万万没想到,最后还是入了算法的坑,虽然学的是工科,但数学能力和正经数学,信息学相关专业毕业的同学没法比,充其量算是半个爱好者,但是逐渐愿意投入时间思考这方面的问题,对于一个年近不惑的中年人来说,不知道是幸还是不幸。
发牢骚不是我的性格,我喜欢说干就干的人和事,不用考虑太多,其实半路出家也有好处,就是有些时候人在不知深浅的情况下,达到的程度可能比受过系统的训练的情况下还要深刻,可能这就是所谓的无知者无畏吧。聊以自勉~~
今天扫盲的是KL散度算法,在神经网络前向传递的过程中,KL散度算法用来评估各层量化前后的信息损失。
下面一段文字来自于网文摘抄,觉得不错,至少感觉假以时日,自己可以理解,权且贴在这里:
K-L散度,全称是Kullback-Leibler Divergence,是一种量化两种概率分布P和Q之间差异的方式,又叫相对熵。K-L散度能帮助我们度量使用一个分布来近似另一个分布时所损失的信息量。
信息熵
1948年,香农提出了“信息熵”的概念,解决了对信息的量化度量问题。信息熵这个词是C.E.Shannon(香农)从热力学中借用过来的。热力学中的热熵是表示分子状态混乱程度的物理量。香农用信息熵的概念来描述信源的不确定度 .
通常,一个信源发送出什么符号是不确定的,衡量它可以根据其出现的概率来度量。概率大,出现机会多,不确定性小;反之不确定性就大。
设函数f(p)是概率p的不确定性函数,函数f需满足两个条件:
1.函数f(p)是概率p的减函数,也就是事件发生的概率越大,f(p)越小.
2.两个独立符号所产生的不确定性应等于各自不确定性之和.也就是
对数函数恰好满足这两个条件,所以定义:
