What does randomness look like?
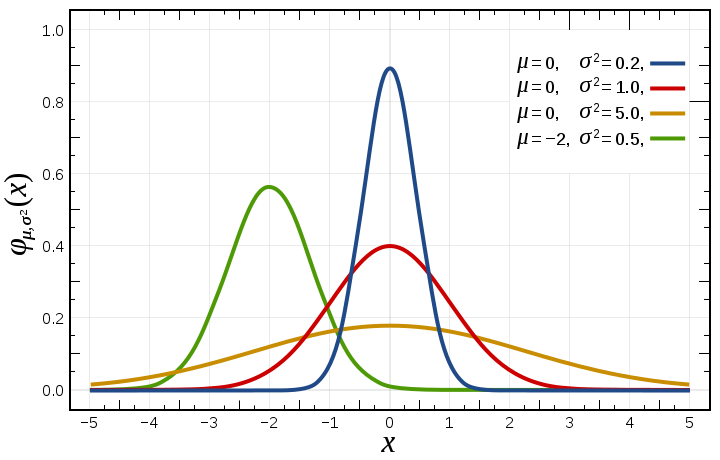
Normal distribution

Uniform distribution
How to access someone's skill?
outcome = a * luck + (1-a) * skill
a is big if someone's outcome depends on luck. So we can say that when we see someone's performence is fluctuated we can say that they depends more on luck.
Paradox of skill
In a compettion, most athletes skills are high, then their luck may play an important role.
Random walk
Assume that we flip a coin, when we get a head we plus 1 point, when we get a tail we minus 1 point. The game we talk about is called random walk. And we can get 3 conclusions from it.
(1) Assume that we play a very long times of this game. The final point we get may be 0.
(2) A is a positive number. The point higher than A or lower than -A is of the same probability.
(3) P(A times to win) = P(A times to lose)
Sometimes we see some companies are so successful, but maybe they are just random walking using the same algorithm. That's like the company flip the coin 10 times, and they get 10 heads results.
Normal random walk
Normal random walk is like random walk, the difference is instead of plus one minus one, normal random walk will plus or minus a random variable obeying normal distribution. Stock prices is an example for normal random walk. We assume that information is impeded and everyone would make use of it. For example,if you know today's stock price is up which will lead to tomorrow's stock price go up too, and you will buy more of it. But everyone knows it, so everyone will buy it. Since the price is so high, tomorrow's price must go down.
Finite memory random walk
The outcome depends on the previous 5 shocks, for example:
(1) Vt = Xt + Xt-1 + Xt-2 + Xt-3 + Xt -4.
Marckov process, random walk, path dependence
Is marckov process a random walk?
No, cuz marckov process depends on the previos state, but random walk doesn't.
Now we have 3 models and we can decide to use one of these 3 models to describe the phenomenon.





 本文探讨了随机性的表现形式,如正态分布与均匀分布,并通过技能悖论解释了运气与技巧的关系。此外,还介绍了随机游走的概念及其三种结论,包括普通随机游走和有限记忆随机游走的区别。
本文探讨了随机性的表现形式,如正态分布与均匀分布,并通过技能悖论解释了运气与技巧的关系。此外,还介绍了随机游走的概念及其三种结论,包括普通随机游走和有限记忆随机游走的区别。
















 2803
2803

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








