1.多边形裁切
1.1 基本流程
cesium117版本添加了多边形裁切功能,本文分析源码,看看是如何处理的。多边形裁切的大概流程分为4部分:
- 通过经纬度坐标传入多个闭合的边界;
- 将多个边界打包成两张纹理,一张是每个多边形的坐标,另一张是每个多边形的边界;
- 将两张多边形纹理通过一个计算着色器(屏幕空间着色器模拟计算着色器)生成一张符号距离场纹理;
- 将这两张图传入地球瓦片和3DTiles的着色器中进行多边形裁切.
1.2 多边形纹理打包
这是在js代码中处理的,使用了ClippingPolygon和ClippingPolygonCollection两个类,ClippingPolygon类负责每个多边形的坐标收集以及每个多边形的范围计算。
以下是ClippingPolygon类的主要代码,过程比较简单。
/**
* Computes a rectangle with the spherical extents that encloses the polygon defined by the list of positions, including cases over the international date line and the poles.
* 根据给定的位置列表计算球上的坐标区域(使用弧度表示),包括越过国际日期线和极点的情况
* @private
*
* @param {Rectangle} [result] An object in which to store the result.
* @returns {Rectangle} The result rectangle with spherical extents.
*/
ClippingPolygon.prototype.computeSphericalExtents = function (result) {
if (!defined(result)) {
result = new Rectangle();
}
// 经纬度范围
const rectangle = this.computeRectangle(scratchRectangle);
// 计算出球面点笛卡尔
let spherePoint = Cartographic.toCartesian(
Rectangle.southwest(rectangle),
this.ellipsoid,
spherePointScratch
);
// Project into plane with vertical for latitude
// 投影到具有垂直纬度的平面中
let magXY = Math.sqrt(
spherePoint.x * spherePoint.x + spherePoint.y * spherePoint.y
);
// Use fastApproximateAtan2 for alignment with shader
// 球面纬度
let sphereLatitude = CesiumMath.fastApproximateAtan2(magXY, spherePoint.z);
// 球面经度
let sphereLongitude = CesiumMath.fastApproximateAtan2(
spherePoint.x,
spherePoint.y
);
// 西南的经纬度
result.south = sphereLatitude;
result.west = sphereLongitude;
// 计算东北点位
spherePoint = Cartographic.toCartesian(
Rectangle.northeast(rectangle),
this.ellipsoid,
spherePointScratch
);
// Project into plane with vertical for latitude
magXY = Math.sqrt(
spherePoint.x * spherePoint.x + spherePoint.y * spherePoint.y
);
// Use fastApproximateAtan2 for alignment with shader
sphereLatitude = CesiumMath.fastApproximateAtan2(magXY, spherePoint.z);
sphereLongitude = CesiumMath.fastApproximateAtan2(
spherePoint.x,
spherePoint.y
);
// 计算东北经纬度
result.north = sphereLatitude;
result.east = sphereLongitude;
return result;
};ClippingPolygonCollection类的过程主要在update函数中,函数过程如下
ClippingPolygonCollection.prototype.update = function (frameState) {
const context = frameState.context;
// 是否支持
if (!ClippingPolygonCollection.isSupported(frameState)) {
throw new RuntimeError(
"ClippingPolygonCollections are only supported for WebGL 2."
);
}
// It'd be expensive to validate any individual position has changed. Instead verify if the list of polygon positions has had elements added or removed, which should be good enough for most cases.