图形表示就是:
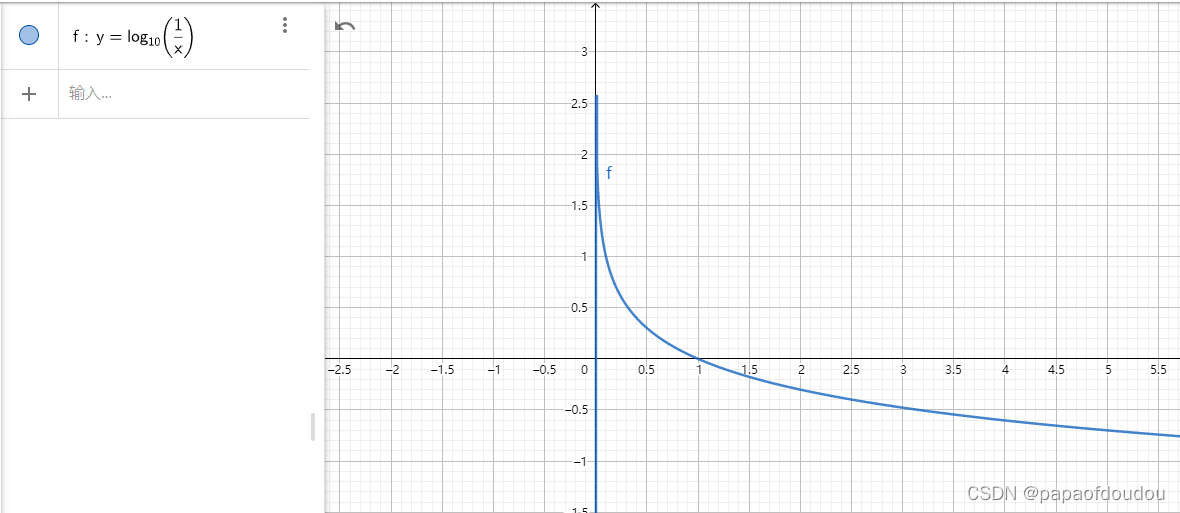
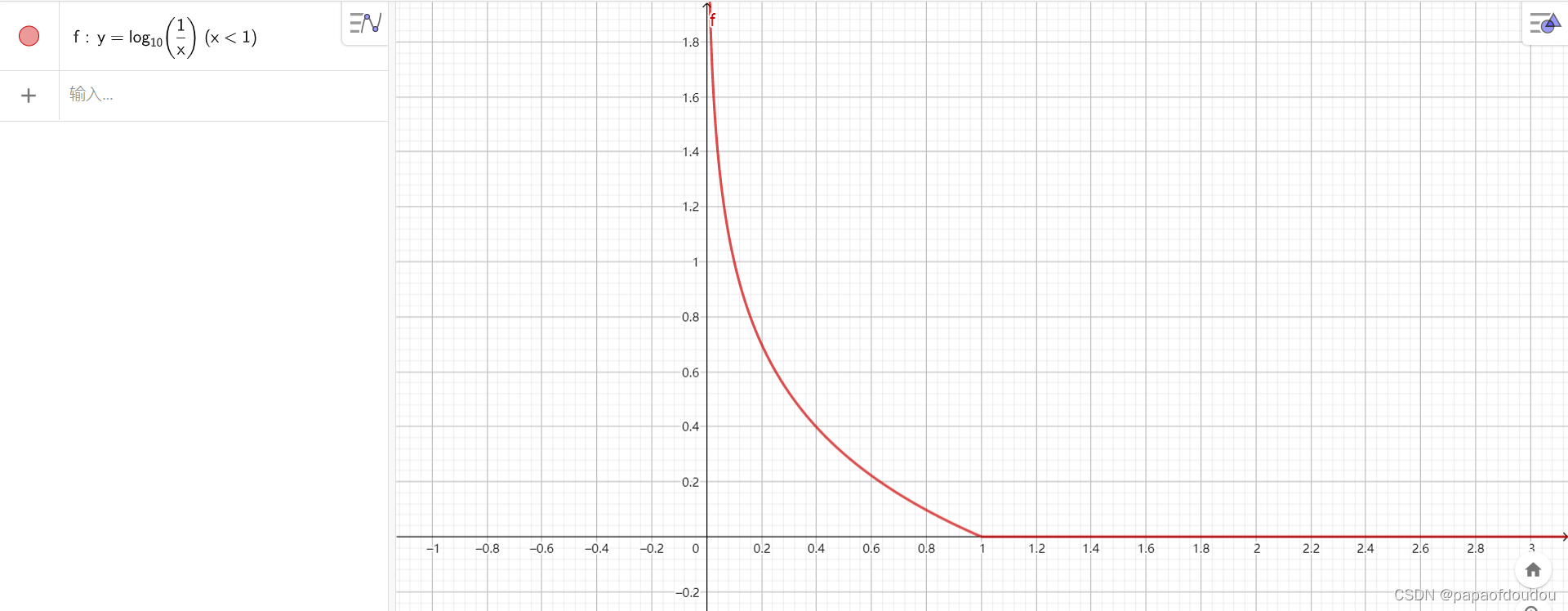
假设某个信源由N种可能的取值,且彼此互相独立,则该信源的不确定性可由下式度量(式中的底数一般取2):
恰好是不确定性的数学期望。
相对熵
信源的真实概率分布为p,近似概率分布q(可以视为由观测数据得到的概率分布)。
就反映了近似概率分布和真实概率分布之间差值的不确定性。按照信息熵的定义,对于信源的N种可能,信源近似概率分布和真实概率分布之前的距离(即:信息损失)可以由下式度量:
如何使用
KL散度的作用主要体现在量化阶段,获取zero point和scale factor上,用来衡量量化前后信息的损失程度,看一篇Nvidia的文章,顺带向人家学学如何做不吹牛逼的PPT:

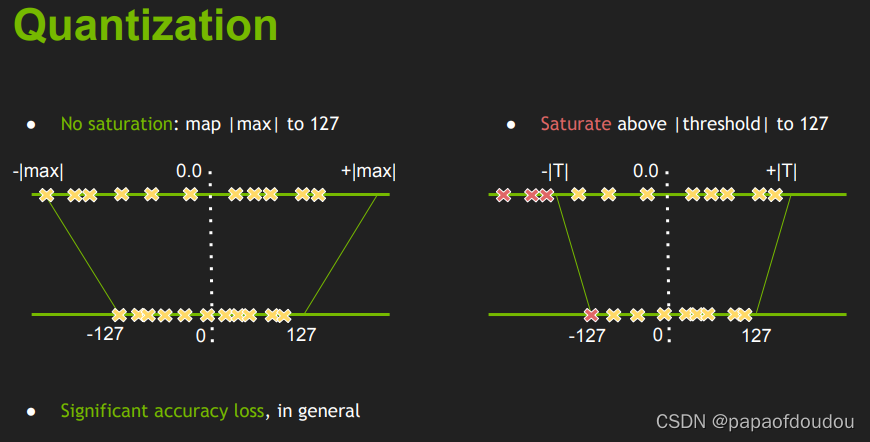
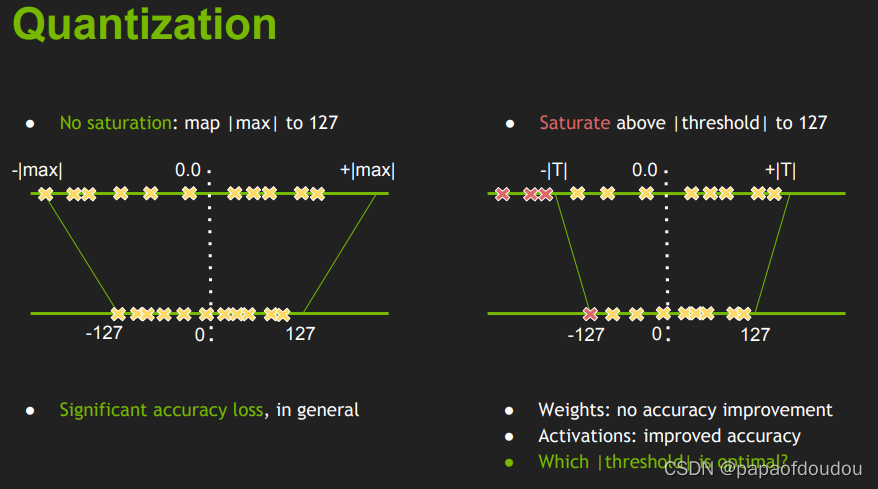
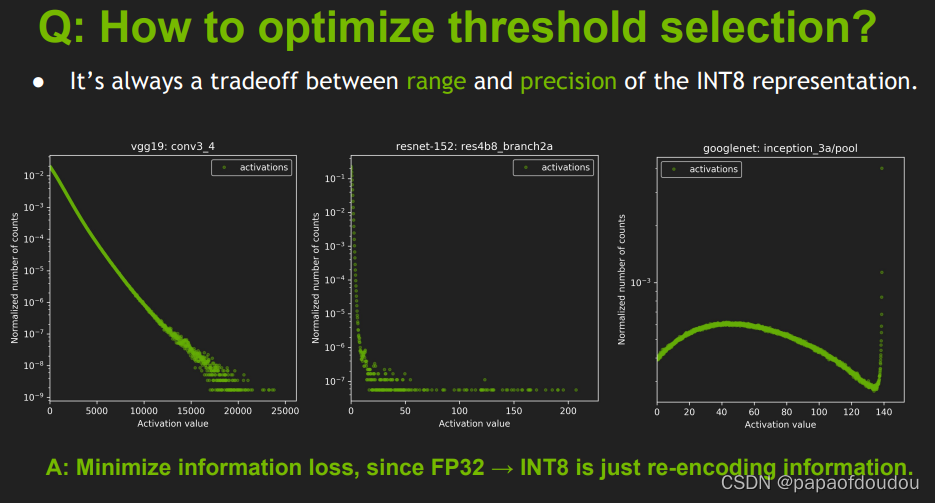


可见,它分为了两种情况,饱和与不饱和不饱和, 我们可以将它全部映射到int8的精度上,但是过饱和时就需要设置阈值(saturate).
那我们如何去优化阈值的选择呢?
最小化信息丢失,因为float32~int8只是重新编码信息。我们选择阈值时应尽量保证信息少丢失就行。下图是几种随着阈值变化而归一化数据指数变化的趋势(针对不同的模型,不同的layer,这个指数是不一样的)
