利用周末时间做了一个MDEV虚拟化PCI设备的小试验,简单记录一下:
DEMO架构,此图参考了内核文档:Documentation/driver-api/vfio-mediated-device.rst

Demo 框架:参考如下文章中的受控直通方案,区别是由于实验中的watchdog是纯粹的模拟设备,包括BAR IO空间实际上对应的都是内存BUFFER,不需要PASS-TRHOUGH。
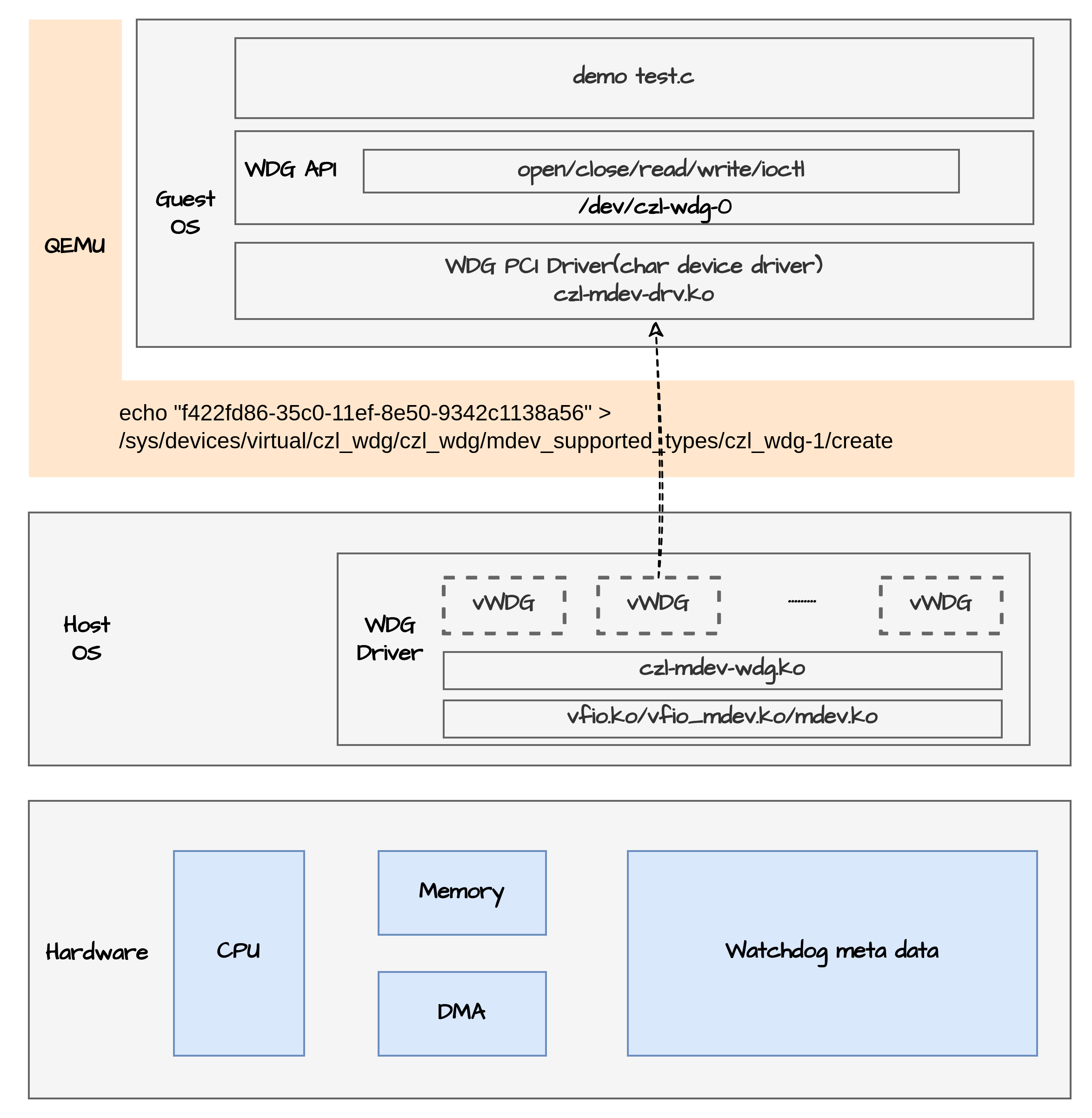
程序由Guest OS 用户态测试程序,Guest OS内核态vWDG驱动,Host OS内核态vWDG mdev设备模拟三份程序构成,Host OS VMM Qemu不需要修改。
MDEV框架的设计哲学
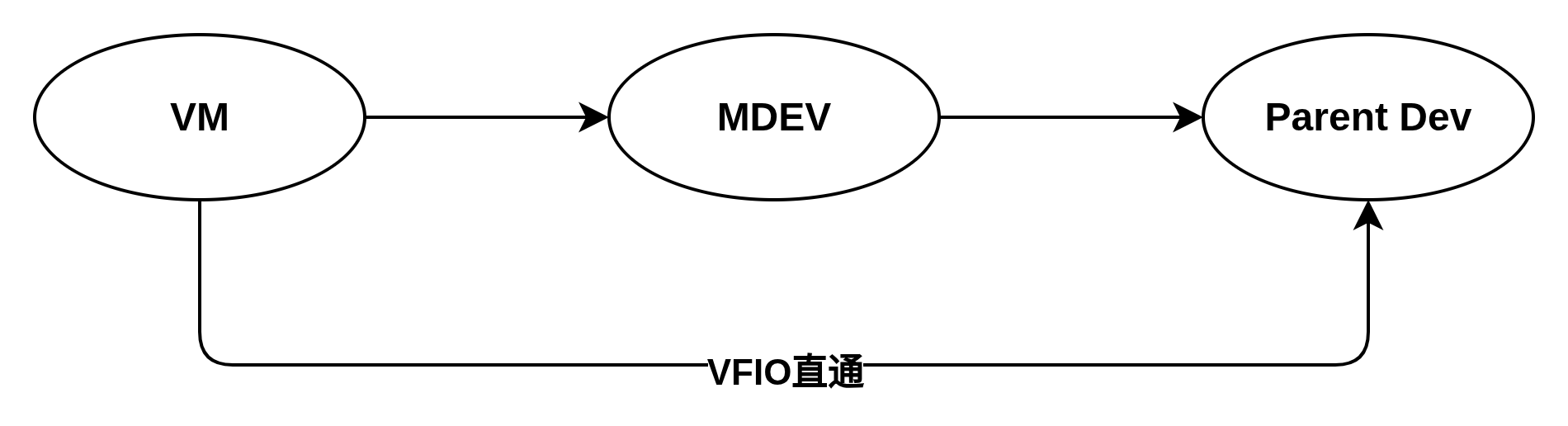
mdev中的m是"Mediated"的缩写,其描述了在设备和虚拟机之间插入一个可控、可管理、可虚拟化的软件中介层的架构设计,这个设备既可以是内存模拟设备,比如本文提到的WDG,也可以是真实的设备,比如PCIe设备。就目前的理解,MDEV应该比VFIO直通更加灵活,虚拟机看到的是MDEV设备,而非真实的物理设备,MDEV设备是真实物理设备和VM之间的一个桥梁,VM对MDEVS设备的调用都会被桥接到真实的物理设备(类似于设计模式中的桥接模式)。而VFIO直通则是VM直面物理设备,MDEV设备的存在使软件有介入的机会,主要表现在:
- 访问中介化:所有VM对设备的访问都经过Host内核的中介层,不是直接硬件访问
- 资源中介化:物理资源被软件层划分和虚拟化,每个VM获得一部分
- 控制中介化:设备状态、配置、DMA操作都由中介层控制和仲裁
- 安全中介化:中介层确保VM间隔离,防止越界访问
- 性能中介化:QoS、调度、监控都由中介层管理
- 迁移中介化:状态保存/恢复通过中介层进行,支持设备迁移

