Dice
关于dice就不再多赘述,作者的另外一篇文章里提及:

HD95
定义
豪斯多夫距离(Hausdorff Distance, HD)衡量两个点集之间的最大边界偏差。但在医学图像中,由于噪声或标注误差,最大距离容易受离群点影响,因此常用 95% 分位数的 HD(HD95)作为更鲁棒的替代。
计算步骤
提取预测结果和真实标签的边界点集(如使用 scipy.ndimage 或 skimage.segmentation.find_boundaries)。
对每个预测边界点,计算其到所有真实边界点的最小欧氏距离。同样,对每个真实边界点,计算其到预测边界的最小距离。合并所有距离,取 95% 分位数 作为 HD95。
特点
(1)物理单位(如毫米,若图像有空间分辨率信息)或像素。
(2)对边界精度高度敏感,能反映分割轮廓的几何准确性。
(3)值越小越好,理想值为 0(边界完全重合)。
接下来对dice与hd95在实际中的计算代码讲解一下,下面的代码是transunet网络结构中的utils.py代码:
import numpy as np
import torch
from medpy import metric
from scipy.ndimage import zoom
import torch.nn as nn
import SimpleITK as sitk
# -------------------- Dice Loss --------------------
class DiceLoss(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, n_classes):
super(DiceLoss, self).__init__()
self.n_classes = n_classes
def _one_hot_encoder(self, input_tensor):
tensor_list = []
for i in range(self.n_classes):
temp_prob = input_tensor == i
tensor_list.append(temp_prob.unsqueeze(1))
output_tensor = torch.cat(tensor_list, dim=1)
return output_tensor.float()
def _dice_loss(self, score, target):
target = target.float()
smooth = 1e-5
intersect = torch.sum(score * target)
y_sum = torch.sum(target * target)
z_sum = torch.sum(score * score)
loss = (2 * intersect + smooth) / (z_sum + y_sum + smooth)
return 1 - loss
def forward(self, inputs, target, weight=None, softmax=False):
if softmax:
inputs = torch.softmax(inputs, dim=1)
target = self._one_hot_encoder(target)
if weight is None:
weight = [1] * self.n_classes
assert inputs.size() == target.size(), \
f'predict {inputs.size()} & target {target.size()} shape do not match'
loss = 0.0
for i in range(self.n_classes):
dice = self._dice_loss(inputs[:, i], target[:, i])
loss += dice * weight[i]
return loss / self.n_classes
# -------------------- Metric Computation --------------------
def calculate_metric_percase(pred, gt, spacing_z=2.5):
"""
Compute Dice and 95% Hausdorff Distance (HD95) for a single organ.
Args:
pred (np.ndarray): Predicted binary mask, shape (D, H, W)
gt (np.ndarray): Ground truth binary mask, shape (D, H, W)
spacing_z (float): Spacing in z-direction (slice thickness) in mm.
x/y spacing is assumed to be 1.0 mm (common simplification).
Returns:
dice (float): Dice Similarity Coefficient [0, 1]
hd95 (float): 95% Hausdorff Distance in mm
"""
pred = (pred > 0).astype(np.bool_)
gt = (gt > 0).astype(np.bool_)
if pred.sum() == 0 and gt.sum() == 0:
# Both empty → perfect match
return 1.0, 0.0
elif pred.sum() == 0 or gt.sum() == 0:
# One empty, the other not → worst case
return 0.0, 100.0 # HD95 capped at 100 mm (common practice)
else:
dice = metric.binary.dc(pred, gt)
# medpy expects voxelspacing in the same order as array dimensions: (z, y, x)
hd95 = metric.binary.hd95(pred, gt, voxelspacing=(spacing_z, 1.0, 1.0))
return dice, hd95
# -------------------- Inference on One Volume --------------------
def test_single_volume(image, label, net, classes, patch_size=[256, 256],
test_save_path=None, case=None, z_spacing=2.5):
"""
Test on a single 3D volume.
