通过前面的学习,我们了解了Babylon.js中Shader的很多用法,这里将前面的内容综合一下,编写一个稍微复杂一点儿的案例。
该Shader将能够使用漫反射颜色Diffuse Color和漫反射纹理Diffuse Texture,同时支持法线纹理并可以反射环境纹理,能够接受环境光照和一个平行光照射,能够产生高光效果。效果参考如下:
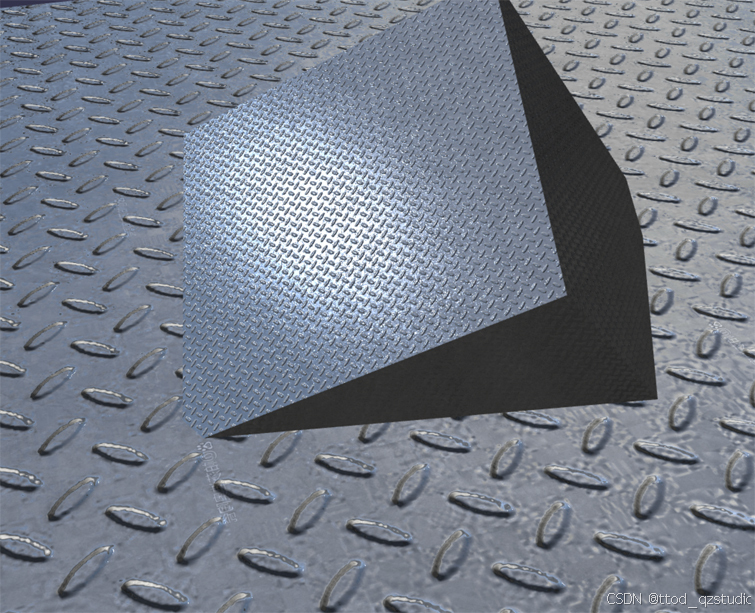
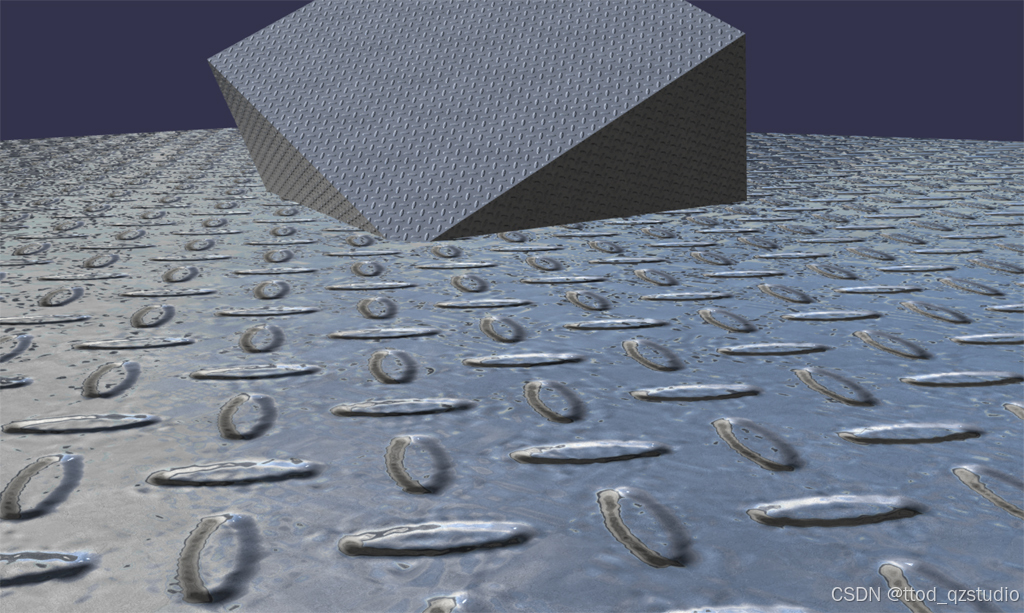
顶点着色器:
attribute vec3 position;
attribute vec3 normal;
attribute vec2 uv;
attribute vec3 tangent;
uniform mat4 world;
uniform mat4 worldViewProjection;
uniform vec3 cameraPosition;
varying vec3 vPositionW;
varying vec2 vUV;
varying mat3 vTBN;
void main() {
// 基础变换
vec4 worldPos = world * vec4(position, 1.0);
vPositionW = worldPos.xyz;
gl_Position = worldViewProjection * vec4(position, 1.0);
// 构建 TBN 矩阵(切线空间 -> 世界空间)
vec3 T = normalize((world * vec4(tangent, 0.0)).xyz);
vec3 N = normalize((world * vec4(normal, 0.0)).xyz);
vec3 B = cross(N, T);
vTBN = mat3(T, B, N);
vUV = uv;
}这部分内容不做解释,如果看不太明白可以参考基于Babylon.js的Shader入门之五:让Shader支持法线贴图这篇博客的顶点着色器的讲解内容,总体内容差不多。
片元着色器:
precision highp float;
// 贴图
uniform sampler2D diffuseTexture; // 漫反射贴图
uniform sampler2D normalTexture; // 法线贴图
uniform samplerCube environmentTexture; // 环境贴图
// 颜色参数
uniform vec3 diffuseColor; // 漫反射颜色
uniform float ambientIntensity; // 环境光强度
uniform vec3 ambientColor; // 环境光颜色
// 平行光参数
uniform vec3 lightDirection; // 平行光方向(世界空间)
uniform vec3 lightColor; // 平行光颜色
uniform float lightIntensity; // 平行光强度
// 高光参数
uniform float specularPower; // 高光范围(指数)
uniform float specularIntensity; // 高光强度
// 菲涅尔参数
uniform float fresnelPower; // 菲涅尔边缘强度
uniform float fresnelBias; // 菲涅尔基础值
// 其他
uniform vec3 cameraPosition; // 相机位置
uniform vec2 scaleDiffuseTex;
uniform vec2 scaleNormalTex;
varying vec3 vPositionW;
varying vec2 vUV;
varying mat3 vTBN;
void main() {
// 采样漫反射贴图并与颜色混合
vec2 uvDiffuse = vUV * scaleDiffuseTex;
vec4 diffuseTextureColor = texture2D(diffuseTexture, uvDiffuse);
vec3 baseColor = diffuseColor * diffuseTextureColor.rgb;
// 采样法线贴图并转换到世界空间
vec2 uvNormal = vUV * scaleNormalTex;
// vec2 uvNormal = vec2(3.0,3.0);
vec3 normalColor = texture2D(normalTexture, uvNormal).xyz * 2.0 - 1.0;