// 验证任何个人立场的改变都是昂贵的。相反,请验证多边形位置列表中是否添加或删除了元素,这在大多数情况下应该足够好。
// 总共的顶点数量
const totalPositions = this._polygons.reduce(
(totalPositions, polygon) => totalPositions + polygon.length,
0
);
// 总共的顶点数量不变
if (totalPositions === this.totalPositions) {
return;
}
this._totalPositions = totalPositions;
// If there are no clipping polygons, there's nothing to update.
if (this.length === 0) {
return;
}
// 符号距离计算命令,命令存在就取消
if (defined(this._signedDistanceComputeCommand)) {
// 如果正在计算就取消
this._signedDistanceComputeCommand.canceled = true;
this._signedDistanceComputeCommand = undefined;
}
// 多边形纹理
let polygonsTexture = this._polygonsTexture;
// 范围纹理
let extentsTexture = this._extentsTexture;
// 符号距离纹理
let signedDistanceTexture = this._signedDistanceTexture;
if (defined(polygonsTexture)) {
// 当前像素数量
const currentPixelCount = polygonsTexture.width * polygonsTexture.height;
// Recreate the texture to double current requirement if it isn't big enough or is 4 times larger than it needs to be.
// Optimization note: this isn't exactly the classic resizeable array algorithm
// * not necessarily checking for resize after each add/remove operation
// * random-access deletes instead of just pops
// * alloc ops likely more expensive than demonstrable via big-O analysis
/*
重建2倍的当前纹理,如果不够到,或者是所需内存的4倍,
优化注意:这不是经典的重新设置数组大小的算法,
不一定要在每次添加/删除操作后检查是否调整大小
随机访问删除而不是弹出
分配操作可能比通过big-O(大O分析法)分析证明的更昂贵
*/
if (
currentPixelCount < this.pixelsNeededForPolygonPositions || // 内存不够大
this.pixelsNeededForPolygonPositions < 0.25 * currentPixelCount // 所需要的比当前四分之一还小,就需要重新分配显存
) {
// 销毁纹理
polygonsTexture.destroy();
polygonsTexture = undefined;
this._polygonsTexture = undefined;
}
}
if (!defined(polygonsTexture)) {
// 获取分辨率
const requiredResolution = ClippingPolygonCollection.getTextureResolution(
polygonsTexture,
this.pixelsNeededForPolygonPositions,
textureResolutionScratch
);
// 创建纹理
polygonsTexture = new Texture({
context: context,
width: requiredResolution.x,