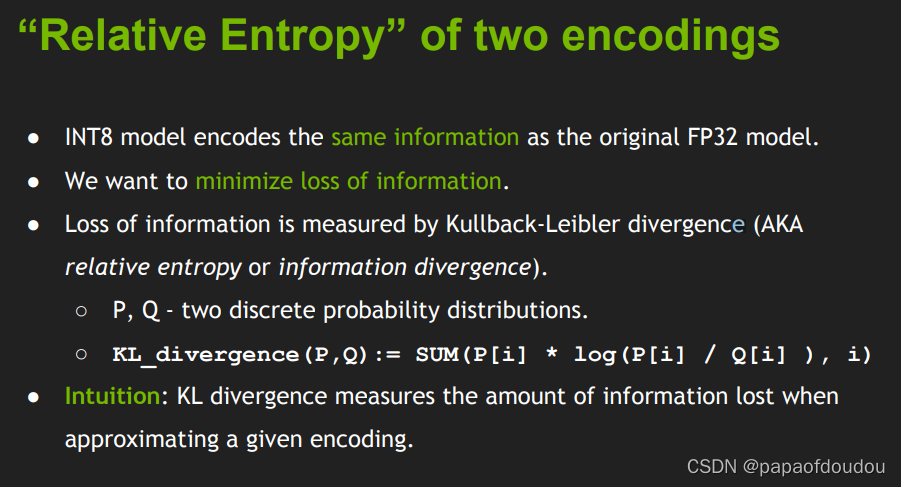
我们用两种编码的相对熵来表示这个映射过程的好坏。
信息损失由Kullback-Leibler divergence (AKA relative entropy or information divergence)来衡量
- P, Q -两个离散概率分布
- KL_divergence(P,Q):= SUM(P[i] * log(P[i] / Q[i] ), i)
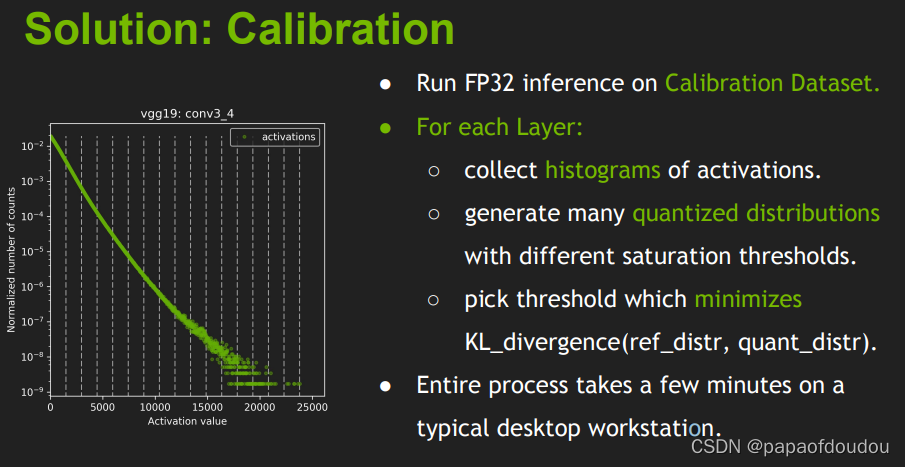
KL_divergence(P,Q)是判断映射的好坏,但如何进行映射呢,这里使用的是一个Calibration(校准器)或者说一个calibration dataset(矫正数据集)
过程如下:
在校准数据集上运行FP32推断。
对每一层
- 收集激活的直方图。
- 基于不同的饱和度阈值,生成多个量化分布
- 取最小阈值的量化
其实上面说起来基本思路是首先构建一种FP32数据向INT8数据的映射关系,该映射中的边界并不是两种数据类型的最大值,而是将FP32设置成一个Threshold,将这个阈值与INT8的最大值(127)构建映射关系,具体实现形式是通过一个scale来进行对应。
首先的问题是,这种映射关系的阈值如何寻找呢?不同的网路显然这一阈值是不同的,因此我们需要一个矫正数据集(calibration dataset)来进行scale的选取,其选择的标准为最小化KL_divergence(: KL_divergence(P,Q):= SUM(P[i] * log(P[i] / Q[i] ), i)).