vec3 normalW = normalize(vTBN * normalColor);
// ================= 光照计算 =================
// 环境光
vec3 ambient = ambientColor * ambientIntensity * baseColor;
// 平行光漫反射
vec3 lightDir = normalize(-lightDirection);
float NdotL = max(dot(normalW, lightDir), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = lightColor * lightIntensity * NdotL * baseColor;
// 平行光高光(Blinn-Phong模型)
vec3 viewDir = normalize(cameraPosition - vPositionW);
vec3 halfDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
float specTerm = pow(max(dot(normalW, halfDir), 0.0), specularPower);
vec3 specular = lightColor * specularIntensity * specTerm;
// ================= 环境反射 =================
vec3 reflectDir = reflect(-viewDir, normalW);
vec3 reflectionColor = textureCube(environmentTexture, reflectDir).rgb;
// 菲涅尔混合
float fresnel = fresnelBias + (1.0 - fresnelBias) * pow(1.0 - max(dot(viewDir, normalW), 0.0), fresnelPower);
vec3 finalColor = mix(baseColor, reflectionColor, fresnel);
// ================= 最终合成 =================
finalColor = (ambient + diffuse + specular) * finalColor;
gl_FragColor = vec4(finalColor, 1.0);
}大部分内容在前面的博客中都讲解过,只有高光处理的部分前面没有涉及,这里单独说一下。高光计算的部分代码如下:
// 平行光高光(Blinn-Phong模型)
vec3 viewDir = normalize(cameraPosition - vPositionW);
vec3 halfDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
float specTerm = pow(max(dot(normalW, halfDir), 0.0), specularPower);
vec3 specular = lightColor * specularIntensity * specTerm;这四行代码是 Blinn-Phong 光照模型 中计算高光(镜面反射)的核心部分,用于模拟光线在物体表面的镜面反射效果。以下是逐行详细解释:
1. vec3 viewDir = normalize(cameraPosition - vPositionW);
作用
计算从表面点到相机的 视角方向(View Direction)。
cameraPosition:相机在世界空间中的位置(Uniform 变量)。vPositionW:当前片段(像素)在世界空间中的位置(从顶点着色器传递)。normalize(...):将方向向量归一化为单位长度(避免长度影响后续计算)。
物理意义
表示人眼(或相机)观察物体表面的方向,用于后续计算反射效果。
2. vec3 halfDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir);
作用
计算 半角向量(Halfway Vector),即光线方向与视角方向的中间向量。
lightDir:平行光的方向(已归一化,通常为normalize(-lightDirection))。viewDir:上一步计算的视角方向。normalize(...):确保半角向量是单位向量。
为什么需要半角向量?
