资料来源
该数据集记录了可能导致个体脱发的各种因素,每行代表一位独特的个体,列则涵盖了遗传、荷尔蒙变化、医疗状况、药物和治疗、营养缺乏、压力水平、年龄、不良护发习惯、环境因素、吸烟习惯、体重减轻以及脱发的有无等信息。
1. 数据可视化分析
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import numpy as np
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, roc_curve, auc, confusion_matrix
import xgboost as xgb
from sklearn.svm import SVC
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
1.1 数据预处理
# 数据预处理
df = pd.read_csv("/home/mw/input/data5086/archive/Predict Hair Fall.csv")
df.head(5)
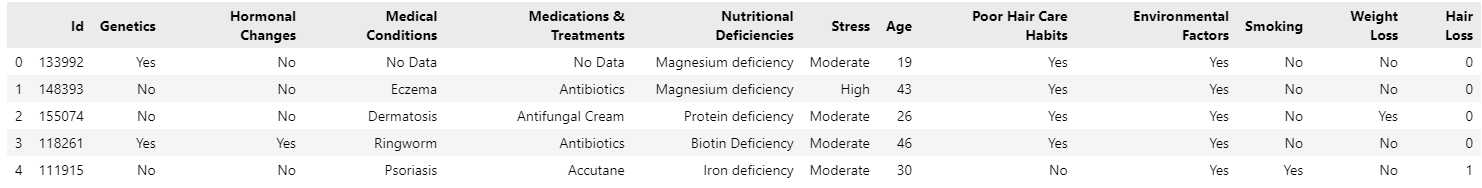
怕代码不显示,故插入图片
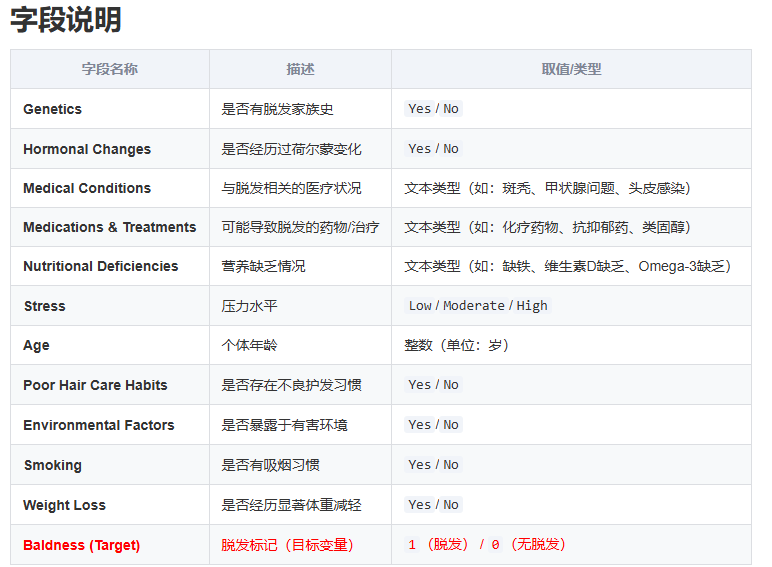
字段说明
| 字段名称 | 描述 | 取值/类型 |
|---|---|---|
| Genetics | 是否有脱发家族史 | Yes/No |
| Hormonal Changes | 是否经历过荷尔蒙变化 | Yes/No |
| Medical Conditions | 与脱发相关的医疗状况 | 文本类型(如:斑秃、甲状腺问题、头皮感染) |
| Medications & Treatments | 可能导致脱发的药物/治疗 | 文本类型(如:化疗药物、抗抑郁药、类固醇) |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | 营养缺乏情况 | 文本类型(如:缺铁、维生素D缺乏、Omega-3缺乏) |
| Stress | 压力水平 | Low/Moderate/High |
| Age | 个体年龄 | 整数(单位:岁) |
| Poor Hair Care Habits | 是否存在不良护发习惯 | Yes/No |
| Environmental Factors | 是否暴露于有害环境 | Yes/No |
| Smoking | 是否有吸烟习惯 | Yes/No |
| Weight Loss | 是否经历显著体重减轻 | Yes/No |
|
Baldness (Target)
|
脱发标记(目标变量)
|
1(脱发) /
0(无脱发)
|
1.2 标准化列名