代码实现
host kernel watchdog pci driver:
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/uuid.h>
#include <linux/vfio.h>
#include <linux/iommu.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/file.h>
#include <linux/mdev.h>
#include <linux/pci.h>
#define IO_BAR0_SIZE 32
#define IO_CONF_SIZE 0x100
#define CZL_WDG_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID 0xbeef
#define CZL_WDG_DEVICE_DEVICE_ID 0x1001
#define API_DBG(fmt, ...) do { \
printk("%s line %d, "fmt, __func__, __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__); \
} while (0)
struct czl_wdg_dev {
dev_t wdg_devt;
struct class *wdg_class;
struct cdev wdg_cdev;
struct device dev;
};
struct mdev_region_info {
u64 start;
u64 phys_start;
u32 size;
u64 vfio_offset;
};
struct wdg_mdev_state {
u8 *config;
u8 *iobase;
struct mdev_device *mdev;
struct mdev_region_info region_info[VFIO_PCI_NUM_REGIONS];
u32 bar_mask[VFIO_PCI_NUM_REGIONS];
struct list_head next;
struct vfio_device_info dev_info;
int index;
struct mutex ops_lock;
};
static const struct file_operations czl_wdg_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
};
static struct mutex wdg_mdev_list_lock;
static struct list_head wdg_mdev_devices_list;
#define WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_SHIFT (40)
#define WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_TO_INDEX(off) (off >> WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_SHIFT)
#define WDG_VFIO_PCI_INDEX_TO_OFFSET(index) \
((u64)(index) << WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_SHIFT)
#define WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_MASK \
(((u64)(1) << WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_SHIFT) - 1)
#define MAX_WDGS (16)
static struct czl_wdg_dev czl_wdg;
static ssize_t
czl_wdg_dev_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "mdev emulated pci watchdog device by caozilong.\n");
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RO(czl_wdg_dev);
static struct attribute *wdg_dev_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_czl_wdg_dev.attr,
NULL,
};
static const struct attribute_group wdg_dev_group = {
.name = "czl_wdg",
.attrs = wdg_dev_attrs,
};
static const struct attribute_group *wdg_dev_groups[] = {
&wdg_dev_group,
NULL,
};
static ssize_t
mdev_dev_show(struct device *dev, struct device_attribute *attr,
char *buf)
{
if (mdev_from_dev(dev)) {
return sprintf(buf, "This is watchdog %s\n", dev_name(dev));
}
return sprintf(buf, "\n");
}
static DEVICE_ATTR_RO(mdev_dev);
static struct attribute *mdev_dev_attrs[] = {
&dev_attr_mdev_dev.attr,
NULL,
};
static const struct attribute_group mdev_dev_group = {
.name = "caozilong",
.attrs = mdev_dev_attrs,
};
static const struct attribute_group *mdev_dev_groups[] = {
&mdev_dev_group,
NULL,
};
static ssize_t name_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct device *dev, char *buf)
{
int i;
char name[128];
const char *name_str[3] = {"Soft Watchdog", "Hardware Watchdog", "Dummy Watchdog"};
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
snprintf(name, 128, "%s-%d", dev_driver_string(dev), i + 1);
if (!strcmp(kobj->name, name)) {
return sprintf(buf, "%s\n", name_str[i]);
}
}
return -EINVAL;
}
static ssize_t device_api_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct device *dev,
char *buf)
{
return sprintf(buf, "%s\n", VFIO_DEVICE_API_PCI_STRING);
}
static ssize_t
available_instances_show(struct kobject *kobj, struct device *dev, char *buf)
{
struct wdg_mdev_state *mds;
int used = 0;
list_for_each_entry(mds, &wdg_mdev_devices_list, next) {
used ++;
}
return sprintf(buf, "%d\n", (MAX_WDGS - used));
}
static MDEV_TYPE_ATTR_RO(name);
static MDEV_TYPE_ATTR_RO(device_api);
static MDEV_TYPE_ATTR_RO(available_instances);
static struct attribute *mdev_types_attrs[] = {
&mdev_type_attr_name.attr,
&mdev_type_attr_device_api.attr,
&mdev_type_attr_available_instances.attr,
NULL,
};
static struct attribute_group mdev_type_group1 = {
.name = "1",
.attrs = mdev_types_attrs,
};
static struct attribute_group mdev_type_group2 = {
.name = "2",
.attrs = mdev_types_attrs,
};
static struct attribute_group mdev_type_group3 = {
.name = "3",
.attrs = mdev_types_attrs,
};
static struct attribute_group *mdev_type_groups[] = {
&mdev_type_group1,
&mdev_type_group2,
&mdev_type_group3,
NULL,
};
static int czl_wdg_open(struct mdev_device *mdev)
{
pr_info("%s line %d, wdg device opened.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
static void czl_wdg_close(struct mdev_device *mdev)
{
pr_info("%s line %d, wdg device close.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return;
}
// fill pci config space meta data & capabilities.
int wdg_create_config_space(struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate)
{
// vendor id, device id.
*((unsigned int *)&mstate->config[0]) = CZL_WDG_DEVICE_VENDOR_ID |
(CZL_WDG_DEVICE_DEVICE_ID << 16);
*((unsigned short *)&mstate->config[4]) = 0x0001;
*((unsigned short *)&mstate->config[6]) = 0x0200;
mstate->config[0x8] = 0x10;
mstate->config[0x9] = 0x02;
mstate->config[0xa] = 0x00;
mstate->config[0xb] = 0x07;
*((unsigned int *)&mstate->config[0x10]) = 0x000001;
mstate->bar_mask[0] = ~(IO_BAR0_SIZE) + 1;
*((unsigned int *)&mstate->config[0x2c]) = 0x10011af4;
// cap ptr.
mstate->config[0x34] = 0x00;
mstate->config[0x3d] = 0x01;
mstate->config[0x40] = 0x23;
mstate->config[0x43] = 0x80;
mstate->config[0x44] = 0x23;
mstate->config[0x48] = 0x23;
mstate->config[0x4c] = 0x23;
mstate->config[0x60] = 0x50;
mstate->config[0x61] = 0x43;
mstate->config[0x62] = 0x49;
mstate->config[0x63] = 0x20;
mstate->config[0x64] = 0x53;
mstate->config[0x65] = 0x65;
mstate->config[0x66] = 0x72;
mstate->config[0x67] = 0x69;
mstate->config[0x68] = 0x61;
mstate->config[0x69] = 0x6c;
mstate->config[0x6a] = 0x2f;
mstate->config[0x6b] = 0x55;
mstate->config[0x6c] = 0x41;
mstate->config[0x6d] = 0x52;
mstate->config[0x6e] = 0x54;
return 0;
}
static int czl_wdg_create(struct kobject *kobj, struct mdev_device *mdev)
{
int i;
struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate;
char name[32];
if (!mdev)
return -EINVAL;
for (i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
snprintf(name, 32, "%s-%d", dev_driver_string(mdev_parent_dev(mdev)), i + 1);
if (!strcmp(kobj->name, name)) {
break;
}
}
if (i >= 3) {
return -EINVAL;
}
mstate = kzalloc(sizeof(struct wdg_mdev_state), GFP_KERNEL);
if (mstate == NULL)
return -ENOMEM;
// group number in mdev_type.
mstate->index = i + 1;
mstate->config = kzalloc(IO_CONF_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (mstate->config == NULL) {
pr_err("%s line %d, alloc pci config buffer failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
kfree(mstate);
return -ENOMEM;
}
mstate->iobase = kzalloc(IO_BAR0_SIZE, GFP_KERNEL);
if (mstate->iobase == NULL) {
pr_err("%s line %d, alloc pci io buffer failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
kfree(mstate->config);
kfree(mstate);
return -ENOMEM;
}
memset(mstate->config, 0x00, IO_CONF_SIZE);
mutex_init(&mstate->ops_lock);
mstate->mdev = mdev;
mdev_set_drvdata(mdev, mstate);
wdg_create_config_space(mstate);
mutex_lock(&wdg_mdev_list_lock);
list_add(&mstate->next, &wdg_mdev_devices_list);
mutex_unlock(&wdg_mdev_list_lock);
return 0;
}
static int czl_wdg_remove(struct mdev_device *mdev)
{
struct wdg_mdev_state *mds, *tmp_mds;
struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate = mdev_get_drvdata(mdev);
int ret = -EINVAL;
mutex_lock(&wdg_mdev_list_lock);
list_for_each_entry_safe(mds, tmp_mds, &wdg_mdev_devices_list, next) {
if (mstate == mds) {
list_del(&mstate->next);
mdev_set_drvdata(mdev, NULL);
kfree(mstate->config);
kfree(mstate->iobase);
kfree(mstate);
ret = 0;
break;
}
}
mutex_unlock(&wdg_mdev_list_lock);
return ret;
}
static void handle_pci_cfg_space_write(struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate, u16 offset,
u8 *buf, u32 count)
{
u32 cfg_addr, bar_mask;
switch (offset) {
case 0x04: /* device control */
case 0x06: /* device status */
// do nothing
break;
case 0x3c:
mstate->config[0x3c] = buf[0];
break;
case 0x3d:
break;
case 0x10: /* BAR0 */
cfg_addr = *(u32 *)buf;
pr_info("BAR0 addr 0x%x\n", cfg_addr);
if (cfg_addr == 0xffffffff) {
bar_mask = mstate->bar_mask[0];
cfg_addr = (cfg_addr & bar_mask);
}
cfg_addr |= (mstate->config[offset] & 0x3ul);
*((unsigned int *)&mstate->config[offset]) = cfg_addr;
break;
case 0x14: /* BAR1 */
case 0x18: /* BAR2 */
case 0x20: /* BAR4 */
*((unsigned int *)&mstate->config[offset]) = 0;
break;
default:
pr_info("PCI config write @0x%x of %d bytes not handled\n",
offset, count);
break;
}
return;
}
static void handle_pci_cfg_space_read(struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate, u16 offset,
u8 *buf, u32 count)
{
memcpy(buf, (mstate->config + offset), count);
return;
}
static void mdev_read_base(struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate)
{
int index, pos;
u32 start_lo, start_hi;
u32 mem_type;
pos = PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_0;
for (index = 0; index <= VFIO_PCI_BAR5_REGION_INDEX; index++) {
if (!mstate->region_info[index].size)
continue;
start_lo = (*(u32 *)(mstate->config + pos)) &
PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_MASK;
mem_type = (*(u32 *)(mstate->config + pos)) &
PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_MASK;
switch (mem_type) {
case PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_64:
start_hi = (*(u32 *)(mstate->config + pos + 4));
pos += 4;
break;
case PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_32:
case PCI_BASE_ADDRESS_MEM_TYPE_1M:
default:
start_hi = 0;
break;
}
pos += 4;
mstate->region_info[index].start = ((u64)start_hi << 32) | start_lo;
}
return;
}
static void handle_bar_write(unsigned int index, struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate,
u16 offset, u8 *buf, u32 count)
{
pr_info("%s line %d, bar %d, write offset 0x%x, count 0x%x, val 0x%x.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, index, offset, count, *buf);
memcpy(mstate->iobase + offset, buf, count);
return;
}
static void handle_bar_read(unsigned int index, struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate,
u16 offset, u8 *buf, u32 count)
{
pr_info("%s line %d, bar %d, read offset 0x%x, count 0x%x, val 0x%x.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, index, offset, count, *buf);
memcpy(buf, mstate->iobase + offset, count);
return;
}
static ssize_t mdev_access(struct mdev_device *mdev, u8 *buf, size_t count,
loff_t pos, bool is_write)
{
int ret = 0;
unsigned int index;
loff_t offset;
struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate;
if (!mdev || !buf)
return -EINVAL;
mstate = mdev_get_drvdata(mdev);
if (!mstate) {
pr_err("%s line %d. get mstate failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -EINVAL;
}
mutex_lock(&mstate->ops_lock);
index = WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_TO_INDEX(pos);
offset = pos & WDG_VFIO_PCI_OFFSET_MASK;
switch (index) {
case VFIO_PCI_CONFIG_REGION_INDEX:
pr_info("%s: PCI config space %s at offset 0x%llx\n",
__func__, is_write ? "write" : "read", offset);
if (is_write) {
handle_pci_cfg_space_write(mstate, offset, buf, count);
} else {
handle_pci_cfg_space_read(mstate, offset, buf, count);
}
break;
case VFIO_PCI_BAR0_REGION_INDEX ... VFIO_PCI_BAR5_REGION_INDEX:
if (!mstate->region_info[index].start)
mdev_read_base(mstate);
if (is_write) {
pr_info("%s: write bar%d offset 0x%llx, val 0x%x.\n",
__func__, index, offset, *buf);
handle_bar_write(index, mstate, offset, buf, count);
} else {
pr_info("%s: read bar%d offset 0x%llx, val 0x%x.\n",
__func__, index, offset, *buf);
handle_bar_read(index, mstate, offset, buf, count);
}
break;
default:
ret = -1;
goto failed;
}
ret = count;
failed:
mutex_unlock(&mstate->ops_lock);
return ret;
}
static ssize_t czl_wdg_read(struct mdev_device *mdev, char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
unsigned int done = 0;
int ret;
pr_info("%s line %d, read count 0x%lx, pos 0x%llx.\n", __func__, __LINE__, count, *ppos);
while (count) {
size_t filled;
if (count >= 4 && !(*ppos % 4)) {
u32 val;
ret = mdev_access(mdev, (u8 *)&val, sizeof(val),
*ppos, false);
if (ret <= 0)
goto read_err;
if (copy_to_user(buf, &val, sizeof(val)))
goto read_err;
filled = 4;
} else if (count >= 2 && !(*ppos % 2)) {
u16 val;
ret = mdev_access(mdev, (u8 *)&val, sizeof(val),
*ppos, false);
if (ret <= 0)
goto read_err;
if (copy_to_user(buf, &val, sizeof(val)))
goto read_err;
filled = 2;
} else {
u8 val;
ret = mdev_access(mdev, (u8 *)&val, sizeof(val),
*ppos, false);
if (ret <= 0)
goto read_err;
if (copy_to_user(buf, &val, sizeof(val)))
goto read_err;
filled = 1;
}
count -= filled;
done += filled;
*ppos += filled;
buf += filled;
}
pr_info("%s line %d, read count 0x%x.\n", __func__, __LINE__, done);
return done;
read_err:
pr_err("%s line %d, read err happend.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -EFAULT;
}
static ssize_t czl_wdg_write(struct mdev_device *mdev, const char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
unsigned int done = 0;
int ret;
pr_info("%s line %d, write count 0x%lx, pos 0x%llx.\n", __func__, __LINE__, count, *ppos);
while (count) {
size_t filled;
if (count >= 4 && !(*ppos % 4)) {
u32 val;
if (copy_from_user(&val, buf, sizeof(val)))
goto write_err;
ret = mdev_access(mdev, (u8 *)&val, sizeof(val),
*ppos, true);
if (ret <= 0)
goto write_err;
filled = 4;
} else if (count >= 2 && !(*ppos % 2)) {
u16 val;
if (copy_from_user(&val, buf, sizeof(val)))
goto write_err;
ret = mdev_access(mdev, (u8 *)&val, sizeof(val),
*ppos, true);
if (ret <= 0)
goto write_err;
filled = 2;
} else {
u8 val;
if (copy_from_user(&val, buf, sizeof(val)))
goto write_err;
ret = mdev_access(mdev, (u8 *)&val, sizeof(val),
*ppos, true);
if (ret <= 0)
goto write_err;
filled = 1;
}
count -= filled;
done += filled;
*ppos += filled;
buf += filled;
}
pr_info("%s line %d, write count 0x%x.\n", __func__, __LINE__, done);
return done;
write_err:
pr_err("%s line %d, write failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -EFAULT;
}
static int wdg_get_device_info(struct mdev_device *mdev, struct vfio_device_info *dev_info)
{
dev_info->flags = VFIO_DEVICE_FLAGS_PCI;
dev_info->num_regions = VFIO_PCI_NUM_REGIONS;
dev_info->num_irqs = VFIO_PCI_NUM_IRQS;
return 0;
}
static int wdg_get_region_info(struct mdev_device *mdev, struct vfio_region_info *region_info)
{
unsigned int size = 0;
struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate;
u32 bar_index;
if (!mdev) {
pr_err("%s line %d,mdev is null.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -EINVAL;
}
mstate = mdev_get_drvdata(mdev);
if (!mstate) {
pr_err("%s line %d,mstat is null.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -EINVAL;
}
bar_index = region_info->index;
if (bar_index >= VFIO_PCI_NUM_REGIONS) {
pr_err("%s line %d,bar index %d exceeds.\n", __func__, __LINE__, bar_index);
return -EINVAL;
}
mutex_lock(&mstate->ops_lock);
switch (bar_index) {
case VFIO_PCI_CONFIG_REGION_INDEX:
size = IO_CONF_SIZE;
break;
case VFIO_PCI_BAR0_REGION_INDEX:
size = IO_BAR0_SIZE;
break;
default:
size = 0;
break;
}
mstate->region_info[bar_index].size = size;
mstate->region_info[bar_index].vfio_offset =
WDG_VFIO_PCI_INDEX_TO_OFFSET(bar_index);
region_info->size = size;
region_info->offset = WDG_VFIO_PCI_INDEX_TO_OFFSET(bar_index);
region_info->flags = VFIO_REGION_INFO_FLAG_READ |
VFIO_REGION_INFO_FLAG_WRITE;
mutex_unlock(&mstate->ops_lock);
return 0;
}
static int wdg_get_irq_info(struct mdev_device *mdev, struct vfio_irq_info *irq_info)
{
switch (irq_info->index) {
case VFIO_PCI_INTX_IRQ_INDEX:
case VFIO_PCI_MSI_IRQ_INDEX:
case VFIO_PCI_REQ_IRQ_INDEX:
break;
default:
pr_err("%s line %d, irq idx %d is invalid.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, irq_info->index);
return -EINVAL;
}
irq_info->flags = VFIO_IRQ_INFO_EVENTFD;
irq_info->count = 1;
if (irq_info->index == VFIO_PCI_INTX_IRQ_INDEX)
irq_info->flags |= (VFIO_IRQ_INFO_MASKABLE |
VFIO_IRQ_INFO_AUTOMASKED);
else
irq_info->flags |= VFIO_IRQ_INFO_NORESIZE;
return 0;
}
static long czl_wdg_ioctl(struct mdev_device *mdev, unsigned int cmd,
unsigned long arg)
{
int ret = 0;
unsigned long minsz;
struct wdg_mdev_state *mstate;
pr_info("czl wdg ioctl enter.\n");
if (!mdev) {
pr_err("%s line %d, mdev is null.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -EINVAL;
}
mstate = mdev_get_drvdata(mdev);
if (!mstate) {
pr_err("%s line %d, cant find mstate data.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -ENODEV;
}
switch (cmd) {
case VFIO_DEVICE_GET_INFO: {
struct vfio_device_info info;
minsz = offsetofend(struct vfio_device_info, num_irqs);
if (copy_from_user(&info, (void __user *)arg, minsz))
return -EFAULT;
if (info.argsz < minsz) {
pr_err("%s line %d, info.argsz %d < minsz %ld.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, info.argsz, minsz);
return -EINVAL;
}
ret = wdg_get_device_info(mdev, &info);
if (ret) {
pr_err("%s line %d, get device info failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return ret;
}
memcpy(&mstate->dev_info, &info, sizeof(info));
if (copy_to_user((void __user *)arg, &info, minsz))
return -EFAULT;
return 0;
}
case VFIO_DEVICE_GET_REGION_INFO: {
struct vfio_region_info info;
minsz = offsetofend(struct vfio_region_info, offset);
if (copy_from_user(&info, (void __user *)arg, minsz))
return -EFAULT;
if (info.argsz < minsz) {
pr_err("%s line %d, info.argsz %d < minsz %ld.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, info.argsz, minsz);
return -EINVAL;
}
ret = wdg_get_region_info(mdev, &info);
if (ret) {
pr_err("%s line %d, get region info failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return ret;
}
if (copy_to_user((void __user *)arg, &info, minsz))
return -EFAULT;
return 0;
}
case VFIO_DEVICE_GET_IRQ_INFO: {
struct vfio_irq_info info;
minsz = offsetofend(struct vfio_irq_info, count);
if (copy_from_user(&info, (void __user *)arg, minsz))
return -EFAULT;
if ((info.argsz < minsz) ||
(info.index >= mstate->dev_info.num_irqs))
return -EINVAL;
ret = wdg_get_irq_info(mdev, &info);
if (ret)
return ret;
if (copy_to_user((void __user *)arg, &info, minsz))
return -EFAULT;
return 0;
}
case VFIO_DEVICE_SET_IRQS: {
pr_info("%s line %d, set irqs.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
case VFIO_DEVICE_RESET:
pr_info("%s line %d, reset.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
return -EINVAL;
}
static const struct mdev_parent_ops wdg_mdev_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.dev_attr_groups = wdg_dev_groups,
.mdev_attr_groups = mdev_dev_groups,
.supported_type_groups = mdev_type_groups,
.create = czl_wdg_create,
.remove = czl_wdg_remove,
.open = czl_wdg_open,
.release = czl_wdg_close,
.read = czl_wdg_read,
.write = czl_wdg_write,
.ioctl = czl_wdg_ioctl,
};
static void wdg_device_release(struct device *dev)
{
pr_info("czl wdg devide release.\n");
}
static int mdev_wdg_init(void)
{
int ret = 0;
pr_info("czl wdg init.\n");
memset(&czl_wdg, 0x00, sizeof(czl_wdg));
ret = alloc_chrdev_region(&czl_wdg.wdg_devt, 0, MINORMASK + 1, "czl_wdg");
if (ret < 0) {
pr_err("error: failed to register czl wdg device, err:%d\n", ret);
return -1;
}
cdev_init(&czl_wdg.wdg_cdev, &czl_wdg_fops);
cdev_add(&czl_wdg.wdg_cdev, czl_wdg.wdg_devt, MINORMASK + 1);
pr_info("major_number:%d\n", MAJOR(czl_wdg.wdg_devt));
czl_wdg.wdg_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "czl_wdg");
if (IS_ERR(czl_wdg.wdg_class)) {
pr_err("error: failed to create wdg class.\n");
ret = -1;
goto failed1;
}
czl_wdg.dev.class = czl_wdg.wdg_class;
czl_wdg.dev.release = wdg_device_release;
dev_set_name(&czl_wdg.dev, "%s", "czl_wdg");
ret = device_register(&czl_wdg.dev);
if (ret) {
pr_err("%s line %d, register wdg device failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
ret = -1;
goto failed2;
}
ret = mdev_register_device(&czl_wdg.dev, &wdg_mdev_fops);
if (ret) {
pr_err("%s line %d, register wdg mdev device failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
ret = -1;
goto failed3;
}
mutex_init(&wdg_mdev_list_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&wdg_mdev_devices_list);
pr_info("czl wdg init success.\n");
goto done;
failed3:
device_unregister(&czl_wdg.dev);
failed2:
class_destroy(czl_wdg.wdg_class);
failed1:
cdev_del(&czl_wdg.wdg_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(czl_wdg.wdg_devt, MINORMASK + 1);
done:
return ret;
}
static void mdev_wdg_exit(void)
{
czl_wdg.dev.bus = NULL;
mdev_unregister_device(&czl_wdg.dev);
device_unregister(&czl_wdg.dev);
cdev_del(&czl_wdg.wdg_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(czl_wdg.wdg_devt, MINORMASK + 1);
class_destroy(czl_wdg.wdg_class);
czl_wdg.wdg_class = NULL;
pr_info("czl_wdg_unload.\n");
return;
}
module_init(mdev_wdg_init)
module_exit(mdev_wdg_exit)
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");qemu virtual machine kernel watchdog pci driver
由于添加的watchdog设备是PCIe设备,因此在驱动程序入口执行后,首先要做的是初始化PCIe设备相关的操作,典型的就是调用pci_register_driver向kernel注册自己所感兴趣的PCIe设备,提供pci device probe回调函数,这样kernel在匹配到驱动所对应的硬件后,就会调用probe函数。所以,从某种角度上来说,PCIe设备的probe回调函数才是绝大多数PCIe驱动的主入口,因为如果没有硬件插入主板的话,驱动可以处于静默状态,此时驱动和设备没有绑定,只有检测到PCIe硬件以后,整个驱动才开始活跃起来。(当然,上述流程是针对PCIe硬件设备的驱动而言的,对于一些例外情况,例如Linux在drivers/infiniband/sw目录中提供的rxe驱动等,是通过软件来模拟硬件行为的,不涉及到真实的硬件,则初始化流程必然会有所差异,这种一般是软件注册设备结构模型,添加设备的路径中一般会调用linux内核的device_add API)。
驱动和设备绑定的规则按照pcie 配置空间中的vendor id/device id 匹配原则进行。
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/poll.h>
#include <linux/slab.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/wait.h>
#include <linux/uuid.h>
#include <linux/vfio.h>
#include <linux/iommu.h>
#include <linux/sysfs.h>
#include <linux/ctype.h>
#include <linux/file.h>
#include <linux/mdev.h>
#include <linux/pci.h>
#include <linux/idr.h>
static int devno;
static DEFINE_IDR(wdg_minors);
static DEFINE_MUTEX(wdg_minors_lock);
#define WDG_MINORS_COUNT 256
struct wdg_pci_state {
struct pci_dev *pdev;
struct device *dev;
int iobase;
int iolen;
int major;
int minor;
};
static struct class *wdg_class;
static const struct pci_device_id czl_pci_table[] = {
{ PCI_DEVICE(0xbeef, 0x1001), },
{ 0, }
};
static int czl_wdg_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
int rc = 0;
int major, minor;
major = imajor(inode);
minor = iminor(inode);
mutex_lock(&wdg_minors_lock);
file->private_data = idr_find(&wdg_minors, minor);
mutex_unlock(&wdg_minors_lock);
if (!file->private_data) {
pr_err("%s line %d, cant find wdg structure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
rc = -1;
}
return rc;
}
static int czl_wdg_release(struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
return 0;
}
ssize_t czl_wdg_read(struct file *file, char __user *buf, size_t size, loff_t *ppos)
{
int i;
struct wdg_pci_state *wdgdev = NULL;
unsigned char *kbuf = NULL;
int actuallen = 0;
wdgdev = file->private_data;
if (!wdgdev) {
pr_err("%s line %d, read failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
if (*ppos > wdgdev->iolen) {
pr_err("%s line %d, read pos %lld exceed max io len %d.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, *ppos, wdgdev->iolen);
return -1;
}
kbuf = kzalloc(GFP_KERNEL, size);
if (kbuf == NULL) {
pr_err("%s line %d, alloc kbuf failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
for (i = 0; (i < size) && ((*ppos + i) < wdgdev->iolen); i++) {
kbuf[i] = inb(wdgdev->iobase + *ppos + i);
actuallen ++;
}
copy_to_user(buf, kbuf, actuallen);
kfree(kbuf);
return actuallen;
}
static ssize_t czl_wdg_write(struct file *file, const char __user *buf,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
int i;
struct wdg_pci_state *wdgdev = NULL;
unsigned char *kbuf = NULL;
int actuallen = 0;
wdgdev = file->private_data;
if (!wdgdev) {
pr_err("%s line %d, read failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
if (*ppos > wdgdev->iolen) {
pr_err("%s line %d, read pos %lld exceed max io len %d.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, *ppos, wdgdev->iolen);
return -1;
}
kbuf = kzalloc(GFP_KERNEL, count);
if (kbuf == NULL) {
pr_err("%s line %d, alloc kbuf failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
copy_from_user(kbuf, buf, count);
for (i = 0; (i < count) && ((*ppos + i) < wdgdev->iolen); i++) {
outb((u8)kbuf[i], wdgdev->iobase + *ppos + i);
actuallen ++;
}
kfree(kbuf);
return actuallen;
}
static const struct file_operations czl_wdg_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = czl_wdg_open,
.release = czl_wdg_release,
.read = czl_wdg_read,
.write = czl_wdg_write,
};
static char *wdg_devnode(struct device *dev, umode_t *mode)
{
if (mode)
*mode = 06666;
return kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "%s", dev_name(dev));
}
static int wdg_pci_probe(struct pci_dev *pdev, const struct pci_device_id *id)
{
struct wdg_pci_state *wdgdev = NULL;
pr_info("%s line %d, wdg pci device & driver binding.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
wdgdev = kzalloc(GFP_KERNEL, sizeof(*wdgdev));
if (!wdgdev) {
pr_err("%s line %d, fail to alloc buffer.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
goto err0;
}
wdgdev->major = devno;
wdgdev->pdev = pci_dev_get(pdev);
wdgdev->iobase = pci_resource_start(pdev, 0);
wdgdev->iolen = pci_resource_len(pdev, 0);
mutex_lock(&wdg_minors_lock);
wdgdev->minor = idr_alloc(&wdg_minors, wdgdev, 0, WDG_MINORS_COUNT, GFP_KERNEL);
mutex_unlock(&wdg_minors_lock);
if (wdgdev->minor < 0) {
pr_err("%s line %d, get minor failure from idr.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
goto err1;
}
pr_info("%s line %d, major %d, minor %d, iobase 0x%x.\n", __func__, __LINE__,
devno, wdgdev->minor, wdgdev->iobase);
wdgdev->dev = device_create(wdg_class, NULL, MKDEV(devno, wdgdev->minor),
NULL, "czl-wdg-%d", wdgdev->minor);
if (!wdgdev->dev || IS_ERR(wdgdev->dev)) {
pr_err("%s line %d, create wdg device failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
goto err2;
}
pci_set_drvdata(pdev, wdgdev);
return 0;
err2:
idr_remove(&wdg_minors, wdgdev->minor);
err1:
if (wdgdev) {
kfree(wdgdev);
}
err0:
return -1;
}
static void wdg_pci_remove(struct pci_dev *pdev)
{
struct wdg_pci_state *wdgdev;
pr_info("%s line %d, wdg pci device & driver removing.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
wdgdev = pci_get_drvdata(pdev);
pci_set_drvdata(pdev, NULL);
pci_dev_put(pdev);
wdgdev->pdev = NULL;
device_destroy(wdg_class, MKDEV(devno, wdgdev->minor));
idr_remove(&wdg_minors, wdgdev->minor);
kfree(wdgdev);
return;
}
static struct pci_driver czl_wdg_driver = {
.name = "czl-mdev-wdg",
.id_table = czl_pci_table,
.probe = wdg_pci_probe,
.remove = wdg_pci_remove,
};
static int czl_wdg_init(void)
{
int ret;
wdg_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "czl-wdg");
if (!wdg_class) {
pr_err("%s line %d, create watchdog class failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
wdg_class->devnode = wdg_devnode;
devno = register_chrdev(0, "czl-wdg", &czl_wdg_fops);
if (devno < 0) {
pr_err("%s line %d, register wdg device chrno failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
class_destroy(wdg_class);
return -1;
}
ret = pci_register_driver(&czl_wdg_driver);
return ret;
}
static void czl_wdg_exit(void)
{
pci_unregister_driver(&czl_wdg_driver);
unregister_chrdev(devno, "czl-wdg");
class_destroy(wdg_class);
idr_destroy(&wdg_minors);
return;
}
module_init(czl_wdg_init)
module_exit(czl_wdg_exit)
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL v2");qemu virtual machine user space wdt test case
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
void dump_buf(unsigned char *buf, int len)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < len; i++) {
if (i % 16 == 0)
printf("\n0x%04x: ", i);
printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n");
return;
}
int main(void)
{
int wdgfd;
int status;
unsigned char buf[32];
wdgfd = open("/dev/czl-wdg-0", O_RDWR);
if (wdgfd < 0) {
printf("%s line %d, open failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
while (1) {
memset(buf, 0x00, 32);
status = read(wdgfd, buf, 32);
if (status < 0) {
printf("%s line %d, read failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
printf("%s line %d, read %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, status);
dump_buf(buf, 32);
memset(buf, 0x5a, 32);
lseek(wdgfd, 0, SEEK_SET);
status = write(wdgfd, buf, 32);
if (status < 0) {
printf("%s line %d, read failure.\n",
__func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
printf("%s line %d, read %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__, status);
sleep(1);
}
close(wdgfd);
return 0;
}测试程序构成:

测试过程:
1.安装WDG MDEV驱动:
sudo insmod mdev.ko
sudo insmod vfio_mdev.ko
sudo insmod czl-mdev-wdg.ko
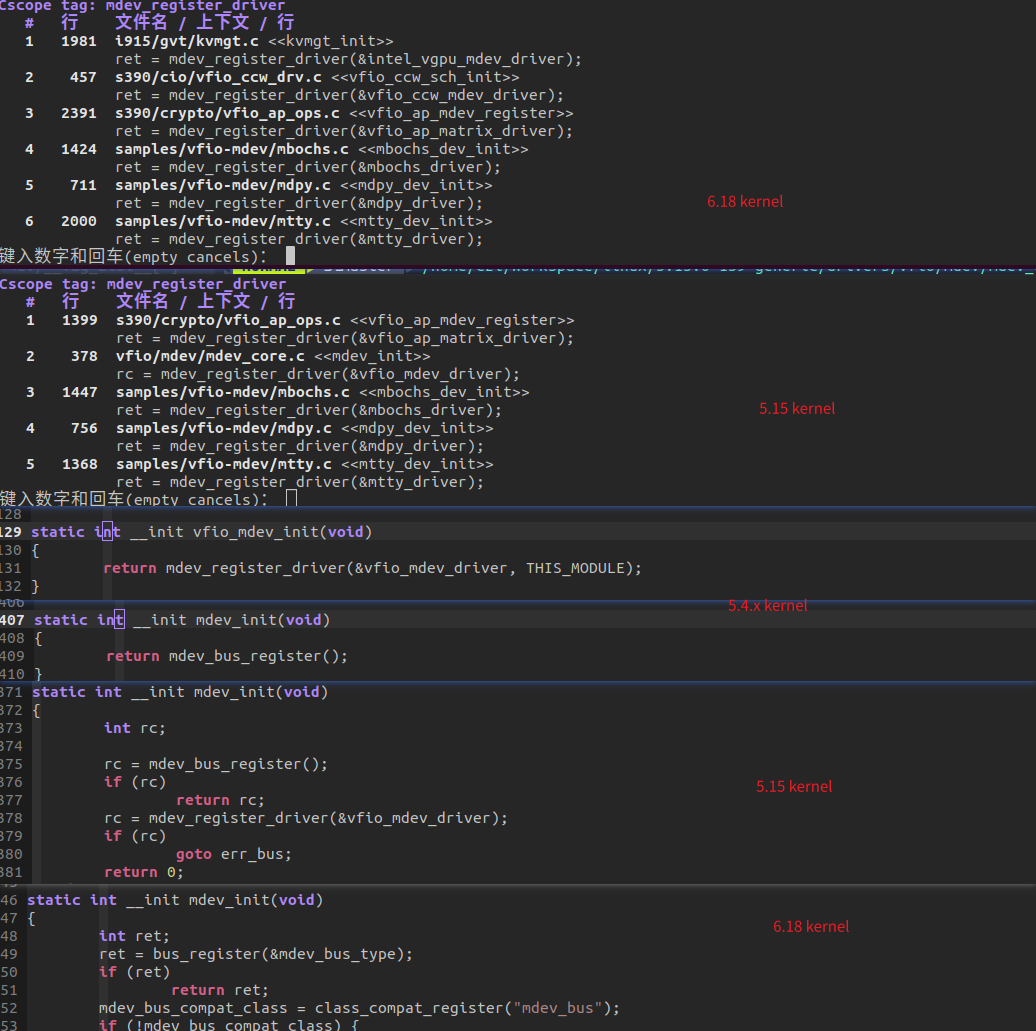
测试主机默认内核的VFIO驱动是BUILT IN到KERNEL中的,如果重新编译内核,并且相关驱动编译为模块,可以看到MDEV实际上是基于VFIO驱动的:
host端的模块依赖关系可以用下图表示:

update:5.15.x内核支持用户自定义的mdev_driver,和vfio_mdev平行,所以vfio_mdev.ko变为了可选的,另外上图没有画出来的是,mdev.ko也依赖vfio.ko.
为了兼顾platform和pci,mdev设备,VFIO统一对外提供了struct vfio_device来描述vfio设备。vfio_device设备就像是MDEV设备,PCI设备或者PLATFORM设备的一个影子。
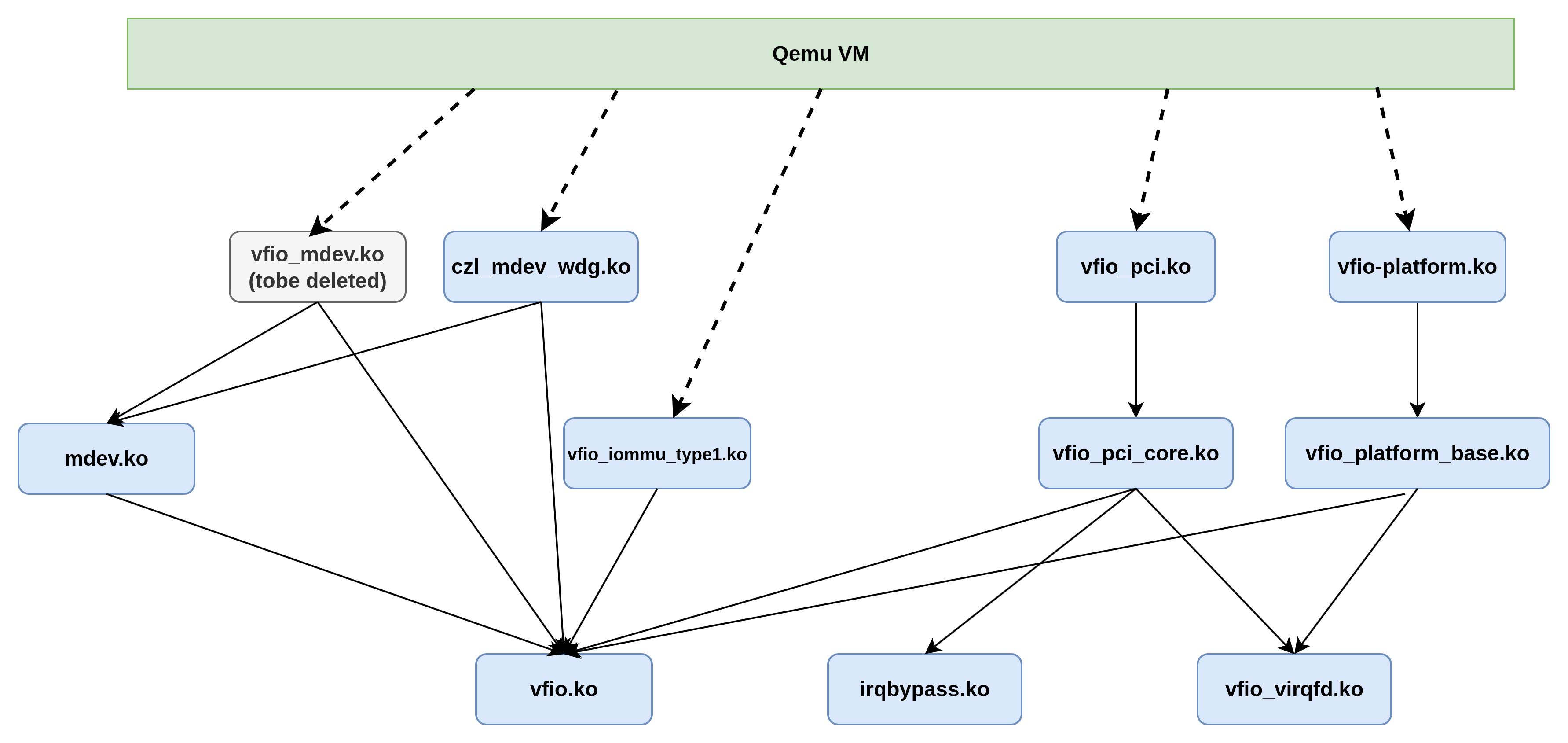
mdev.ko对vfio.ko的依赖限于vfio_uninit_group_dev/vfio_unregister_group_devvfio_register_group_dev/vfio_init_group_dev少数几个接口,在6.2内核中引入IOMMUFD之后,这层耦合被解开,mdev.ko只依赖内核,不再依赖vfio.ko.
update: 上图展示的模块架构是在提交7b96953bc640b6b25665fe17ffca4b668b371f14开始奠定的,当时的版本是v4.9-rc5-1-g7b96953bc640
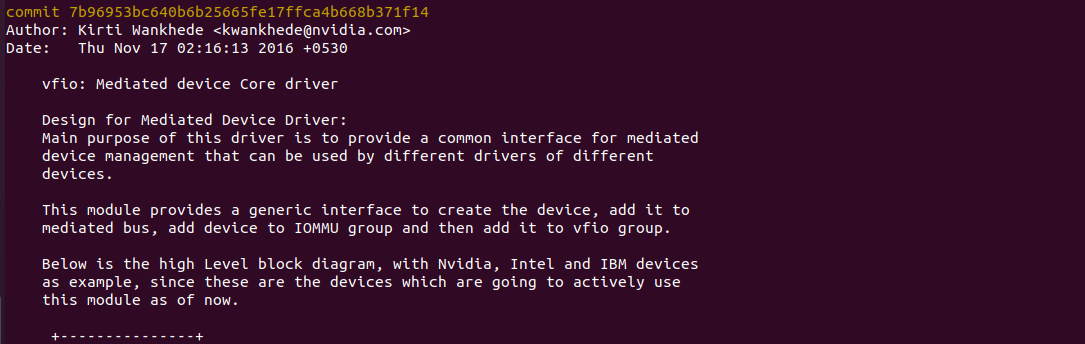
后来,在v5.13-rc6-6-gaf3ab3f9b986版本,删除了vfio_mdev.ko,将其代码融合到了mdev.ko里面。
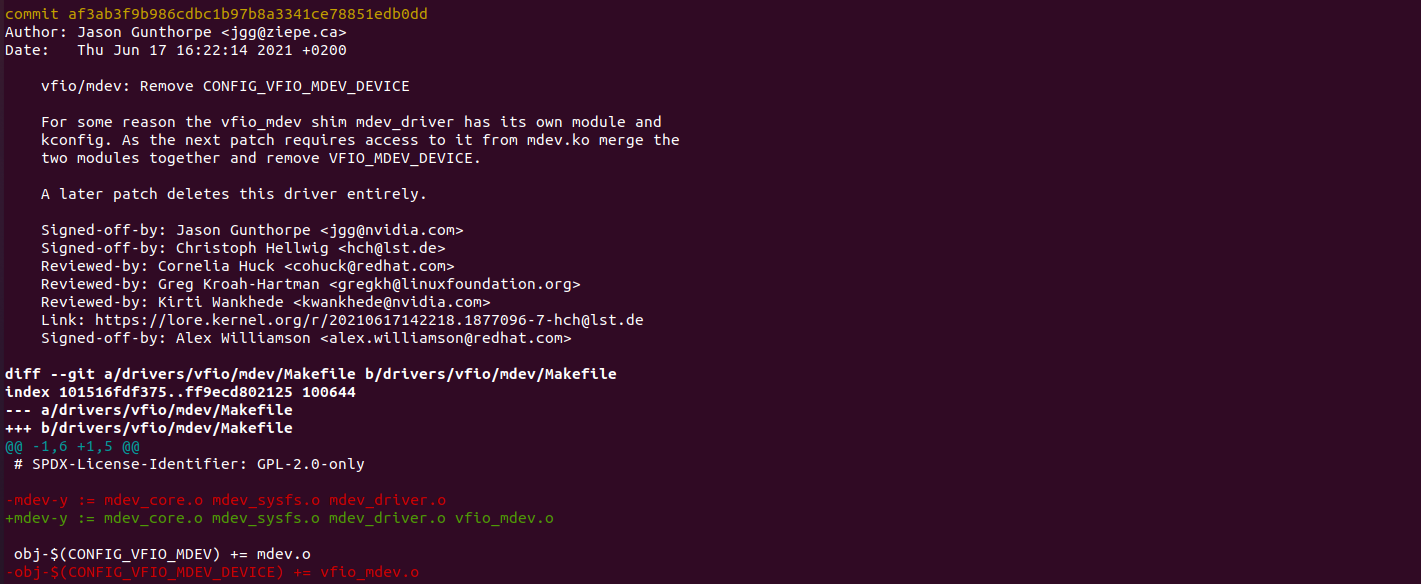
再后来,v5.18-rc1-33-g6c7f98b334a3版本,彻底删除了vfio_mdev.c,将其融入到了mdev.ko中。
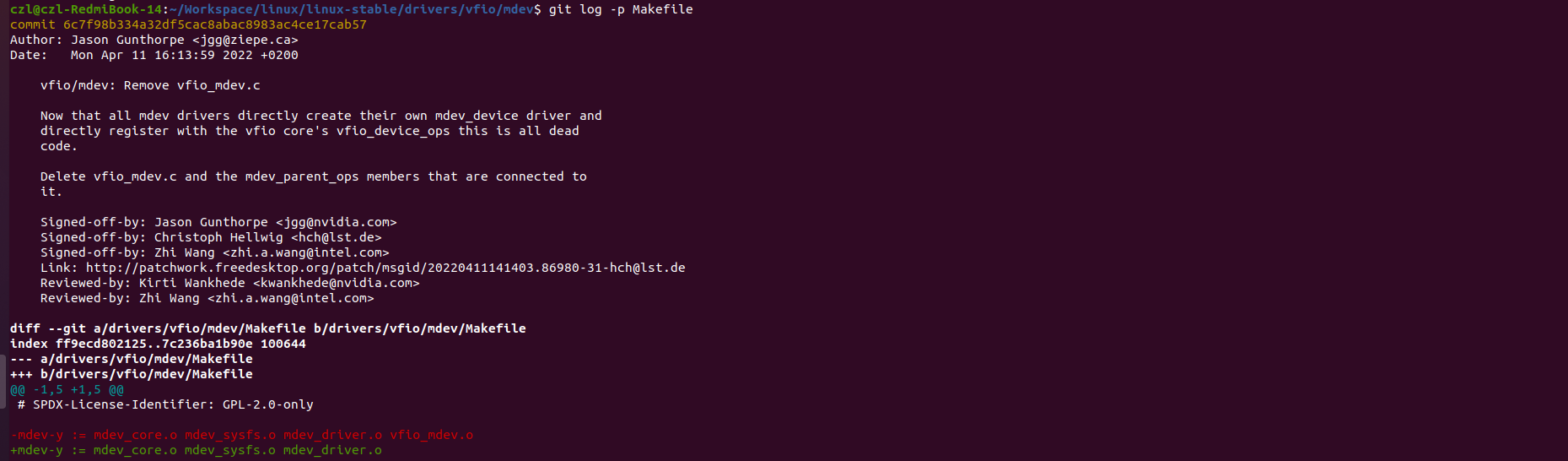
所以,从5.13开始,就没有vfio_mdev.ko模块了,不过此时仍然是形式上的删除,具体vfio_mdev.ko的逻辑仍然存在,只是融合到了mdev.ko中。从5.18开始,vfio_mdev逻辑上才真正融合进了mdev.ko中。
也就是说,最新内核的模块依赖图是基于上图,删除掉了vfio_mdev.ko.
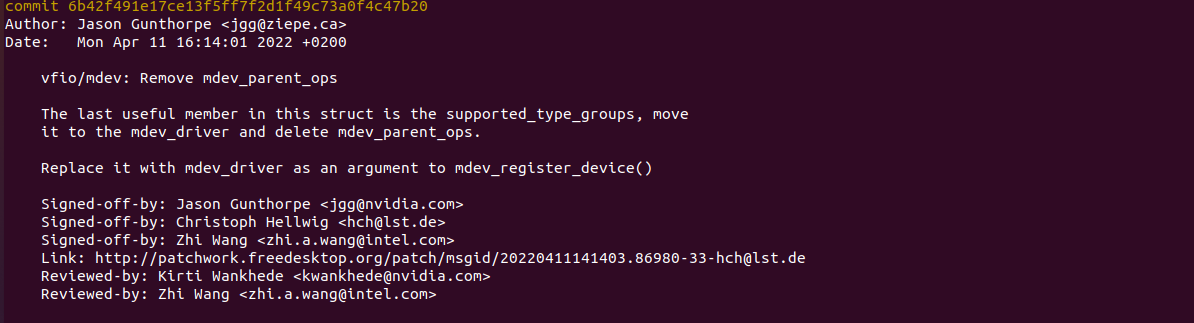
从版本v5.18-rc1-35-g6b42f491e17c,v6.0-rc4-65-gda44c340c4fe开始,删除了mdev_parent_ops,supported_type_groups等关键数据结构,本测试用例不能跑了,需要基于新的MDEV框架重新适配。
2.创建mdev设备
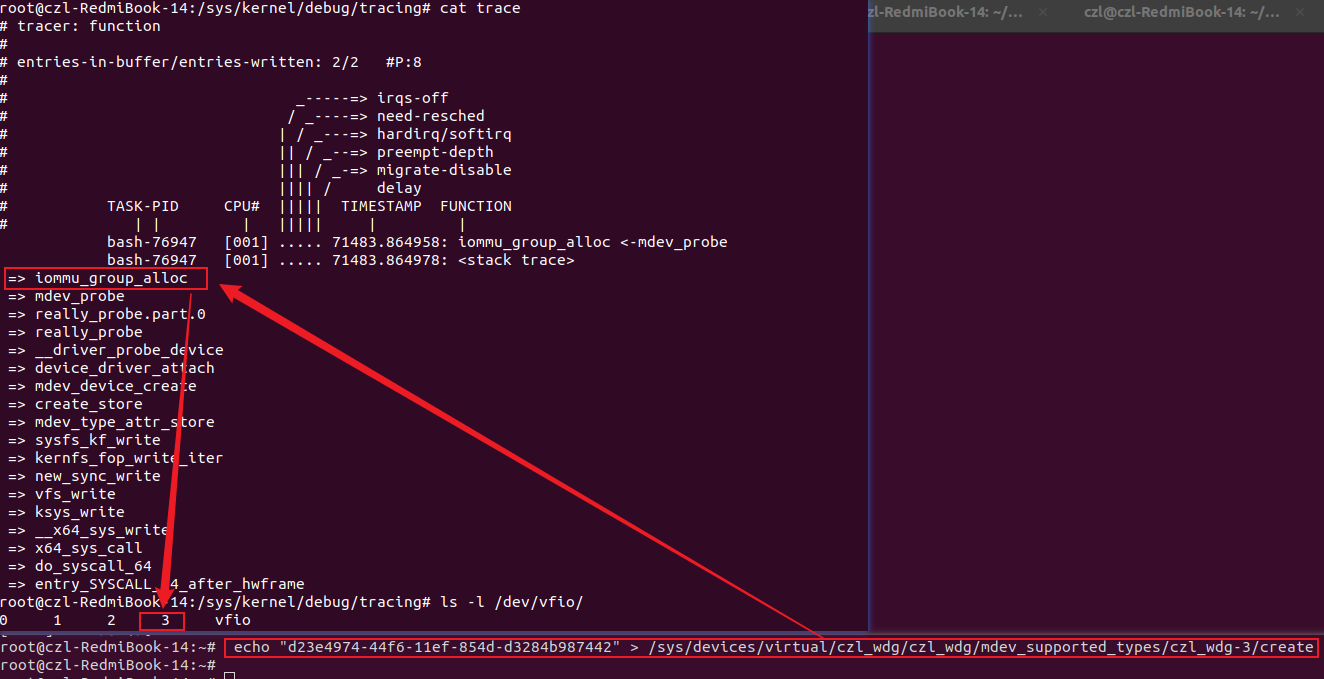
创建两个mdev设备
echo "f422fd86-35c0-11ef-8e50-9342c1138a56" > /sys/devices/virtual/czl_wdg/czl_wdg/mdev_supported_types/czl_wdg-1/create
echo "c04de378-35d8-11ef-95c3-339660dfc874" > /sys/devices/virtual/czl_wdg/czl_wdg/mdev_supported_types/czl_wdg-2/create
3.将第二步创建的mdev设别透传给QEMU虚拟机启动:
qemu-system-x86_64 -m 4096 -smp 4 --enable-kvm -drive file=/home/zlcao/Workspace/iso/ps.img -device vfio-pci,sysfsdev=/sys/bus/mdev/devices/f422fd86-35c0-11ef-8e50-9342c1138a56 -device vfio-pci,sysfsdev=/sys/bus/mdev/devices/c04de378-35d8-11ef-95c3-339660dfc874如果环境没有安装SDL库,执行上述命令后并不会启动QEMU虚拟机的GUI界面,这个时候要么安装正确的依赖库,要么根据控制台提示,使用gvncviewer等VNC客户端工具连接图形界面:
sudo gvncviewer 127.0.0.1:0

系统启动后,可以看到虚拟机环境下出现了透传的MDEV PCI设备,设备vendor/device id为0xbeef1001,符合代码设定。

4.虚拟机内安装WDG PCI设备驱动:
上图中可以看到,两个透传的MDEV设备已经和一个名为"serial"的PCI设备驱动绑定,这并不符合预期,需要将默认的"serial"驱动和MDEV设备解绑,在QEMU虚拟机控制台中输入如下命令解绑驱动:
echo -n 0000:00:04.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/serial/unbind
echo -n 0000:00:05.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/serial/unbind
之后就可以安装我们的WDG PCI驱动了:
sudo insmod czl-mdev-drv.ko安装成功后,虚拟机设备目录下出现了WDG PCI的设备节点:

此时,两个MDEV PCI设备也显示绑定到了正确的驱动:

为何创建的PCI设备绑定了"serial" pci driver?
serial_pci_driver定义在内核文件linux-5.4.260/drivers/tty/serial/8250/8250_pci.c中

