2.1、Vectors
2.1.1、Vectors0
Vectors are used to group related signals using one name to make it more convenient to manipulate. For example, wire [7:0] w; declares an 8-bit vector named w that is functionally equivalent to having 8 separate wires.
Notice that the declaration of a vector places the dimensions before the name of the vector, which is unusual compared to C syntax. However, the part select has the dimensions after the vector name as you would expect.
Solution:
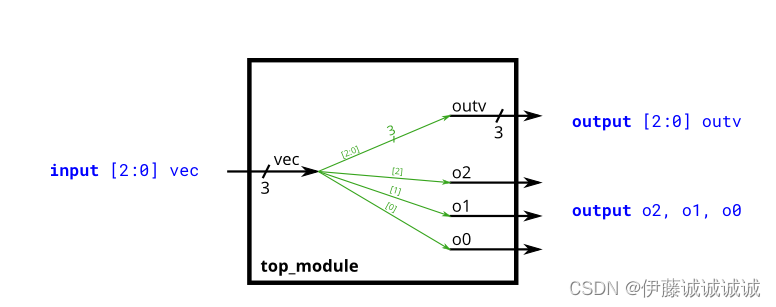
module top_module (
input wire [2:0] vec,
output wire [2:0] outv,
output wire o2,
output wire o1,
output wire o0 ); // Module body starts after module declaration
assign outv = vec;
assign o2 = vec[2];
assign o1= vec[1];
assign o0= vec[0];
endmoduleSubmit:

2.1.2、Vectors in more detail
Vectors are used to group related signals using one name to make it more convenient to manipulate. For example, wire [7:0] w; declares an 8-bit vector named w that is equivalent to having 8 separate wires.
A Bit of Practice
Build a combinational circuit that splits an input half-word (16 bits, [15:0] ) into lower [7:0] and upper [15:8] bytes.
Solution:
`default_nettype none // Disable implicit nets. Reduces some types of bugs.
module top_module(
input wire [15:0] in,
output wire [7:0] out_hi,
output wire [7:0] out_lo );
assign out_hi = in [15:8];
assign out_lo = in [7:0];
endmodule
Submit:

2.1.2、Vectors in more detail
A 32-bit vector can be viewed as containing 4 bytes (bits [31:24], [23:16], etc.). Build a circuit that will reverse the byte ordering of the 4-byte word.
AaaaaaaaBbbbbbbbCcccccccDddddddd => DdddddddCcccccccBbbbbbbbAaaaaaaaThis operation is often used when the endianness of a piece of data needs to be swapped, for example between little-endian x86 systems and the big-endian formats used in many Internet protocols.
Solution:
module top_module(
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
assign out [31:24] = in [7:0];
assign out [23:16] = in [15:8];
assign out [15:8] = in [23:16];
assign out [7:0] = in [31:24];
endmoduleSumbit:

2.1.3、bitwise operators
Vectorgates
Build a circuit that has two 3-bit inputs that computes the bitwise-OR of the two vectors, the logical-OR of the two vectors, and the inverse (NOT) of both vectors. Place the inverse of
bin the upper half ofout_not(i.e., bits [5:3]), and the inverse ofain the lower half.
Solution:
module top_module(
input [2:0] a,
input [2:0] b,
output [2:0] out_or_bitwise,
output out_or_logical,
output [5:0] out_not
);
assign out_or_bitwise = a | b; //out与a.b位数相同
assign out_or_logical = a || b; // || 全或用于只有一个输出
assign out_not = ~{b, a}; //位拼接运算
//assign out_not[2:0]=~a;
//assign out_not[5:3]=~b;
endmodule
Submit:

2.2.5、Four-input gates
Build a combinational circuit with four inputs, in[3:0].
There are 3 outputs:
- out_and: output of a 4-input AND gate.
- out_or: output of a 4-input OR gate.
- out_xor: output of a 4-input XOR gate.
To review the AND, OR, and XOR operators, see andgate, norgate, and xnorgate.
See also: Even wider gates.
Solution:
module top_module(
input [3:0] in,
output out_and,
output out_or,
output out_xor
);
assign out_and = in[3] & in[2] & in[1] & in[0];
assign out_or = in[3] | in[2] | in[1] | in[0];
assign out_xor = in[3] ^ in[2] ^ in[1] ^ in[0];
endmoduleSubmit:

2.2.6、Vector concatenation operator
A Bit of Practice
Given several input vectors, concatenate them together then split them up into several output vectors. There are six 5-bit input vectors: a, b, c, d, e, and f, for a total of 30 bits of input. There are four 8-bit output vectors: w, x, y, and z, for 32 bits of output. The output should be a concatenation of the input vectors followed by two 1 bits:
Solution:
module top_module (
input [4:0] a, b, c, d, e, f,
output [7:0] w, x, y, z );//
// assign { ... } = { ... };
assign {w[7:0], x[7:0], y[7:0], z[7:0]} = {a, b, c, d, e, f, 2'b11};
endmoduleSubmit:

2.2.7、Vector reversal1
Vectorr:
Given an 8-bit input vector [7:0], reverse its bit ordering.
See also: Reversing a longer vector.
Solution:
module top_module(
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] out
);
//assign out = {in[0], in[1], in[2], in[3], in[4], in[5], in[6], in[7]};
integer i;//定义一个整型变量
always @(*) begin //@(*)组合逻辑电路
begin //begin-end串行语句
for(i = 0; i <= 7; i++)
out[i] = in[7 - i];
end
end
endmoduleSumbit:

2.2.8、Replication operator
Vector4:
The concatenation operator allowed concatenating together vectors to form a larger vector. But sometimes you want the same thing concatenated together many times, and it is still tedious to do something like assign a = {b,b,b,b,b,b};. The replication operator allows repeating a vector and concatenating them together:
{num{vector}}This replicates vector by num times. num must be a constant. Both sets of braces are required.
Solution:
module top_module (
input [7:0] in,
output [31:0] out );//
// assign out = { replicate-sign-bit , the-input };
assign out = {{24{in[7]}}, in};
endmodule2.2.9、More replication
Vector5:
Given five 1-bit signals (a, b, c, d, and e), compute all 25 pairwise one-bit comparisons in the 25-bit output vector. The output should be 1 if the two bits being compared are equal.
out[24] = ~a ^ a; // a == a, so out[24] is always 1. out[23] = ~a ^ b; out[22] = ~a ^ c; ... out[ 1] = ~e ^ d; out[ 0] = ~e ^ e;
As the diagram shows, this can be done more easily using the replication and concatenation operators.
- The top vector is a concatenation of 5 repeats of each input
- The bottom vector is 5 repeats of a concatenation of the 5 inputs
Solution:
module top_module (
input a, b, c, d, e,
output [24:0] out
);
assign out=~{5{a,b,c,d,e}}^{{5{a}},{5{b}},{5{c}},{5{d}},{5{e}}};
endmodule




























 615
615

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










