递归
递归,是分治策略的一个具体实现,通过将一个大问题分解为同样的小问题,逐层分解到边界之后,再向上“归”,最终得到整个问题的答案。
1.二叉树相关递归问题
二叉树的节点的定义:
//=========================C++版本========================
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
//==================Java版本====================
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
//=====================python版本=======================
//# Definition for a binary tree node.
//# class TreeNode(object):
//# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
//# self.val = val
//# self.left = left
//# self.right = right
1.1 二叉树的最大深度
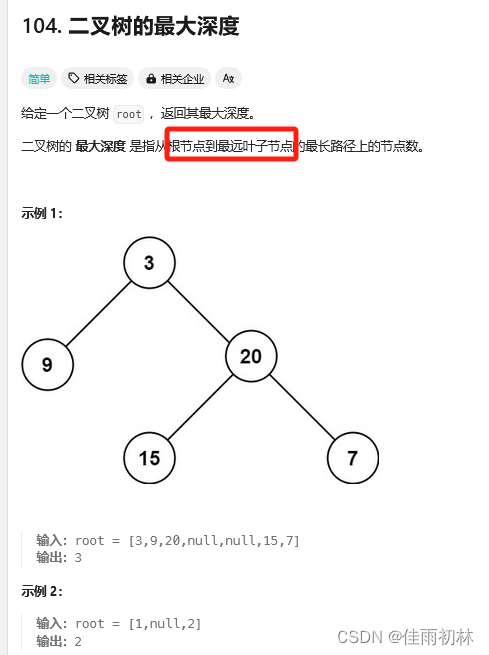
递归方法一:自己本身就是递归函数
class Solution {
public:
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL) return 0;
int left_depth = maxDepth(root -> left);
int right_depth = maxDepth(root -> right);
//这里+1是指加上当前节点
return max(left_depth, right_depth) + 1;
}
};
递归方法二:自定义一个递归函数
class Solution {
public:
int ans = 0;
void function(TreeNode* node, int cnt){
if(node == NULL){
return;
}
cnt += 1;
ans = max(ans, cnt);
function(node -> left, cnt);
function(node -> right, cnt);
}
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
function(root, 0);
return ans;
}
};
1.2 二叉树的最小深度
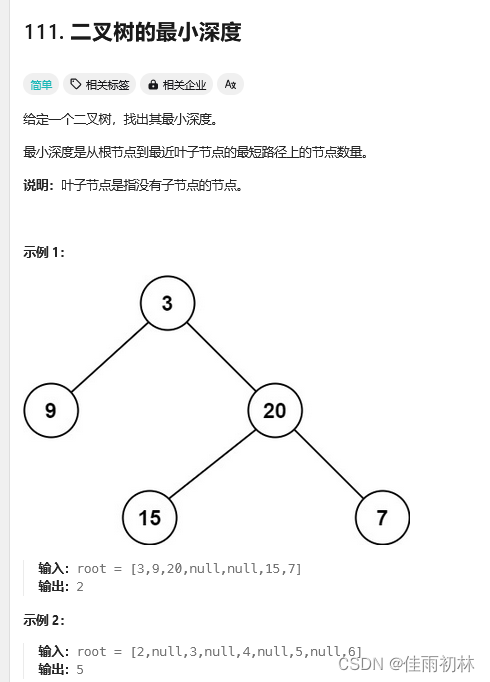
官方题解:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == nullptr) {
return 0;
}
if (root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr) {
return 1;
}
int min_depth = INT_MAX;
if (root->left != nullptr) {
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->left), min_depth);
}
if (root->right != nullptr) {
min_depth = min(minDepth(root->right), min_depth);
}
return min_depth + 1;
}
};
自己些的题解:
class Solution {
public:
int minDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(root == NULL){
return 0;
}
int left_depth = minDepth(root->left);
int right_depth = minDepth(root -> right);
if(left_depth == 0 || right_depth == 0){
//题目路径的定义的是根节点到叶子节点,所出现左子树或者右子树为空的情况下,我们需要请用非空的子树部分
return max(left_depth, right_depth) + 1;
}else{
return min(left_depth,right_depth) + 1;
}
}
};
1.3 路径总和
