前言
Attention机制是深度学习中的一种技术,特别是在自然语言处理和计算机视觉领域中得到了广泛的应用。它的核心思想是模仿人类的注意力机制,即人类在处理信息时会集中注意力在某些关键部分上,而忽略其他不那么重要的信息。在机器学习模型中,这可以帮助模型更好地捕捉到输入数据中的关键信息。
一、Attention机制的基本原理
1.输入表示
在自然语言处理(NLP)任务中,输入数据通常是文本形式的,我们需要将这些文本转换为模型可以处理的数值形式。这个过程称为嵌入(Embedding)。嵌入层将每个单词映射到一个高维空间中的向量,这些向量被称为词向量。词向量能够捕捉单词的语义信息,并且可以被神经网络处理。
# 定义一个简单的嵌入层class EmbeddingLayer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim): super(EmbeddingLayer, self).__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_dim) def forward(self, x): return self.embedding(x)# 随机生成一个输入序列input_seq = torch.randint(0, vocab_size, (32, 50)) # (batch_size, seq_len)# 获取输入表示input_repr = embedding_layer(input_seq)
在代码中,我们定义了一个EmbeddingLayer类,它包含一个nn.Embedding层,用于将输入的索引转换为对应的词向量。然后,我们生成一个随机的输入序列input_seq,它模拟了一个批量大小为32,序列长度为50的文本数据。通过嵌入层,我们将这些索引转换为词向量,得到输入表示input_repr。
2.计算注意力权重
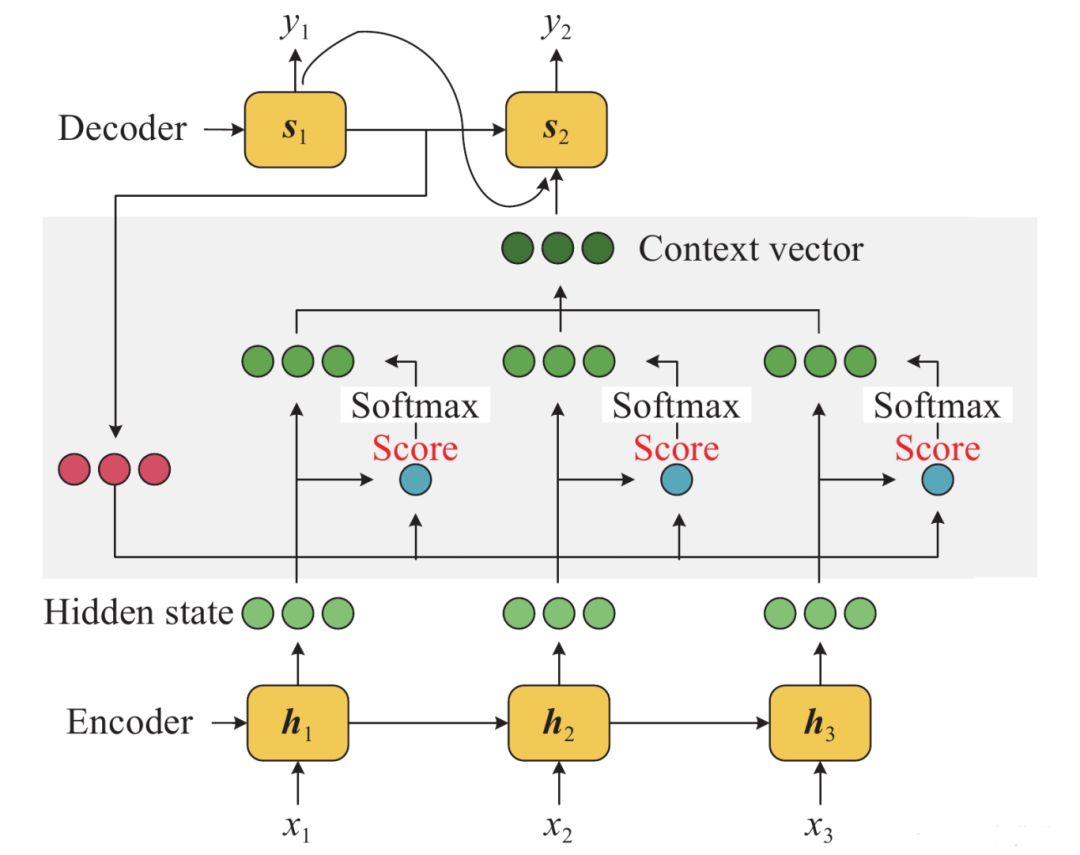
注意力机制允许模型在处理序列数据时,动态地聚焦于当前步骤最相关的信息。在自注意力(Self-Attention)中,每个元素都会计算与其他所有元素的关联程度,这通过计算查询(Q)、键(K)和值(V)的线性变换来实现。
class Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim): super(Attention, self).__init__() self.query = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.key = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.value = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) def forward(self, x): Q = self.query(x) K = self.key(x) V = self.value(x) attention_scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-1, -2)) / math.sqrt(embed_dim) attention_weights = F.softmax(attention_scores, dim=-1) return attention_weights
在这段代码中,我们定义了一个Attention类,它包含三个线性层,分别用于计算Q、K和V。然后,我们通过矩阵乘法和softmax函数计算注意力权重,这些权重表示序列中每个元素对当前元素的重要性。
3.加权求和
一旦我们有了注意力权重,我们就可以使用它们来加权求和序列中的元素,从而生成一个综合了所有元素信息的表示。
def weighted_sum(attention_weights, input_repr): return torch.matmul(attention_weights, input_repr)
这个简单的函数weighted_sum接受注意力权重和输入表示作为输入,然后通过矩阵乘法计算加权求和,得到一个综合了序列中所有元素信息的新表示。
4.输出
最后,我们使用一个输出层将加权求和得到的表示转换为最终的输出,这可以是分类任务的类别概率,也可以是其他任务的预测结果。
class OutputLayer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim, output_dim): super(OutputLayer, self).__init__() self.fc = nn.Linear(embed_dim, output_dim) def forward(self, x): return self.fc(x)
在这个代码段中,我们定义了一个OutputLayer类,它包含一个线性层,用于将模型的内部表示映射到输出空间。例如,在分类任务中,我们可以将嵌入维度的表示映射到类别数量的输出空间,并通过softmax函数或其他激活函数得到最终的预测概率。
5.实例代码
以下是使用Python和PyTorch实现上述内容的示例代码。这段代码将展示如何使用一个简单的Transformer模型来处理文本数据,包括输入表示、计算注意力权重、加权求和以及输出。
import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fclass TransformerBlock(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim, num_heads, dropout=0.1): super(TransformerBlock, self).__init__() self.attn = nn.MultiheadAttention(embed_dim, num_heads, dropout=dropout) self.ffn = nn.Sequential( nn.Linear(embed_dim, 4 * embed_dim), nn.GELU(), nn.Linear(4 * embed_dim, embed_dim), ) self.norm1 = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim) self.norm2 = nn.LayerNorm(embed_dim) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self, x): # 输入表示 # x: (seq_len, batch_size, embed_dim) attn_output, _ = self.attn(x, x, x) # 自注意力,输入和输出都是x attn_output = self.dropout(attn_output) x = self.norm1(x + attn_output) # 加权求和和残差连接 # 前馈网络 ffn_output = self.ffn(x) ffn_output = self.dropout(ffn_output) x = self.norm2(x + ffn_output) # 加权求和和残差连接 return xclass TextTransformer(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, embed_dim, num_heads, num_layers, dropout=0.1): super(TextTransformer, self).