PCI设备驱动探测的时候绑定规则是检测设备的VENDROR ID和DEVICE ID是否和驱动给定的过滤器匹配,巧的是,serial_pci_driver驱动的serial_pci_tbl过滤器包含的一个映射规则是PCI_ANY_ID,也就是说,serial_pci_driver可以和任意的PCI设备绑定,所以才会出现创建的vWDG设备和serial驱动绑定的情况,虽然绑定了驱动,但是由于vWDG是我们自定义的设备,默认的serial是无法驱动的,所以必须卸载。

并且发现一个很有意思的现象,当只有BAR0 IO空间的时候,GUEST OS启动默认使用serial_pci_driver,但是当修改程序,增加一些BAR空间后,发现GUEST启动后,两个vWDG设备就没有默认的驱动绑定了,也就不需要执行unbind的echo了。
5.运行测试用例,读写WDG PCI设备的BAR0地址空间:
此时可以看到,虚拟机中对WDG设备BAR0空间的读写调用被“透传"到了HOST机的MDEV PCI设备驱动上,可以基于对BAR0空间的回调实现我们的业务逻辑。
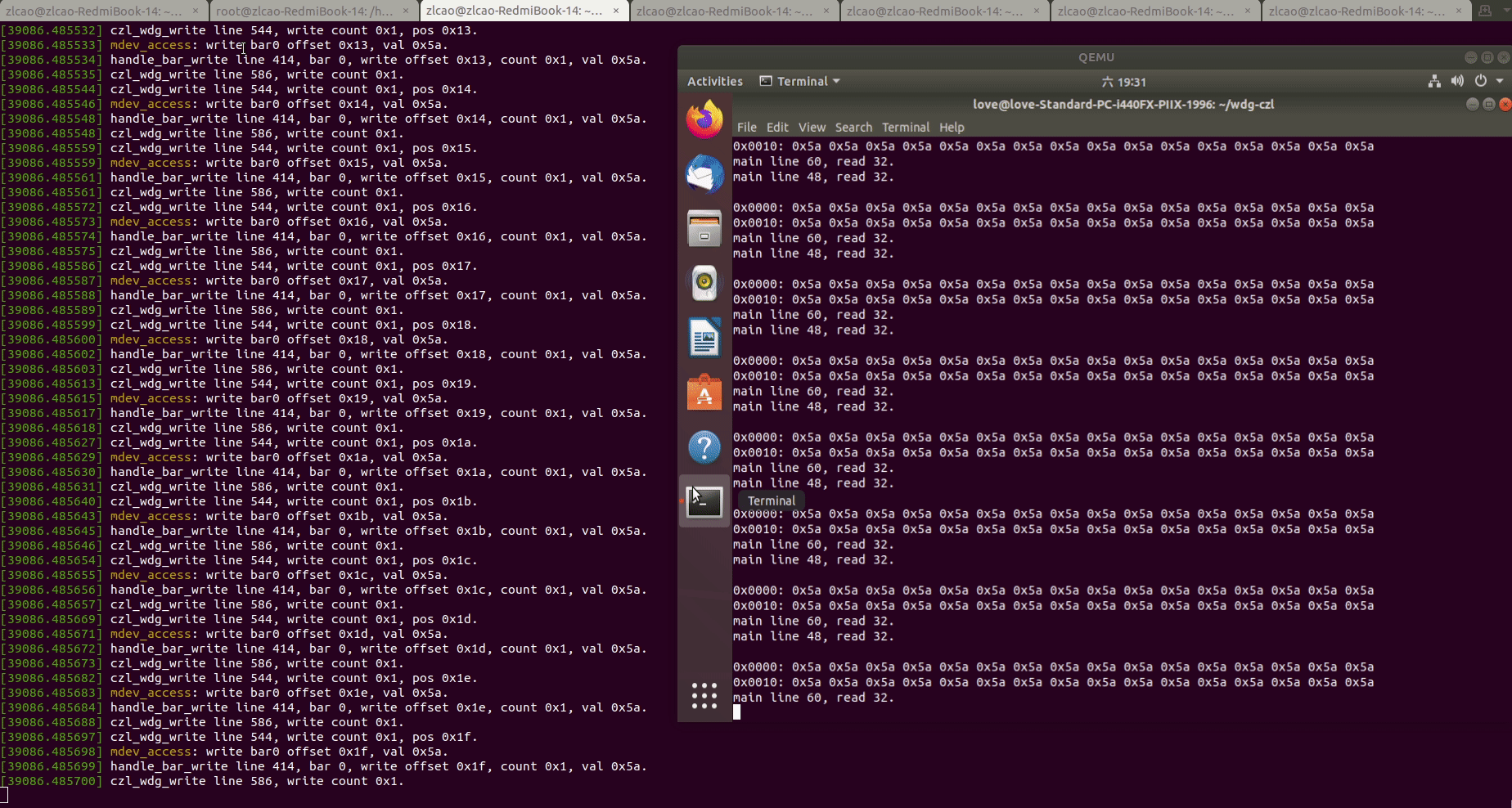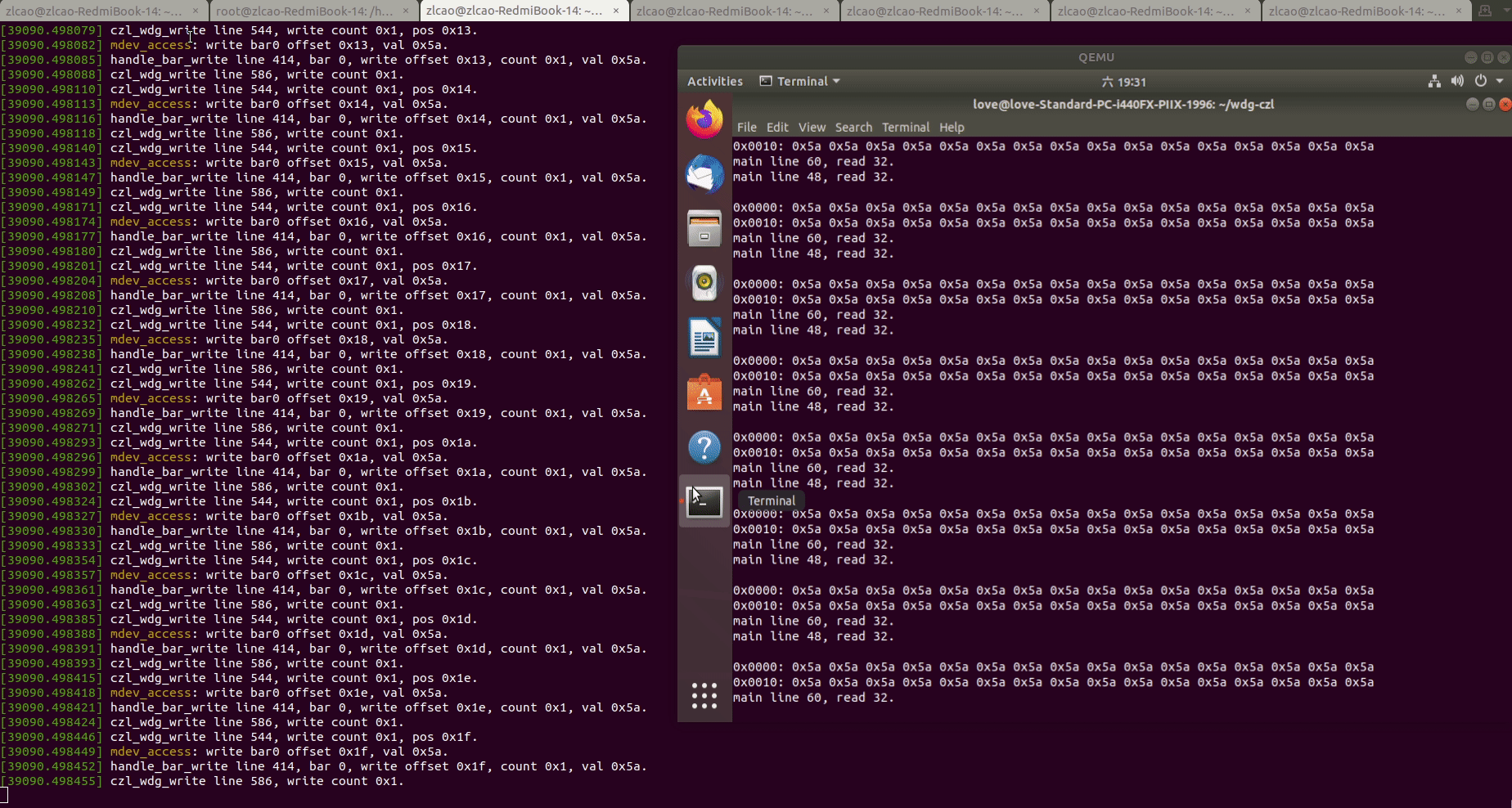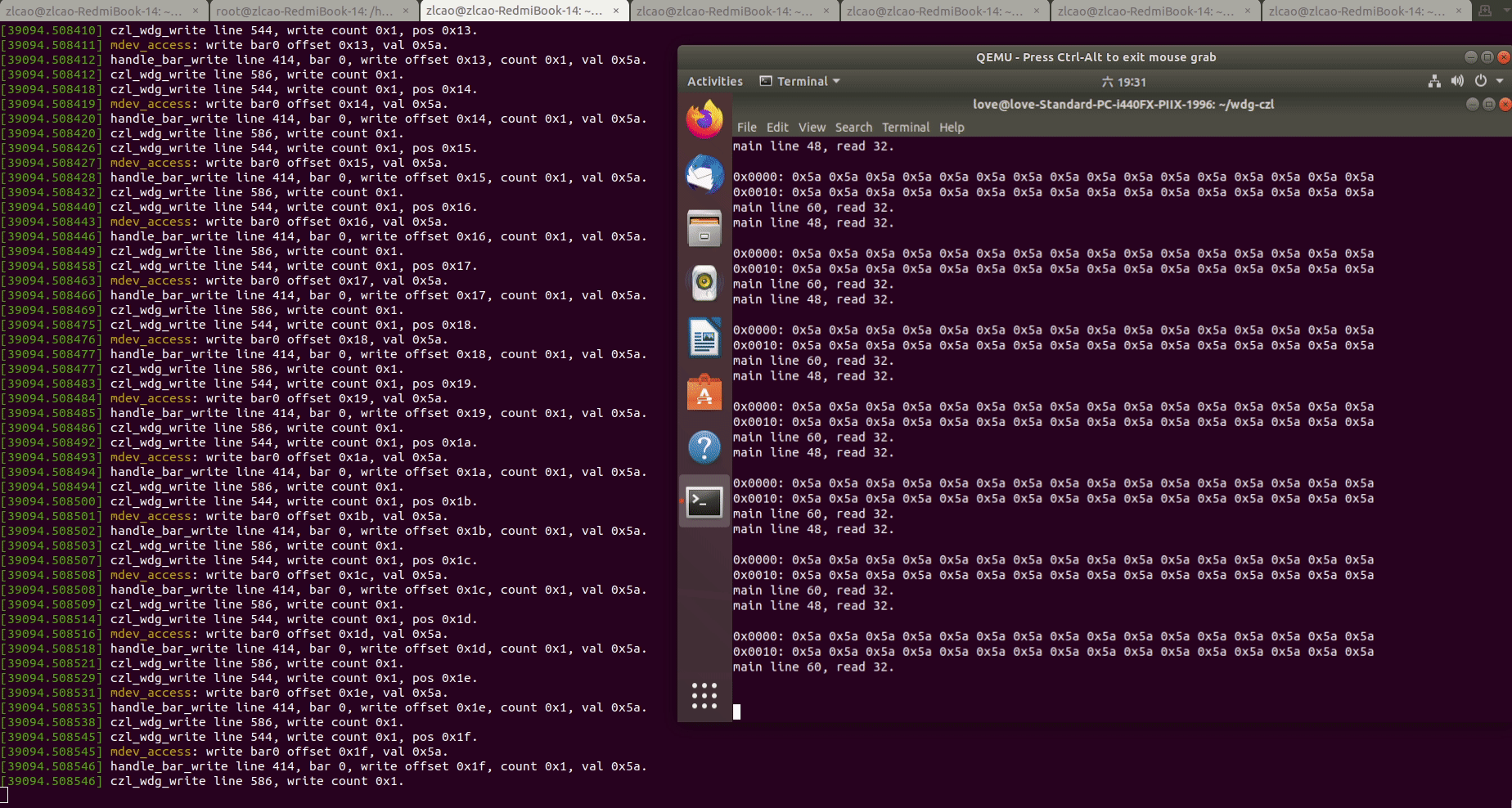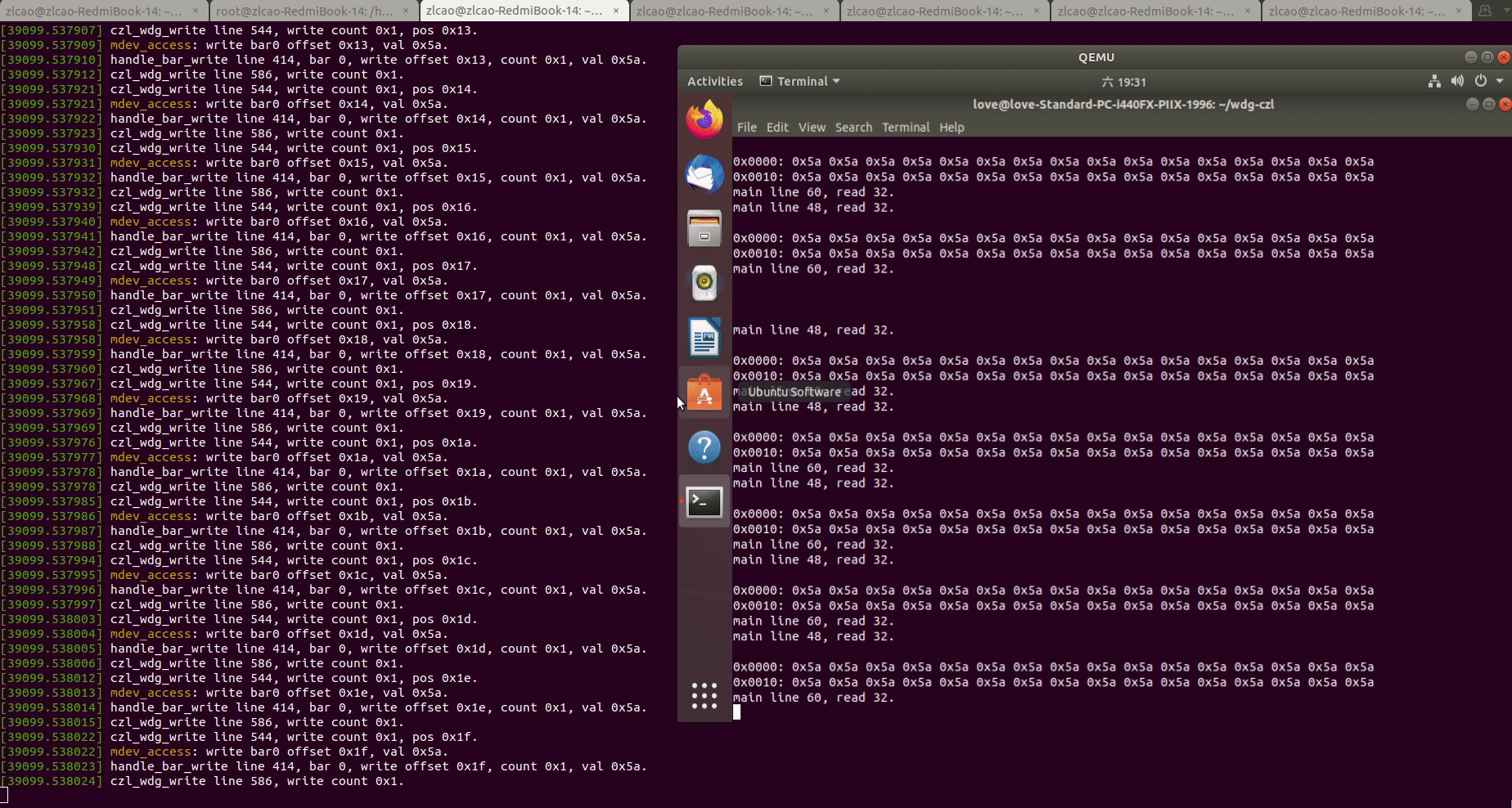
BAR空间映射:
经过改进的vWDG支持全部的BAR空间映射,这是通过虚拟化设备的配置空间得到的:

中断注入模拟
利用EVENTFD机制从MDEV中开始,通过KVM向GUEST 中的虚拟PCI DOG设备注入中断,下图显示GUEST OS 驱动成功接受到来自于HOST OS MDEV框架parent回调注入的中断。

step1: host os mdev vendor callback trigger interrupt,wake up irqfd_inject

step 2: irqfd worker start to run and inject interrupt to virtual iopic:

step 3:当虚拟机投入运行时,调用ARCH的.set_irq handler将中断请求写入VMCS,出发VCPU处理中断:

所以看起来eventfd唤醒的并非是POLL,而是irqfd_inject worker,也就是说中断DISPATCH是通过KVM来作的,而非QEMU,这也是为什么在用户态抓不到POLL调用的原因。
中断注入也可以由QEMU来做,如下图所示,QEMU E1000 PCI模拟网卡在接受到数据包后,向GUESET OS注入中断的过程。

配置空间确认
配置空间是mdev回调OPS中模拟的,control信息表示支持IO和MMIO访问,不支持BUS MASTER。状态寄存器表示medium设备,并且不支持capabilities.这些和MDEV中给定的虚拟设备配置空间相符。

bar空间读写测试
虚拟机内的的BAR空间读写测试用例,当访问IO BAR时,虚拟机会陷入VMM,reason number为KVM_IO_EXIT,当访问MMIO BAR时,虚拟机同样也会陷入VMM,此时的reason number为 KVM_MMIO_EXIT. QEMU处理接下来的IO/MMIO读写,以后者为例,对应QEMU中的调用调用堆栈现场为:

callstack:
#0 0x00005555558fb597 in vfio_region_write (opaque=0x555557bcacb8, addr=790560, data=197640, size=4) at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/hw/vfio/common.c:183
#1 0x000055555587fd68 in memory_region_write_accessor (mr=0x555557bd3610, addr=790560, value=0x7fffdd050f38, size=4, shift=0, mask=4294967295, attrs=...)
at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/memory.c:483
#2 0x000055555587ff4f in access_with_adjusted_size (addr=790560, value=0x7fffdd050f38, size=4, access_size_min=1, access_size_max=8, access_fn=
0x55555587fca8 <memory_region_write_accessor>, mr=0x555557bd3610, attrs=...) at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/memory.c:544
#3 0x0000555555882ef9 in memory_region_dispatch_write (mr=0x555557bd3610, addr=790560, data=197640, op=MO_32, attrs=...) at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/memory.c:1475
#4 0x0000555555821364 in flatview_write_continue (fv=0x7fffc4004b10, addr=4270592032, attrs=..., buf=0x7ffff7fec028 "\b\004\003", len=4, addr1=790560, l=4, mr=0x555557bd3610)
at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/exec.c:3129
#5 0x00005555558214a9 in flatview_write (fv=0x7fffc4004b10, addr=4270592032, attrs=..., buf=0x7ffff7fec028 "\b\004\003", len=4) at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/exec.c:3169
#6 0x00005555558217f6 in address_space_write (as=0x5555567ffb60 <address_space_memory>, addr=4270592032, attrs=..., buf=0x7ffff7fec028 "\b\004\003", len=4)
at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/exec.c:3259
#7 0x0000555555821863 in address_space_rw (as=0x5555567ffb60 <address_space_memory>, addr=4270592032, attrs=..., buf=0x7ffff7fec028 "\b\004\003", len=4, is_write=true)
at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/exec.c:3269
#8 0x000055555589b6d4 in kvm_cpu_exec (cpu=0x555556d19b00) at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/accel/kvm/kvm-all.c:2374
#9 0x0000555555870f64 in qemu_kvm_cpu_thread_fn (arg=0x555556d19b00) at /home/zlcao/Workspace/qemu/qemu-4.2.1/cpus.c:1318
#10 0x0000555555e0c0b4 in qemu_thread_start (args=0x555556b051e0) at util/qemu-thread-posix.c:519
#11 0x00007ffff365d6db in start_thread (arg=0x7fffdd054700) at pthread_create.c:463
#12 0x00007ffff338661f in clone () at ../sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/x86_64/clone.S:95

可以看到此时访问的0xfe8c1020地址正是虚拟WATCHDOGS设备的BAR1空间中的地址:

DMA重定向支持
例子中的vWDG设备为纯模拟设备,设备本身没有私有存储,不需要作PASS-THROUGH,所以无论mdev_device_create/mdev_register_device创建的两个设备结构体默认不属于任何一个系统已知IOMMU GROUP和IOMMU DOMAIN。
但是对于支持iommu-group的PCI设备使用MDEV框架作透传时,虽然mdev framework在调用mdev_device_create创建MDEV设备时仍然是一个虚拟设备,但是其利用mdev_register_device注册的parent设备必须对应一个真实的PCI设备对象.以内核中的 INTEL显卡设备为例,mdev_register_device调用为下图,追踪代码可以知道,第一个参数就是显卡对应的struct pci_dev.dev对象指针。

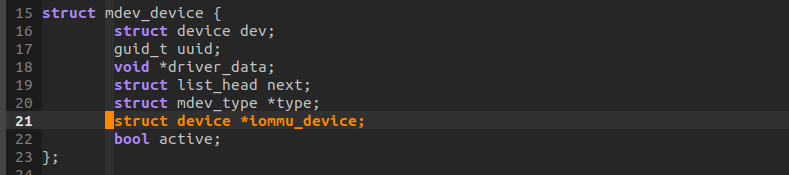
MDEV设备怎么知道自己用哪个IOMMU呢?毕竟MDEV设备所在的总线是mdev_bus_type,并非拥有IOMMU设备的pci_bus_type. 方法是MDEV Vendor driver通过调用mdev_set_iommu_device将PARENT设备设置给mdev_dev->iommu_device对象,这样就将虚拟的MDEV设备和真实的PCI设备联系起来:

之后在vfio_iommu_type1_attach_group这一步获取mdev_dev->iommu_device对象,进而得到IOMMU DEVICE对象所在的BUS,BUS是和IOMMU操作绑定的,从而也就知道了该MDEV设备所在的 IOMMU DOMAIN,调用iommu_domain_alloc分配新的IOMMU DOMAIN 给MDEV设备,相当于真实PCI设备将IOMMU能力委托给了MDEV设备,之后就可以用MDEV设备的上下文调用iommu_map进行GPA(IOVA)到HPA的映射了。

mdev iommu group的分配
iommu group是IOMMU隔离的最小单位,不同于VFIO PCI透传框架不分配新的IOMMU GROUP,而是使用透传设备的IOMMU GROUP,所有的MDEV设备在总线探测的第一步就会分配独立的IOMMU GROUP,也就是说,每个MDEV设备属于一个独立的IOMMU GROUP,并且每个IOMMU GROUP也仅仅只有一个MDEV设备。并在后面的流程中把新创建的IOMMU GROUP和上一步根据PARENT 设备总线创建的IOMMU DOMAIN 绑定在一起。注:这个IOMMU GROUP是一个DUMMY IOMMU GROUP,因为并未和IOMMU DOMAIN绑定,没有DMA功能,只是用来管理MDEV设备。
注册GROUP设备的调用堆栈,创建GROUP节点,节点名为/dev/vfio/#group-id
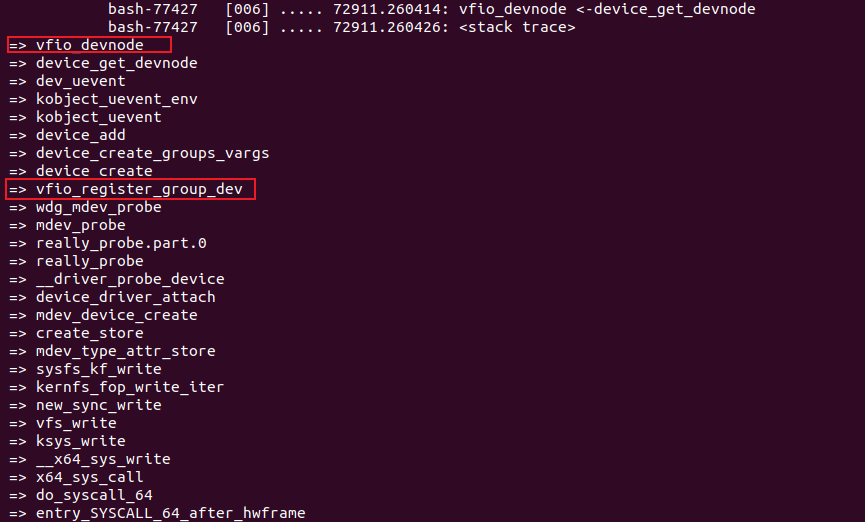
mdev 设备如何绑定到系统IOMMU?
mdev设备的IOMMU绑定完全依赖于其Parent设备。在Linux内核中,mdev设备本身不直接绑定到系统IOMMU,而是通过其Parent设备(或者mdev_set_iommu_device指定的设备)进行IOMMU DMA映射。Parent设备本身支持DMA操作。内核中的mtty例子和本文设计的WDG 是一个纯软件的示例驱动,没有关联到某条BUS上(父设别注册时,struct device->bus赋值为空,BUS和IOMMU有直接关联,因为IOMMU OPS记录在BUS上)。没有真实的硬件DMA能力,所以无法支持DMA MAP的能力,只能模拟字节流的操作。
那么如何使模拟出来的WDG MDEV设备具备访问IOMMU的能力呢? 只能换一个能够访问IOMMU的“父亲”,在X86平台上,这个父亲只能是PCIe设备,我们修改代码,让parent设备从czl_wdg.dev变更为NVIDIA显卡设备(提前将NOUVEAU显卡驱动加入黑名单)。
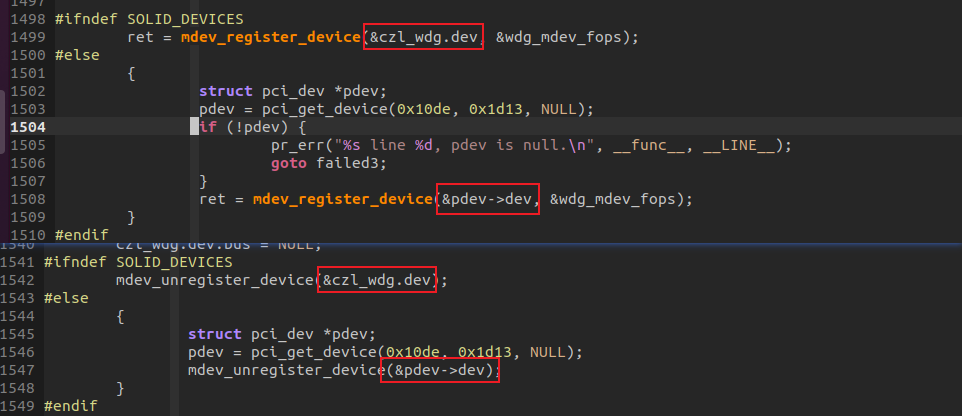
然后,在创建WDG MDEV设备的PROBE函数中调用mdev_set_iommu_device函数,将父设备对象赋值给struct mdev_device iommu_device字段。