height: requiredResolution.y,
pixelFormat: PixelFormat.RG,
pixelDatatype: PixelDatatype.FLOAT,
sampler: Sampler.NEAREST,
flipY: false,
});
// 数据
this._float32View = new Float32Array(
requiredResolution.x * requiredResolution.y * 2
);
// 纹理
this._polygonsTexture = polygonsTexture;
}
// 处理范围纹理
if (defined(extentsTexture)) {
const currentPixelCount = extentsTexture.width * extentsTexture.height;
// Recreate the texture to double current requirement if it isn't big enough or is 4 times larger than it needs to be.
// Optimization note: this isn't exactly the classic resizeable array algorithm
// * not necessarily checking for resize after each add/remove operation
// * random-access deletes instead of just pops
// * alloc ops likely more expensive than demonstrable via big-O analysis
if (
currentPixelCount < this.pixelsNeededForExtents ||
this.pixelsNeededForExtents < 0.25 * currentPixelCount
) {
extentsTexture.destroy();
extentsTexture = undefined;
this._extentsTexture = undefined;
}
}
if (!defined(extentsTexture)) {
// 获取范围纹理的分辨率
const requiredResolution = ClippingPolygonCollection.getTextureResolution(
extentsTexture,
this.pixelsNeededForExtents,
textureResolutionScratch
);
// 创建范围纹理
extentsTexture = new Texture({
context: context,
width: requiredResolution.x,
height: requiredResolution.y,
pixelFormat: PixelFormat.RGBA,
pixelDatatype: PixelDatatype.FLOAT,
sampler: Sampler.NEAREST,
flipY: false,
});
// 范围纹理依赖的数据内存
this._extentsFloat32View = new Float32Array(
requiredResolution.x * requiredResolution.y * 4
);
this._extentsTexture = extentsTexture;
}
// 打包多边形
packPolygonsAsFloats(this);
// 拷贝范围的纹理数据
extentsTexture.copyFrom({
source: {
width: extentsTexture.width,
height: extentsTexture.height,
arrayBufferView: this._extentsFloat32View,
},
});
// 拷贝多边形纹理数据
polygonsTexture.copyFrom({
source: {
width: polygonsTexture.width,
height: polygonsTexture.height,
arrayBufferView: this._float32View,
