
1.unique_ptr指针的基本使用!
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
// 在这个范围之外,unique_ptr 被释放
{
auto i = unique_ptr<int>(new int(10)); // 创建一个 unique_ptr 管理的动态分配内存
cout << *i << endl; // 输出 10
} // 离开作用域时,unique_ptr `i` 自动释放内存
// 使用 std::make_unique 进行初始化
auto w = std::make_unique<int>(10);
cout << *(w.get()) << endl; // 输出 10
// 尝试复制 unique_ptr 会导致编译错误
// auto w2 = w; // 编译错误:unique_ptr 不支持复制语义
// unique_ptr 支持移动语义
auto w2 = std::move(w); // w 的所有权转移给 w2
cout << ((w.get() != nullptr) ? (*w.get()) : -1) << endl; // 输出 -1,因为 w 已经是 nullptr
cout << ((w2.get() != nullptr) ? (*w2.get()) : -1) << endl; // 输出 10,w2 现在拥有该内存
return 0;
}

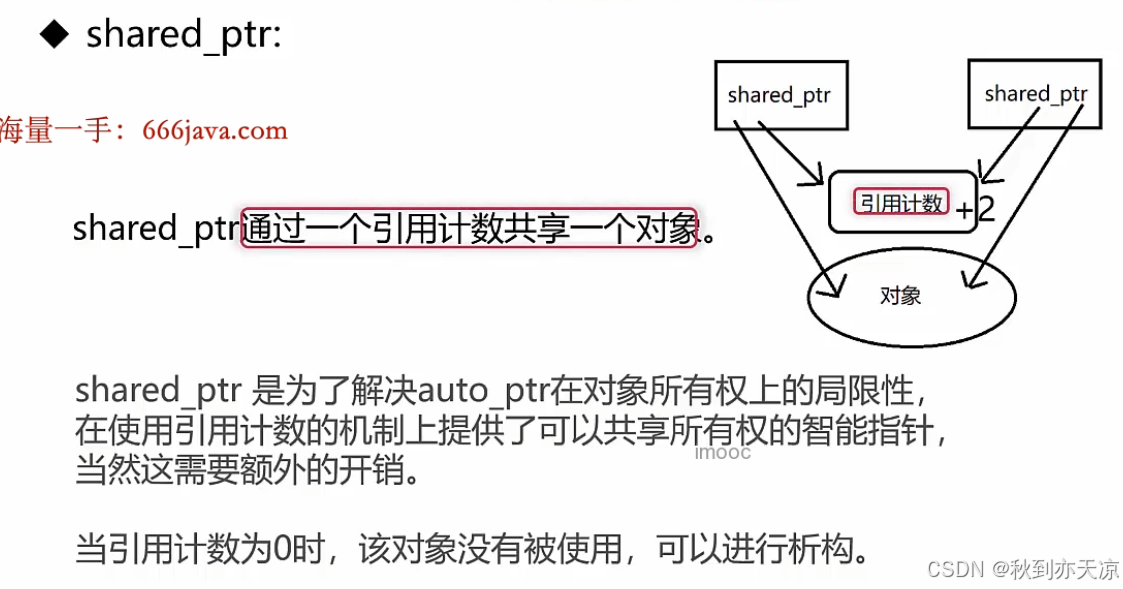
2.shared_ptr 的基本使用
#include <memory>
#include <iostream>
struct B;
struct A {
std::shared_ptr<B> ptrB;
~A() { std::cout << "A destroyed\n"; }
};
struct B {
std::weak_ptr<A> ptrA; // 使用 weak_ptr 打破循环引用
~B() { std::cout << "B destroyed\n"; }
};
int main() {
auto a = std::make_shared<A>();
auto b = std::make_shared<B>();
a->ptrB = b; // A 拥有 shared_ptr 指向 B
b->ptrA = a; // B 拥有 weak_ptr 指向 A,避免循环引用
return 0; // a 和 b 离开作用域时,资源会被正常释放
}
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
#include <memory>
using namespace std;