__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embed_dim) self.positional_encoding = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(1, 1, embed_dim)) self.encoder = nn.Sequential(*[TransformerBlock(embed_dim, num_heads, dropout) for _ in range(num_layers)]) self.fc_out = nn.Linear(embed_dim, vocab_size) # 假设是分类任务 def forward(self, x): # 输入表示 embeds = self.embedding(x) # (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim) embeds = embeds + self.positional_encoding[:, :embeds.size(1), :] # 添加位置编码 embeds = embeds.transpose(0, 1) # (seq_len, batch_size, embed_dim) # 计算注意力权重和加权求和 out = self.encoder(embeds) # 输出 out = out.transpose(0, 1) # (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim) out = self.fc_out(out[:, -1, :]) # 假设只取序列的最后一个向量进行分类 return out# 模型参数vocab_size = 10000 # 词汇表大小embed_dim = 256 # 嵌入层维度num_heads = 8 # 注意力头数num_layers = 6 # Transformer层数# 实例化模型model = TextTransformer(vocab_size, embed_dim, num_heads, num_layers)# 随机生成一个输入序列input_seq = torch.randint(0, vocab_size, (32, 100)) # (batch_size, seq_len)# 前向传播output = model(input_seq)print(output.shape) # 应该输出 (batch_size, vocab_size)
这段代码首先定义了一个TransformerBlock类,它包含了自注意力机制和前馈网络,然后定义了一个TextTransformer类,它包含了嵌入层、位置编码、编码器和输出层。在TextTransformer的前向传播中,我们首先将输入序列转换为嵌入表示,然后通过Transformer编码器进行处理,最后通过一个全连接层输出结果。这个例子展示了如何使用Transformer模型处理文本数据,并进行分类任务。
二、Attention机制的类型
1.Soft Attention
这种类型的注意力机制会输出一个概率分布,每个输入元素都有一个对应的权重,这些权重的和为1。Soft attention通常可以微分,因此可以用于梯度下降。Soft Attention输出一个概率分布,可以通过梯度下降进行优化。
import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.nn.functional as Fclass SoftAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim): super(SoftAttention, self).__init__() self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.randn(embed_dim, 1)) def forward(self, x): # x: (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim) scores = torch.matmul(x, self.weight).squeeze(-1) # (batch_size, seq_len) weights = F.softmax(scores, dim=-1) # Softmax to get probabilities return weights# 示例使用embed_dim = 128soft_attn = SoftAttention(embed_dim)input_seq = torch.randn(32, 50, embed_dim) # (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim)attention_weights = soft_attn(input_seq)print("Soft Attention Weights:", attention_weights.sum(dim=1)) # 应该接近于1
2.Hard Attention
与soft attention不同,hard attention会随机或确定性地选择一个输入元素,并只关注这个元素。Hard attention通常不可微分,因此训练时可能需要使用强化学习或变分方法。Hard Attention随机选择一个输入元素,这里我们使用一个简单的采样策略。
import torchclass HardAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim): super(HardAttention, self).__init__() def forward(self, x): # x: (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim) probs = torch.rand(x.size(0), x.size(1), device=x.device) _, idx = torch.topk(probs, k=1, dim=1) selected = torch.gather(x, 1, idx.unsqueeze(-1).expand(-1, -1, x.size(-1))) return selected.squeeze(1)# 示例使用hard_attn = HardAttention(embed_dim)selected_elements = hard_attn(input_seq)print("Hard Attention Selected Elements:", selected_elements.shape) # (batch_size, embed_dim)
3.Self-Attention
即自注意力机制,这是一种特殊的注意力机制,它允许输入序列中的元素相互之间计算注意力权重,这在Transformer模型中得到了广泛应用。Self-Attention允许输入序列中的元素相互之间计算注意力权重。
class SelfAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim): super(SelfAttention, self).__init__() self.query = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.key = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.value = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) def forward(self, x): # x: (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim) Q = self.query(x) K = self.key(x) V = self.value(x) attention_scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-1, -2)) / math.sqrt(embed_dim) attention_weights = F.softmax(attention_scores, dim=-1) output = torch.matmul(attention_weights, V) return output, attention_weights# 示例使用self_attn = SelfAttention(embed_dim)output, weights = self_attn(input_seq)print("Self Attention Output:", output.shape) # (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim)
