能否在这段代码中加入回环估计,使得每一变换矩阵可以校准import math
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
matplotlib.rc("font", family='YouYuan')
EPS = 0.0001
MAX_ITER = 100
show_animation = False
def icp_matching(previous_points, current_points):
"""
Iterative Closest Point matching
"""
H = None
dError = np.inf
preError = np.inf
count = 0
while dError >= EPS:
count += 1
indexes, error = nearest_neighbor_association(previous_points, current_points)
Rt, Tt = svd_motion_estimation(previous_points[:, indexes], current_points)
# 更新当前点
current_points = (Rt @ current_points) + Tt[:, np.newaxis]
dError = preError - error
if dError < 0:
break
preError = error
H = update_homogeneous_matrix(H, Rt, Tt)
if dError <= EPS or MAX_ITER <= count:
break
R = np.array(H[0:-1, 0:-1])
T = np.array(H[0:-1, -1])
return R, T
def update_homogeneous_matrix(Hin, R, T):
r_size = R.shape[0]
H = np.zeros((r_size + 1, r_size + 1))
H[0:r_size, 0:r_size] = R
H[0:r_size, r_size] = T
H[r_size, r_size] = 1.0
if Hin is None:
return H
else:
return Hin @ H
def nearest_neighbor_association(previous_points, current_points):
"""
找到 current_points 中每个点在 previous_points 中的最近邻索引。
支持两组点数不同。
"""
# 计算两组点的欧氏距离矩阵
n_prev = previous_points.shape[1]
n_curr = current_points.shape[1]
d = np.zeros((n_curr, n_prev))
for i in range(n_curr):
diff = previous_points - current_points[:, i:i+1]
d[i, :] = np.linalg.norm(diff, axis=0)
indexes = np.argmin(d, axis=1)
error = np.mean(np.min(d, axis=1))
return indexes, error
def svd_motion_estimation(previous_points, current_points):
pm = np.mean(previous_points, axis=1)
cm = np.mean(current_points, axis=1)
p_shift = previous_points - pm[:, np.newaxis]
c_shift = current_points - cm[:, np.newaxis]
W = c_shift @ p_shift.T
u, s, vh = np.linalg.svd(W)
R = (u @ vh).T
t = pm - (R @ cm)
return R, t
# ===== 新增功能部分 =====
def generate_rectangle_points(length=20, width=10, n_points=2000, noise=0.05):
"""生成矩形边界点云并加噪声"""
n_side = n_points // 4
top = np.vstack((np.linspace(-length / 2, length / 2, n_side),
np.ones(n_side) * width / 2))
bottom = np.vstack((np.linspace(-length / 2, length / 2, n_side),
np.ones(n_side) * -width / 2))
left = np.vstack((np.ones(n_side) * -length / 2,
np.linspace(-width / 2, width / 2, n_side)))
right = np.vstack((np.ones(n_side) * length / 2,
np.linspace(-width / 2, width / 2, n_side)))
points = np.hstack((top, bottom, left, right))
points += np.random.randn(2, points.shape[1]) * noise
return points
def split_by_angle(points, center=np.array([0, 0]), start=-30, step=0.2):
"""按角度扇区划分点云"""
sectors = []
angles = np.degrees(np.arctan2(points[1, :] - center[1],
points[0, :] - center[0]))
angles = (angles + 360) % 360
t=int(360/step)
for k in range(t):
theta1 = (start + k * step) % 360
theta2 = (theta1 + 60) % 360 # 每个扇区宽度为60°
if theta1 < theta2:
mask = (angles >= theta1) & (angles <= theta2)
else: # 角度跨越360°边界
mask = (angles >= theta1) | (angles <= theta2)
Ak = points[:, mask]
sectors.append(Ak)
return sectors
def merge_point_clouds(A_list, R_list, T_list):
"""将所有点云A_k变换到A1坐标系并融合"""
merged = [A_list[0]]
R_total = [np.eye(2)]
T_total = [np.zeros(2)]
# 累积每个点云的全局变换
for k in range(1, len(A_list)):
Rk, Tk = R_list[k - 1], T_list[k - 1]
R_acc = R_total[-1] @ Rk
T_acc = R_total[-1] @ T_list[k - 1] + T_total[-1]
R_total.append(R_acc)
T_total.append(T_acc)
Ak_global = R_acc @ A_list[k] + T_acc[:, None]
merged.append(Ak_global)
merged_points = np.hstack(merged)
merged_points = np.unique(np.round(merged_points, 2), axis=1)
return merged_points, R_total, T_total
# ===== 主逻辑 =====
def main():
print("开始运行改造后的 ICP 例子...")
