("获取网页内容失败"):
print(f"错误: {html_content}")
return
print(f"成功获取网页内容,长度: {len(html_content)} 字符")
chain = prompt | llm
# 处理网页内容
print("正在分析网页内容...")
result = chain.invoke({"requests_result": html_content})
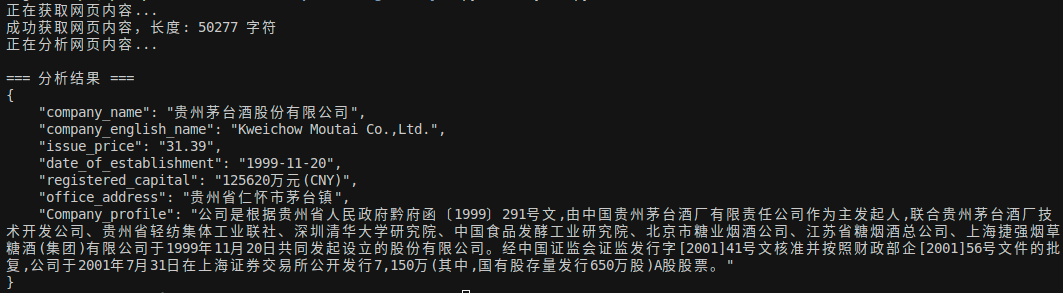
print("\n=== 分析结果 ===")
print(result.content)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
输出效果:
五. 总结
希望大家能通过这篇文章的学习有所收获。这篇文章只是对 LangChain 一个初级的讲解,高级的功能希望大家继续探索。
并且因为 LangChain 迭代极快,所以后面肯定会随着AI继续的发展,还会迭代出更好用的功能,所以我非常看好这个开源库。
希望大家能结合 LangChain 开发出更有创意的产品,而不仅仅只搞一堆各种一键搭建chatgpt聊天客户端的那种产品。
后面出现了更好的技术我还是希望能继续更新这个系列。
欢迎关注微信公众号:AIWorkshopLab,自动获取完整教程:智能体(AI+Agent)开发指南.pdf。























 942
942

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










