注:本文更偏向于作者的学习记录,有些内容描述可能有误,请见谅。
关于nnunet的使用可以看博主的这篇文章:
下面的内容均是基于nnunetv1以及3d Synapse(BTCV)数据集,但是与代码整体逻辑讲解关系不大。下面就nnunet框架的几个重要的部分进行讲解。
数据预处理与plan生成
这是 nnU-Net 自动化 pipeline 的核心第一步,分为两个阶段:planning(规划) + preprocessing(预处理)。
nnUNet_plan_and_preprocess.py代码如下:
# Copyright 2020 Division of Medical Image Computing, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import nnunet
from batchgenerators.utilities.file_and_folder_operations import *
from nnunet.experiment_planning.DatasetAnalyzer import DatasetAnalyzer
from nnunet.experiment_planning.utils import crop
from nnunet.paths import *
import shutil
from nnunet.utilities.task_name_id_conversion import convert_id_to_task_name
from nnunet.preprocessing.sanity_checks import verify_dataset_integrity
from nnunet.training.model_restore import recursive_find_python_class
def main():
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("-t", "--task_ids", nargs="+", help="List of integers belonging to the task ids you wish to run"
" experiment planning and preprocessing for. Each of these "
"ids must, have a matching folder 'TaskXXX_' in the raw "
"data folder")
parser.add_argument("-pl3d", "--planner3d", type=str, default="ExperimentPlanner3D_v21",
help="Name of the ExperimentPlanner class for the full resolution 3D U-Net and U-Net cascade. "
"Default is ExperimentPlanner3D_v21. Can be 'None', in which case these U-Nets will not be "
"configured")
parser.add_argument("-pl2d", "--planner2d", type=str, default="ExperimentPlanner2D_v21",
help="Name of the ExperimentPlanner class for the 2D U-Net. Default is ExperimentPlanner2D_v21. "
"Can be 'None', in which case this U-Net will not be configured")
parser.add_argument("-no_pp", action="store_true",
help="Set this flag if you dont want to run the preprocessing. If this is set then this script "
"will only run the experiment planning and create the plans file")
parser.add_argument("-tl", type=int, required=False, default=8,
help="Number of processes used for preprocessing the low resolution data for the 3D low "
"resolution U-Net. This can be larger than -tf. Don't overdo it or you will run out of "
"RAM")
parser.add_argument("-tf", type=int, required=False, default=8,
help="Number of processes used for preprocessing the full resolution data of the 2D U-Net and "
"3D U-Net. Don't overdo it or you will run out of RAM")
parser.add_argument("--verify_dataset_integrity", required=False, default=False, action="store_true",
help="set this flag to check the dataset integrity. This is useful and should be done once for "
"each dataset!")
parser.add_argument("-overwrite_plans", type=str, default=None, required=False,
help="Use this to specify a plans file that should be used instead of whatever nnU-Net would "
"configure automatically. This will overwrite everything: intensity normalization, "
"network architecture, target spacing etc. Using this is useful for using pretrained "
"model weights as this will guarantee that the network architecture on the target "
"dataset is the same as on the source dataset and the weights can therefore be transferred.\n"
"Pro tip: If you want to pretrain on Hepaticvessel and apply the result to LiTS then use "
"the LiTS plans to run the preprocessing of the HepaticVessel task.\n"
"Make sure to only use plans files that were "
"generated with the same number of modalities as the target dataset (LiTS -> BCV or "
"LiTS -> Task008_HepaticVessel is OK. BraTS -> LiTS is not (BraTS has 4 input modalities, "
"LiTS has just one)). Also only do things that make sense. This functionality is beta with"
"no support given.\n"
"Note that this will first print the old plans (which are going to be overwritten) and "
"then the new ones (provided that -no_pp was NOT set).")
