- Article
- 06/09/2021
- 7 minutes to read
- 7 contributors
Note
UVAtlas was originally shipped in the now-deprecated D3DX9 utilty library. The latest version is available at UV Atlas Command-Line Tool (uvatlas.exe).
笔记
UVAtlas最初是在现已弃用的D3DX9 utilty库中发布的。最新版本可在 UV Atlas Command-Line Tool (uvatlas.exe)中找到。
Many rendering and content generation techniques require a unique, non-overlapping map of a 2D signal (such as a texture) onto a mesh. Such techniques include:
- Normal/displacement mapping
- Texture-space PRT simulations and light maps
- Surface painting
- Texture-space lighting
很多的渲染和内容构建技术需要将唯一的、不重叠的2D信号映射到一个网格上(例如2D图片映射到网格上),这样的技术包括:
- 法线/位移贴图
- 预处理全局光照贴图和灯光贴图
- 表面纹理绘制
- 环境光贴图
Generating a unique UV mapping manually is often time-consuming and tedious; this is especially true when the input geometry is complex and efficient/low-distortion texture-space utilization is desired. The following illustration shows an example mesh and its corresponding texture atlas.
通常手工制作一张uv映射贴图是费时、乏味的,特别是当输入几何体复杂且需要高效/低失真纹理空间利用率时尤其如此,下图显示了一个示例网格及其相应的纹理图集。
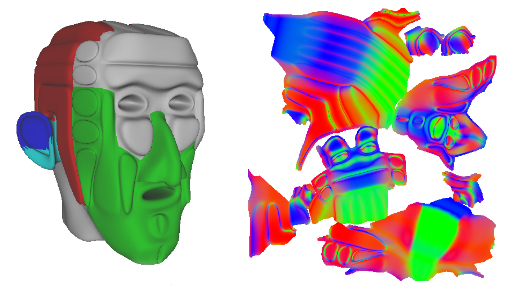
This example shows a mesh (on the left) and the corresponding UV-space normal map (on the right). Notice that the texture atlas contains several groups or clusters of data; each cluster is called a chart and in the example above, displays contains the normal data for a portion of the mesh.
这个例子中显示了一个网格(在左边)和相应的uv空间法线贴图(在这右边),注意纹理图集包含了几个数据组或者数据簇;在上面的例子中,每一个簇被叫做一个chart,显示包含部分网格的法线数据。
The D3DX UVAtlas APIs automatically generate an optimal, non-overlapping texture atlas. The APIs provide input parameters that allow you to:
- Minimize texture stretch, distortion, and undersampling.
- Maximize texture-space packing density for efficient use of memory.
- Provide an even sampling across the mesh, minimizing discontinuities in sampling frequency.
D3DX UVAtlas APIs默认使用了一个最优的参数来创建有重叠的纹理图集,APIs允许你设置下面的参数:
- 最小化纹理拉伸、变形和下采样
- 最大化纹理空间填充密度,有效利用内存
- 在整个网格中提供均匀的采样,最大限度地减少采样频率的不连续性。
How UVAtlas Works
The UVAtlas APIs (see UVAtlas Functions) generate a texture atlas by partitioning a surface into charts and packing the charts into a texture atlas. Use D3DXUVAtlasPartition and D3DXUVAtlasPack to perform these steps separately; or use D3DXUVAtlasCreate to partition, parameterize and pack in a single call.





 本文介绍UV Atlas在渲染和内容生成中的应用,讲解其自动创建纹理图集的过程,包括参数设置、控制参数化(如IMT)和处理用户指定折痕。通过实例展示如何使用API减少不连续性和提高效率,最后讨论如何整合到开发流程中以提升模型质量。
本文介绍UV Atlas在渲染和内容生成中的应用,讲解其自动创建纹理图集的过程,包括参数设置、控制参数化(如IMT)和处理用户指定折痕。通过实例展示如何使用API减少不连续性和提高效率,最后讨论如何整合到开发流程中以提升模型质量。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 8186
8186

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