4.Multi-Head Attention
在Transformer模型中,为了捕捉不同子空间中的信息,会使用多头注意力机制,即并行地运行多个自注意力机制,然后将结果合并。Multi-Head Attention并行地运行多个自注意力机制,然后将结果合并。
class MultiHeadAttention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, embed_dim, num_heads): super(MultiHeadAttention, self).__init__() self.num_heads = num_heads self.head_dim = embed_dim // num_heads assert self.head_dim * num_heads == embed_dim, "embed_dim must be divisible by num_heads" self.query = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.key = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.value = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) self.fc_out = nn.Linear(embed_dim, embed_dim) def forward(self, x): # x: (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim) batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim = x.size() Q = self.query(x).view(batch_size, seq_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2) K = self.key(x).view(batch_size, seq_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2) V = self.value(x).view(batch_size, seq_len, self.num_heads, self.head_dim).transpose(1, 2) attention_scores = torch.matmul(Q, K.transpose(-1, -2)) / math.sqrt(self.head_dim) attention_weights = F.softmax(attention_scores, dim=-1) output = torch.matmul(attention_weights, V).transpose(1, 2).contiguous() output = output.view(batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim) output = self.fc_out(output) return output# 示例使用num_heads = 8multi_head_attn = MultiHeadAttention(embed_dim, num_heads)multi_head_output = multi_head_attn(input_seq)print("Multi-Head Attention Output:", multi_head_output.shape) # (batch_size, seq_len, embed_dim)
Soft Attention和Self-Attention可以直接用于梯度下降优化,而Hard Attention由于其不可微分的特性,可能需要特殊的训练技巧。Multi-Head Attention则通过并行处理捕捉更丰富的信息。
三、Attention机制的应用
1.机器翻译
机器翻译是注意力机制最著名的应用之一。在这个任务中,模型需要将一种语言(源语言)的文本转换为另一种语言(目标语言)的文本。注意力机制在这里的作用是在生成目标语言的每个单词时,动态地聚焦于源语言中相关的部分,这有助于捕捉长距离依赖关系,并提高翻译的准确性和流畅性。
import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.optim as optimclass Encoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout): super().__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_dim, emb_dim) self.rnn = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout=dropout) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self, src): embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(src)) outputs, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedded) return hidden, cellclass Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, enc_hid_dim, dec_hid_dim): super().__init__() self.attn = nn.Linear((enc_hid_dim * 2) + dec_hid_dim, dec_hid_dim) self.v = nn.Linear(dec_hid_dim, 1, bias=False) def forward(self, hidden, encoder_outputs): hidden = hidden.repeat(encoder_outputs.shape[0], 1).transpose(0, 1) encoder_outputs = encoder_outputs.transpose(0, 1) attn_energies = self.score(hidden, encoder_outputs) return F.softmax(attn_energies, dim=-1) def score(self, hidden, encoder_outputs): energy = torch.tanh(self.attn(torch.cat([hidden, encoder_outputs], dim=2))) energy = self.v(energy).squeeze(2) return energyclass Decoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, output_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout): super().