parser.add_argument("-overwrite_plans_identifier", type=str, default=None, required=False,
help="If you set overwrite_plans you need to provide a unique identifier so that nnUNet knows "
"where to look for the correct plans and data. Assume your identifier is called "
"IDENTIFIER, the correct training command would be:\n"
"'nnUNet_train CONFIG TRAINER TASKID FOLD -p nnUNetPlans_pretrained_IDENTIFIER "
"-pretrained_weights FILENAME'")
args = parser.parse_args()
task_ids = args.task_ids
dont_run_preprocessing = args.no_pp
tl = args.tl
tf = args.tf
planner_name3d = args.planner3d
planner_name2d = args.planner2d
if planner_name3d == "None":
planner_name3d = None
if planner_name2d == "None":
planner_name2d = None
if args.overwrite_plans is not None:
if planner_name2d is not None:
print("Overwriting plans only works for the 3d planner. I am setting '--planner2d' to None. This will "
"skip 2d planning and preprocessing.")
assert planner_name3d == 'ExperimentPlanner3D_v21_Pretrained', "When using --overwrite_plans you need to use " \
"'-pl3d ExperimentPlanner3D_v21_Pretrained'"
# we need raw data
tasks = []
for i in task_ids:
i = int(i)
task_name = convert_id_to_task_name(i)
if args.verify_dataset_integrity:
verify_dataset_integrity(join(nnUNet_raw_data, task_name))
crop(task_name, False, tf)
tasks.append(task_name)
search_in = join(nnunet.__path__[0], "experiment_planning")
if planner_name3d is not None:
planner_3d = recursive_find_python_class([search_in], planner_name3d, current_module="nnunet.experiment_planning")
if planner_3d is None:
raise RuntimeError("Could not find the Planner class %s. Make sure it is located somewhere in "
"nnunet.experiment_planning" % planner_name3d)
else:
planner_3d = None
if planner_name2d is not None:
planner_2d = recursive_find_python_class([search_in], planner_name2d, current_module="nnunet.experiment_planning")
if planner_2d is None:
raise RuntimeError("Could not find the Planner class %s. Make sure it is located somewhere in "
"nnunet.experiment_planning" % planner_name2d)
else:
planner_2d = None
for t in tasks:
print("\n\n\n", t)
cropped_out_dir = os.path.join(nnUNet_cropped_data, t)
preprocessing_output_dir_this_task = os.path.join(preprocessing_output_dir, t)
#splitted_4d_output_dir_task = os.path.join(nnUNet_raw_data, t)
#lists, modalities = create_lists_from_splitted_dataset(splitted_4d_output_dir_task)
# we need to figure out if we need the intensity propoerties. We collect them only if one of the modalities is CT
dataset_json = load_json(join(cropped_out_dir, 'dataset.json'))
modalities = list(dataset_json["modality"].values())
collect_intensityproperties = True if (("CT" in modalities) or ("ct" in modalities)) else False
dataset_analyzer = DatasetAnalyzer(cropped_out_dir, overwrite=False, num_processes=tf) # this class creates the fingerprint
_ = dataset_analyzer.analyze_dataset(collect_intensityproperties) # this will write output files that will be used by the ExperimentPlanner
maybe_mkdir_p(preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
shutil.copy(join(cropped_out_dir, "dataset_properties.pkl"), preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
shutil.copy(join(nnUNet_raw_data, t, "dataset.json"), preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
threads = (tl, tf)
print("number of threads: ", threads, "\n")
if planner_3d is not None:
if args.overwrite_plans is not None:
assert args.overwrite_plans_identifier is not None, "You need to specify -overwrite_plans_identifier"
exp_planner = planner_3d(cropped_out_dir, preprocessing_output_dir_this_task, args.overwrite_plans,
args.overwrite_plans_identifier)
else:
exp_planner = planner_3d(cropped_out_dir, preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
exp_planner.plan_experiment()
if not dont_run_preprocessing: # double negative, yooo
exp_planner.run_preprocessing(threads)
if planner_2d is not None:
exp_planner = planner_2d(cropped_out_dir, preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
exp_planner.plan_experiment()
if not dont_run_preprocessing: # double negative, yooo
exp_planner.run_preprocessing(threads)
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
代码整个流程分为两大阶段:
(1)Crop(裁剪):去除图像中的全零边界(空白区域)
(2)Analyze + Plan + Preprocess:
分析数据统计特性(DatasetAnalyzer)
生成网络配置计划 plans.pkl
执行实际预处理(重采样、归一化等)
第一部分:导入与参数解析
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("-t", "--task_ids", nargs="+", ...)