Blinn-Phong 模型通过 半角向量与法线的夹角 计算高光,比传统的 Phong 模型(直接计算反射向量)更高效。
3. float specTerm = pow(max(dot(normalW, halfDir), 0.0), specularPower);
作用
计算高光强度项(Specular Term),决定高光的亮度和范围。
normalW:世界空间中的法线方向(来自法线贴图或顶点法线)。dot(normalW, halfDir):法线与半角向量的点积,表示它们的夹角余弦值(范围[-1, 1])。max(..., 0.0):将点积结果限制在[0, 1],避免负值影响。pow(..., specularPower)specularPower(高光指数)控制高光的集中程度。值越大,高光越锐利(如金属);值越小,高光越扩散(如塑料)。
数学意义
![]()
其中:
-
N 是法线,H 是半角向量。
4. vec3 specular = lightColor * specularIntensity * specTerm;
作用
合成最终的高光颜色。
lightColor:平行光的颜色(如vec3(1.0, 1.0, 1.0)表示白光)。specularIntensity:高光强度系数(Uniform 变量),用于艺术调节。specTerm:上一步计算的高光强度项。
物理意义
高光颜色 = 光源颜色 × 高光强度 × 高光衰减项。
- 当法线与半角向量对齐时(
dot(normalW, halfDir) ≈ 1),高光最亮。 - 当夹角增大时,高光强度按指数衰减。
完整流程图示
graph LR
A[相机位置] --> B[viewDir = normalize(cameraPosition - vPositionW)]
C[光源方向] --> D[halfDir = normalize(lightDir + viewDir)]
B --> D
D --> E[specTerm = pow(max(dot(normalW, halfDir), 0.0), specularPower)]
E --> F[specular = lightColor * specularIntensity * specTerm]关键参数的影响
| 参数 | 作用 | 典型值 |
|---|---|---|
specularPower | 控制高光范围(值越大,高光越集中) | 32.0(金属) / 8.0(塑料) |
specularIntensity | 控制高光亮度 | 0.5 ~ 1.0 |
lightColor | 高光的基础颜色 | 与光源一致 |
与其他光照模型的对比
-
Phong 模型:直接计算反射向量 R 与视角向量的夹角,计算量较大。
-
Blinn-Phong 模型:改用半角向量,效率更高,适合实时渲染。
-
PBR 模型:基于物理的镜面反射(如 BRDF),更复杂但更真实。
使用示例:
export function SetMaterial(scene:Scene):void{
SceneLoader.Append("Models/","Plane.gltf", scene, (scene)=>{
// 创建 ShaderMaterial
const material = new ShaderMaterial("Water", scene,
"./src/assets/Shaders/Water/Water",
{
attributes: ["position", "normal", "uv", "tangent", "bitangent"],
uniforms: [
"world", "worldViewProjection", "cameraPosition",
"diffuseColor", "ambientIntensity", "ambientColor",
"lightDirection", "lightColor", "lightIntensity",
"specularPower", "specularIntensity",
"fresnelPower", "fresnelBias",
"scaleDiffuseTex","scaleNormalTex"
],
samplers: ["diffuseTexture", "normalTexture", "environmentTexture"]
});
const diffuseTexture = new Texture("./src/assets/Textures/DaLiShi.jpg", scene);
const normalTexture = new Texture("./src/assets/Textures/Metal06.jpg", scene);
const environmentTexture = new CubeTexture("./src/assets/Textures/Environment/Environment", scene);
// 设置贴图
material.setTexture("diffuseTexture", diffuseTexture );
material.setVector2("scaleDiffuseTex", new Vector2(5, 5));
material.setTexture("normalTexture", normalTexture);
material.setVector2("scaleNormalTex", new Vector2(5, 5));
material.setTexture("environmentTexture", environmentTexture);
// 设置颜色参数
material.setVector3("diffuseColor", new Vector3(1, 1, 1));
material.setFloat("ambientIntensity", 0.3);
material.setVector3("ambientColor", new Vector3(1, 1, 1));
// 设置平行光参数
