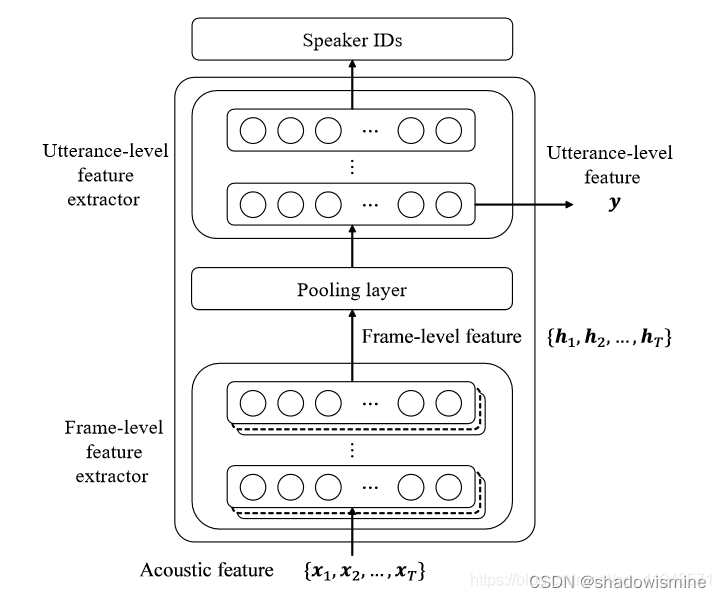
Pooling layer将变长的frame-level features转换为一个定长的向量。
1. Statistics Pooling
链接:http://danielpovey.com/files/2017_interspeech_embeddings.pdf
The default pooling method for x-vector is statistics pooling.
The statistics pooling layer calculates the mean vector µ as well as the second-order statistics as the standard deviation vector σ over frame-level features ht (t = 1, · · · , T ).
2. Attentive Statistics Pooling
链接:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.10963.pdf
在一段话中,往往某些帧的帧级特征比其他帧的特征更为独特重要,因此使用attention赋予每帧feature不同的权值。

其中f(.)代表非线性变换,如tanh or ReLU function。

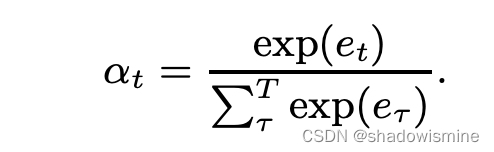
最后将每帧特征加劝求和





 本文介绍了几种在语音识别中常用的特征池化方法,如统计池化、注意力机制驱动的池化(如自注意力和多头注意力)、NetVLAD、LDE和ABP等,强调了不同方法如何捕捉帧级别特征的重要性。短时谱池化及其改进版也被提及,以提高对时序信息的利用。
本文介绍了几种在语音识别中常用的特征池化方法,如统计池化、注意力机制驱动的池化(如自注意力和多头注意力)、NetVLAD、LDE和ABP等,强调了不同方法如何捕捉帧级别特征的重要性。短时谱池化及其改进版也被提及,以提高对时序信息的利用。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1003
1003

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