parser.add_argument("-pl3d", "--planner3d", default="ExperimentPlanner3D_v21")
parser.add_argument("-pl2d", "--planner2d", default="ExperimentPlanner2D_v21")
parser.add_argument("-no_pp", action="store_true") # 只 plan,不 preprocess
parser.add_argument("-tl", type=int, default=8) # low-res 预处理线程数
parser.add_argument("-tf", type=int, default=8) # full-res 预处理线程数
...
args = parser.parse_args()| 参数 | 命令行写法 | 作用 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
-t / --task_ids | -t 500 或 -t 100 101 | 指定要处理的一个或多个任务 ID | 必须提供 |
-pl3d / --planner3d | -pl3d ExperimentPlanner3D_v21 | 指定用于 3D 模型的规划器类名 | "ExperimentPlanner3D_v21" |
-pl2d / --planner2d | -pl2d ExperimentPlanner2D_v21 | 指定用于 2D 模型的规划器类名 | "ExperimentPlanner2D_v21" |
-no_pp | -no_pp | 只做实验规划(生成 plans.pkl),不做预处理(不生成 .npy) | False(默认会做预处理) |
-tl | -tl 4 | 用于 low-resolution 阶段(如 cascade 中的低分辨率 U-Net)的预处理线程数 | 8 |
-tf | -tf 6 | 用于 full-resolution 阶段(3D fullres / 2D)的预处理线程数 | 8 |
我使用的命令:
nnUNet_plan_and_preprocess -t 500 -tl 8 处理 Task500
使用默认 planner(3D v21 + 2D v21)
-tl 8 覆盖了 low-res 线程数为 8
-tf 没指定 → 用默认值 8
会执行 crop + analyze + plan + preprocess
第二部分:任务名称转换与数据完整性检查
# we need raw data
tasks = []
for i in task_ids:
i = int(i)
task_name = convert_id_to_task_name(i)
if args.verify_dataset_integrity:
verify_dataset_integrity(join(nnUNet_raw_data, task_name))
crop(task_name, False, tf)
tasks.append(task_name)for:
for i in task_ids:task_ids: 来自命令行参数 -t(例如 -t 500 501),一个字符串列表(因为 argparse 默认读成 str),比如 ["500", "501"]
循环变量 i :每个任务 ID 的字符串形式
i = int(i):把字符串转为整数(如 "500" → 500),后续函数(如 convert_id_to_task_name)要求输入是 int
convert_id_to_task_name:根据 nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/ 下的文件夹名反推任务名(将数字 ID 转为实际的任务文件夹名)。
例如:
i = 500 → task_name = "Task500_Synapse"
i = 100 → task_name = "Task100_MyDataset"
这个映射依赖于 nnUNet_raw_data 目录下的文件夹命名规范:必须是 TaskXXX_Name 格式
verify_dataset_integrity:检查 imagesTr/, labelsTr/ 是否一一对应,dataset.json 是否合法
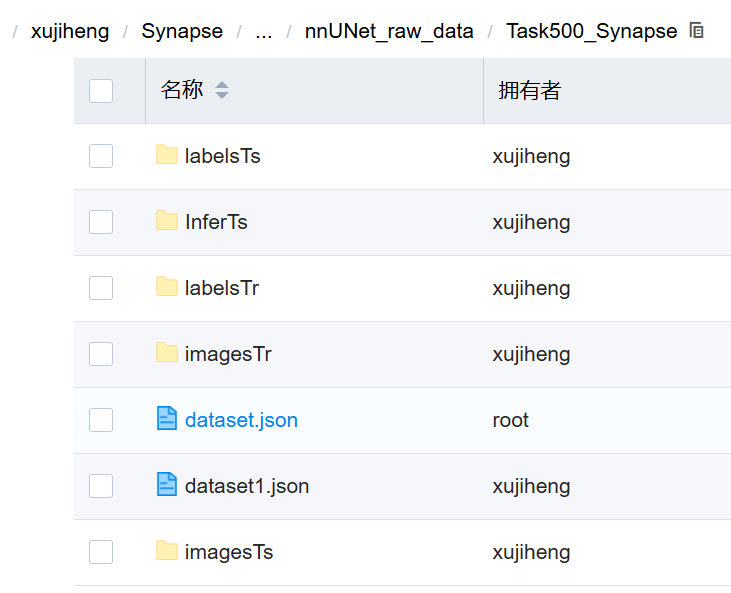
注:dataset.json 是 nnUNet 数据集的元数据配置文件,用于定义数据结构、模态、标签语义和样本路径,在数据验证(verify_dataset_integrity)、规划(planning)和预处理阶段被读取使用。
我的synapse的dataset.json:
{
"name": "SYNAPSE",
"description": "Synapse transitional zone and peripheral zone segmentation",
"reference": "Radboud University, Nijmegen Medical Centre",
"licence": "CC-BY-SA 4.0",
"release": "1.0 04/05/2018",
"tensorImageSize": "3D",
"modality": {
"0": "CT"
},
"labels": {
"0": "background",
"1": "Aorta",
"2": "Gallbladder",
"3": "Kidney(L)",
"4": "Kidney(R)",
"5": "Liver",
"6": "Pancreas",
"7": "Spleen",
"8": "Stomach"
},
"numTraining": 18,
"numTest": 12,
"training": [
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0005.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0005.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0006.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0006.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0007.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0007.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0009.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0009.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0010.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0010.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0021.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0021.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0023.