参考链接:http://www.alimirjalili.com/SMA.html
https://tinyurl.com/Slime-mould-algorithm.
这个优化算法是2020年提出来的,还算比较新的算法,上面两个链接都有源码。
本着能用的代码就是好代码的原则,我把人家的代码搬了过来组合了一下,测试后可以使用...
直接上代码
粘液霉菌算法(SMA)
这一段是定义优化算法一般的功能
from numpy import where, clip, logical_and, ones, array, ceil
from numpy.random import uniform, choice
from copy import deepcopy
from numpy import abs, zeros, log10, where, arctanh, tanh
class Root:
""" This is root of all Algorithms """
ID_MIN_PROB = 0 # min problem
ID_MAX_PROB = -1 # max problem
ID_POS = 0 # Position
ID_FIT = 1 # Fitness
EPSILON = 10E-10
def __init__(self, obj_func=None, lb=None, ub=None, problem_size=50, verbose=True):
"""
Parameters
----------
obj_func : function
lb : list
ub : list
problem_size : int, optional
batch_size: int, optional
verbose : bool, optional
"""
self.obj_func = obj_func
if (lb is None) or (ub is None):
if problem_size is None:
print("Problem size must be an int number")
exit(0)
elif problem_size <= 0:
print("Problem size must > 0")
exit(0)
else:
self.problem_size = int(ceil(problem_size))
self.lb = -1 * ones(problem_size)
self.ub = 1 * ones(problem_size)
else:
if isinstance(lb, list) and isinstance(ub, list) and not (problem_size is None):
if (len(lb) == len(ub)) and (problem_size > 0):
if len(lb) == 1:
self.problem_size = problem_size
self.lb = lb[0] * ones(problem_size)
self.ub = ub[0] * ones(problem_size)
else:
self.problem_size = len(lb)
self.lb = array(lb)
self.ub = array(ub)
else:
print("Lower bound and Upper bound need to be same length. Problem size must > 0")
exit(0)
else:
print("Lower bound and Upper bound need to be a list. Problem size is an int number")
exit(0)
self.verbose = verbose
self.epoch, self.pop_size = None, None
self.solution, self.loss_train = None, []
def create_solution(self, minmax=0):
""" Return the position position with 2 element: position of position and fitness of position
Parameters
----------
minmax
0 - minimum problem, else - maximum problem
"""
position = uniform(self.lb, self.ub)
fitness = self.get_fitness_position(position=position, minmax=minmax)
return [position, fitness]
def get_fitness_position(self, position=None, minmax=0):
""" Assumption that objective function always return the original value
:param position: 1-D numpy array
:param minmax: 0- min problem, 1 - max problem
:return:
"""
return self.obj_func(position) if minmax == 0 else 1.0 / (self.obj_func(position) + self.EPSILON)
def get_sorted_pop_and_global_best_solution(self, pop=None, id_fit=None, id_best=None):
""" Sort population and return the sorted population and the best position """
sorted_pop = sorted(pop, key=lambda temp: temp[id_fit])
return sorted_pop, deepcopy(sorted_pop[id_best])
def amend_position(self, position=None):
return clip(position, self.lb, self.ub)
def amend_position_random(self, position=None):