费了半天劲,难道KL算法的目的,就是为了找到一个合适的threshold?
口说无凭,程序为证,我们分别用Python和C对KL散度进行实现:
Python实现:
import numpy as np
# 随机生成两个离散型分布
x = [np.random.uniform(1, 11) for i in range(10)]
px = x / np.sum(x)
# golden distribution
y = [np.random.uniform(1, 11) for i in range(10)]
py = y / np.sum(y)
print (px)
print (py)
KL = 0.0
# 计算KL散度
for i in range(10):
KL += px[i] * np.log(px[i] / py[i])
print(KL)
KL = 0.0
# 计算KL散度
for i in range(10):
KL += py[i] * np.log(py[i] / px[i])
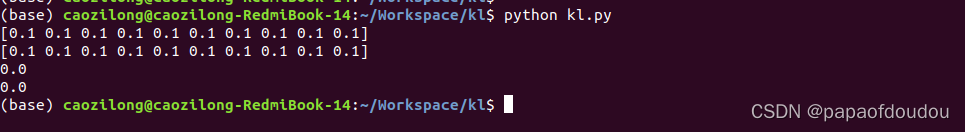
print(KL)运行结果:
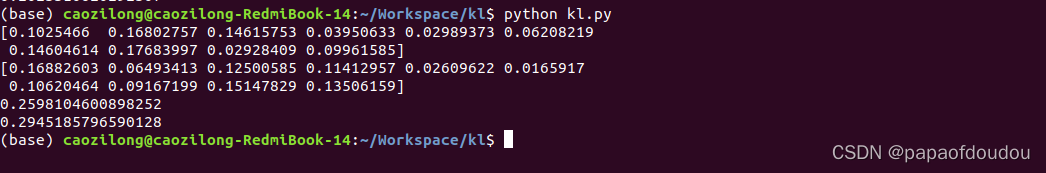
可以看到,KL散度不具备对称性,也就是说,P相对于Q的信息损失并不等于Q相对于P的信息损失。
如果PX和PY的分布相同,则按照定义,他们的信息损失应该是0,距离是0,我们看看是不是:
import numpy as np
# 随机生成两个离散型分布
x = [np.random.uniform(1, 1) for i in range(10)]
px = x / np.sum(x)
# golden distribution
y = [np.random.uniform(1, 1) for i in range(10)]
py = y / np.sum(y)
print (px)
print (py)
KL = 0.0
# 计算KL散度
for i in range(10):
KL += px[i] * np.log(px[i] / py[i])
print(KL)
KL = 0.0
# 计算KL散度
for i in range(10):
KL += py[i] * np.log(py[i] / px[i])
print(KL)输出不出所料:
C语言实现:
我们以之前计算余弦相似度的代码作为母板,添加上KL散度算法的实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define DBG(fmt, ...) do { printf("%s line %d, "fmt"\n", __func__, __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__); } while (0)
static void dump_memory(uint8_t *buf, int32_t len)
{
int i;
printf("\n\rdump file memory:");
for (i = 0; i < len; i ++)
{
if ((i % 16) == 0)
{
printf("\n\r%p: ", buf + i);
}
printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n\r");
return;
}
int get_tensor_from_txt_file(char *file_path, float **buf)
{
int len = 0;
static float *memory = NULL;
static int max_len = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
FILE *fp = NULL;
if(memory == NULL)
{
memory = (float*) malloc(max_len * sizeof(float));
}
if((fp = fopen(file_path, "r")) == NULL)
{
DBG("open tensor error.");
exit(-1);
}
while(!feof(fp))
{
fscanf(fp, "%f", &memory[len ++]);
}
*buf = (float*)malloc(len * sizeof(float));
if(len == 0 || *buf == NULL)
{
DBG("read tensor error, len %d, *buf %p", len, *buf);
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(*buf, memory, len * sizeof(float));
fclose(fp);
return len;
}
float calculate_ojilide(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float sum = 0.00;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
float square = (data0[i]-data1[i]) * (data0[i]-data1[i]);
sum += square;
}
return sqrt(sum);
}
float yuxianxiangsidu(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float fenzi = 0.00;
float fenmu = 0.00;
float len_vec0 = 0.00;
float len_vec1 = 0.00;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
fenzi += data0[i]*data1[i];
len_vec0 += data0[i]*data0[i];
len_vec1 += data1[i]*data1[i];
}
len_vec0 = sqrt(len_vec0);