},
});
// 定义符号距离场景
if (!defined(signedDistanceTexture)) {
// 符号距离场纹理分辨率
const textureDimensions = ClippingPolygonCollection.getClippingDistanceTextureResolution(
this,
textureResolutionScratch
);
// 符号距离纹理
signedDistanceTexture = new Texture({
context: context,
width: textureDimensions.x,
height: textureDimensions.y,
pixelFormat: context.webgl2 ? PixelFormat.RED : PixelFormat.LUMINANCE, // 只有一个通道
pixelDatatype: PixelDatatype.FLOAT,
sampler: new Sampler({
wrapS: TextureWrap.CLAMP_TO_EDGE,
wrapT: TextureWrap.CLAMP_TO_EDGE,
minificationFilter: TextureMinificationFilter.LINEAR,
magnificationFilter: TextureMagnificationFilter.LINEAR,
}),
flipY: false,
});
this._signedDistanceTexture = signedDistanceTexture;
}
// 创建符号距离场命令
this._signedDistanceComputeCommand = createSignedDistanceTextureCommand(this);
};这个过程中主要是如很将多边形信息打包到两个纹理中,以及创建一张距离场纹理,用于后续将计算着色器(像素着色器模拟计算着色器)的计算结果存入距离场纹理中。
打包的两张纹理的结构图如下:
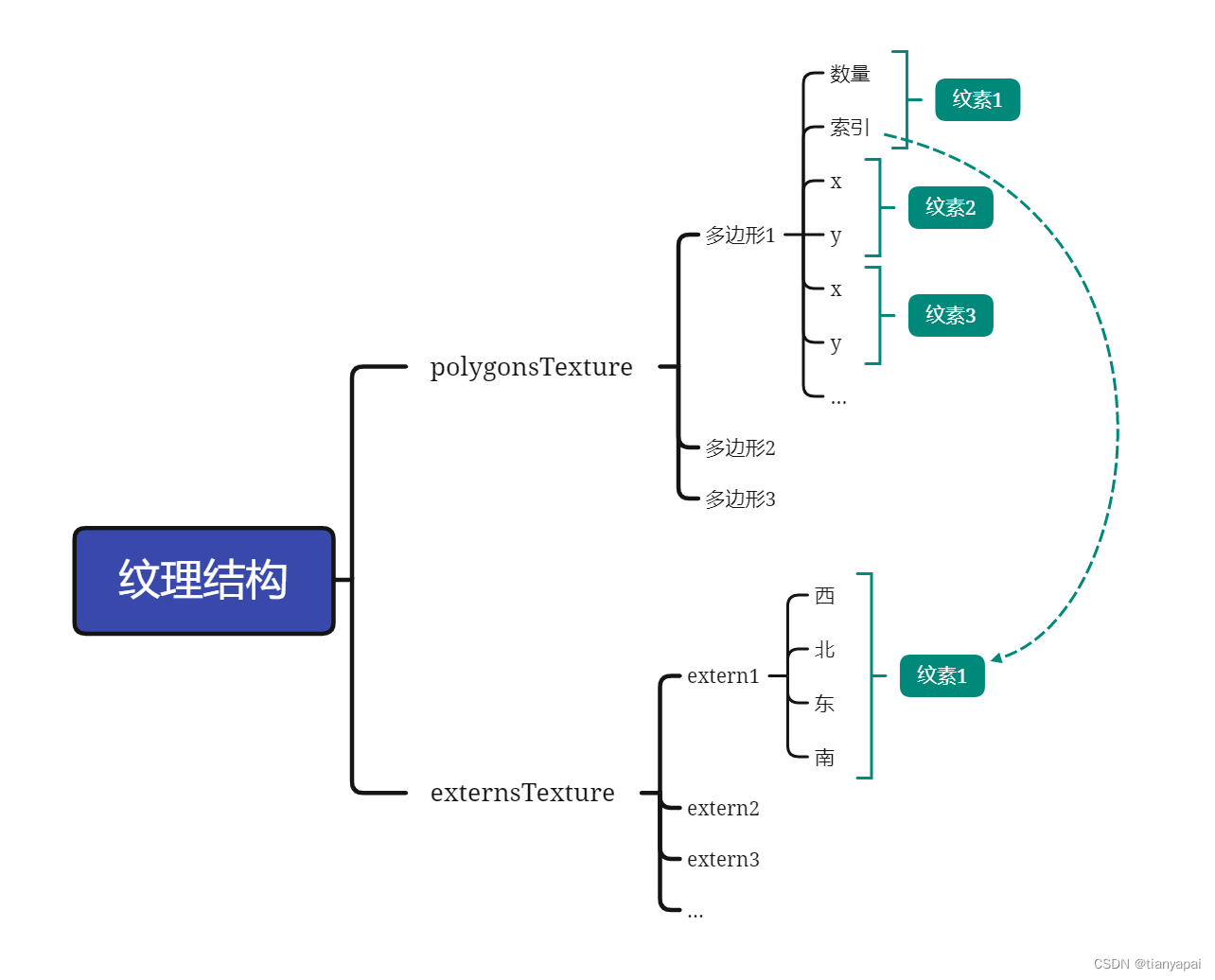
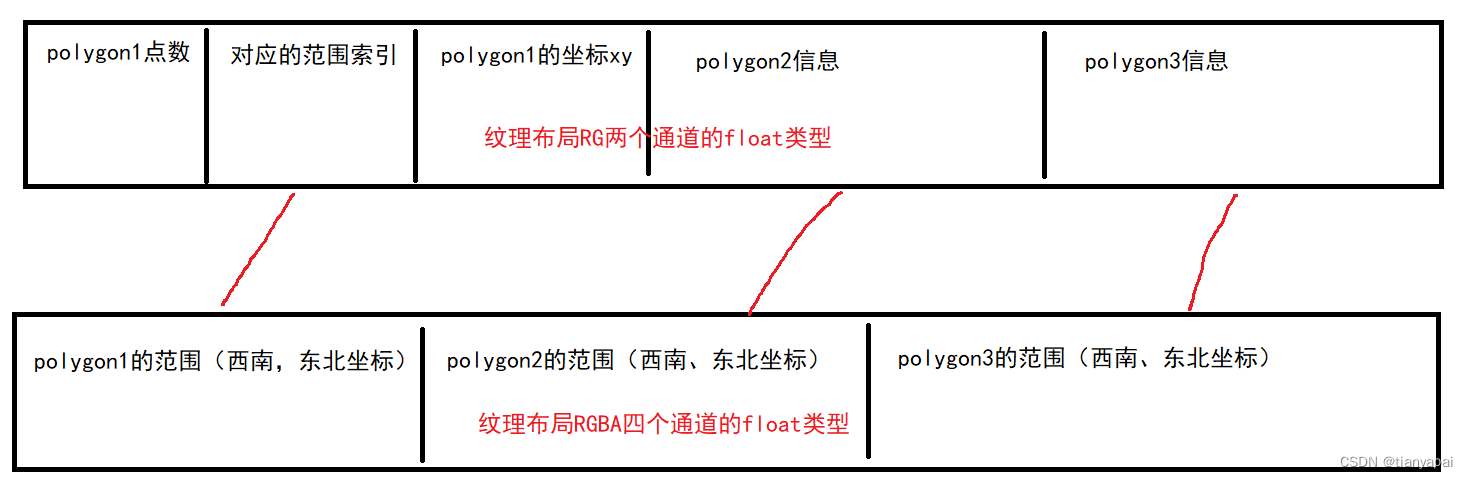
1.3 计算命令
接着就是计算命令的创建过程:
// 创建距离场纹理命令
function createSignedDistanceTextureCommand(collection) {
// 多边形纹理、范围纹理
const polygonTexture = collection._polygonsTexture;
const extentsTexture = collection._extentsTexture;
// 计算命令
return new ComputeCommand({
fragmentShaderSource: PolygonSignedDistanceFS, // 只有光栅化过程
outputTexture: collection._signedDistanceTexture, // 输出纹理
uniformMap: {
u_polygonsLength: function () { // 多少个多边形
return collection.length;
},
u_extentsLength: function () { // 多少个范围
return collection.extentsCount;
},
u_extentsTexture: function () { // 范围纹理
return extentsTexture;
},
u_polygonTexture: function () { // 多边形纹理
return polygonTexture;
},
},
persists: false, // 持续使用这个命令,还是使用一次就释放
owner: collection, // 归属
postExecute: () => { // 执行完成后
collection._signedDistanceComputeCommand = undefined;
},
});
}这个过程涉及到了ComputeCommand和ComputeEngine类,ComputeCommand类主要是收集信息,ComputeEngine类主要是update函数
// 执行
ComputeEngine.prototype.execute = function (computeCommand) {