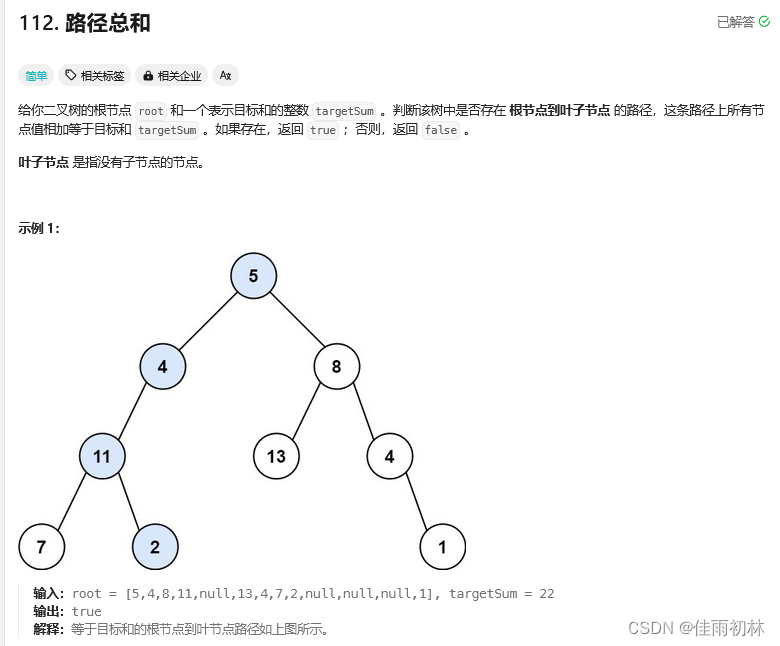
class Solution {
public:
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root == nullptr) return false;
//表示到达了叶子节点,此时判断一下总和是否达到了targetSum
if(root->right == nullptr && root->left == nullptr){
return targetSum == root->val;
}
//每一次往下“递”时,减去当前节点的值
return hasPathSum(root->left, targetSum - root->val) || hasPathSum(root -> right, targetSum - root->val);
}
};
1.4 路径总和II
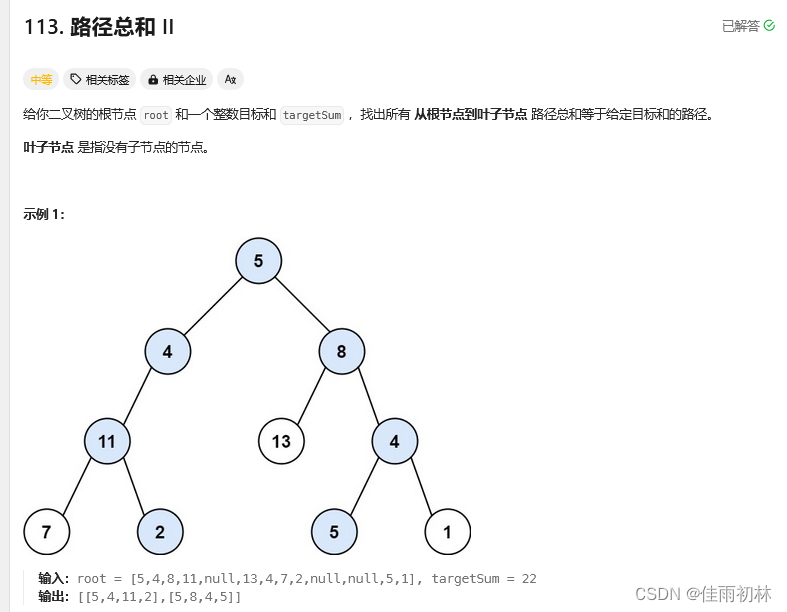
这个题目的难度相较于之前的题目难度大,实现过程中需要利用其他数据结构的帮助
java版题解:
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> ret = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
Deque<Integer> path = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ret;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum){
if(root == null){
return;
}
path.offerLast(root.val);
targetSum -= root.val;
if(root.left == null && root.right == null && targetSum == 0){
ret.add(new LinkedList<Integer>(path));
}
dfs(root.left, targetSum);
dfs(root.right, targetSum);
path.pollLast();
}
}
C++版本题解:
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> ret;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
dfs(root, targetSum);
return ret;
}
void dfs(TreeNode* root, int targetSum){
if(root == nullptr){
return;
}
//尝试性地将当前值添加到路径中
path.push_back(root->val);
//减去加入的值
targetSum -= root->val;
//当前节点为叶子节点同时满足总和要求
if(root->left == nullptr && root->right == nullptr && targetSum == 0){
ret.push_back(path);
}
//继续遍历左子树
dfs(root->left, targetSum);
//继续遍历右子树
dfs(root->right, targetSum);
//将尝试性加入的节点值弹出来
path.pop_back();
}
};
1.5 根节点到叶子节点数字之和
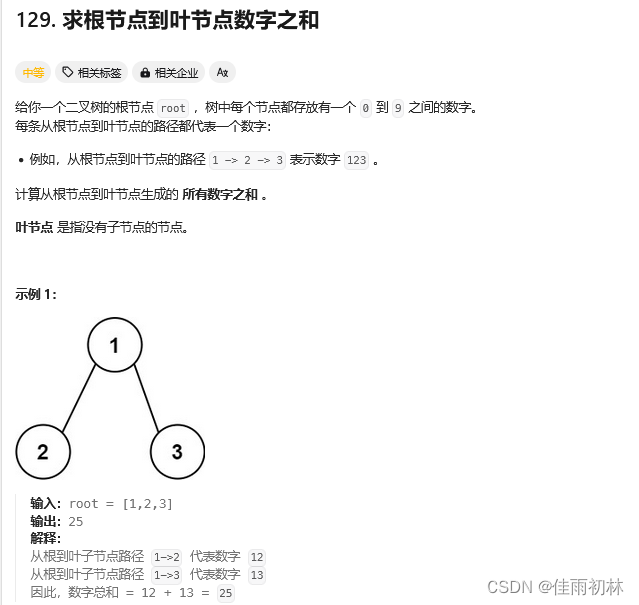
//java题解
class Solution {
int sum = 0;
public int sumNumbers(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, 0);
return sum;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root, int cnt){
if(root == null) return;
cnt = cnt * 10 + root.val;
//到达了根节点,加入到总和中
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
sum += cnt;
}
//遍历左子树和右子树
dfs(root.left, cnt);
dfs(root.right, cnt);
}
}
1.6 二叉树的所有路径