struct B;
struct A {
shared_ptr<B> pb;
~A()
{
cout << "~A()" << endl;
}
};
struct B {
shared_ptr<A> pa;
~B()
{
cout << "~B()" << endl;
}
};
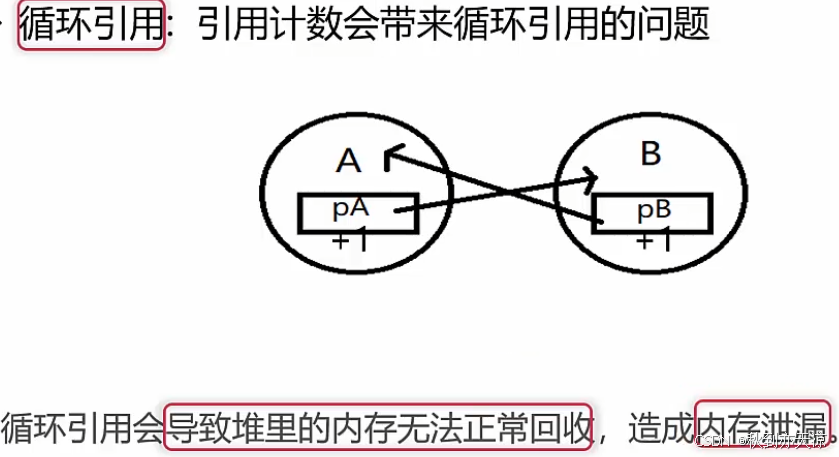
// pa 和 pb 存在着循环引用,根据 shared_ptr 引用计数的原理,pa 和 pb 都无法被正常的释放。
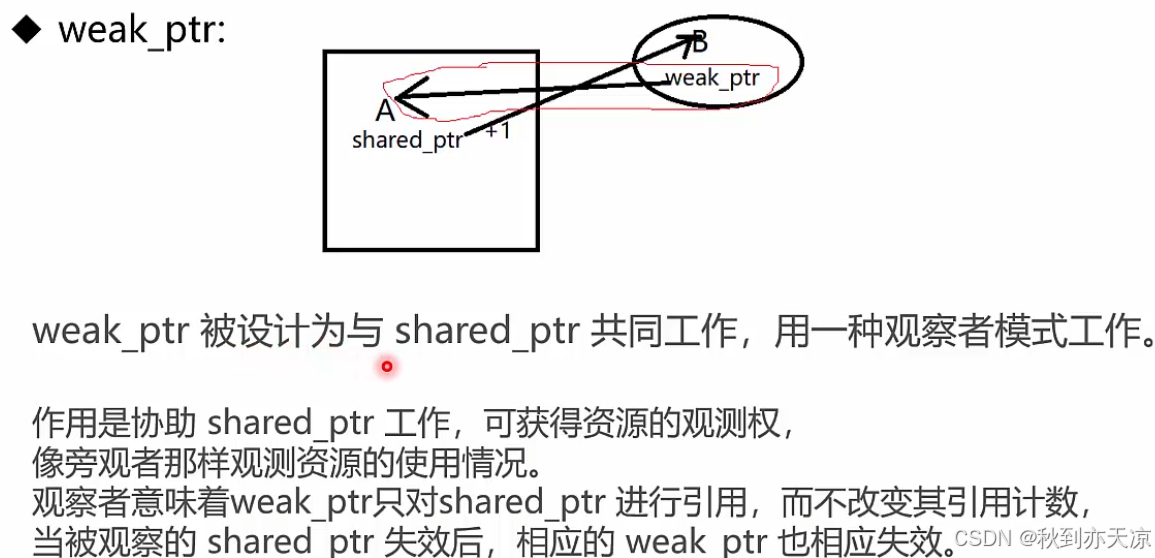
// weak_ptr 是为了解决 shared_ptr 双向引用的问题。
struct BW;
struct AW
{
shared_ptr<BW> pb;
~AW()
{
cout << "~AW()" << endl;
}
};
struct BW
{
weak_ptr<AW> pa;
~BW()
{
cout << "~BW()" << endl;
}
};
void Test()
{
cout << "Test shared_ptr and shared_ptr: " << endl;
shared_ptr<A> tA(new A()); // 1
shared_ptr<B> tB(new B()); // 1
cout << tA.use_count() << endl;
cout << tB.use_count() << endl;
tA->pb = tB;
tB->pa = tA;
cout << tA.use_count() << endl; // 2
cout << tB.use_count() << endl; // 2
}
void Test2()
{
cout << "Test weak_ptr and shared_ptr: " << endl;
shared_ptr<AW> tA(new AW());
shared_ptr<BW> tB(new BW());
cout << tA.use_count() << endl; // 1
cout << tB.use_count() << endl; // 1
tA->pb = tB;
tB->pa = tA;
cout << tA.use_count() << endl; // 1
cout << tB.use_count() << endl; // 2
}
int main()
{
Test();
Test2();
return 0;
}

下面总结四种指针
























 1435
1435

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