Args:
image (torch.Tensor): Input image, shape (1, D, H, W)
label (torch.Tensor): Ground truth label, shape (1, D, H, W)
net (nn.Module): Segmentation model
classes (int): Number of classes (including background)
patch_size (list): Patch size for 2D inference [H, W]
test_save_path (str): Path to save predictions (optional)
case (str): Case name for saving
z_spacing (float): Slice thickness in mm
Returns:
metric_list (list): List of (dice, hd95) for classes 1 to classes-1
"""
image = image.squeeze(0).cpu().detach().numpy() # (D, H, W)
label = label.squeeze(0).cpu().detach().numpy() # (D, H, W)
if len(image.shape) == 3:
prediction = np.zeros_like(label, dtype=np.uint8)
for ind in range(image.shape[0]): # iterate over slices (z-axis)
slice = image[ind, :, :] # (H, W)
x, y = slice.shape
# Resize to patch_size if needed
if x != patch_size[0] or y != patch_size[1]:
slice = zoom(slice, (patch_size[0] / x, patch_size[1] / y), order=3)
input_tensor = torch.from_numpy(slice).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).float().cuda()
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = net(input_tensor)
out = torch.argmax(torch.softmax(outputs, dim=1), dim=1).squeeze(0)
out = out.cpu().detach().numpy()
# Resize back to original slice size
if x != patch_size[0] or y != patch_size[1]:
pred = zoom(out, (x / patch_size[0], y / patch_size[1]), order=0)
else:
pred = out
prediction[ind] = pred.astype(np.uint8)
else:
# 2D case (unlikely for Synapse)
input_tensor = torch.from_numpy(image).unsqueeze(0).unsqueeze(0).float().cuda()
net.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
out = torch.argmax(torch.softmax(net(input_tensor), dim=1), dim=1).squeeze(0)
prediction = out.cpu().detach().numpy().astype(np.uint8)
# Compute metrics for each class (skip class 0: background)
metric_list = []
for i in range(1, classes):
dice, hd95 = calculate_metric_percase(
pred=(prediction == i),
gt=(label == i),
spacing_z=z_spacing
)
metric_list.append((dice, hd95))
# Optional: Save results as NIfTI
if test_save_path is not None:
img_itk = sitk.GetImageFromArray(image.astype(np.float32))
prd_itk = sitk.GetImageFromArray(prediction.astype(np.uint8))
lab_itk = sitk.GetImageFromArray(label.astype(np.uint8))
# Set spacing: (x, y, z) for SimpleITK
img_itk.SetSpacing((1.0, 1.0, z_spacing))
prd_itk.SetSpacing((1.0, 1.0, z_spacing))
lab_itk.SetSpacing((1.0, 1.0, z_spacing))
sitk.WriteImage(prd_itk, f'{test_save_path}/{case}_pred.nii.gz')
sitk.WriteImage(img_itk, f'{test_save_path}/{case}_img.nii.gz')
sitk.WriteImage(lab_itk, f'{test_save_path}/{case}_gt.nii.gz')
return metric_list
结构如下:
训练阶段:
model → DiceLoss(Part 1) → loss → backward()
测试阶段:
test_single_volume(Part 3)