len_vec1 = sqrt(len_vec1);
fenmu = len_vec0 * len_vec1;
return fenzi/fenmu;
}
float manhadun_distance(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float distance = 0.000;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
distance += abs(data0[i]-data1[i]);
}
return distance;
}
float qiebixuefu_distance(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float distance = 0.000;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
if (distance < abs(data0[i]-data1[i]))
{
distance = abs(data0[i]-data1[i]);
}
}
return distance;
}
float calculate_kl_diverage(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
float kl;
float sumpx, sumpy;
int i;
float *px=(float *)malloc(tensor_len * sizeof(float));
float *py=(float *)malloc(tensor_len * sizeof(float));
if(px == NULL || py == NULL)
{
DBG("fatal error, malloc px or py buffer failure.");
exit(-1);
}
memset(px, 0x00, tensor_len * sizeof(float));
memset(py, 0x00, tensor_len * sizeof(float));
sumpx = sumpy = 0.00f;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
sumpx += data0[i];
sumpy += data1[i];
}
//DBG("px %f, py %f", sumpx, sumpy);
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
px[i] = data0[i]/sumpx;
py[i] = data1[i]/sumpy;
}
kl = 0.00f;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
if(py[i] != 0.00f && px[i]/py[i] > 0.00f)
kl += px[i]*(log(px[i]/py[i])/log(2));
}
return kl;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *file;
DBG("in");
if(argc != 3)
{
DBG("input error, you should use this program like that: program tensor0 tensor1.");
exit(-1);
}
int tensor0_len, tensor1_len;
float *tensor0_dat, *tensor1_dat;
tensor0_len = tensor1_len = 0;
tensor0_dat = tensor1_dat = NULL;
tensor0_len = get_tensor_from_txt_file(argv[1], &tensor0_dat);
tensor1_len = get_tensor_from_txt_file(argv[2], &tensor1_dat);
if(tensor0_len != tensor1_len)
{
DBG("%d:%d the two tensor are mismatch on dimisons, caculate cant continue!", tensor0_len, tensor1_len);
exit(-1);
}
float sum = calculate_ojilide(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("oujilide sum = %f", sum);
float similar = yuxianxiangsidu(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("cosin similar is = %f", similar);
float manhadun = manhadun_distance(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("manhadun distance is = %f", manhadun);
float qiebixuefu = qiebixuefu_distance(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("qiebixuefu distance is = %f", qiebixuefu);
float kl = calculate_kl_diverage(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("kl diverage distance is = %f", kl);
DBG("out");
return 0;
}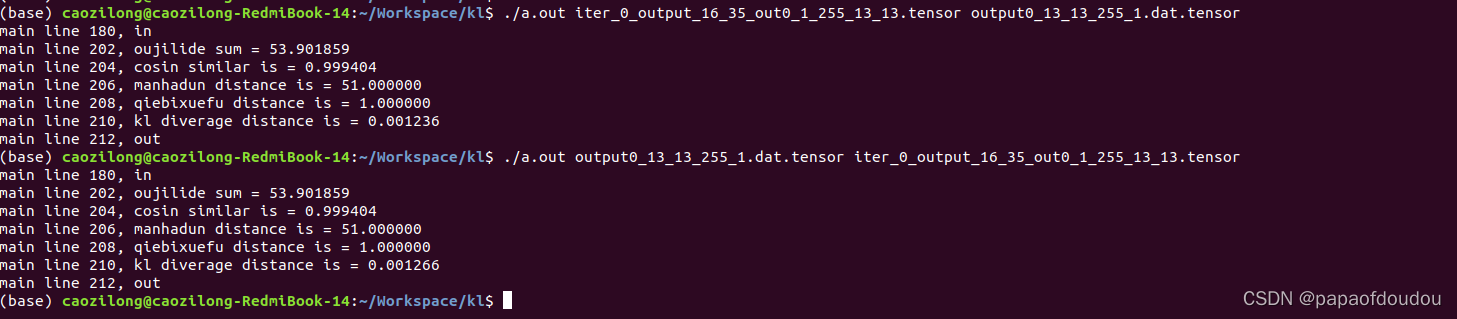
对于相同的tensor,他们的kl-diverage为0

这里有个问题,tensor数值能当权重用去计算概率么? 暂无思路,日后再说吧~!