//>>includeStart('debug', pragmas.debug);
Check.defined("computeCommand", computeCommand);
//>>includeEnd('debug');
// This may modify the command's resources, so do error checking afterwards
// 可能会更改命令的分辨率,后续会做错误检查
if (defined(computeCommand.preExecute)) {
computeCommand.preExecute(computeCommand);
}
//>>includeStart('debug', pragmas.debug);
if (
!defined(computeCommand.fragmentShaderSource) &&
!defined(computeCommand.shaderProgram)
) {
throw new DeveloperError(
"computeCommand.fragmentShaderSource or computeCommand.shaderProgram is required."
);
}
Check.defined("computeCommand.outputTexture", computeCommand.outputTexture);
//>>includeEnd('debug');
// 输出的纹理
const outputTexture = computeCommand.outputTexture;
const width = outputTexture.width;
const height = outputTexture.height;
const context = this._context;
// 定义顶点数组
const vertexArray = defined(computeCommand.vertexArray)
? computeCommand.vertexArray
: context.getViewportQuadVertexArray(); // 获取视口四边形顶点
// 着色程序
const shaderProgram = defined(computeCommand.shaderProgram)
? computeCommand.shaderProgram
: createViewportQuadShader(context, computeCommand.fragmentShaderSource); // 创建视口着色器
// 创建帧缓冲
const framebuffer = createFramebuffer(context, outputTexture);
// 创建渲染状态
const renderState = createRenderState(width, height);
const uniformMap = computeCommand.uniformMap;
// 执行清空命令
const clearCommand = clearCommandScratch;
clearCommand.framebuffer = framebuffer;
clearCommand.renderState = renderState;
clearCommand.execute(context);
// 执行绘制命令
const drawCommand = drawCommandScratch;
drawCommand.vertexArray = vertexArray;
drawCommand.renderState = renderState;
drawCommand.shaderProgram = shaderProgram;
drawCommand.uniformMap = uniformMap;
drawCommand.framebuffer = framebuffer;
drawCommand.execute(context);
// 执行完成销毁
framebuffer.destroy();
// 非持久的计算命令(一次性的)
if (!computeCommand.persists) {
shaderProgram.destroy();