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0023.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0024.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0024.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0026.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0026.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0027.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0027.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0028.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0028.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0030.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0030.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0031.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0031.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0033.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0033.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0034.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0034.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0037.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0037.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0039.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0039.nii.gz"
},
{
"image": "./imagesTr/img0040.nii.gz",
"label": "./labelsTr/img0040.nii.gz"
}
],
"test": [
"./imagesTs/img0001.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0002.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0003.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0004.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0008.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0022.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0025.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0029.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0032.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0035.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0036.nii.gz",
"./imagesTs/img0038.nii.gz"
]
}
标准的dataset.json schema(nnunet v1),用于描述医学图像分割任务:
{
"name": "...",
"description": "...",
"reference": "...",
"licence": "...",
"release": "...",
"tensorImageSize": "3D",
"modality": { ... },
"labels": { ... },
"numTraining": N,
"numTest": M,
"training": [ ... ],
"test": [ ... ]
}下面的表格是对每个字段的解释:
| 字段名称 | 示例值/格式 | 重要性说明 | 对应检查或使用场景 |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | "SYNAPSE" | 数据集的名称,用于标识。 | 在数据集管理和展示时使用,不影响功能。 |
| description | "Synapse transitional zone..." | 数据集的描述信息。 | 提供背景信息,便于理解和引用,不影响功能。 |
| reference | "Radboud University, Nijmegen..." | 数据来源或参考文献。 | 同样提供背景信息,对于学术引用很重要。 |
| licence | "CC-BY-SA 4.0" | 数据集使用的许可证类型。 | 明确数据使用的法律条款,对数据共享和再利用至关重要。 |
| release | "1.0 04/05/2018" | 数据集版本号及发布日期。 | 标识数据集的不同版本,有助于跟踪更新和改进。 |
| tensorImageSize | "3D" | 指定图像数据是三维还是二维。 | 影响预处理流程的选择(如3D vs 2D)。 |
| modality | {"0": "CT"} | 定义输入图像的模态类型,键为通道索引,值为模态名称。 | 决定了归一化策略等预处理步骤。 |
| labels | {"0": "background", ..., "8": "Stomach"} | 定义类别标签及其对应的语义含义,必须从0开始连续编号。 | 确保训练和评估过程中正确解析标签信息。 |
| numTraining | 18 | 声明训练样本的数量。 | 验证与实际提供的训练样本数量是否一致。 |
| numTest | 12 | 声明测试样本的数量。 | 验证与实际提供的测试样本数量是否一致。 |
| training | [{ "image": "...img0005.nii.gz", "label": "...img0005.nii.gz"}, ...] | 列出所有训练样本的image-label配对路径。 | 验证文件存在性、空间维度一致性、标签值范围合法性等。 |
| test | ["...img0001.nii.gz", "...img0002.nii.gz", ...] | 列出所有测试样本的路径(只有image,没有label)。 | 验证文件存在性。 |
执行 Crop(关键一步!)