针对这个问题,应该可以把,前面python代码不是直接把数据当作比重去计算概率了么?这里的kl-diverage很小,说明两个tensor的损失很小吧。并且也验证了交换两个tensor, kl diverage计算结果不相同,说明KL计算公式不是对称的。
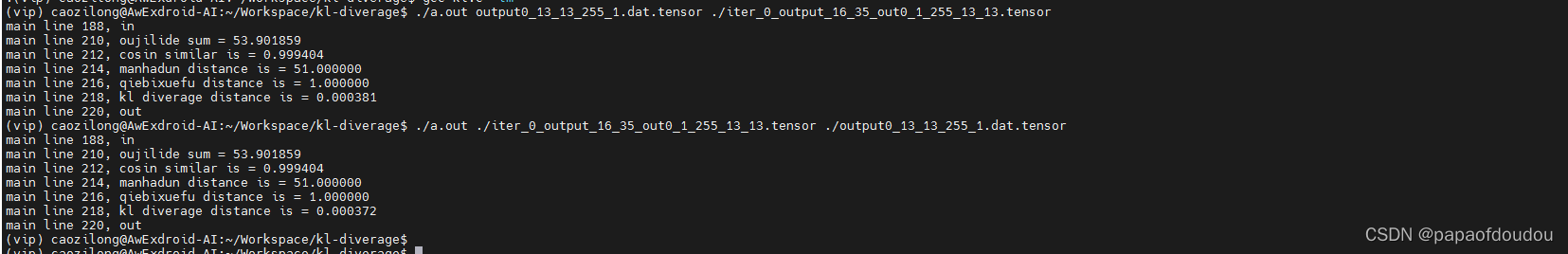
并且,KL算法是以10为地的对数,修改程序如下:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define DBG(fmt, ...) do { printf("%s line %d, "fmt"\n", __func__, __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__); } while (0)
static void dump_memory(uint8_t *buf, int32_t len)
{
int i;
printf("\n\rdump file memory:");
for (i = 0; i < len; i ++)
{
if ((i % 16) == 0)
{
printf("\n\r%p: ", buf + i);
}
printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n\r");
return;
}
int get_tensor_from_txt_file(char *file_path, float **buf)
{
int len = 0;
static float *memory = NULL;
static int max_len = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
FILE *fp = NULL;
if(memory == NULL)
{
memory = (float*) malloc(max_len * sizeof(float));
}
if((fp = fopen(file_path, "r")) == NULL)
{
DBG("open tensor error.");
exit(-1);
}
while(!feof(fp))
{
fscanf(fp, "%f", &memory[len ++]);
}
*buf = (float*)malloc(len * sizeof(float));
if(len == 0 || *buf == NULL)
{
DBG("read tensor error, len %d, *buf %p", len, *buf);
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(*buf, memory, len * sizeof(float));
fclose(fp);
return len;
}
float calculate_ojilide(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float sum = 0.00;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
float square = (data0[i]-data1[i]) * (data0[i]-data1[i]);
sum += square;
}
return sqrt(sum);
}
float yuxianxiangsidu(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float fenzi = 0.00;
float fenmu = 0.00;
float len_vec0 = 0.00;
float len_vec1 = 0.00;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
fenzi += data0[i]*data1[i];
len_vec0 += data0[i]*data0[i];
len_vec1 += data1[i]*data1[i];
}
len_vec0 = sqrt(len_vec0);
len_vec1 = sqrt(len_vec1);
fenmu = len_vec0 * len_vec1;
return fenzi/fenmu;
}
float manhadun_distance(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float distance = 0.000;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
distance += abs(data0[i]-data1[i]);
}
return distance;
}
float qiebixuefu_distance(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float distance = 0.000;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
if (distance < abs(data0[i]-data1[i]))
{
distance = abs(data0[i]-data1[i]);
}
}
return distance;
}
float calculate_kl_diverage(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
float kl;
float sumpx, sumpy;
int i;
float *px=(float *)malloc(tensor_len * sizeof(float));
float *py=(float *)malloc(tensor_len * sizeof(float));
if(px == NULL || py == NULL)
{
DBG("fatal error, malloc px or py buffer failure.");
exit(-1);
}
memset(px, 0x00, tensor_len * sizeof(float));
memset(py, 0x00, tensor_len * sizeof(float));
sumpx = sumpy = 0.00f;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
sumpx += data0[i];
sumpy += data1[i];
}
//DBG("px %f, py %f", sumpx, sumpy);
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
px[i] = data0[i]/sumpx;
py[i] = data1[i]/sumpy;
}
kl = 0.00f;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
if(py[i] == 0.00f)
continue;
if((px[i]/py[i]) == 0.00f)
continue;
if((px[i]/py[i]) < 0.00f)
continue;
kl += px[i]*(log10(px[i]/py[i]));
}
return kl;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *file;
DBG("in");
if(argc != 3)
{
DBG("input error, you should use this program like that: program tensor0 tensor1.");
exit(-1);
}
int tensor0_len, tensor1_len;
float *tensor0_dat, *tensor1_dat;
tensor0_len = tensor1_len = 0;