__init__() self.output_dim = output_dim self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_dim, emb_dim) self.rnn = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout=dropout) self.attention = Attention(hid_dim, hid_dim) self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hid_dim, output_dim) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self, input, hidden, cell, encoder_outputs): input = input.unsqueeze(0) embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(input)) attn_weights = self.attention(hidden, encoder_outputs) context = attn_weights.bmm(encoder_outputs.transpose(0, 1)) rnn_input = torch.cat((embedded, context), dim=2) output, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(rnn_input, (hidden, cell)) output = output.squeeze(0) out = self.fc_out(output) return out, hidden, cell# 假设参数input_dim = 1000 # 源语言词汇表大小output_dim = 1000 # 目标语言词汇表大小emb_dim = 256 # 嵌入层维度hid_dim = 512 # 隐藏层维度n_layers = 2 # LSTM层数dropout = 0.1 # Dropout# 实例化模型encoder = Encoder(input_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout)decoder = Decoder(output_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout)# 假设输入src = torch.randint(0, input_dim, (10, 32)) # (seq_len, batch_size)input = torch.randint(0, output_dim, (1, 32)) # (seq_len, batch_size)# 前向传播hidden, cell = encoder(src)output, hidden, cell = decoder(input, hidden, cell, src)print("Translation Output:", output.shape) # (batch_size, output_dim)
在示例代码中,我们定义了一个基于注意力的Seq2Seq模型,它由一个编码器和一个解码器组成。编码器读取源语言文本,并输出一个上下文向量和隐藏状态。解码器则使用这个上下文向量来生成目标语言文本,同时更新隐藏状态。注意力机制通过计算源语言文本中每个单词的重要性,并将这些信息合并到解码器的每一步中,从而允许模型在生成每个单词时“回顾”源语言文本的相关部分。
2.文本摘要
在自动文本摘要任务中,模型需要从长文本中提取关键信息,并生成一个简短的摘要。注意力机制可以帮助模型识别哪些句子或短语对于理解全文内容最为重要,从而在生成摘要时保留这些关键信息。
import torchimport torch.nn as nnimport torch.optim as optimclass Encoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout): super().__init__() self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_dim, emb_dim) self.rnn = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout=dropout) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self, src): embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(src)) outputs, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedded) return hidden, cellclass Attention(nn.Module): def __init__(self, enc_hid_dim, dec_hid_dim): super().__init__() self.attn = nn.Linear((enc_hid_dim * 2) + dec_hid_dim, dec_hid_dim) self.v = nn.Linear(dec_hid_dim, 1, bias=False) def forward(self, hidden, encoder_outputs): hidden = hidden.repeat(encoder_outputs.shape[0], 1).transpose(0, 1) encoder_outputs = encoder_outputs.transpose(0, 1) attn_energies = self.score(hidden, encoder_outputs) return F.softmax(attn_energies, dim=-1) def score(self, hidden, encoder_outputs): energy = torch.tanh(self.attn(torch.cat([hidden, encoder_outputs], dim=2))) energy = self.v(energy).squeeze(2) return energyclass Decoder(nn.Module): def __init__(self, output_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout): super().