return where(logical_and(self.lb <= position, position <= self.ub), position, uniform(self.lb, self.ub))
def update_sorted_population_and_global_best_solution(self, pop=None, id_best=None, g_best=None):
""" Sort the population and update the current best position. Return the sorted population and the new current best position """
sorted_pop = sorted(pop, key=lambda temp: temp[self.ID_FIT])
current_best = sorted_pop[id_best]
g_best = deepcopy(current_best) if current_best[self.ID_FIT] < g_best[self.ID_FIT] else deepcopy(g_best)
return sorted_pop, g_best下面是两种不同的SMA算法的类
class BaseSMA(Root):
"""
Modified version of: Slime Mould Algorithm (SMA)
(Slime Mould Algorithm: A New Method for Stochastic Optimization)
Notes:
+ Selected 2 unique and random solution to create new solution (not to create variable) --> remove third loop in original version
+ Check bound and update fitness after each individual move instead of after the whole population move in the original version
"""
ID_WEI = 2
def __init__(self, obj_func=None, lb=None, ub=None, problem_size=50, verbose=True, epoch=750, pop_size=100, z=0.03):
Root.__init__(self, obj_func, lb, ub, problem_size, verbose)
self.epoch = epoch
self.pop_size = pop_size
self.z = z
def create_solution(self, minmax=0):
pos = uniform(self.lb, self.ub)
fit = self.get_fitness_position(pos)
weight = zeros(self.problem_size)
return [pos, fit, weight]
def train(self):
pop = [self.create_solution() for _ in range(self.pop_size)]
pop, g_best = self.get_sorted_pop_and_global_best_solution(pop, self.ID_FIT, self.ID_MIN_PROB) # Eq.(2.6)
for epoch in range(self.epoch):
s = pop[0][self.ID_FIT] - pop[-1][self.ID_FIT] + self.EPSILON # plus eps to avoid denominator zero
# calculate the fitness weight of each slime mold
for i in range(0, self.pop_size):
# Eq.(2.5)
if i <= int(self.pop_size / 2):
pop[i][self.ID_WEI] = 1 + uniform(0, 1, self.problem_size) * log10((pop[0][self.ID_FIT] - pop[i][self.ID_FIT]) / s + 1)
else:
pop[i][self.ID_WEI] = 1 - uniform(0, 1, self.problem_size) * log10((pop[0][self.ID_FIT] - pop[i][self.ID_FIT]) / s + 1)
a = arctanh(-((epoch + 1) / self.epoch) + 1) # Eq.(2.4)
b = 1 - (epoch + 1) / self.epoch
# Update the Position of search agents
for i in range(0, self.pop_size):
if uniform() < self.z: # Eq.(2.7)
pos_new = uniform(self.lb, self.ub)
else:
p = tanh(abs(pop[i][self.ID_FIT] - g_best[self.ID_FIT])) # Eq.(2.2)
vb = uniform(-a, a, self.problem_size) # Eq.(2.3)
vc = uniform(-b, b, self.problem_size)
# two positions randomly selected from population, apply for the whole problem size instead of 1 variable
id_a, id_b = choice(list(set(range(0, self.pop_size)) - {i}), 2, replace=False)
pos_1 = g_best[self.ID_POS] + vb * (pop[i][self.ID_WEI] * pop[id_a][self.ID_POS] - pop[id_b][self.ID_POS])
pos_2 = vc * pop[i][self.ID_POS]
pos_new = where(uniform(0, 1, self.problem_size) < p, pos_1, pos_2)
