Little Sub is about to take a math exam at school. As he is very confident, he believes there is no need for a review.
Little Sub’s father, Mr.Potato, is nervous about Little Sub’s attitude, so he gives Little Sub a task to do. To his surprise, Little Sub finishes the task quickly and perfectly and even solves the most difficult problem in the task.
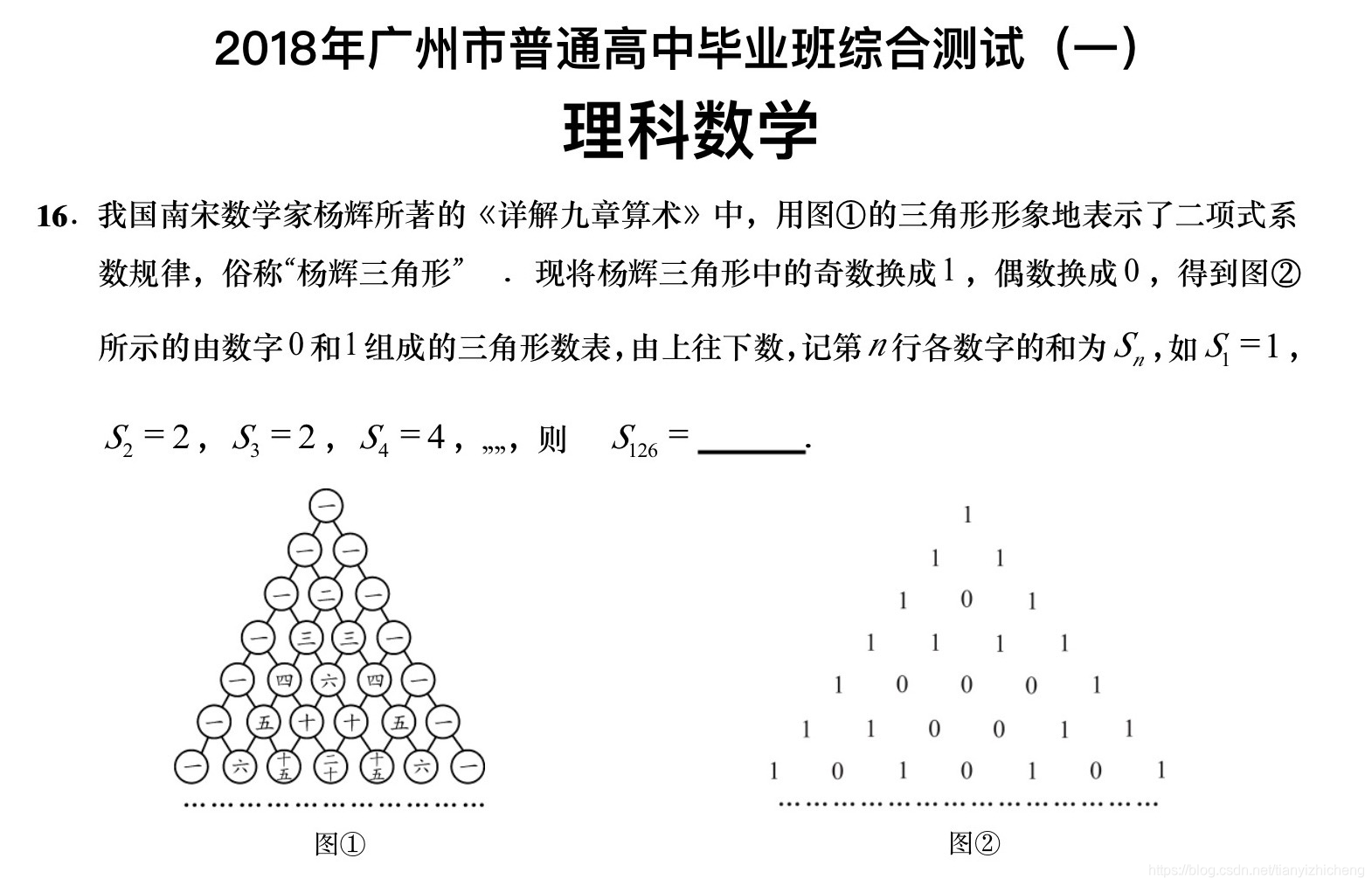
Mr.Potato trys to find any possible mistake on the task paper and suddenly notices an interesting problem. It’s a problem related to Pascal’s Triangle.
“math”/
The definition of Pascal’s Triangle is given below:
The first element and the last element of each row in Pascal’s Triangle is , and the -th element of the -th row equals to the sum of the -th and the -th element of the -th row.
According to the definition, it’s not hard to deduce the first few lines of the Pascal’s Triangle, which is:

In the task, Little Sub is required to calculate the number of odd elements in the 126th row of Pascal’s Triangle.
Mr.Potato now comes up with a harder version of this problem. He gives you many queries on this problem, but the row number may be extremely large. For each query, please help Little Sub calculate the number of odd elements in the -th row of Pascal’s Triangle.
Input
There are multiple test cases. The first line of the input contains an integer (), indicating the number of test cases. For each test case:
The first and only line contains an integer (), indicating the required row number in Pascal’s Triangle.
Output
For each test case, output the number of odd numbers in the -th line.
Sample Input
3
3
4
5
Sample Output
2
4
2
题意:
统计杨辉三角中第i排中奇数的个数。
题解:
打个表就会发现,如果这个数大于(第一个大于等于它的2的幂次的数+第一个小于它的2的幂次的数)/2,那么就是对应(第一个小于它的2的幂次的数-(第一个大于等于它的2的幂次的数-这个数)*2否则就与对应的数相等。举个例子:5<(8+4)/2,5=(4/2+(5-4)) = 2。6>=(8+4)/2 , 6 = (4-(8-6))*2 = 2*2 = 4
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
ll dfs(ll x,ll ret)
{
while(ret>=x*2)
ret/=2;
if(x==1)
return 1;
if(x==2)
return 2;
if(ret-x<=ret/2/2)
return dfs(ret/2-(ret-x),ret/2)*2;
else return dfs(ret/2/2+(x-ret/2),ret/2);
}
int main()
{
ll a[3];
a[1]=1,a[2]=2;
int t;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
ll k;
scanf("%lld",&k);
ll ret=1;
while(ret<k)
ret*=2;
printf("%lld\n",dfs(k,ret));
}
return 0;
}








 本文探讨了如何高效计算杨辉三角特定行中奇数元素的数量,通过观察和数学推导,提出了一种新颖的算法,该算法能快速解决大规模行号的问题。
本文探讨了如何高效计算杨辉三角特定行中奇数元素的数量,通过观察和数学推导,提出了一种新颖的算法,该算法能快速解决大规模行号的问题。
















 390
390

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