tensor0_dat = tensor1_dat = NULL;
tensor0_len = get_tensor_from_txt_file(argv[1], &tensor0_dat);
tensor1_len = get_tensor_from_txt_file(argv[2], &tensor1_dat);
if(tensor0_len != tensor1_len)
{
DBG("%d:%d the two tensor are mismatch on dimisons, caculate cant continue!", tensor0_len, tensor1_len);
exit(-1);
}
float sum = calculate_ojilide(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("oujilide sum = %f", sum);
float similar = yuxianxiangsidu(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("cosin similar is = %f", similar);
float manhadun = manhadun_distance(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("manhadun distance is = %f", manhadun);
float qiebixuefu = qiebixuefu_distance(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("qiebixuefu distance is = %f", qiebixuefu);
float kl = calculate_kl_diverage(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("kl diverage distance is = %f", kl);
DBG("out");
return 0;
}
上面的程序实现中,概率直接来源于原的数值,虽然结果趋势是对的,但是正确的做法应该是根据直方图求解概率,如下面的实现:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#define DBG(fmt, ...) do { printf("%s line %d, "fmt"\n", __func__, __LINE__, ##__VA_ARGS__); } while (0)
static void dump_memory(uint8_t *buf, int32_t len)
{
int i;
printf("\n\rdump file memory:");
for (i = 0; i < len; i ++)
{
if ((i % 16) == 0)
{
printf("\n\r%p: ", buf + i);
}
printf("0x%02x ", buf[i]);
}
printf("\n\r");
return;
}
int get_tensor_from_txt_file(char *file_path, float **buf)
{
int len = 0;
static float *memory = NULL;
static int max_len = 10 * 1024 * 1024;
FILE *fp = NULL;
if(memory == NULL)
{
memory = (float*) malloc(max_len * sizeof(float));
}
if((fp = fopen(file_path, "r")) == NULL)
{
DBG("open tensor error.");
exit(-1);
}
while(!feof(fp))
{
fscanf(fp, "%f", &memory[len ++]);
}
*buf = (float*)malloc(len * sizeof(float));
if(len == 0 || *buf == NULL)
{
DBG("read tensor error, len %d, *buf %p", len, *buf);
exit(-1);
}
memcpy(*buf, memory, len * sizeof(float));
fclose(fp);
return len;
}
float calculate_ojilide(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float sum = 0.00;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
float square = (data0[i]-data1[i]) * (data0[i]-data1[i]);
sum += square;
}
return sqrt(sum);
}
float yuxianxiangsidu(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float fenzi = 0.00;
float fenmu = 0.00;
float len_vec0 = 0.00;
float len_vec1 = 0.00;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
fenzi += data0[i]*data1[i];
len_vec0 += data0[i]*data0[i];
len_vec1 += data1[i]*data1[i];
}
len_vec0 = sqrt(len_vec0);
len_vec1 = sqrt(len_vec1);
fenmu = len_vec0 * len_vec1;
return fenzi/fenmu;
}
float manhadun_distance(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float distance = 0.000;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
distance += abs(data0[i]-data1[i]);
}
return distance;
}
float qiebixuefu_distance(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
int i;
float distance = 0.000;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
if (distance < abs(data0[i]-data1[i]))
{
distance = abs(data0[i]-data1[i]);
}
}
return distance;
}
float calculate_kl_diverage(int tensor_len, float *data0, float *data1)
{
float kl;
float sumpx, sumpy;
int i;
float *px=(float *)malloc(tensor_len * sizeof(float));
float *py=(float *)malloc(tensor_len * sizeof(float));
if(px == NULL || py == NULL)
{
DBG("fatal error, malloc px or py buffer failure.");
exit(-1);
}
memset(px, 0x00, tensor_len * sizeof(float));
memset(py, 0x00, tensor_len * sizeof(float));