__init__() self.output_dim = output_dim self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_dim, emb_dim) self.rnn = nn.LSTM(emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout=dropout) self.attention = Attention(hid_dim, hid_dim) self.fc_out = nn.Linear(hid_dim, output_dim) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self, input, hidden, cell, encoder_outputs): input = input.unsqueeze(0) embedded = self.dropout(self.embedding(input)) attn_weights = self.attention(hidden, encoder_outputs) context = attn_weights.bmm(encoder_outputs.transpose(0, 1)) rnn_input = torch.cat((embedded, context), dim=2) output, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(rnn_input, (hidden, cell)) output = output.squeeze(0) out = self.fc_out(output) return out, hidden, cell# 假设参数input_dim = 1000 # 源语言词汇表大小output_dim = 1000 # 目标语言词汇表大小emb_dim = 256 # 嵌入层维度hid_dim = 512 # 隐藏层维度n_layers = 2 # LSTM层数dropout = 0.1 # Dropout# 实例化模型encoder = Encoder(input_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout)decoder = Decoder(output_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, n_layers, dropout)# 假设输入src = torch.randint(0, input_dim, (10, 32)) # (seq_len, batch_size)input = torch.randint(0, output_dim, (1, 32)) # (seq_len, batch_size)# 前向传播hidden, cell = encoder(src)output, hidden, cell = decoder(input, hidden, cell, src)print("Translation Output:", output.shape) # (batch_size, output_dim)
虽然示例代码没有详细展示,但可以想象,一个基于注意力的文本摘要模型会有一个编码器来处理输入文本,并生成一系列隐藏状态。然后,一个解码器会使用这些隐藏状态和注意力权重来生成摘要,同时关注输入文本中与当前生成摘要最相关的部分。这样,生成的摘要不仅包含了原文的核心信息,而且更加紧凑和连贯。
3.图像识别
在图像识别任务中,模型的目标是识别图像中的对象。注意力机制可以帮助模型集中注意力在图像中的关键特征上,例如人脸的眼睛或汽车的轮子,这些特征对于识别任务至关重要。
import torchvision.models as modelsclass AttentionCNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self): super().__init__() self.cnn = models.resnet18(pretrained=True) self.fc = nn.Linear(512, 1000) # 假设有1000个类别 def forward(self, x): x = self.cnn(x) # 假设我们添加一个简单的注意力层 attention_weights = torch.sigmoid(self.cnn.fc.weight) x = torch.sum(x * attention_weights, dim=1) x = self.fc(x) return x# 实例化模型attention_cnn = AttentionCNN()# 假设输入input_image = torch.randn(32, 3, 224, 224) # (batch_size, channels, height, width)# 前向传播output = attention_cnn(input_image)print("Image Recognition Output:", output.shape) # (batch_size, num_classes)
在示例代码中,我们定义了一个带有简单注意力层的CNN模型。这个注意力层通过学习图像中不同区域的重要性,为每个特征分配权重。这样,模型就可以更加关注于对分类任务最重要的特征,而不是平等对待图像中的所有像素。这种方法可以提高模型对图像中关键信息的敏感性,从而提高识别的准确性。
4.语音识别
语音识别是将语音信号转换为文本的任务。在这个任务中,模型需要理解语音中的语义信息,并将其转换为书面语言。注意力机制可以帮助模型在处理语音信号时,关注那些携带重要信息的部分,例如特定的音素或单词。
class SpeechRecognitionModel(nn.Module): def __init__(self, input_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, output_dim, n_layers, dropout): super().__init__() self.rnn = nn.LSTM(input_dim, emb_dim, n_layers, dropout=dropout, batch_first=True) self.attention = Attention(emb_dim, emb_dim) self.fc_out = nn.Linear(emb_dim, output_dim) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(dropout) def forward(self, x): # x: (batch_size, seq_len, input_dim) outputs, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(x) attn_weights = self.attention(hidden, outputs) context = torch.bmm(attn_weights, outputs) output = self.fc_out(context.squeeze(1)) return output# 假设参数input_dim = 128 # 特征维度output_dim = 1000 # 词汇表大小# 实例化模型speech_recognition = SpeechRecognitionModel(input_dim, emb_dim, hid_dim, output_dim, n_layers, dropout)# 假设输入speech_signal = torch.randn(32, 100, input_dim) # (batch_size, seq_len, input_dim)# 前向传播output = speech_recognition(speech_signal)print("Speech Recognition Output:", output.shape) # (batch_size, output_dim)
在示例代码中,我们定义了一个基于注意力的RNN模型,用于处理语音信号。模型的RNN部分处理序列化的语音特征,而注意力机制则帮助模型在生成每个单词时,关注语音信号中最相关的部分。这样,模型可以更准确地捕捉到语音中的语义信息,并将其转换为正确的文本输出。
最后
为什么要学AI大模型
当下,⼈⼯智能市场迎来了爆发期,并逐渐进⼊以⼈⼯通⽤智能(AGI)为主导的新时代。企业纷纷官宣“ AI+ ”战略,为新兴技术⼈才创造丰富的就业机会,⼈才缺⼝将达 400 万!
DeepSeek问世以来,生成式AI和大模型技术爆发式增长,让很多岗位重新成了炙手可热的新星,岗位薪资远超很多后端岗位,在程序员中稳居前列。