部分英文列名可能会不标准或者乱码,所以自己定义一下
# 定义中文列名(12个特征和目标)
chinese_columns = [
'遗传因素',
'荷尔蒙变化',
'医疗状况',
'药物及治疗',
'营养缺乏',
'压力水平',
'年龄',
'不良护发习惯',
'环境因素',
'吸烟习惯',
'体重减轻',
'脱发标记' # 目标变量
]
# 将原始数据集的列名改为:第一列为'ID',后面依次为chinese_columns中的12个列名
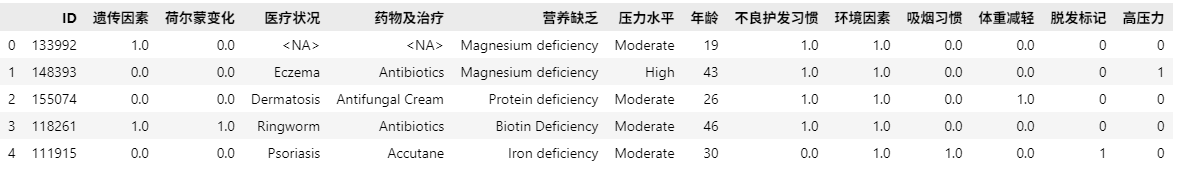
df.columns = ['ID'] + chinese_columns
df.head(5)
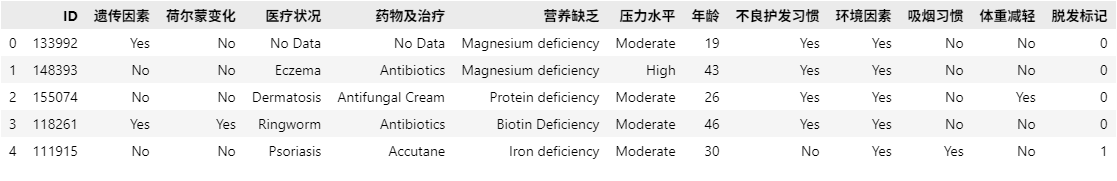
1.3 缺失值处理
# 缺失值处理
df.replace("No Data", pd.NA, inplace=True)
df.head(5)
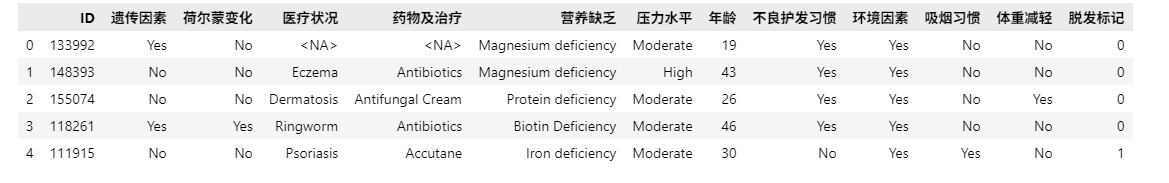
1.4 部分字段处理
# 二值列转换
binary_cols = ['遗传因素', '荷尔蒙变化', '不良护发习惯', '环境因素', '吸烟习惯', '体重减轻']
for col in binary_cols:
df[col] = df[col].map({'Yes': 1, 'No': 0, pd.NA: np.nan})
# 创建高压力分组
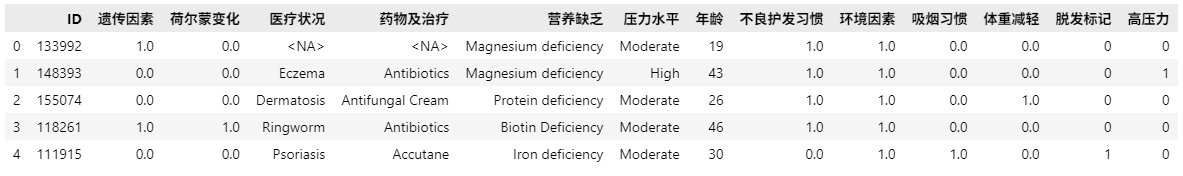
df['高压力'] = df['压力水平'].apply(lambda x: 1 if x == 'High' else 0)
df.head(5)
df.head(5)
1.5 数据可视化
脱发标记分布
# 脱发标记分布
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
sns.countplot(x='脱发标记', data=df, legend=False, hue='脱发标记', palette=['#7fcdbb', '#2c7fb8'])
plt.title('脱发标记分布 (0=无脱发, 1=有脱发)', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('')
plt.ylabel('样本数量', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks([0, 1], ['无脱发', '有脱发'], fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 计算脱发比例