# Check bound and re-calculate fitness after each individual move
pos_new = self.amend_position(pos_new)
fit_new = self.get_fitness_position(pos_new)
pop[i][self.ID_POS] = pos_new
pop[i][self.ID_FIT] = fit_new
# Sorted population and update the global best
pop, g_best = self.update_sorted_population_and_global_best_solution(pop, self.ID_MIN_PROB, g_best)
self.loss_train.append(g_best[self.ID_FIT])
if self.verbose:
print("> Epoch: {}, Best fit: {}".format(epoch + 1, g_best[self.ID_FIT]))
self.solution = g_best
return g_best[self.ID_POS], g_best[self.ID_FIT], self.loss_train
class OriginalSMA(Root):
"""
The original version of: Slime Mould Algorithm (SMA)
(Slime Mould Algorithm: A New Method for Stochastic Optimization)
Link:
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.future.2020.03.055
"""
ID_WEI = 2
def __init__(self, obj_func=None, lb=None, ub=None, problem_size=50, verbose=True, epoch=750, pop_size=100, z=0.03):
Root.__init__(self, obj_func, lb, ub, problem_size, verbose)
self.epoch = epoch
self.pop_size = pop_size
self.z = z
def create_solution(self, minmax=0):
pos = uniform(self.lb, self.ub)
fit = self.get_fitness_position(pos)
weight = zeros(self.problem_size)
return [pos, fit, weight]
def train(self):
pop = [self.create_solution() for _ in range(self.pop_size)]
pop, g_best = self.get_sorted_pop_and_global_best_solution(pop, self.ID_FIT, self.ID_MIN_PROB) # Eq.(2.6)
for epoch in range(self.epoch):
s = pop[0][self.ID_FIT] - pop[-1][self.ID_FIT] + self.EPSILON # plus eps to avoid denominator zero
# calculate the fitness weight of each slime mold
for i in range(0, self.pop_size):
# Eq.(2.5)
if i <= int(self.pop_size / 2):
pop[i][self.ID_WEI] = 1 + uniform(0, 1, self.problem_size) * log10((pop[0][self.ID_FIT] - pop[i][self.ID_FIT]) / s + 1)
else:
pop[i][self.ID_WEI] = 1 - uniform(0, 1, self.problem_size) * log10((pop[0][self.ID_FIT] - pop[i][self.ID_FIT]) / s + 1)
a = arctanh(-((epoch + 1) / self.epoch) + 1) # Eq.(2.4)
b = 1 - (epoch + 1) / self.epoch
# Update the Position of search agents
for i in range(0, self.pop_size):
if uniform() < self.z: # Eq.(2.7)
pop[i][self.ID_POS] = uniform(self.lb, self.ub)
else:
p = tanh(abs(pop[i][self.ID_FIT] - g_best[self.ID_FIT])) # Eq.(2.2)
vb = uniform(-a, a, self.problem_size) # Eq.(2.3)
vc = uniform(-b, b, self.problem_size)
for j in range(0, self.problem_size):
# two positions randomly selected from population
id_a, id_b = choice(list(set(range(0, self.pop_size)) - {i}), 2, replace=False)
if uniform() < p: # Eq.(2.1)
pop[i][self.ID_POS][j] = g_best[self.ID_POS][j] + vb[j] * (
pop[i][self.ID_WEI][j] * pop[id_a][self.ID_POS][j] - pop[id_b][self.ID_POS][j])
else:
pop[i][self.ID_POS][j] = vc[j] * pop[i][self.ID_POS][j]
# Check bound and re-calculate fitness after the whole population move
for i in range(0, self.pop_size):
pos_new = self.amend_position(pop[i][self.ID_POS])