# Step 1: 生成矩形点云
rect_points = generate_rectangle_points()
# Step 2: 按角度扇区切分
sectors = split_by_angle(rect_points)
R_list, T_list = [], []
used_sectors = []
# Step 3: 对相邻扇区进行 ICP
for k in range(1, len(sectors)):
A_prev = sectors[k - 1]
A_curr = sectors[k]
if A_prev.shape[1] < 5 or A_curr.shape[1] < 5:
continue
R, T = icp_matching(A_prev, A_curr)
R_list.append(R)
T_list.append(T)
used_sectors.append(A_curr)
print(f"ICP {k}: R=\n{R}\nT={T}")
# Step 4: 融合所有点云到A1坐标系
merged_points, R_total, T_total = merge_point_clouds(sectors, R_list, T_list)
# Step 5: 可视化结果
plt.figure()
plt.scatter(rect_points[0, :], rect_points[1, :], s=3, label="原始矩形点云")
plt.scatter(merged_points[0, :], merged_points[1, :], s=3, label="ICP融合点云")
plt.legend()
plt.axis("equal")
plt.title("ICP融合结果对比")
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
最新发布
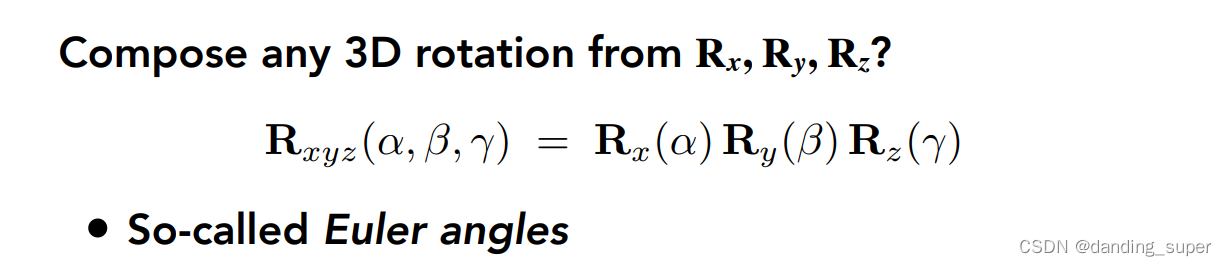
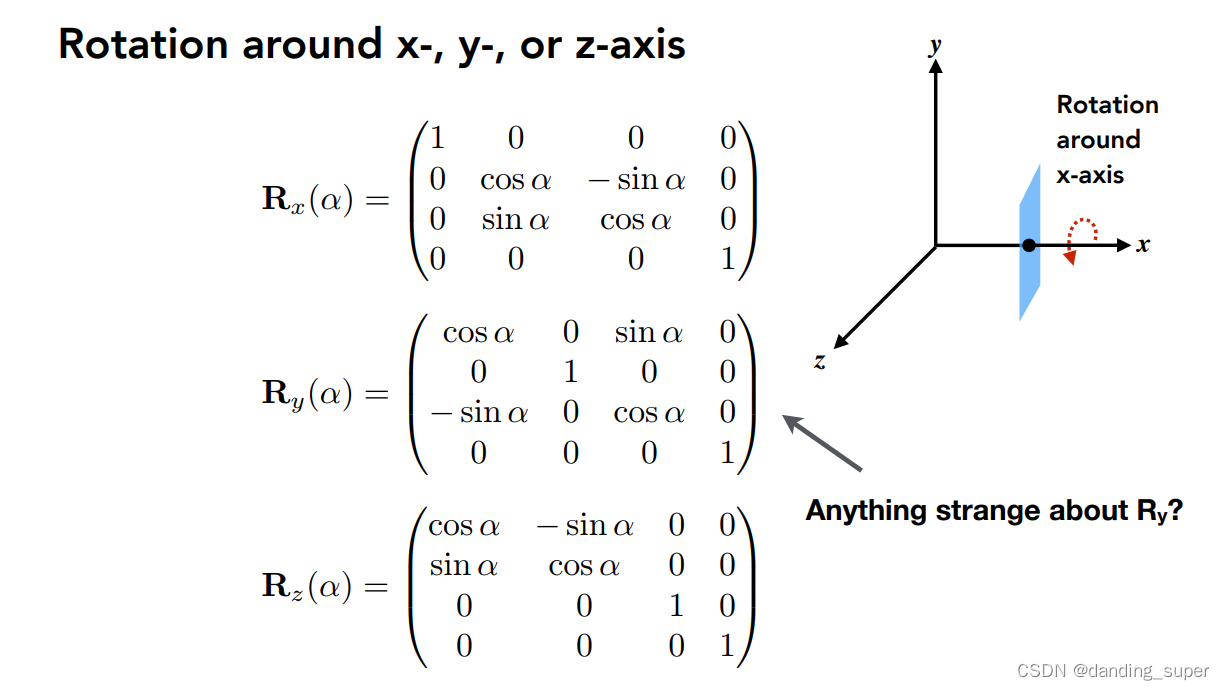





 这篇博客介绍了3D几何变换中的旋转操作,包括沿着对齐轴的旋转、任意轴旋转、从一个向量到另一个向量的旋转以及从一组点集到另一组点集的旋转。文章详细阐述了每种旋转的方法,并提供了相应的Python代码实现,还引用了相关论文和资源来解决实际问题。
这篇博客介绍了3D几何变换中的旋转操作,包括沿着对齐轴的旋转、任意轴旋转、从一个向量到另一个向量的旋转以及从一组点集到另一组点集的旋转。文章详细阐述了每种旋转的方法,并提供了相应的Python代码实现,还引用了相关论文和资源来解决实际问题。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 242
242

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