hair_loss_rate = df['脱发标记'].mean() * 100
print(f"脱发比例: {hair_loss_rate:.1f}%")
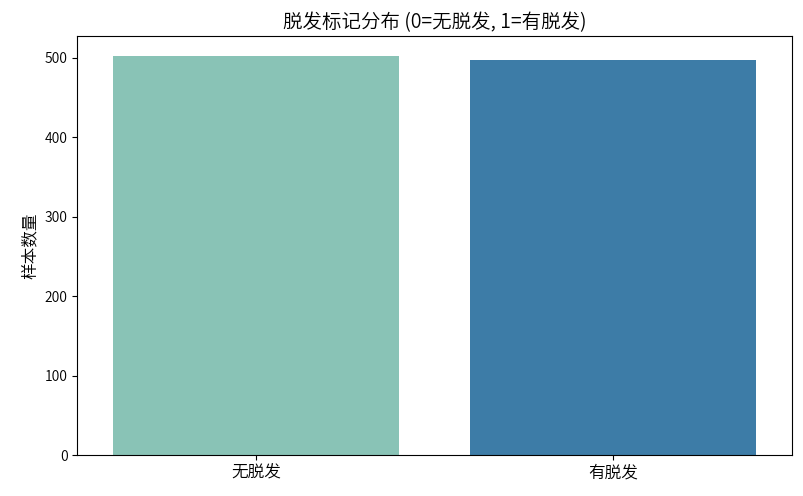
脱发比例: 49.7%
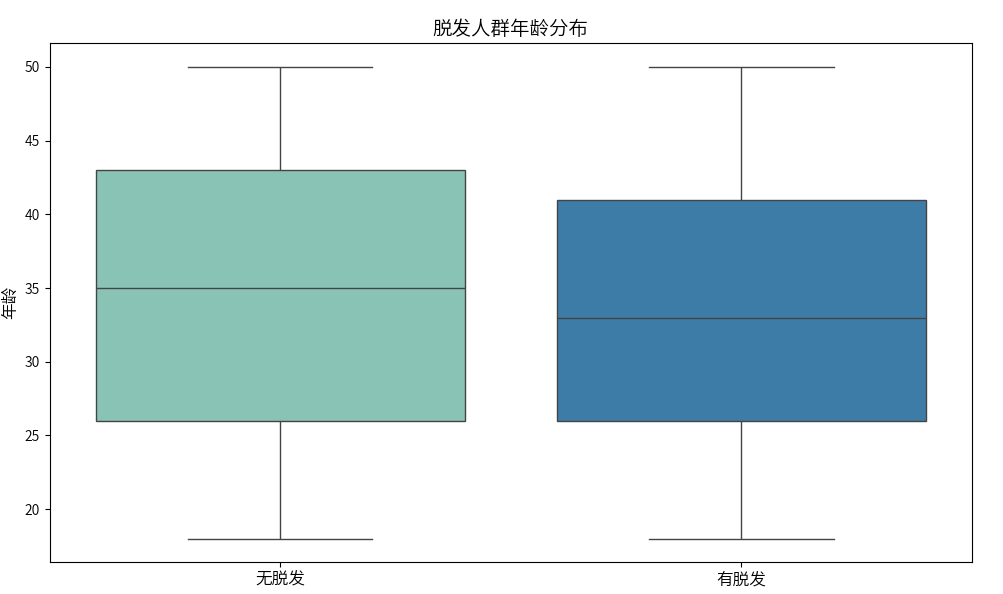
年龄与脱发关系
# 年龄与脱发关系
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
sns.boxplot(x='脱发标记', y='年龄', data=df, legend=False, hue='脱发标记', palette=['#7fcdbb', '#2c7fb8'])
plt.title('脱发人群年龄分布', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('')
plt.ylabel('年龄', fontsize=12)
plt.xticks([0, 1], ['无脱发', '有脱发'], fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
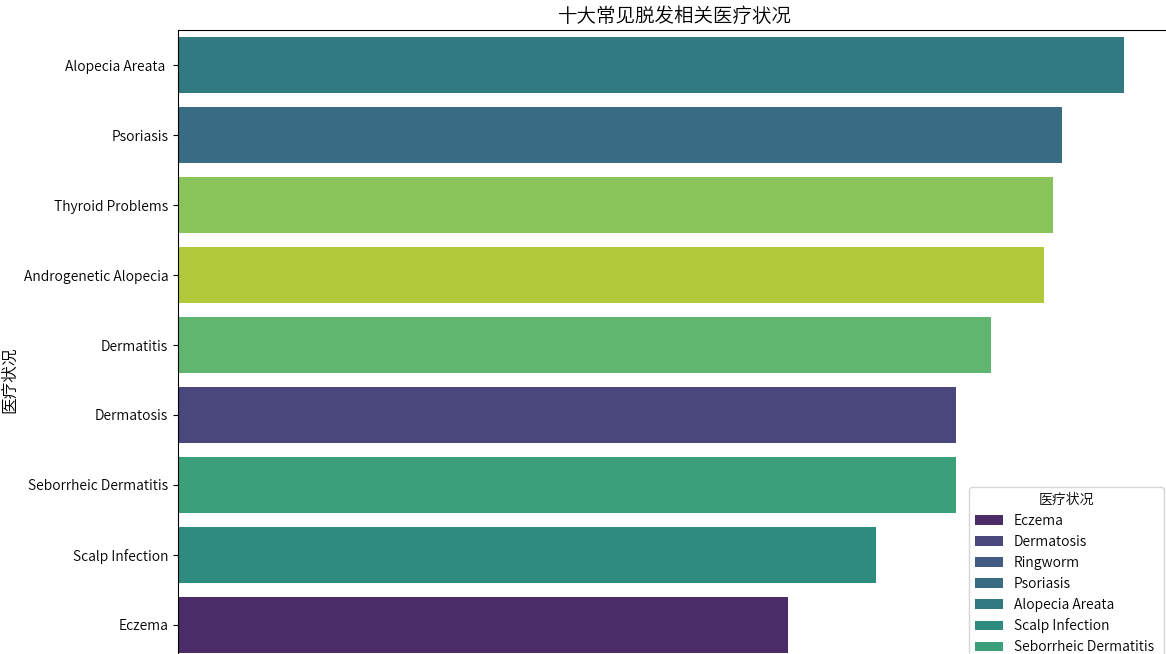
常见医疗状况分析
# 常见医疗状况分析
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
top_conditions = df['医疗状况'].value_counts().head(10).index
ax = sns.countplot(y='医疗状况', data=df, hue = '医疗状况',
order=top_conditions,
palette=sns.color_palette("viridis", 10))
plt.title('十大常见脱发相关医疗状况', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('样本数量', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('医疗状况', fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
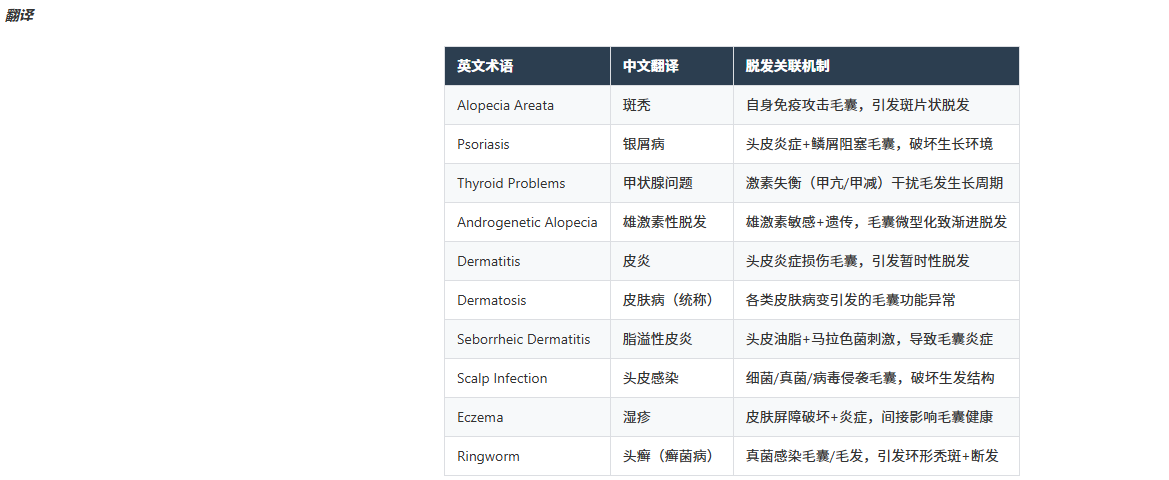
翻译
| 英文术语 | 中文翻译 | 脱发关联机制 |
|---|---|---|
| Alopecia Areata | 斑秃 | 自身免疫攻击毛囊,引发斑片状脱发 |
| Psoriasis | 银屑病 | 头皮炎症+鳞屑阻塞毛囊,破坏生长环境 |