在将IOMMU GROUP ATTACH到DOMAIN中的时候,在vfio_iommu_type1_attach_group会调用mdev_get_iommu_device获取父设备,进而获取父设备所在的总线,分配IOMMU DOAMIN。
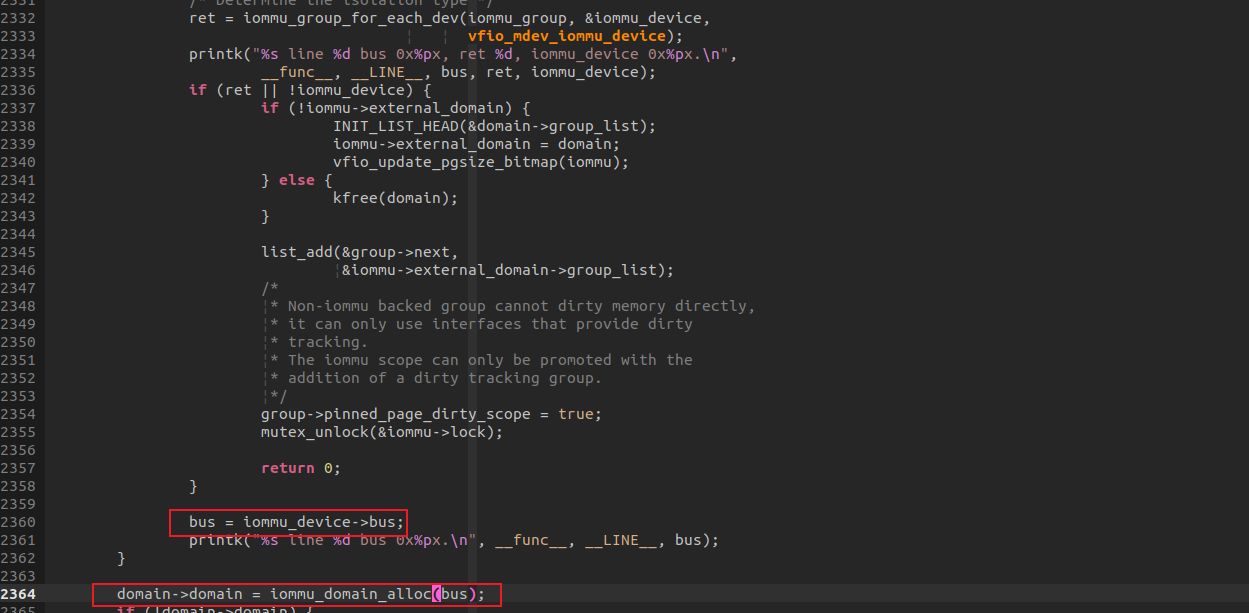
最后,在将新分配的DOMAIN 加入vfio_iommu的 domain_list中,方便在进行DMA MAP时逐个遍历,将映射做进每个IOMMU DOMAIN。 list_add(&domain->next, &iommu->domain_list);
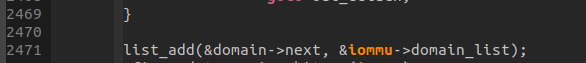
DOMAIN LIST遍历映射:
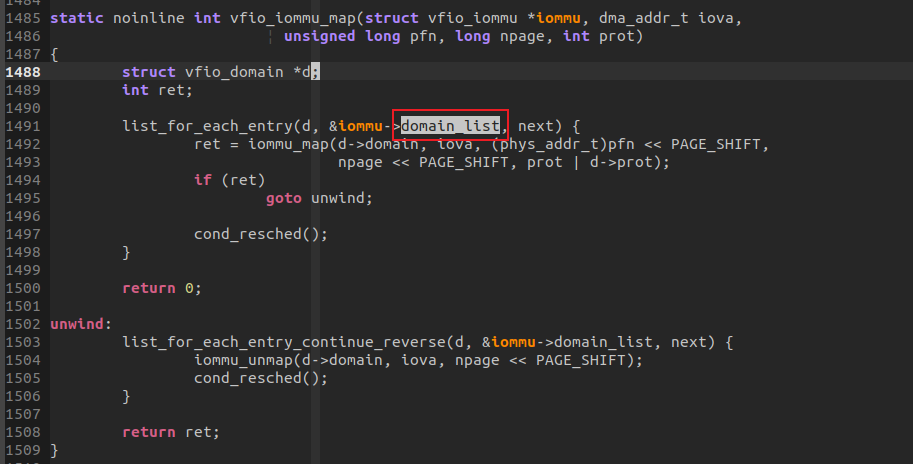
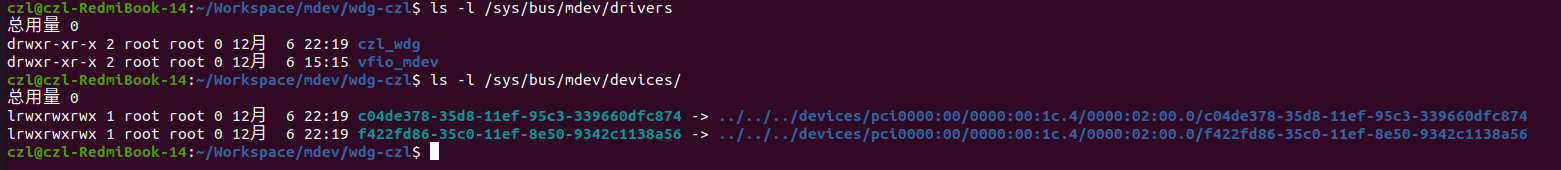
按照前述改动修改驱动,使MDEV设备使用PCIE设备作为父设备后,MDEV设备的创建目录从/sys/devices/virtual移到了“/sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:02:00.0”。然后使用如下命令创建MDEV设备:
echo "f422fd86-35c0-11ef-8e50-9342c1138a56" > /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:02:00.0/mdev_supported_types/pci-1/create
echo "c04de378-35d8-11ef-95c3-339660dfc874" > /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:02:00.0/mdev_supported_types/pci-1/create
echo "d23e4974-44f6-11ef-854d-c3284b987442" > /sys/devices/pci0000:00/0000:00:1c.4/0000:02:00.0/mdev_supported_types/pci-1/create
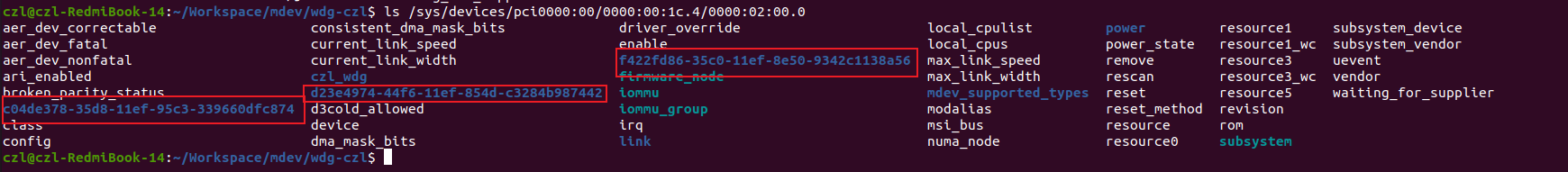
创建三个MDEV设备,每个独立一个IOMMU GROUP:
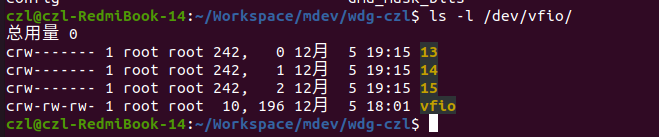
使用如下测试用例对WDG MDV设备做 DMA MAP:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/mman.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <linux/vfio.h>
/*
*container
*+------------------------+
*| group0 group1 |
*| +-------+ +------+ |
*| | dev0 | | dev2 | |
*| | dev1 | +------+ |
*| +-------+ |
*+------------------------+
*/
// /dev/vfio/vfio is the container, there maybe more than 1 iommu domain in container.
// /dev/vfio/#NUM is the group.
#define IOVA_DMA_MAPSZ (1*1024UL*1024UL)
#define IOVA_START (0UL)
#define VADDR 0x400000000000
// refer https://www.cnblogs.com/dream397/p/13546968.html
// container fd: the container provides little functionality, with all but a couple version and extension query interfaces.
// 1. first identify the group associated wth the desired device.
// 2. unbinding the device from the host driver and binding it to a vfio driver, then a new group would appear for the group as /dev/vfio/$group.
// make sure all the devices belongs to the group are all need to do the unbind and binding operations or error will got for next group ioctl.
// 3. group is ready, then add to the caontainer by opening the vfio group character device and use VFIO_GROUP_SET_CONTAINER ioctl to add the group
// fd to container.depending the iommu, multi group can be set to one container.
// 4. after group adding to container, the remaning ioctls became available. enable the iommu device access.now you can get each device belongs the
// iommu group and get the fd.
// 5. the vfio device ioctls includes for describing the device, the IO regions, and their read/write/mmap operations, and others such as describing
// and registering interrupt notificactions.
// before do that, please must be sure the IOMMU was enabled and default iommu group was created during bootup.
/*
* #1:echo vfio-pci > /sys/bus/pci/devices/0000:02:00.0/driver_override
* #2:echo "10de 1d13" > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/vfio-pci/new_id
* #3:echo -n 0000:02:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/$old_driver_name/unbind
* #4:echo -n 0000:02:00.0 > /sys/bus/pci/drivers/vfio-pci/bind
*
*root@zlcao-RedmiBook-14:~# ls -l /dev/vfio/
*总用量 0
*crw------- 1 root root 243, 0 11月 8 12:40 12
*crw-rw-rw- 1 root root 10, 196 11月 8 12:31 vfio
*/
// container: 在不同的IOMMU GROUP之间共享 TLB和 PAGE TABLES,是一个IOMMU GROUP的集合.
// 多个IOMMU GROUP的设备共享同一个 IOMMU DOMAIN。
// iommu doamin:可以理解为一段地址空间的抽象。
int main(void)
{
int container, group, device, i;
void *maddr = NULL;
struct vfio_group_status group_status = { .argsz = sizeof(group_status) };
struct vfio_iommu_type1_info *iommu_info = NULL;
size_t iommu_info_size = sizeof(*iommu_info);
struct vfio_device_info device_info = { .argsz = sizeof(device_info) };
struct vfio_iommu_type1_dma_map dma_map;
struct vfio_iommu_type1_dma_unmap dma_unmap;
container = open("/dev/vfio/vfio", O_RDWR);
if (container < 0) {
printf("%s line %d, open vfio container error.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
if (ioctl(container, VFIO_GET_API_VERSION) != VFIO_API_VERSION) {
printf("%s line %d, vfio api version check failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
if (ioctl(container, VFIO_CHECK_EXTENSION, VFIO_TYPE1_IOMMU) == 0) {
printf("%s line %d, vfio check extensin failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
group = open("/dev/vfio/13", O_RDWR);
if (group < 0) {
printf("%s line %d, open vfio group error.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
if (ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_GET_STATUS, &group_status)) {
printf("%s line %d, failed to get vfio group status.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
// to judge whether all the device belongs to this group are detached with driver.
if ((group_status.flags & VFIO_GROUP_FLAGS_VIABLE) == 0) {
printf("%s line %d, vfio group is not viable.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
if (ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_SET_CONTAINER, &container)) {
printf("%s line %d, vfio group set conatiner failure.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
if (ioctl(container, VFIO_SET_IOMMU, VFIO_TYPE1_IOMMU) != 0) {
printf("%s line %d, vfio set type1 mode failure %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
iommu_info = malloc(iommu_info_size);
if (iommu_info == NULL) {
printf("%s line %d, vfio alloc iommu info failure %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
memset(iommu_info, 0x00, iommu_info_size);
iommu_info->argsz = iommu_info_size;
if (ioctl(container, VFIO_IOMMU_GET_INFO, iommu_info)) {
printf("%s line %d, vfio failed to get iomu info, %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, strerror(errno));
return 0;
}
// todo
// collect available iova regions from VFIO_IOMMU_GET_INFO.
// get device fd on this group, 0000:02:00.0 must in this group.
// device = ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_GET_DEVICE_FD, "0000:02:00.0");
device = ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_GET_DEVICE_FD, "f422fd86-35c0-11ef-8e50-9342c1138a56");
if (device < 0) {
printf("%s line %d, get vfio group device error.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_RESET);
if (ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_INFO, &device_info)) {
printf("%s line %d, get vfio group device info error.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
{
struct vfio_region_info region = {
.index = VFIO_PCI_CONFIG_REGION_INDEX,
.argsz = sizeof(struct vfio_region_info),
};
if (ioctl(device, VFIO_DEVICE_GET_REGION_INFO, ®ion)) {
printf("%s line %d, get vfio group device region info error.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return 0;
}
}
maddr = mmap((void *)VADDR, IOVA_DMA_MAPSZ, PROT_READ | PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED | MAP_ANONYMOUS | MAP_FIXED, -1, 0);
if (maddr == MAP_FAILED) {
printf("%s line %d, faild to map buffer, error %s.\n", __func__, __LINE__, strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
memset(maddr, 0x5a, IOVA_DMA_MAPSZ);
memset(&dma_map, 0x00, sizeof(dma_map));
dma_map.argsz = sizeof(dma_map);
dma_map.flags = VFIO_DMA_MAP_FLAG_READ | VFIO_DMA_MAP_FLAG_WRITE;
dma_map.iova = IOVA_START;
dma_map.vaddr = (unsigned long)maddr;
dma_map.size = IOVA_DMA_MAPSZ;
if (ioctl(container, VFIO_IOMMU_MAP_DMA, &dma_map)) {
printf("%s line %d, faild to do dma map on this conatainer.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
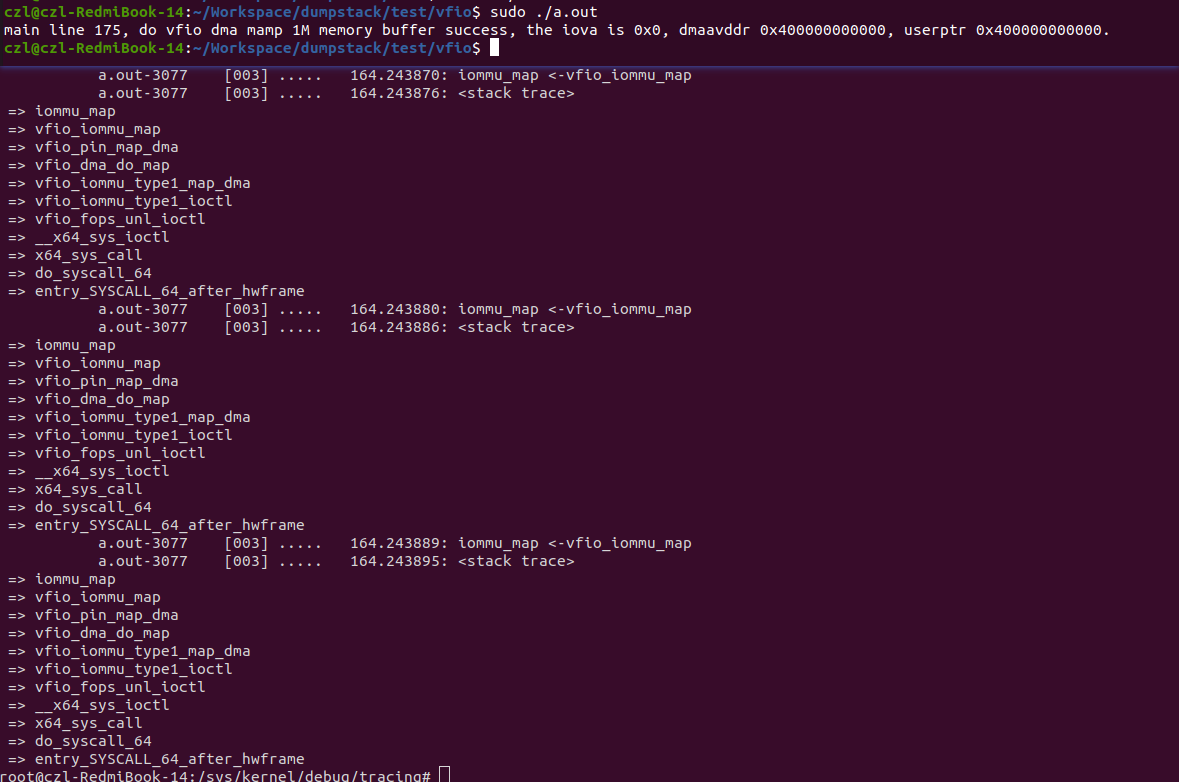
printf("%s line %d, do vfio dma mamp 1M memory buffer success, the iova is 0x%llx, dmaavddr 0x%llx, userptr %p.\n",
__func__, __LINE__, dma_map.iova, dma_map.vaddr, maddr);
#if 0
while (1)
sleep(1);
#endif
memset(&dma_unmap, 0x00, sizeof(dma_unmap));
dma_unmap.argsz = sizeof(dma_unmap);
dma_unmap.iova = IOVA_START;
dma_unmap.size = IOVA_DMA_MAPSZ;
if (ioctl(container, VFIO_IOMMU_UNMAP_DMA, &dma_unmap)) {
printf("%s line %d, faild to do dma unmap on this conatainer.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
return -1;
}
#if 0
while(1) {
printf("%s line %d.\n", __func__, __LINE__);
sleep(1);
}
#endif
munmap((void *)maddr, IOVA_DMA_MAPSZ);
ioctl(group, VFIO_GROUP_UNSET_CONTAINER, &container);
close(device);
close(group);
close(container);
free(iommu_info);
return 0;
}
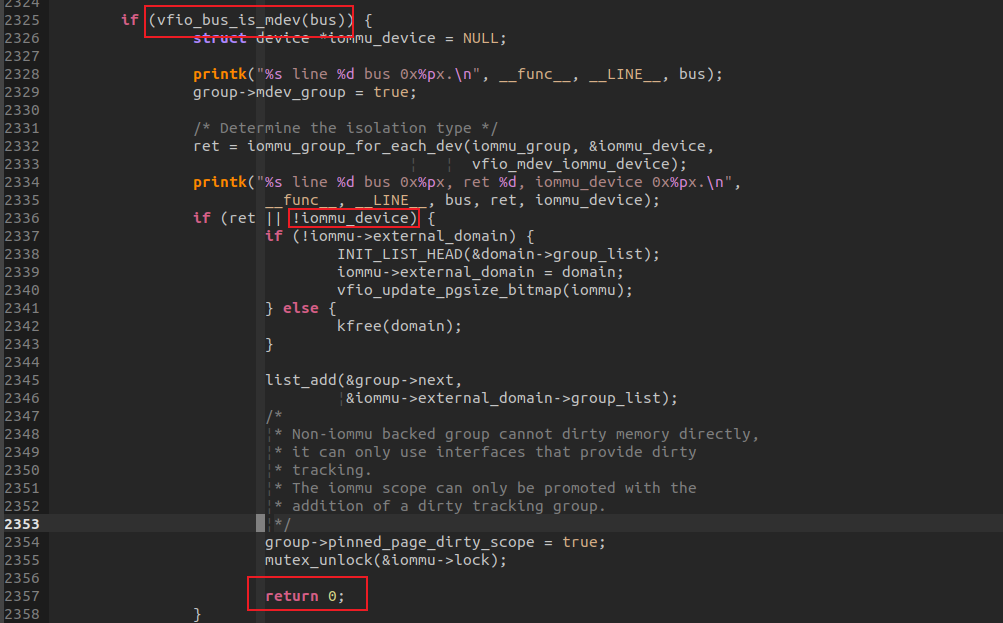
而对于纯粹内存模拟的设备来说,因为没有调用mdev_set_iommu_device函数设置MDEV设备的IOMMU DEVICE,导致在如下逻辑中,iommu_device设备为空,最后进入return 0.没有创建IOMMU DOMAIN并且注册进vfio_iommu的domain_list,导致后面即便调用DMA MAP,也没有IOMMU DOMAIN去做实际的DMA MAP。
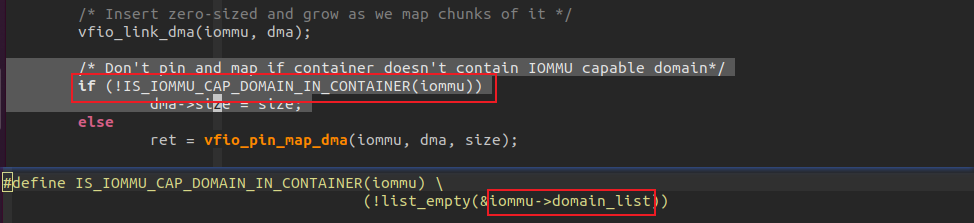
那调用mdev_set_iommu_device不就好了? 也不行,即便避免了进入1区提前退出,但是模拟的设备没有挂到BUS上,导致设备BUS为空,在调用iommu_domain_alloc时,会因为BUS为空返回错误。同样不可以。所以,调用mdev_set_iommu_device设置的IOMMU DEVICE设备一定要是关联到某条BUS上,具备DMA MAP能力的设备,MDEV设备会借用它的DMA MAP能力。
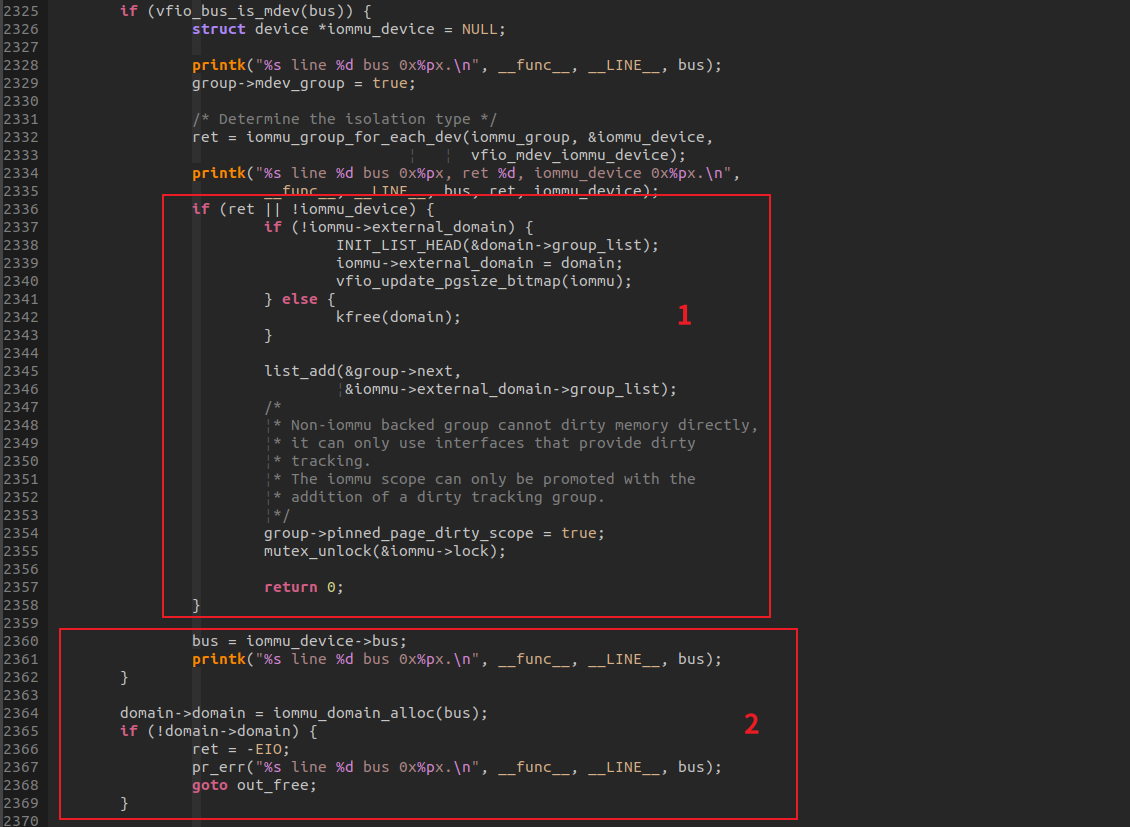
所以,模拟设备是没有IOMMU DOMAIN关联的,不能设置为IOMMU DEVICE, 只有以PCIE等实体设备作为PARENT的MDEV设备,或者强制设置某个具有DMA映射能力的设备为MDEV设备的IOMMU DEVICE, MDEV设备才具有DMA访问的能力。
vfio mdev框架核心操作函数集
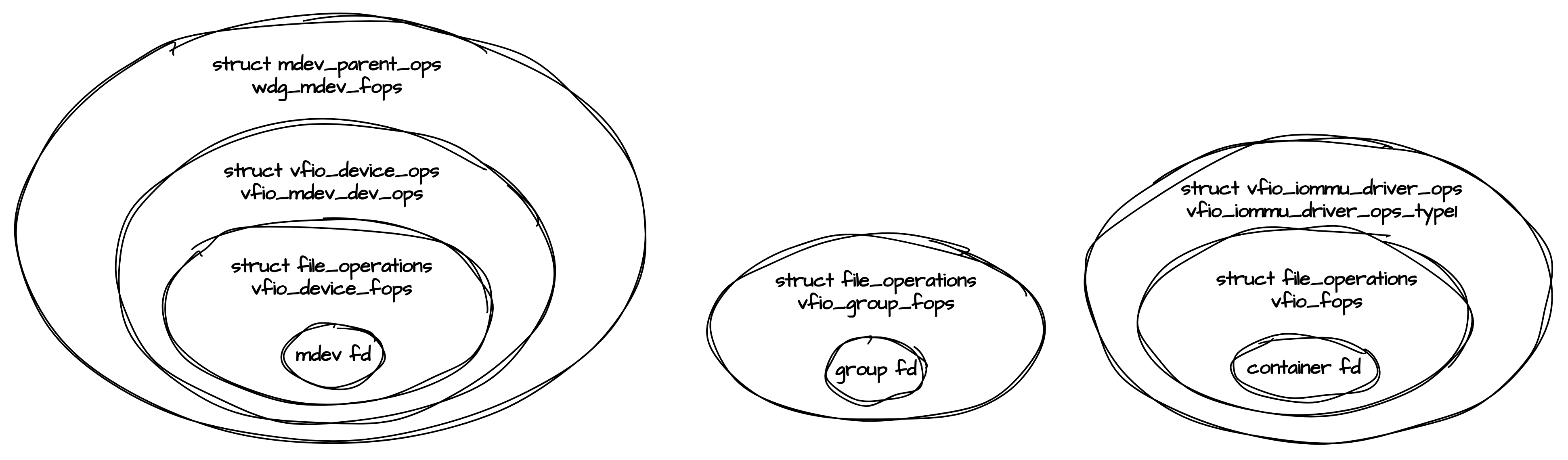
mdev driver的演进
本实验在5.4内核和5.15内核上,5.4内核mdev_bus没有实现match函数,所以整个系统只挂载vfio_mdev一套struct mdev_driver,来匹配所有的设备,用户不需要注册自己的struct mdev_driver。
到了5.15内核,mdev_bus实现了match函数,但是固定返回0,所以必须进行MDEV驱动和设备的显示匹配(device_driver_attach(&drv->driver, &mdev->dev);这个绑定在调用mdev_register_device注册父设备时,隐含在./create sysfs文件节点中,echo "uuid" > create时从节点中获取struct mdev_driver进行显示绑定。vfio_mdev 驱动仍然存在,但是已经有被架空的趋势了,MDEV设备使用驱动模块自己注册的struct mdev_driver(通过mdev_register_driver)。vfio_mdev只有在用户没有定义自己的struct mdev_driver时,作为fallback方案发挥作用:
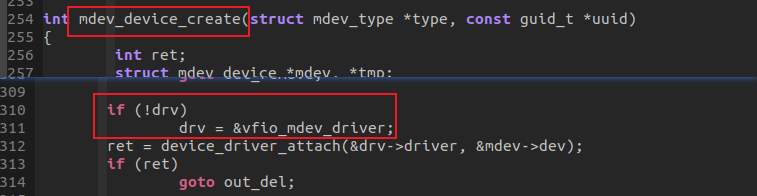
到了6.18内核,vfio_mdev 驱动从内核中被彻底删除,vfio_mdev.ko也不见了,MDEV用户必须要自己注册struct mdev_driver驱动。
前面提到,5.15内核,可以FALLBACK使用vfio_mdev驱动MDEV设备,最新的WDG实现打开
USE_LINUX_VFIO_MDEV宏,就可以利用MDEV,而非struct mdev_driver wdg_mdev_driver驱动运行整个测试,下图是使用vfio_mdev驱动MDE设备的SYSFS结构,可以看到两个MDEV设备使用了VFIO_MDEV驱动,并且mdev bus下只有这个一个struct mdev_driver,没有其他mdev_driver。