crop(task_name, False, tf)调用函数:nnunet/experiment_planning/utils.py → crop()
作用:对每个训练样本,裁剪掉全零的边界(减少无效计算)
输入:
原始图像:./imagesTr/case_0000.nii.gz
标签:./labelsTr/case.nii.gz
输出:
裁剪后图像/标签 → 存入 nnUNet_cropped_data/Task500_Synapse/;同时保留 bbox(bounding box)信息,用于后续还原预测结果
对于 Synapse(腹部 CT),通常上下有很多黑边,crop 能显著减小体积。
第三部分:动态加载 Planner 类
planner_3d = recursive_find_python_class([search_in], planner_name3d, ...)recursive_find_python_class:在 nnunet/experiment_planning/ 目录下查找名为 ExperimentPlanner3D_v21 的类。
这是一种插件式设计,允许用户自定义 planner,灵活切换不同的规划策略(如 v21 vs v22 vs 自定义)。
第四部分:主循环 —— 对每个任务执行分析与规划
for t in tasks:
cropped_out_dir = join(nnUNet_cropped_data, t)
preprocessing_output_dir_this_task = join(preprocessing_output_dir, t)Step 1: 判断是否需要收集强度属性(Intensity Properties)
modalities = list(dataset_json["modality"].values())
collect_intensityproperties = True if (("CT" in modalities) or ("ct" in modalities)) else FalseCT 数据:需要统计全局 intensity(如 -1000~1000 HU),用于窗宽窗位归一化。
MRI 数据:按 case 归一化(z-score),不需要全局统计。
Step 2: 实例化 DatasetAnalyzer 并分析数据
dataset_analyzer = DatasetAnalyzer(cropped_out_dir, overwrite=False, num_processes=tf)
_ = dataset_analyzer.analyze_dataset(collect_intensityproperties)关键类:nnunet/experiment_planning/DatasetAnalyzer.py
功能:遍历所有训练样本,计算以下统计量并保存为 dataset_properties.pkl:
| 统计量 | 说明 |
|---|---|
all_sizes | 每个样本的空间尺寸(如 [128, 128, 64]) |
all_spacings | 每个样本的 voxel spacing(如 [1.0, 1.0, 2.5]) |
intensityproperties | (仅 CT)全局均值、标准差、分位数(用于归一化) |
然后脚本将其复制到预处理目录:
shutil.copy(join(cropped_out_dir, "dataset_properties.pkl"), preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
shutil.copy(join(nnUNet_raw_data, t, "dataset.json"), preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)Step 3: 实例化 ExperimentPlanner 执行 plan + preprocess
exp_planner = planner_3d(cropped_out_dir, preprocessing_output_dir_this_task)
exp_planner.plan_experiment()
if not dont_run_preprocessing:
exp_planner.run_preprocessing(threads)ExperimentPlanner3D_v21 等规划器在 plan_experiment() 阶段完成的关键任务:
| 功能 | 说明 | 为什么重要 |
|---|---|---|
| 分析图像空间属性 | 统计所有训练样本的: • voxel spacing(如 [0.8, 0.8, 2.5] mm) • 各向异性程度 • 图像尺寸分布 | 决定是否需要重采样、是否使用 transpose U-Net(处理厚层CT) |