| Thyroid Problems | 甲状腺问题 | 激素失衡(甲亢/甲减)干扰毛发生长周期 |
| Androgenetic Alopecia | 雄激素性脱发 | 雄激素敏感+遗传,毛囊微型化致渐进脱发 |
| Dermatitis | 皮炎 | 头皮炎症损伤毛囊,引发暂时性脱发 |
| Dermatosis | 皮肤病(统称) | 各类皮肤病变引发的毛囊功能异常 |
| Seborrheic Dermatitis | 脂溢性皮炎 | 头皮油脂+马拉色菌刺激,导致毛囊炎症 |
| Scalp Infection | 头皮感染 | 细菌/真菌/病毒侵袭毛囊,破坏生发结构 |
| Eczema | 湿疹 | 皮肤屏障破坏+炎症,间接影响毛囊健康 |
| Ringworm | 头癣(癣菌病) | 真菌感染毛囊/毛发,引发环形秃斑+断发 |
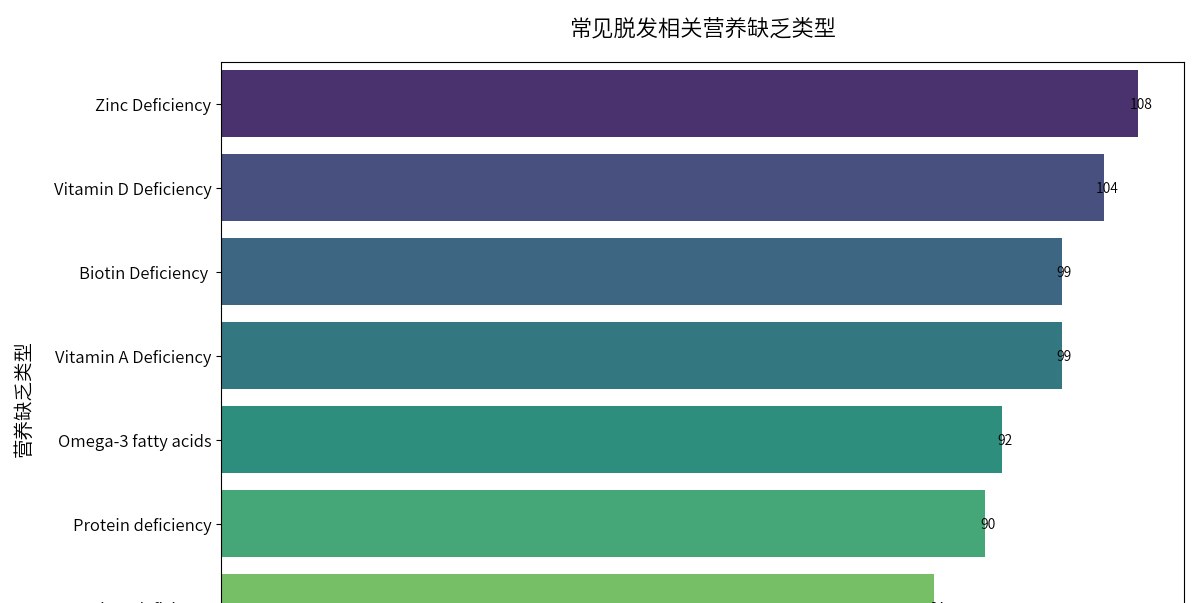
常见脱发相关营养缺乏类型
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
# 获取Top8类别
top_nutrition = df['营养缺乏'].value_counts().head(8).index
ax = sns.countplot(
y='营养缺乏',
data=df,
hue='营养缺乏',
order=top_nutrition,
hue_order=top_nutrition,
palette=sns.color_palette("viridis", len(top_nutrition)), # 动态匹配颜色数量
legend=False
)
# 添加数据标签
for p in ax.patches:
ax.annotate(f'{int(p.get_width())}',
(p.get_width() + 0.3, p.get_y() + p.get_height()/2),
ha='center', va='center', fontsize=10)
plt.title('常见脱发相关营养缺乏类型', fontsize=16, pad=20)
plt.xlabel('样本数量', fontsize=14)
plt.ylabel('营养缺乏类型', fontsize=14)
plt.xticks(fontsize=12)
plt.yticks(fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()

| 英文术语 | 中文翻译 | 脱发关联机制 |
|---|---|---|
| Zinc Deficiency | 锌缺乏 | 参与毛囊细胞分裂与角蛋白合成,缺乏时头发生长缓慢、易折断 |