fit_new = self.get_fitness_position(pos_new)
pop[i][self.ID_POS] = pos_new
pop[i][self.ID_FIT] = fit_new
# Sorted population and update the global best
pop, g_best = self.update_sorted_population_and_global_best_solution(pop, self.ID_MIN_PROB, g_best)
self.loss_train.append(g_best[self.ID_FIT])
if self.verbose:
print("> Epoch: {}, Best fit: {}".format(epoch + 1, g_best[self.ID_FIT]))
self.solution = g_best
return g_best[self.ID_POS], g_best[self.ID_FIT], self.loss_train定义问题参数,可以定义任意自己想优化的问题,寻找最小值
#from SMA import BaseSMA, OriginalSMA
#from numpy import sum, pi, exp, sqrt, cos
import numpy as np
## You can create whatever function you want here
def func_sum(solution):
return np.sum(solution ** 2)
def func_ackley(solution):
a, b, c = 20, 0.2, 2 * np.pi
d = len(solution)
sum_1 = -a * np.exp(-b * np.sqrt(np.sum(solution ** 2) / d))
sum_2 = np.exp(np.sum(np.cos(c * solution)) / d)
return sum_1 - sum_2 + a + np.exp(1)
## You can create different bound for each dimension like this
# lb = [-15, -10, -3, -15, -10, -3, -15, -10, -3, -15, -10, -3, -15, -10, -3, -100, -40, -50]
# ub = [15, 10, 3, 15, 10, 3, 15, 10, 3, 15, 10, 3, 15, 10, 3, 20, 200, 1000]
# problem_size = 18
## if you choose this way, the problem_size need to be same length as lb and ub
## Or bound is the same for all dimension like this
lb = [-100]
ub = [100]
problem_size = 100
## if you choose this way, the problem_size can be anything you want
## Setting parameters
obj_func = func_ackley
verbose = True
epoch = 100
pop_size = 50开始使用两种SMA进行测试
第一种基础的SMA
md1 = BaseSMA(obj_func, lb, ub, problem_size, verbose, epoch, pop_size)
best_pos1, best_fit1, list_loss1 = md1.train()
# return : the global best solution, the fitness of global best solution and the loss of training process in each epoch/iteration
print(md1.solution[0])
print(md1.solution[1])
#print(md1.loss_train)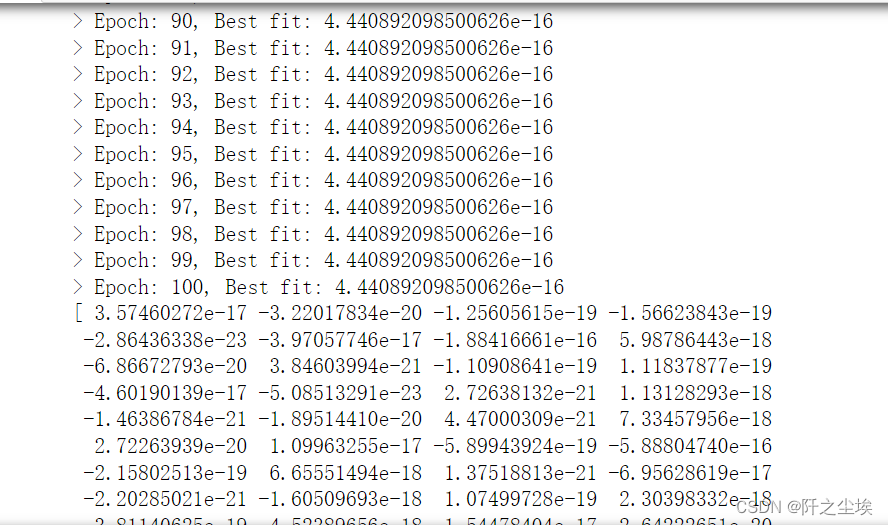
verbose开着的话会显示每轮迭代的损失的大小,md1.solution[0]打印最优的X,md1.solution[1]打印最优的y值。
md1.loss_train可以返回每轮迭代的损失y的变化,是一个数组,画图什么很方便。
第二种SMA
md2 = OriginalSMA(obj_func, lb, ub, problem_size, verbose, epoch, pop_size)
best_pos2, best_fit2, list_loss2 = md2.train()
# return : the global best solution, the fitness of global best solution and the loss of training process in each epoch/iteration
print(best_pos2)
print(best_fit2)
#print(list_loss2)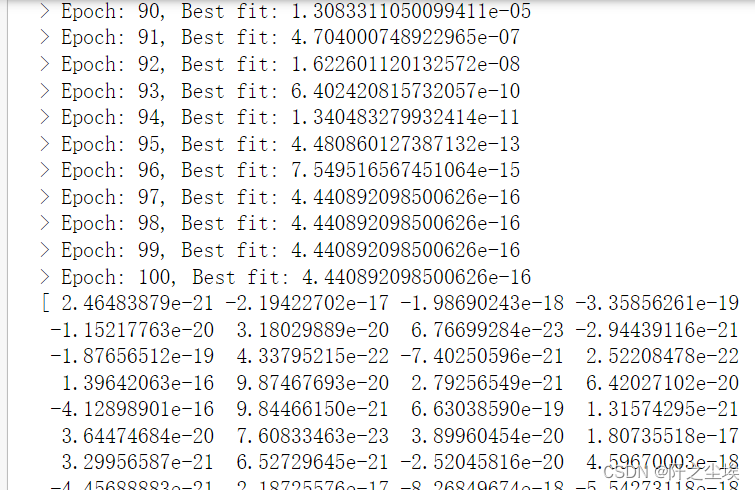
返回值都差不多,但是这种SMA 的运行时间有点略微的长,想来是更加复杂点。
如有兴趣研究原理的同学可以进下面的链接,是这篇算法的论文的链接。








 该博客介绍了黏菌算法(Slime Mould Algorithm, SMA)的两种实现方式,一种是基础版,另一种是原版。这是一种用于随机优化的新方法,源码已提供。算法通过模拟黏菌寻找食物的过程来优化问题。博客中给出了详细代码,并提供了测试用例,包括求解函数的定义。此外,还提供了算法的论文链接以供深入研究。
该博客介绍了黏菌算法(Slime Mould Algorithm, SMA)的两种实现方式,一种是基础版,另一种是原版。这是一种用于随机优化的新方法,源码已提供。算法通过模拟黏菌寻找食物的过程来优化问题。博客中给出了详细代码,并提供了测试用例,包括求解函数的定义。此外,还提供了算法的论文链接以供深入研究。

















 491
491

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