| 确定目标 spacing | 自动选择一个统一的 target spacing(如各向同性 1.5mm)用于后续重采样 | 平衡计算效率与细节保留;避免因原始spacing差异导致训练不稳定 |
| 计算典型 patch size | 基于器官大小和 GPU 显存估算最大可行 patch(如 [128,128,128]) | patch 太小 → 感受野不足;太大 → batch size=1 或 OOM |
| 设计网络拓扑结构 | 推导 encoder/decoder 层数、卷积核数量(基于 patch size 和 spacing) | 确保网络能有效下采样到合理 bottleneck 尺寸(通常 ≥4) |
| 设置 normalization 方式 | 根据 modality(CT/MR)选择: • CT: 固定窗宽窗位 [-1000, 1000] • MR: per-case 0.5%~99.5% 百分位归一化 | 保证输入分布稳定,提升泛化能力 |
| 定义数据增强策略 | 推荐旋转范围、缩放比例、弹性形变强度等(写入 plans 文件) | 增强需匹配图像物理特性(如 CT 不应做 intensity augment) |
| 生成 plans.pkl 文件 | 将上述所有决策保存为 nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans_3D.pkl | 预处理和训练阶段都依赖此文件,确保一致性 |
注:这个 .pkl 文件就是后续训练时 nnUNetTrainerV2 的“蓝图”。
run_preprocessing(threads) 做了什么?
调用:self.preprocessor.run() → 实际是 GenericPreprocessor.run()
位于:nnunet/preprocessing/preprocessing.py
预处理步骤:
(1)重采样(Resample):
图像:用三线性插值 → 目标 spacing
标签:用最近邻插值(避免产生新类别)
(2)强度归一化(Normalize):
CT:(image - clip_min) / (clip_max - clip_min),clip 范围由 intensityproperties 决定(如 0.5% ~ 99.5% 分位数)
MRI:(image - mean) / std(per-case)
(3)保存为 .npy:
图像:case_0000.npy(float32)
标签:case_0000_seg.npy(int16)
存放路径:nnUNet_preprocessed/Task500_Synapse/nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_stage0/
注:使用 .npy 是为了训练时快速加载(比 NIfTI 快 10 倍以上)。
预处理后生成文件:
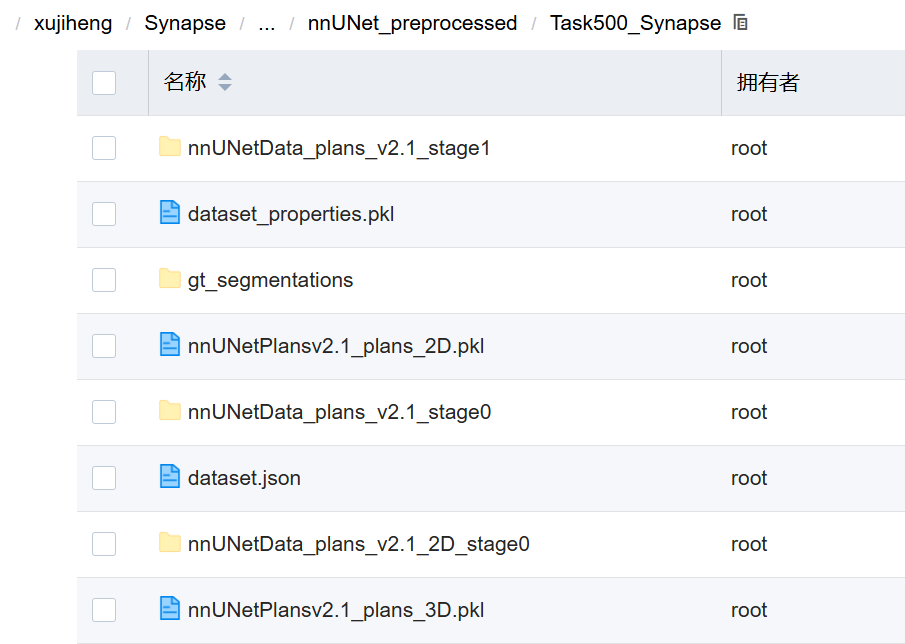
| 名称 | 类型 | 是否为预处理结果? | 作用 |
|---|---|---|---|
nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_stage1/ | 文件夹 | 是 | 存放 3D high-res 模型用的数据(如果启用了 cascade) |
dataset_properties.pkl | .pkl | 是 | 记录整个数据集的统计特性(spacing、mean/std、intensity range 等) |
gt_segmentations/ | 文件夹 | 是 | 存放原始标注(ground truth)的 .nii.gz 文件(未处理版本) |
nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans_2D.pkl | .pkl | 是 | 2D 模型的规划配置(patch size, normalization, etc.) |
nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_stage0/ | 文件夹 | 是 | 存放 3D low-res 模型用的数据(所有模型都依赖它) |
dataset.json | .json | 是 | 原始元数据(labels, modality)的副本,保持一致性 |
nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_2D_stage0/ | 文件夹 | 是 | 存放 2D U-Net 模型用的数据 |
nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans_3D.pkl | .pkl | 是 | 3D 模型的规划配置(核心参数来源) |
注:Cascade(级联)是 nnUNet 中一种用于提升分割精度的两阶段训练策略,特别适用于目标结构尺度变化大、细节要求高的医学图像分割任务(比如腹部多器官 CT 分割)。