| Vitamin D Deficiency | 维生素D缺乏 | 调节毛囊周期(如休止期→生长期转换),缺乏与「休止期脱发」「斑秃」等非瘢痕性脱发密切相关 |
| Biotin Deficiency | 生物素(维生素B₇)缺乏 | 参与头发健康维护,缺乏可能引发头皮脂溢性皮炎、头发变细易脱(普通人群单纯缺乏罕见,多与特殊饮食/疾病相关) |
| Vitamin A Deficiency | 维生素A缺乏 | 参与头皮油脂分泌以维持毛囊湿润环境,缺乏致头皮干燥、毛囊代谢紊乱; *过量摄入也会加速脱发*,需平衡 |
| Omega-3 fatty acids | Omega-3脂肪酸缺乏 | 作为「抗炎脂肪酸」,缺乏会升高头皮炎症风险、恶化毛囊微环境,间接引发脱发 |
| Protein deficiency | 蛋白质缺乏 | 头发主要由角蛋白(蛋白质)构成,缺乏时身体优先供应内脏,毛囊营养不足,表现为头发稀疏、易脱落 |
| Magnesium deficiency | 镁缺乏 | 参与300余种酶促反应,缺乏影响头皮血液循环与毛囊能量代谢,长期缺镁削弱头发生长动力 |
| Vitamin E deficiency | 维生素E缺乏 | 作为抗氧化剂,缺乏降低毛囊抗自由基能力,加速毛囊老化,使头发变脆、易折断 |
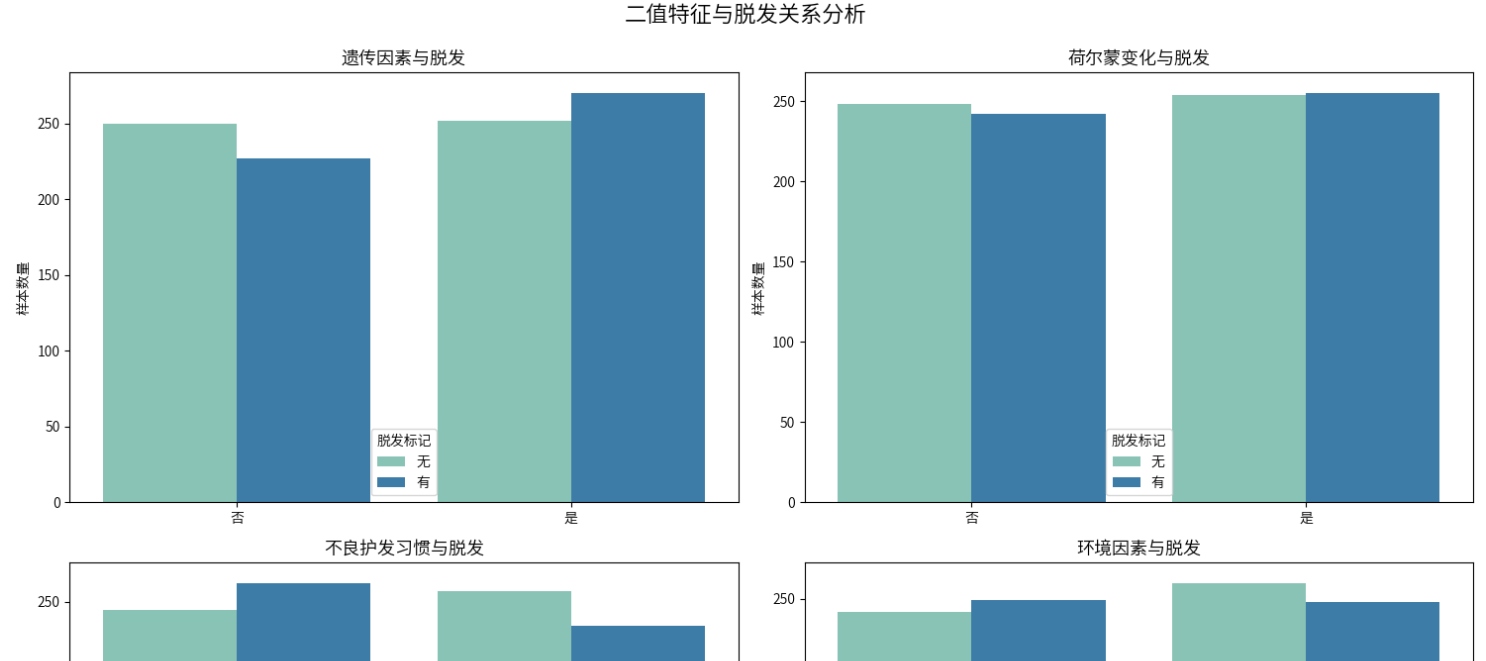
二值特征与脱发关系
# 二值特征与脱发关系
features = ['遗传因素', '荷尔蒙变化', '不良护发习惯', '环境因素', '吸烟习惯', '体重减轻']
fig, axes = plt.subplots(3, 2, figsize=(15, 15))
axes = axes.flatten()
for i, feature in enumerate(features):
if i < len(axes):
sns.countplot(x=feature, hue='脱发标记', data=df,
palette=['#7fcdbb', '#2c7fb8'], ax=axes[i])
axes[i].set_title(f'{feature}与脱发', fontsize=13)
axes[i].set_xlabel('')
axes[i].set_xticklabels(['否' if t == 0 else '是' for t in [0, 1]])
axes[i].set_ylabel('样本数量')
axes[i].legend(title='脱发标记', labels=['无', '有'])
plt.tight_layout()
plt.suptitle('二值特征与脱发关系分析', fontsize=16, y=1.02)
plt.show()
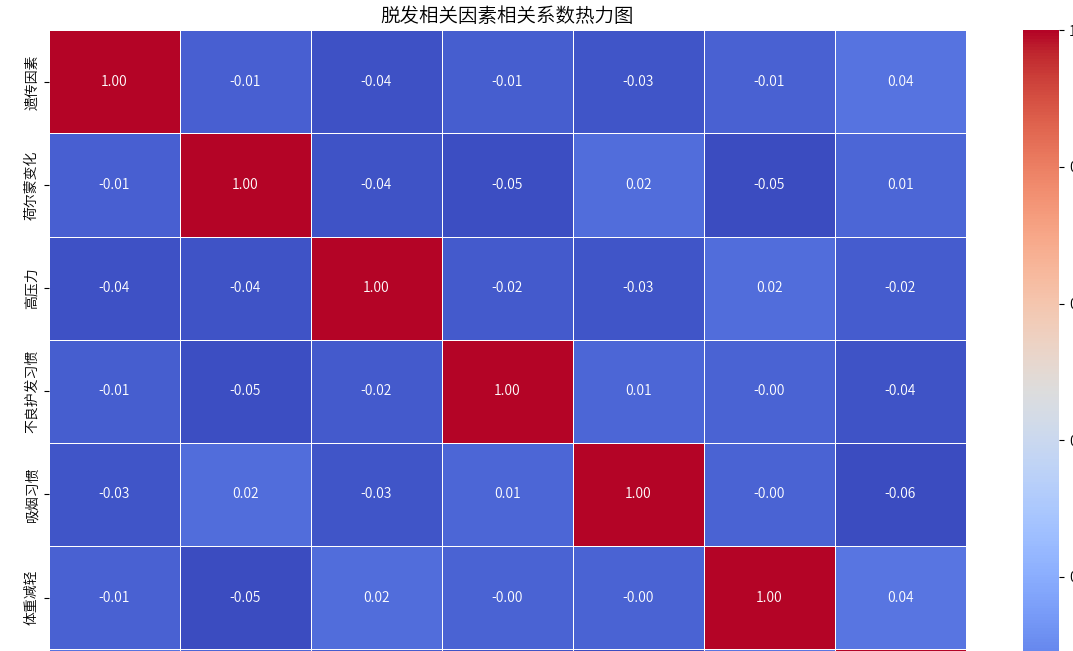