if (defined(computeCommand.vertexArray)) {
vertexArray.destroy();
}
}
// 处理完成后的回调
if (defined(computeCommand.postExecute)) {
computeCommand.postExecute(outputTexture);
}
};类似一个后处理过程,创建一个四边形,占满整个屏幕,然后使用像素着色器进行距离场插值计算。
1.4 生成距离场纹理
这个过程是在着色器中处理的,PolygonSignedDistanceFS.glsl文件中是计算过程
in vec2 v_textureCoordinates;
uniform int u_polygonsLength;
uniform int u_extentsLength;
uniform highp sampler2D u_polygonTexture;
uniform highp sampler2D u_extentsTexture;
// 获取多边形索引
int getPolygonIndex(float dimension, vec2 coord) {
// 将当前的纹理坐标(按照0~1的比例)转换到(范围纹理的)整数坐标
vec2 uv = coord.xy * dimension;
return int(floor(uv.y) * dimension + floor(uv.x));
}
// 获取范围
vec2 getLookupUv(ivec2 dimensions, int i) {
//
int pixY = i / dimensions.x;
int pixX = i - (pixY * dimensions.x);
// 获取宽度、高度步长
float pixelWidth = 1.0 / float(dimensions.x);
float pixelHeight = 1.0 / float(dimensions.y);
// 计算uv
float u = (float(pixX) + 0.5) * pixelWidth; // sample from center of pixel
float v = (float(pixY) + 0.5) * pixelHeight;
return vec2(u, v);
}
// 获取范围
vec4 getExtents(int i) {
return texture(u_extentsTexture, getLookupUv(textureSize(u_extentsTexture, 0), i));
}
//
ivec2 getPositionsLengthAndExtentsIndex(int i) {
//
vec2 uv = getLookupUv(textureSize(u_polygonTexture, 0), i);
vec4 value = texture(u_polygonTexture, uv);
return ivec2(int(value.x), int(value.y));
}
vec2 getPolygonPosition(int i) {
vec2 uv = getLookupUv(textureSize(u_polygonTexture, 0), i);
return texture(u_polygonTexture, uv).xy;
}
vec2 getCoordinates(vec2 textureCoordinates, vec4 extents) {
// 插值出中间坐标 extents.x:范围开始的地方,extents.x + 1.0 / extents.z:范围结束的地方
float latitude = mix(extents.x, extents.x + 1.0 / extents.z, textureCoordinates.y);
float longitude = mix(extents.y, extents.y + 1.0 / extents.w, textureCoordinates.x);
return vec2(latitude, longitude);
}
/*
具体的逻辑好像是:
如果是4个范围,则将整个4096*4096的图像分成四部分,每一个部分进行距离场计算,如果是8个范围,则就缩小每个距离范围的分辨率,
*/
void main() {
int lastPolygonIndex = 0;
out_FragColor = vec4(1.0);