│
├─ 逐 slice 推理(模型前向)
│
└─ 对每个器官调用 calculate_metric_percase(Part 2)
│
├─ 计算 Dice(用 medpy)
└─ 计算 HD95(用 medpy + spacing)注:Dice 损失(Dice Loss)和 Dice 系数(Dice Coefficient / Dice Score)密切相关,但本质不同,它们的关系可以概括为:Dice 损失 = 1 − Dice 系数
用途不同
Dice 系数:是一个评价指标(metric),用于衡量模型分割结果与真值的重叠程度。
→ 用在 test_single_volume 中,报告“模型表现好不好”。
Dice 损失:是一个损失函数(loss function),用于指导模型训练。
→ 用在 train.py 中,告诉模型“往哪个方向更新参数”。
输入形式不同
Dice 系数(评估时):
输入必须是二值化的硬分割结果(如 pred = (output > 0.5) 或 argmax 后的整数图)。
Dice 损失(训练时):
输入是连续的概率值(通常经过 softmax/sigmoid),保留梯度信息。
代码讲解
utils.py 中,Dice 和 HD95 的计算发生在测试阶段,由以下两个函数协作完成:
(1)test_single_volume:对一个 3D 医学图像(如 CT)进行 slice-by-slice 推理,生成完整 3D 预测。
(2)calculate_metric_percase:对每个器官类别(如肝脏、脾脏)分别计算 Dice 和 HD95。
calculate_metric_percase
给定一个器官的 3D 预测和真值,安全、准确地计算出它在“区域重叠”(Dice)和“边界精度”(HD95,单位 mm)上的表现。
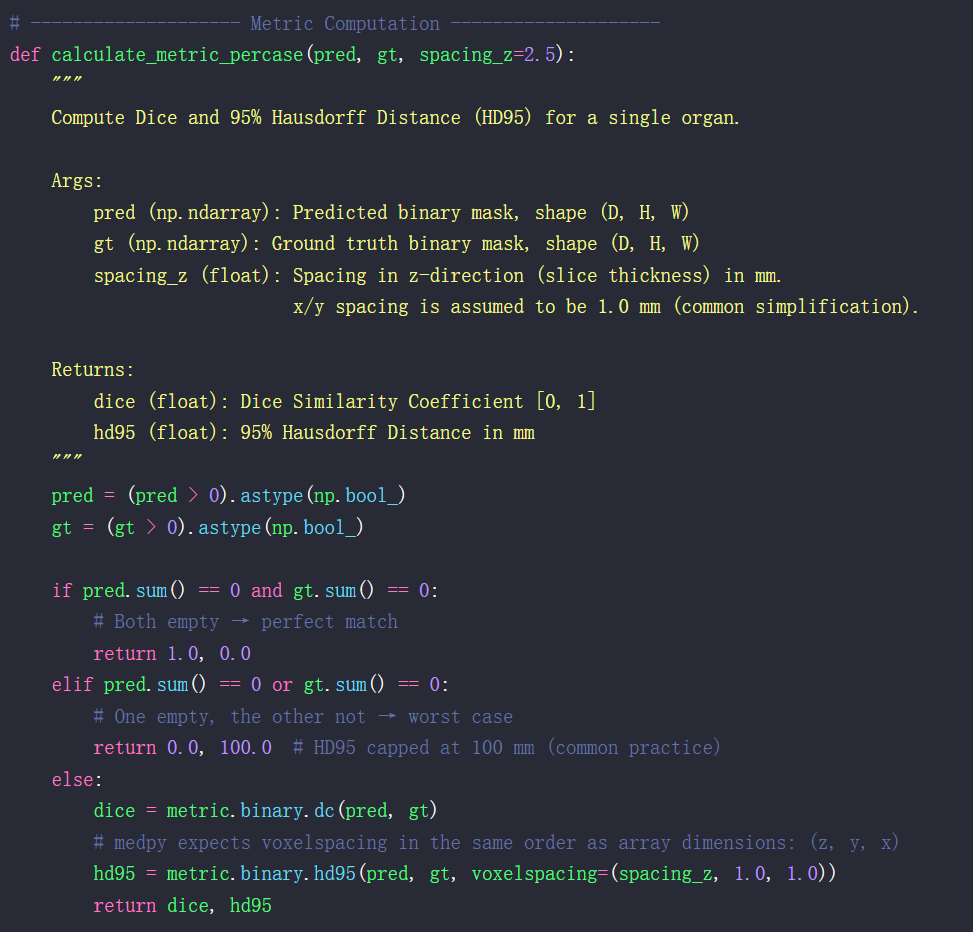
第 1 步:二值化处理
pred = (pred > 0).astype(np.bool_)
gt = (gt > 0).astype(np.bool_)确保输入是布尔型(True/False),这是 medpy 的要求。即使输入是整数标签(如 0/1),也显式转为 bool。
第 2 步:处理极端情况(避免崩溃)
if pred.sum() == 0 and gt.sum() == 0:
return 1.0, 0.0 # 都没这个器官 → 完美
elif pred.sum() == 0 or gt.sum() == 0:
return 0.0, 100.0 # 一个有,一个没有 → 最差如果不做这个判断,当预测或真值全为 0 时,medpy 会报错或返回无效值(如 inf)。这是医学图像中常见情况(某些器官可能缺失或未标注)。
第 3 步:计算 Dice 系数
dice = metric.binary.dc(pred, gt)第 4 步:计算 HD95(边界精度)
hd95 = metric.binary.hd95(pred, gt, voxelspacing=(spacing_z, 1.0, 1.0))参数:
pred:模型预测的该器官的 3D 二值掩码(shape: (D, H, W),值为 True/False 或 0/1)
gt:医生标注的该器官的 3D 真实掩码(同样 shape 和类型)
spacing_z:CT/MRI 切片在 z 轴(层厚)的物理间距,单位 mm(例如 2.5 mm)
voxelspacing:
medpy 要求 voxelspacing 的顺序与数组维度一致。如果 pred 和 gt 是 (D, H, W),对应:
D → z 轴(切片方向)
H → y 轴
W → x 轴
所以 voxelspacing=(z_spacing, y_spacing, x_spacing) = (spacing_z, 1.0, 1.0)
为什么 x 与 y 是 1.0?
在很多公开数据集(如 Synapse multi-organ CT)中,原始图像的 x/y 分辨率接近 1mm,而 z 间距变化较大(如 2.5mm、5mm)。为简化,常假设 x/y=1.0,只校正 z 方向。
内部原理(由 medpy 实现)
medpy.metric.binary.hd95 内部执行以下操作:
提取前景点坐标:
pred_points = np.argwhere(pred) # shape: (N, 3)
gt_points = np.argwhere(gt) # shape: (M, 3)将像素坐标转换为物理坐标(mm):
pred_points_mm = pred_points * np.array([spacing_z, 1.0, 1.0])
gt_points_mm = gt_points * np.array([spacing_z, 1.0, 1.0])计算双向最近距离:
对每个 pred_point,找最近的 gt_point → 得到 N 个距离
对每个 gt_point,找最近的 pred_point → 得到 M 个距离
合并所有距离,取 95% 分位数:
all_distances = np.concatenate([dist_pred_to_gt, dist_gt_to_pred])
hd95 = np.percentile(all_distances, 95)medpy.metric.binary.hd95 内部操作可能不好理解,下面是通俗理解的例子,可以试着看一下。
| 概念 | 通俗理解 |
|---|---|
| 图像数组 (D, H, W) | 一本 CT 相册:D 页,每页 H 行 W 列 |
| voxelspacing | 告诉你:翻一页走多远(z),一行=几毫米(y),一列=几毫米(x) |
| 坐标转换 | 把“第几页第几行第几列” → 换算成“多少毫米”的真实位置 |
| HD95 计算 | 看预测和真实的器官边界,95% 的地方最大差多少毫米 |
| 为什么用 95% | 防止一个“手抖画错”的点毁掉整个评分 |




















 1030
1030

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