与此同时AI与各行各业深度融合,飞速发展,成为炙手可热的新风口,企业非常需要了解AI、懂AI、会用AI的员工,纷纷开出高薪招聘AI大模型相关岗位。

最近很多程序员朋友都已经学习或者准备学习 AI 大模型,后台也经常会有小伙伴咨询学习路线和学习资料,我特别拜托北京清华大学学士和美国加州理工学院博士学位的鲁为民老师给大家这里给大家准备了一份涵盖了AI大模型入门学习思维导图、精品AI大模型学习书籍手册、视频教程、实战学习等录播视频 全系列的学习资料,这些学习资料不仅深入浅出,而且非常实用,让大家系统而高效地掌握AI大模型的各个知识点。
这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】

AI大模型系统学习路线
在面对AI大模型开发领域的复杂与深入,精准学习显得尤为重要。一份系统的技术路线图,不仅能够帮助开发者清晰地了解从入门到精通所需掌握的知识点,还能提供一条高效、有序的学习路径。

但知道是一回事,做又是另一回事,初学者最常遇到的问题主要是理论知识缺乏、资源和工具的限制、模型理解和调试的复杂性,在这基础上,找到高质量的学习资源,不浪费时间、不走弯路,又是重中之重。
AI大模型入门到实战的视频教程+项目包
看视频学习是一种高效、直观、灵活且富有吸引力的学习方式,可以更直观地展示过程,能有效提升学习兴趣和理解力,是现在获取知识的重要途径

光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。

海量AI大模型必读的经典书籍(PDF)
阅读AI大模型经典书籍可以帮助读者提高技术水平,开拓视野,掌握核心技术,提高解决问题的能力,同时也可以借鉴他人的经验。对于想要深入学习AI大模型开发的读者来说,阅读经典书籍是非常有必要的。

600+AI大模型报告(实时更新)
这套包含640份报告的合集,涵盖了AI大模型的理论研究、技术实现、行业应用等多个方面。无论您是科研人员、工程师,还是对AI大模型感兴趣的爱好者,这套报告合集都将为您提供宝贵的信息和启示。

AI大模型面试真题+答案解析
我们学习AI大模型必然是想找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题都是总结当前最新、最热、最高频的面试题,并且每道题都有详细的答案,面试前刷完这套面试题资料,小小offer,不在话下


这份完整版的大模型 AI 学习资料已经上传优快云,朋友们如果需要可以微信扫描下方优快云官方认证二维码免费领取【保证100%免费】





















 2853
2853

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