// Get the relevant region of the texture 获取纹理的相关区域
// 范围个数,例如100个
float dimension = float(u_extentsLength);
// 多于2个范围
if (u_extentsLength > 2) {
//转化成一个正方形的范围
dimension = ceil(log2(float(u_extentsLength)));
}
// 坐标转换成索引(这个像素gl_FragCoord)对应的范围索引
int regionIndex = getPolygonIndex(dimension, v_textureCoordinates);
// 遍历多边形
for (int polygonIndex = 0; polygonIndex < u_polygonsLength; polygonIndex++) {
// 获取每一个多边形的顶点个数和这个多边形的范围索引
ivec2 positionsLengthAndExtents = getPositionsLengthAndExtentsIndex(lastPolygonIndex);
// 长度
int positionsLength = positionsLengthAndExtents.x;
// 索引
int polygonExtentsIndex = positionsLengthAndExtents.y;
lastPolygonIndex += 1;
// Only compute signed distance for the relevant part of the atlas
// 仅计算图集相关部分的有符号距离
// 找到对应的区域
if (polygonExtentsIndex == regionIndex) {
float clipAmount = czm_infinity;
// 这个多边形对应的范围
vec4 extents = getExtents(polygonExtentsIndex);
// 偏移,将范围左边转换到一个正方形的范围内
vec2 textureOffset = vec2(mod(float(polygonExtentsIndex), dimension), floor(float(polygonExtentsIndex) / dimension)) / dimension;
// 插值出的坐标
vec2 p = getCoordinates((v_textureCoordinates - textureOffset) * dimension, extents);
float s = 1.0;
// Check each edge for absolute distance 绝对距离检查每个边
// 这个多边形的遍历坐标
for (int i = 0, j = positionsLength - 1; i < positionsLength; j = i, i++) {
// 获取多边形的坐标a,和上一个坐标b
vec2 a = getPolygonPosition(lastPolygonIndex + i);
vec2 b = getPolygonPosition(lastPolygonIndex + j);
// 两个点(经纬度点)之间的差
vec2 ab = b - a;
//
vec2 pa = p - a;
// 直线pa在直线ab上的投影(在单位直线ab)
// pa在ab单位向量上的投影,然后在除以ab,即占pa总长度的百分比
float t = dot(pa, ab) / dot(ab, ab);
// 百分比限制在【0.0~1.0】之间
t = clamp(t, 0.0, 1.0);
// 计算垂线
vec2 pq = pa - t * ab;
// 计算垂线距离
float d = length(pq);
// Inside / outside computation to determine sign
// 内外计算决定符号
bvec3 cond = bvec3(p.y >= a.y,
p.y < b.y,
ab.x * pa.y > ab.y * pa.x);
if (all(cond) || all(not(cond))) s = -s;
// 找到距离最小的一个
if (abs(d) < abs(clipAmount)) {
// 裁切数量(有向距离场的垂线)
