7-5 Tree Traversals Again(25 分)
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
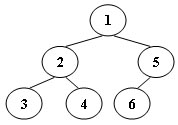
Figure 1
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: "Push X" where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or "Pop" meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1思路:
1、主要是根据中序遍历堆栈push和pop的操作来建立树的过程。
2、走一遍就会发现一个规律,对于push操作而言,如果它的前一个操作是pop,那么push进来的这个节点就是前一个pop出来的节点的右孩子。如果它的前一个操作是push,那这个节点就是前一个push进来的节点的左孩子。用循环结合stack容器即可把树用静态链表建立起来。
3、树建好之后,用递归即可把树用后序遍历打印出来。
4、几个单词记住。inorder 中序;preorder 前序; postorder 后序; binary tree 二叉树;traversal 遍历;
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%分割线%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
看了标准答案,是直接根据前序和中序的数组递归求出后序遍历的数组。还是建议用堆栈的方法模拟系统的递归实现。
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Stack;
public class Main {
public static int flag=0;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
Jiedian [] tree = build(in);
// for(Jiedian jd :tree) {
// System.out.println(jd.element+" "+jd.left+" "+jd.right);
// }
int root=0;
print(tree,root);
}
private static void print(Jiedian[] tree,int root) { //用递归后序遍历输出
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(root!=-1)
{
print(tree,tree[root].left);
print(tree,tree[root].right);
if(flag==0)
{
System.out.print(tree[root].element);
flag++;
}
else
System.out.print(" "+tree[root].element);
}
}
private static Jiedian[] build(Scanner in) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int n = in.nextInt();
Jiedian [] jd = new Jiedian[n];
String [] str = new String[2*n];
Stack<Jiedian> st = new Stack<>();
for(int i=0,j=0,k=0;i<2*n;i++) { //读入数据,建立push和pop操作的String数组
str[i]=new String(in.next());
Jiedian temp = new Jiedian(); //建立按push顺序建立的Jiedian数组。
if(str[i].equals("Push")) {
temp.element=in.nextInt();
jd[j]=temp;
j++;
}
}
st.push(jd[0]);
Jiedian temp = new Jiedian();
Jiedian pop = new Jiedian();
for(int i =1,j=1;i<2*n;i++) { //用静态链表建立树
if(str[i].equals("Push")) {
if(str[i-1].equals("Push")) {
temp=st.peek();
temp.left=j;
st.push(jd[j]);
j++;
}
else
{
pop.right=j;
st.push(jd[j]);
j++;
}
}
else
pop=st.pop();
}
return jd;
}
}
class Jiedian{
public int local;
public int element;
public int left=-1;
public int right=-1;
}








 本文介绍了一种通过模拟栈操作来构建二叉树并进行后序遍历的方法。通过对给定的推入和弹出操作序列进行解析,可以唯一确定一棵二叉树,并进一步实现了该树的后序遍历。
本文介绍了一种通过模拟栈操作来构建二叉树并进行后序遍历的方法。通过对给定的推入和弹出操作序列进行解析,可以唯一确定一棵二叉树,并进一步实现了该树的后序遍历。
















 674
674

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