特征相关性分析
# 特征相关性分析
corr_features = ['遗传因素', '荷尔蒙变化', '高压力', '不良护发习惯', '吸烟习惯', '体重减轻', '脱发标记']
corr = df[corr_features].corr()
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.heatmap(corr, annot=True, cmap='coolwarm', fmt=".2f", linewidths=.5)
plt.title('脱发相关因素相关系数热力图', fontsize=14)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
2. 模型预测
使用随机森林及xgboost
df.head(5)
2.1 特征工程
字段处理及编码
# 缺失值处理(删除少量缺失行)
df.dropna(subset=['脱发标记', '医疗状况', '药物及治疗', '营养缺乏'], inplace=True)
# 复合变量
# 遗传因素+高压力组合
df['遗传高压力组合'] = ((df['遗传因素'] == 1) & (df['高压力'] == 1)).astype(int)
# 标签编码分类变量
label_encoders = {}
categorical_cols = ['医疗状况', '药物及治疗', '营养缺乏', '压力水平']
for col in categorical_cols:
le = LabelEncoder()
df[col] = le.fit_transform(df[col].astype(str))
label_encoders[col] = le
2.2 数据集划分
数据集比例选择85:15,因为数据太少了
# 特征选择(部分可能部分重复,但影响不大)
features = [
'遗传因素', '荷尔蒙变化', '医疗状况', '药物及治疗',
'营养缺乏', '压力水平', '年龄', '不良护发习惯',
'环境因素', '吸烟习惯', '体重减轻', '高压力',
'遗传高压力组合'
]
X = df[features]
y = df['脱发标记']
# 划分训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.15, random_state=42, stratify=y
)
2.3 选择模型并自适应参数
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
param_grid_rf = {
'n_estimators': [50, 100],