sumpx = sumpy = 0.00f;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
sumpx += data0[i];
sumpy += data1[i];
}
//DBG("px %f, py %f", sumpx, sumpy);
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
px[i] = data0[i]/sumpx;
py[i] = data1[i]/sumpy;
}
kl = 0.00f;
for(i = 0; i < tensor_len; i ++)
{
if(py[i] == 0.00f)
continue;
if((px[i]/py[i]) == 0.00f)
continue;
if((px[i]/py[i]) < 0.00f)
continue;
kl += px[i]*(log10(px[i]/py[i]));
/*printf("%s line %d, i = %d, kl = %f, p = %f\n", __func__, __LINE__, i, kl, px[i]/py[i]);*/
}
return kl;
}
#define max(a, b) ((a>b)? a:b)
#define min(a, b) ((a<b)? a:b)
static void compute_histogram(float *tensor, int len, unsigned int *histgram, int hislen)
{
int i = 0;
float absmax = 0.f;
for(i = 0; i < len; i ++)
{
absmax = max(absmax, tensor[i]);
}
for(i = 0; i < len; i ++)
{
const int index = min((int)(fabs(tensor[i])/absmax * hislen), hislen - 1);
histgram[index] += 1;
}
return;
}
static void compute_hist(unsigned int *histgram, int hislen, float *pres)
{
int i = 0;
unsigned int sum = 0;
for(i = 0; i < hislen; i ++)
{
sum += histgram[i];
}
for(i = 0; i < hislen; i ++)
{
pres[i] = (float)histgram[i] / (double)sum;
}
return ;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
FILE *file;
DBG("in");
if(argc != 3)
{
DBG("input error, you should use this program like that: program tensor0 tensor1.");
exit(-1);
}
int tensor0_len, tensor1_len;
float *tensor0_dat, *tensor1_dat;
tensor0_len = tensor1_len = 0;
tensor0_dat = tensor1_dat = NULL;
tensor0_len = get_tensor_from_txt_file(argv[1], &tensor0_dat);
tensor1_len = get_tensor_from_txt_file(argv[2], &tensor1_dat);
if(tensor0_len != tensor1_len)
{
DBG("%d:%d the two tensor are mismatch on dimisons, caculate cant continue!", tensor0_len, tensor1_len);
exit(-1);
}
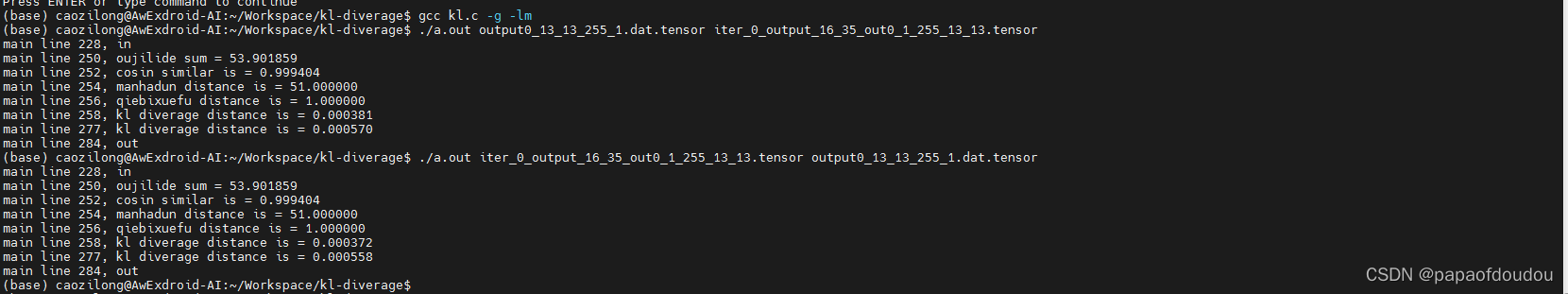
float sum = calculate_ojilide(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("oujilide sum = %f", sum);
float similar = yuxianxiangsidu(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("cosin similar is = %f", similar);
float manhadun = manhadun_distance(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("manhadun distance is = %f", manhadun);
float qiebixuefu = qiebixuefu_distance(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("qiebixuefu distance is = %f", qiebixuefu);
float kl = calculate_kl_diverage(tensor0_len, tensor0_dat, tensor1_dat);
DBG("kl diverage distance is = %f", kl);
unsigned int *pA=malloc(sizeof(unsigned int) * 2048);
unsigned int *pB=malloc(sizeof(unsigned int) * 2048);
memset(pA, 0x00, sizeof(unsigned int) * 2048);
memset(pB, 0x00, sizeof(unsigned int) * 2048);
compute_histogram(tensor0_dat, tensor0_len, pA, 2048);
compute_histogram(tensor1_dat, tensor1_len, pB, 2048);
float *presA=malloc(sizeof(float) * 2048);
float *presB=malloc(sizeof(float) * 2048);
memset(presA, 0x00, sizeof(float) * 2048);
memset(presB, 0x00, sizeof(float) * 2048);
compute_hist(pA, 2048, presA);
compute_hist(pB, 2048, presB);
kl = calculate_kl_diverage(2048, presA, presB);
DBG("kl diverage distance is = %f", kl);
free(presA);
free(presB);
free(pA);
free(pB);
DBG("out");
return 0;
}添加了两个函数,compute_xxxx,用来分别计算直方图和直方概率,运行结果如下:
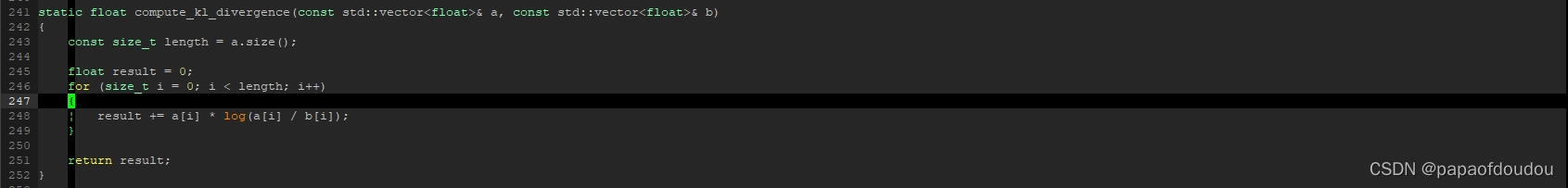
NCNN中KL-Diverage算法的实现:







 https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/tugouxp/article/details/122266262?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/tugouxp/article/details/122266262?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501

















 2506
2506

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