clipAmount = d;
}
}
// Normalize the range to [0,1] 归一化范围到【0-1】
// clipAmount * length(extents.zw)转换到【-1~1】,然后添加s符号,然后/2为转换到【-0.5~0.5】,然后+0.5为转换到【0~1】
vec4 result = (s * vec4(clipAmount * length(extents.zw))) / 2.0 + 0.5;
// In the case where we've iterated through multiple polygons, take the minimum
// 在我们迭代多个多边形的情况下,取最小值
out_FragColor = min(out_FragColor, result);
}
lastPolygonIndex += positionsLength;
}
}
上述过程有点绕,主要过程如下:
- 根据光栅化插值的特点将每个像素转换到对应的范围纹理坐标中,这个坐标是一个索引;
- 根据上述索引,遍历多边形纹理中的数据,看看那个多边形的范围索引与1中计算出来的索引对应;
- 遍历这个索引下的多边形中的相邻的两个顶点坐标并计算向量,然后再计算像素坐标对应的边界插值坐标,将插值坐标投影到计算向量上,然后计算垂向量,垂向量的长度就是距离场;
- 当前像素点对应的坐标距离最短的那个边界的长度,然后计算符号,最后存入纹理中。
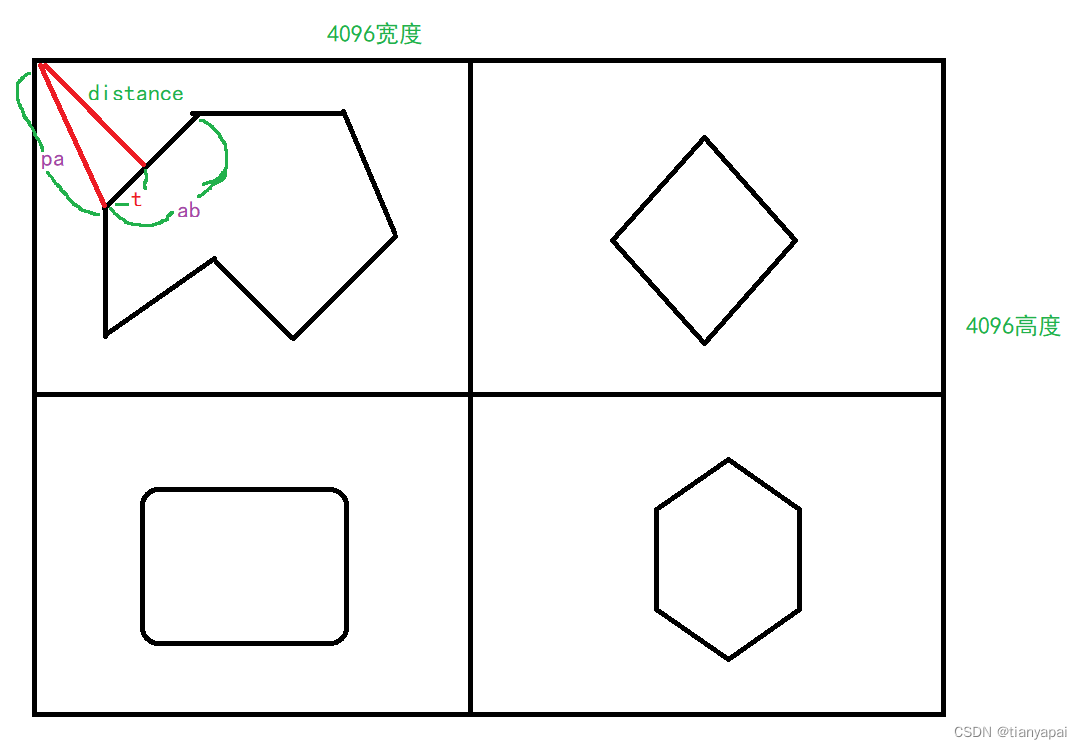
上面glsl的过程中,原来的范围长度是一维数组,经过如下计算会转换为边长为dimension的正方形,对应于上图四个图中的一个。
// Get the relevant region of the texture 获取纹理的相关区域
// 范围个数,例如100个
float dimension = float(u_extentsLength);
// 多于2个范围
if (u_extentsLength > 2) {
//转化成一个正方形的范围
dimension = ceil(log2(float(u_extentsLength)));
}由于uv坐标是【0~1】范围内的,所以需要将uv坐标 转换成externsTexture纹理的像素坐标,计算这是第几个范围,引文一个纹素对应者一个范围,第几个纹素就是第几个范围。
// 获取多边形索引
int getPolygonIndex(float dimension, vec2 coord) {
// 将当前的纹理坐标(按照0~1的比例)转换到(范围纹理的)整数坐标
vec2 uv = coord.xy * dimension;
return int(floor(uv.y) * dimension + floor(uv.x));
}
例如:dimension是2x2的4个像素,而coord是【0~1】的范围,假设是coord=(0.6, 0.6)则计算出来就是coord*2 =(1.2, 1.2)取整数就是(1,1),就是这个像素,所以(0,0)到(0.5,0.0)范围对应第一行第一列的像素,所以(0.5,0)到(1.0,0.0)范围对应第一行第二列的像素,(0.0,0.5)到(0.0,1.0)范围对应第二行第一列的像素,所以(0.5,0.5)到(1.0,1.0)范围对应第二行第二列的像素。
将整个4096x4096的距离场纹理划分成4个部分,每个部分就是一个polygon,然后按照如下
// 这个多边形对应的范围
vec4 extents = getExtents(polygonExtentsIndex);
// 偏移,将范围左边转换到一个正方形的范围内
vec2 textureOffset = vec2(mod(float(polygonExtentsIndex), dimension), floor(float(polygonExtentsIndex) / dimension)) / dimension;
// 插值出的坐标
vec2 p = getCoordinates((v_textureCoordinates - textureOffset) * dimension, extents);代码进行计算,索引找到就能查出范围externs,textureOffset为映射出的uv坐标,p就是映射出的uv坐标对应的经纬度坐标。





















 1204
1204