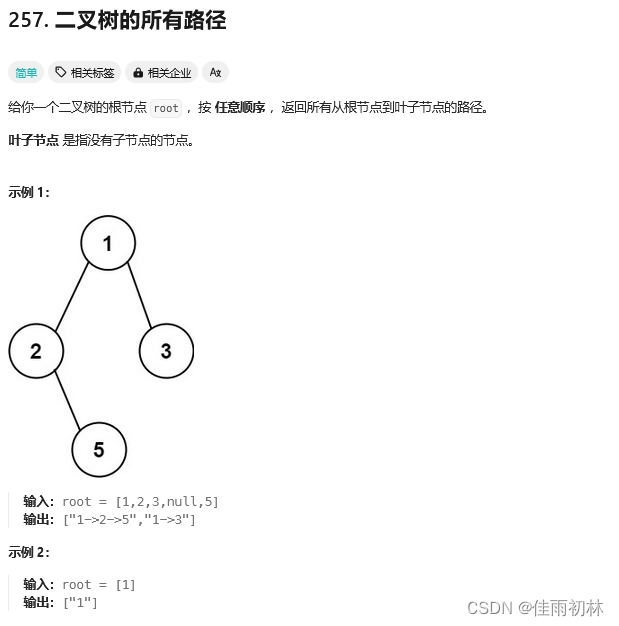 自己写的解法(StringBuffer处的来回处理过于冗杂)
自己写的解法(StringBuffer处的来回处理过于冗杂)
class Solution {
List<String> ans = new LinkedList<>();
StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer();
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return;
sb.append(root.val + "");
sb.append("->");
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){
ans.add(sb.substring(0, sb.length()-2));
}
dfs(root.left);
dfs(root.right);
sb.delete(sb.length() - 2 - (root.val + "").length(), sb.length());
}
}
参考题解:
class Solution {
public List<String> binaryTreePaths(TreeNode root) {
List<String> paths = new ArrayList<String>();
constructPaths(root,"", paths);
return paths;
}
public void constructPaths(TreeNode root, String path, List<String> paths){
if(root != null){
StringBuffer pathSB = new StringBuffer(path);
pathSB.append(Integer.toString(root.val));
if(root.left == null && root.right == null){//在当前节点时叶子节点
paths.add(pathSB.toString());
}else{
pathSB.append("->");
constructPaths(root.left, pathSB.toString(),paths);
constructPaths(root.right, pathSB.toString(), paths);
}
}
}
}
1.7 统计二叉树中好节点的数目
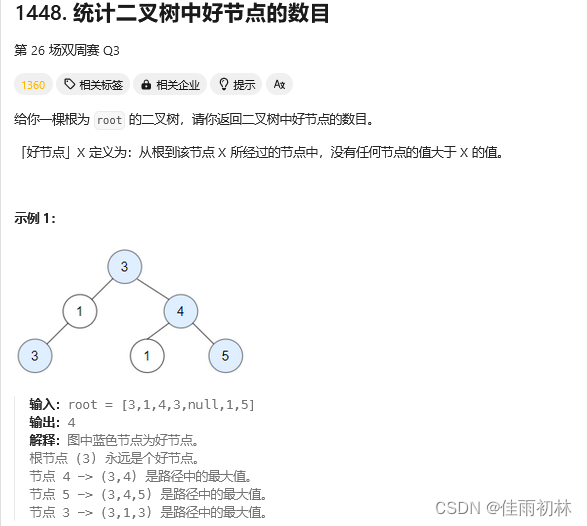
自己写的题解,通过定义全局变量实现题目解答:
class Solution {
int ans = 0;
public int goodNodes(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root, -10001);
return ans;
}
void dfs(TreeNode root, int max){
if(root == null){
return;
}
if(root.val >= max){
ans++;
max = root.val;
}
dfs(root.left, max);
dfs(root.right, max);
}
}
参考题解,无需定义全局变量版本:
class Solution {
public int goodNodes(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root, Integer.MIN_VALUE);
}
int dfs(TreeNode root, int mx){
if(root == null){
return 0;
}
int left = dfs(root.left,Math.max(mx, root.val));
int right = dfs(root.right, Math.max(mx, root.val));
return left + right + (mx <= root.val ? 1 : 0);
}
}





 本文详细介绍了二叉树中的多个递归问题,包括最大深度、最小深度、路径总和、根节点到叶子节点的数字之和、所有路径以及统计好节点的数目,提供了C++、Java和Python的代码实现示例。
本文详细介绍了二叉树中的多个递归问题,包括最大深度、最小深度、路径总和、根节点到叶子节点的数字之和、所有路径以及统计好节点的数目,提供了C++、Java和Python的代码实现示例。
















 765
765