'max_depth': [5, 7],
'min_samples_split': [10, 15],
'class_weight': ['balanced', None]
}
grid_rf = GridSearchCV(
RandomForestClassifier(random_state=42),
param_grid_rf,
cv=3, # 小数据用3折交叉验证(减少计算量)
scoring='f1',# 用F1平衡precision/recall
n_jobs=-1 # 并行加速
)
grid_rf.fit(X_train, y_train)
best_rf = grid_rf.best_estimator_
param_grid_xgb = {
'n_estimators': [50, 100],
'max_depth': [3, 5],
'learning_rate': [0.1, 0.2],
'subsample': [0.8, 0.9],
'colsample_bytree': [0.8, 0.9]
}
grid_xgb = GridSearchCV(
xgb.XGBClassifier(objective='binary:logistic', random_state=42),
param_grid_xgb,
cv=3,
scoring='f1',
n_jobs=-1
)
grid_xgb.fit(X_train, y_train)
best_xgb = grid_xgb.best_estimator_
2.4 定义模型评估函数
# 模型评估函数
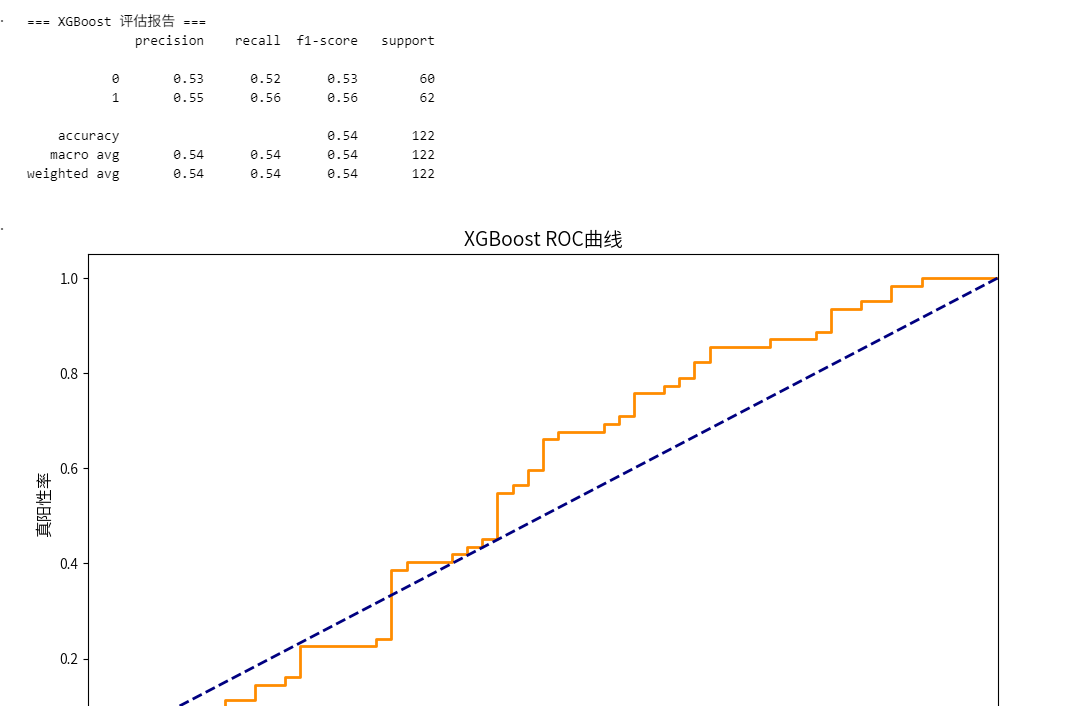
def evaluate_model(model, X_test, y_test, model_name):
"""评估模型并绘制ROC曲线"""
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
y_proba = model.predict_proba(X_test)[:, 1]
# 评估报告
print(f"=== {model_name} 评估报告 ===")
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
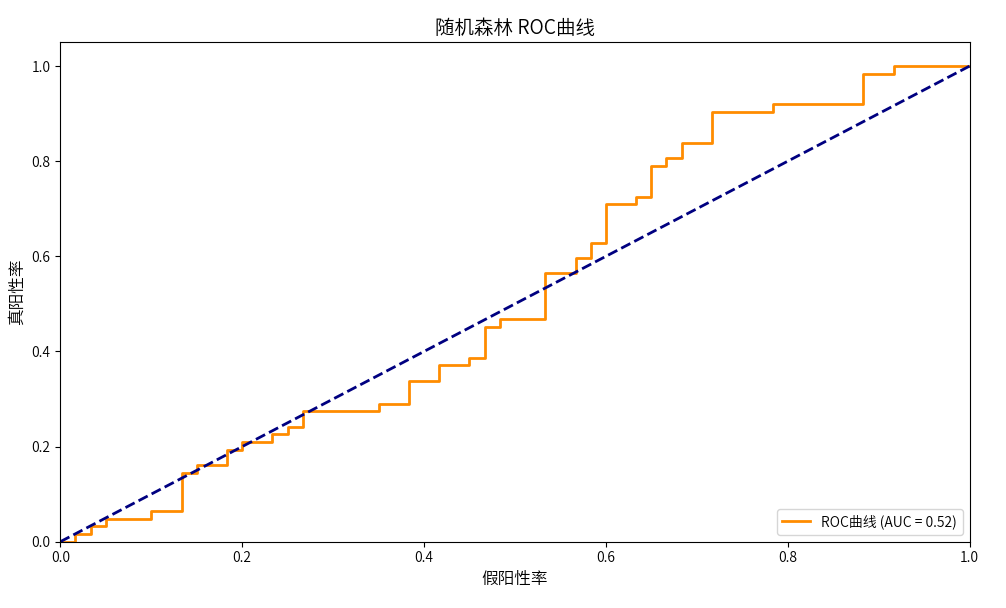
# ROC曲线
fpr, tpr, thresholds = roc_curve(y_test, y_proba)
roc_auc = auc(fpr, tpr)
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 6))
plt.plot(fpr, tpr, color='darkorange', lw=2,