material.setVector3("lightDirection", new Vector3(-1, -1, -1));
material.setVector3("lightColor", new Vector3(1, 1, 1));
material.setFloat("lightIntensity", 1.0);
// 设置高光参数
material.setFloat("specularPower", 128.0);
material.setFloat("specularIntensity", 1.0);
// 设置菲涅尔参数
material.setFloat("fresnelPower", 5.0);
material.setFloat("fresnelBias", 0.6);
// 绑定相机位置(每帧更新)
scene.onBeforeRenderObservable.add(() => {
if(scene.activeCamera){
material.setVector3("cameraPosition", scene.activeCamera.position); // 设置相机位置
}
});
scene.meshes.forEach((mesh)=>{
// 获取网格的顶点数据
if (mesh.isVerticesDataPresent(VertexBuffer.TangentKind)) {
// 应用材质到网格
console.log("mesh contain tangent = " + mesh.name);
}
else{
const tangentsArray = ComputeTangents(mesh);
if(tangentsArray && tangentsArray.length > 2){
console.log("mesh don't contain tangent = " + mesh.name);
mesh.setVerticesData(VertexBuffer.TangentKind, tangentsArray, false);
}
}
mesh.material = material;
});
}
);
}
function ComputeTangents(mesh:AbstractMesh){
const positions = mesh.getVerticesData( VertexBuffer.PositionKind);
const uvs = mesh.getVerticesData( VertexBuffer.UVKind);
const indices = mesh.getIndices();
if(positions && uvs && indices){
let tangents = new Array(positions.length).fill(0);
for (let i = 0; i < indices.length; i += 3) {
let i0 = indices[i];
let i1 = indices[i + 1];
let i2 = indices[i + 2];
let p0 = new Vector3(positions[i0 * 3], positions[i0 * 3 + 1], positions[i0 * 3 + 2]);
let p1 = new Vector3(positions[i1 * 3], positions[i1 * 3 + 1], positions[i1 * 3 + 2]);
let p2 = new Vector3(positions[i2 * 3], positions[i2 * 3 + 1], positions[i2 * 3 + 2]);
let uv0 = new Vector2(uvs[i0 * 2], uvs[i0 * 2 + 1]);
let uv1 = new Vector2(uvs[i1 * 2], uvs[i1 * 2 + 1]);
let uv2 = new Vector2(uvs[i2 * 2], uvs[i2 * 2 + 1]);
let deltaPos1 = p1.subtract(p0);
let deltaPos2 = p2.subtract(p0);
let deltaUV1 = uv1.subtract(uv0);
let deltaUV2 = uv2.subtract(uv0);
let r = 1.0 / (deltaUV1.x * deltaUV2.y - deltaUV1.y * deltaUV2.x);
let tangent = deltaPos1.scale(deltaUV2.y).subtract(deltaPos2.scale(deltaUV1.y)).scale(r);
tangents[i0 * 4] = tangent.x;
tangents[i0 * 4 + 1] = tangent.y;
tangents[i0 * 4 + 2] = tangent.z;
tangents[i0 * 4 + 3] = 1;
tangents[i1 * 4] = tangent.x;
tangents[i1 * 4 + 1] = tangent.y;
tangents[i1 * 4 + 2] = tangent.z;
tangents[i1 * 4 + 3] = 1;
tangents[i2 * 4] = tangent.x;
tangents[i2 * 4 + 1] = tangent.y;
tangents[i2 * 4 + 2] = tangent.z;
tangents[i2 * 4 + 3] = 1;
}
return tangents;
}
return null;
}补充说明:
由于这里使用了法线贴图,如果使用Shader的物体表面完全是黑色的,很可能是顶点切线的问题,具体解决方法参考基于Babylon.js的Shader入门之五:让Shader支持法线贴图。


























 1610
1610

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