可以对比使用struct mdev_driver wdg_mdev_driver时SYSFS的结构,可以看出明显区别:
自编译内核,PASS THROUGH MDEV设备命令:
qemu-system-x86_64 -m 4096 -smp 4 --enable-kvm -kernel arch/x86/boot/bzImage -append "rdinit=/linuxrc loglevel=8" -device pcie-root-port,id=rp1,slot=1 -device pcie-pci-bridge,id=br1,bus=rp1 -device vfio-pci,sysfsdev=/sys/bus/mdev/devices/f422fd86-35c0-11ef-8e50-9342c1138a56,bus=br1,addr=1 -device vfio-pci,sysfsdev=/sys/bus/mdev/devices/c04de378-35d8-11ef-95c3-339660dfc874,bus=br1,addr=2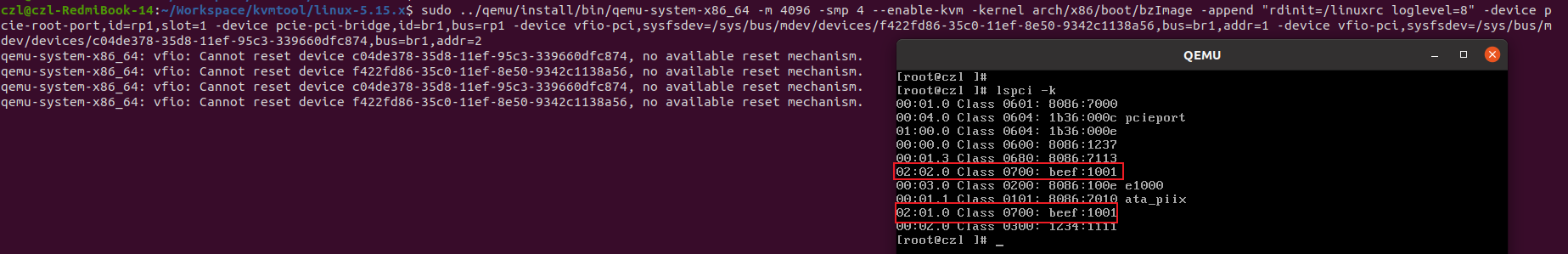
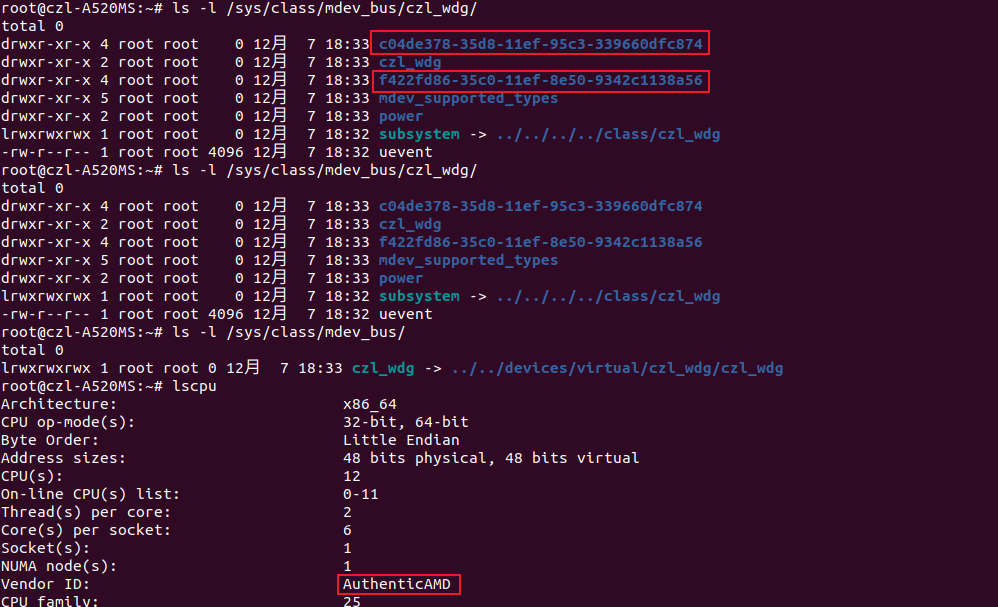
MDEV DEV on AMD
总结:
mdev受控直通体现了架构设计中的控制平面和数据平面分离的思想,平面可以理解为动作发生的地方,也就是让控制信号和数据流动发生在不同的地方,通过mdev设备虚拟化,让访问配置空间,MMIO寄存器这种低带宽配置面操作走trap-and-emulation路径,这是控制路径,而让设备存储访问(比如网络内存,GPU数据存储)以IOMMU DMA MAP的方式直通进行,控制和数据两个方向正交,彼此可以独立变化互不影响,同时兼顾了划分灵活性和访问性能

以RDMA实现为例,RDMA分为用户态ibv_xxx驱动和内核态ib_xxx驱动,提高数据传输性能,RDMA数据流被称为快路径(BYPASS 内核)而控制流为慢路径(需要经过/dev/infinitband/uverbsX设备节点的系统调用访问).

至于把数据通路和控制通路分开的原因,可以这样理解,一般和控制有关的操作所需的权限较高,所以需要进入内核态处理(会议室小圈子决策),消耗的时间较长,不过实际进行的操作次数有限(决策完后就不需要再开会了),属于低频且耗时的操作,而数据首发相关的操作所需要的权限较低,直接在用户态处理(工厂,车间处理),这样不用每个操作都需要开会决策,并且程序运行的大部分时间里面,执行的都是这种高频操作(生产操作)。
参考文档
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/665433040
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/677290147
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/681103883
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/683020073
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/13547099456
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/714893750
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/18631008327
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/7533614103
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/c_1704793480654675968




























 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










