题目
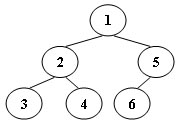
An inorder binary tree traversal can be implemented in a non-recursive way with a stack. For example, suppose that when a 6-node binary tree (with the keys numbered from 1 to 6) is traversed, the stack operations are: push(1); push(2); push(3); pop(); pop(); push(4); pop(); pop(); push(5); push(6); pop(); pop(). Then a unique binary tree (shown in Figure 1) can be generated from this sequence of operations. Your task is to give the postorder traversal sequence of this tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (≤30) which is the total number of nodes in a tree (and hence the nodes are numbered from 1 to N). Then 2N lines follow, each describes a stack operation in the format: “Push X” where X is the index of the node being pushed onto the stack; or “Pop” meaning to pop one node from the stack.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print the postorder traversal sequence of the corresponding tree in one line. A solution is guaranteed to exist. All the numbers must be separated by exactly one space, and there must be no extra space at the end of the line.
Sample Input:
6
Push 1
Push 2
Push 3
Pop
Pop
Push 4
Pop
Pop
Push 5
Push 6
Pop
Pop
Sample Output:
3 4 2 6 5 1
思路
这个题我的思路是:由入栈顺序得到树的先序遍历结果,由出栈顺序得到树的中序遍历结果,然后再推出树,进行后序遍历。看起来有点麻烦,有需要的可以参考一下。
代码
节点类
public class Node {
private int data;
private int left;
private int right;
public Node() {
this.data = -1;
this.left = -1;
this.right = -1;
}
public Node(int a) {
this.data = a;
this.left = -1;
this.right = -1;
}
public Node(int a, int left, int right) {
this.data = a;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
public int getData() {
return data;
}
public void setData(int data) {
this.data = data;
}
public int getLeft() {
return left;
}
public void setLeft(int left) {
this.left = left;
}
public int getRight() {
return right;
}
public void setRight(int right) {
this.right = right;
}
}
测试类
public class Test {
public static int flag=0;
public static Node[] getTree(Scanner sc, int a) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();//模拟出入栈操作
Node[] n = new Node[a];
Node[] preorder = new Node[a]; //先序遍历结果
Node[] inorder = new Node[a]; //中序遍历结果
for (int i = 0,j = 0, k = 0; i < 2*a; i++) { //出入栈加起来一共有2a个
String s = sc.next(); //接受输入数据
Node node = new Node();
if (s.equals("Push")) { //push顺序相当于树先序遍历结果
int num = sc.nextInt();
stack.push(num); //入栈,以便得到出栈的值
node.setData(num);
preorder[j] = node;
j+=1;
}
if (s.equals("Pop")) { //pop顺序相当于树中序遍历结果
int num = stack.pop();
node.setData(num);
inorder[k] = node;
k+=1;
}
}
n = toTree(preorder, 0, a-1, inorder, 0, a-1);//获取树
return n;
}
//根据先序中序推出树
public static Node[] toTree(Node[] n1, int start1, int end1,
Node[] n2, int start2, int end2) {
if(start1 > end1 || start2 > end2){//防止越界
return null;
}
int root = n1[start1].getData();//获取根节点的值
int rootIndex = findIndexInArray(n2, root);//获取中序遍历中根节点下标
int value = rootIndex - start2; //为左子树长度
//构建左子树
toTree(n1, start1+1, start1+value, n2, start2, rootIndex-1);
//构建右子树
toTree(n1, start1+value+1, end1, n2, rootIndex+1, end2);
if (start1 < end1) {//防止越界
n1[start1].setLeft(n1[start1+1].getData() - 1);
} //此时getData得到的是孩子节点的值:1,2,3,4,5,6,而他们对应的数组中的下标要-1
if (start1+value < end1) {//防止越界
n1[start1].setRight(n1[start1+value+1].getData()-1);
} //同上
return n1;
}
//查找中序遍历的根节点下标
private static int findIndexInArray(Node[] n, int rootData) {
for (int i = 0; i < n.length; i++) {
if(n[i].getData() == rootData){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//后续遍历数组
public static void postorder(Node[] n, int root) {
if (root != -1){
postorder(n, n[root].getLeft());//添加左子树下标
postorder(n, n[root].getRight()); //添加右子树下标
if (flag == 0){//用来规范输出结果,保证末尾没有多余的空格
System.out.print(n[root].getData());
flag++;
} else {
System.out.print(" "+n[root].getData());
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
Node[] n = getTree(sc, a);
// for (Node aaa: n) { //打印出树
// System.out.println(aaa.getData() +" "+aaa.getLeft()+" "+aaa.getRight());
// }
postorder(n, 0); //调用方法后序遍历并输出
}
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