label=f'ROC曲线 (AUC = {roc_auc:.2f})')
plt.plot([0, 1], [0, 1], color='navy', lw=2, linestyle='--')
plt.xlim([0.0, 1.0])
plt.ylim([0.0, 1.05])
plt.xlabel('假阳性率', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('真阳性率', fontsize=12)
plt.title(f'{model_name} ROC曲线', fontsize=14)
plt.legend(loc="lower right")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
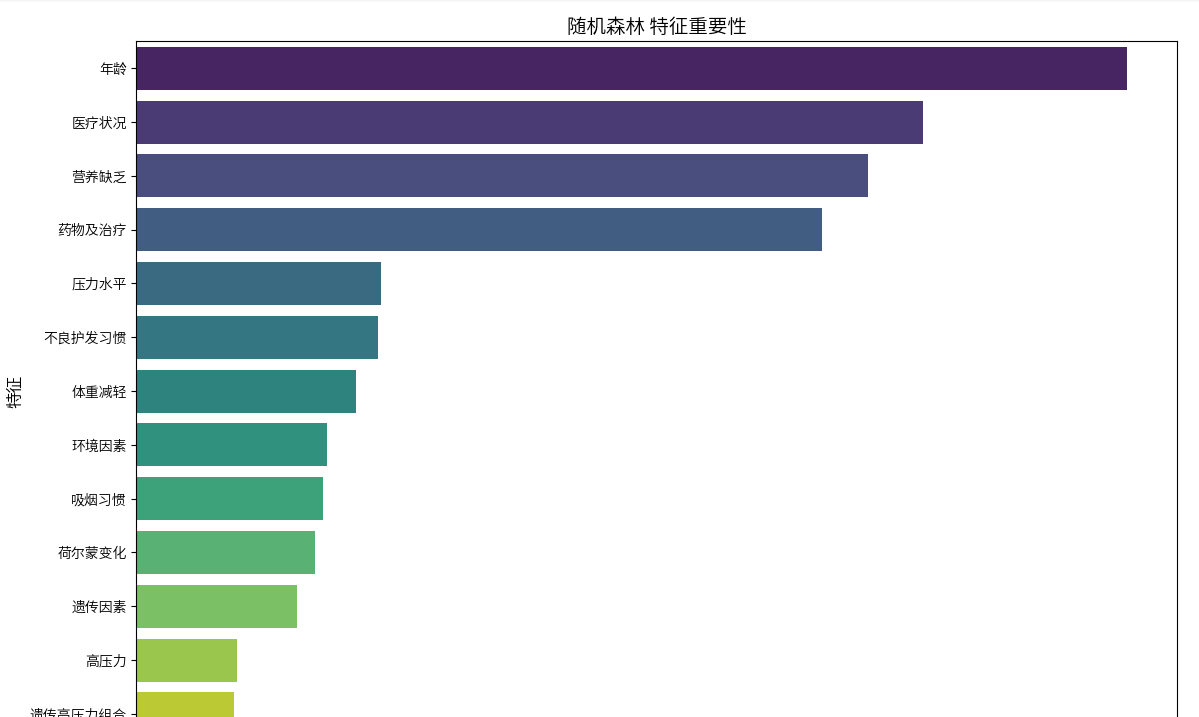
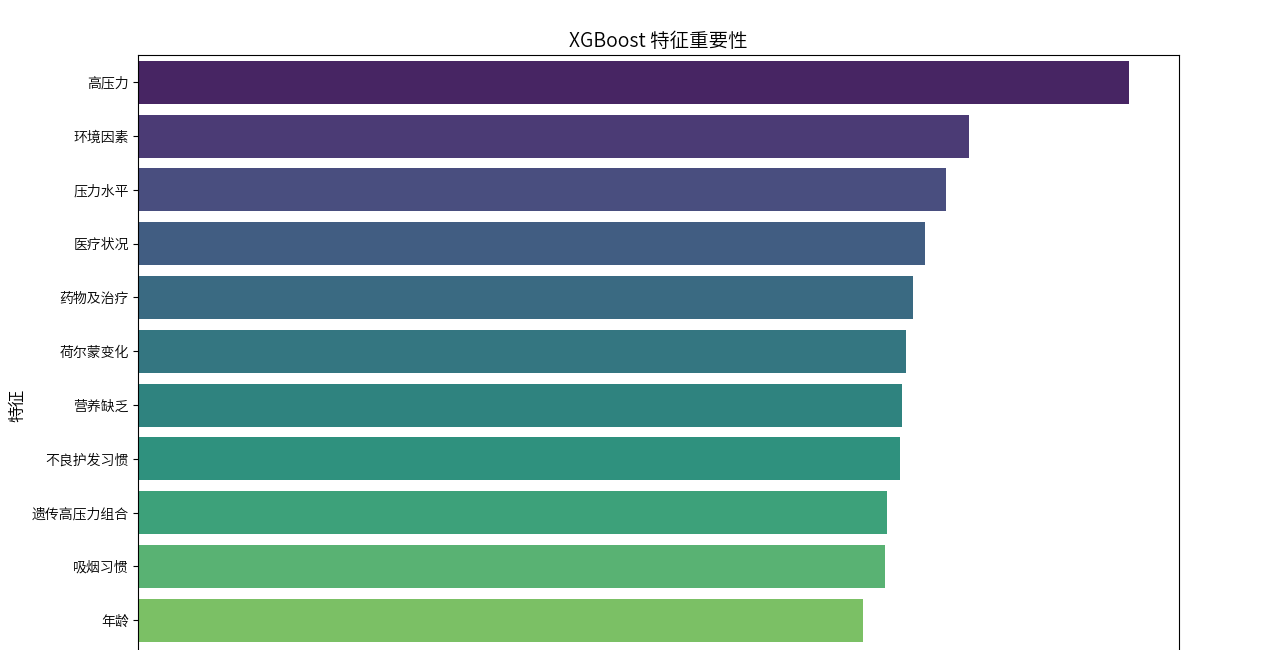
# 特征重要性
if hasattr(model, 'feature_importances_'):
feature_imp = pd.DataFrame({
'特征': features,
'重要性': model.feature_importances_
}).sort_values('重要性', ascending=False)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 8))
sns.barplot(x='重要性', y='特征', data=feature_imp, palette='viridis')
plt.title(f'{model_name} 特征重要性', fontsize=14)
plt.xlabel('重要性', fontsize=12)
plt.ylabel('特征', fontsize=12)
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
return roc_auc
2.5 评估模型
由于数据很少,所以不是很准,但是模型训练步骤差不多就这样了
如果觉得准确率太低可以使用重采样或过采样生成点数据
# 评估模型
rf_auc = evaluate_model(best_rf, X_test, y_test, "随机森林")
xgb_auc = evaluate_model(best_xgb, X_test, y_test, "XGBoost")























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