Cascade 的工作流程
第一阶段:3d_lowres(低分辨率模型)
输入:将原始图像下采样到较低分辨率(如各向同性 3mm)
patch size:较小(如 [64,64,64])
输出:一个粗糙但覆盖全局的分割结果
保存为:nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_stage0/ 中的数据
模型输出:概率图(soft prediction)
第二阶段:3d_cascade_fullres(高分辨率级联模型)
输入:原始高分辨率图像 + 第一阶段的概率图(作为额外通道)
patch size:较大(如 [128,128,64])
网络输入通道数:原模态数 + num_classes
(例如 CT 是 1 通道 + 9 类 = 10 通道)
目标:修正第一阶段的错误,细化边界
使用数据:nnUNetData_plans_v2.1_stage1/
注:第二阶段不是从头训练,而是以第一阶段模型权重为初始化,进行微调(fine-tune)。
训练(重点!)
训练的代码是run_training.py。
第一部分:导入与函数定义
import argparse
from batchgenerators.utilities.file_and_folder_operations import *
from nnunet.run.default_configuration import get_default_configuration
from nnunet.paths import default_plans_identifier
from nnunet.run.load_pretrained_weights import load_pretrained_weights
from nnunet.training.cascade_stuff.predict_next_stage import predict_next_stage
from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainer import nnUNetTrainer
from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainerCascadeFullRes import nnUNetTrainerCascadeFullRes
from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainerV2_CascadeFullRes import nnUNetTrainerV2CascadeFullRes
from nnunet.utilities.task_name_id_conversion import convert_id_to_task_name这里讲一下,如果后续要使用nnunet框架的话,这些import语句是否要变动:
| Import 语句 | 是否影响模型替换 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
argparse | ❌ 否 | 命令行解析,无关 |
file_and_folder_operations | ❌ 否 | 工具函数 |
get_default_configuration | ⚠️ 间接相关 | 需确保你的 Trainer 能被正确加载 |
default_plans_identifier | ❌ 否 | plans 配置,不影响网络结构 |
load_pretrained_weights | ❌ 否 | 只管加载权重 |
predict_next_stage | ⚠️ 仅 cascade 时相关 | 若用 cascade,需确保你的模型输出能被正确保存/读取 |
| Trainer 类导入 | ✅ 核心! | 你需要继承它们,并重写 initialize_network() |
其中可能要改动的:
导入各种 Trainer 类
from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainer import nnUNetTrainer
from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainerCascadeFullRes import nnUNetTrainerCascadeFullRes
from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainerV2_CascadeFullRes import nnUNetTrainerV2CascadeFullRes作用:
这些是训练器(Trainer)类,封装了完整的训练逻辑,这些类会被 get_default_configuration 动态选择并实例化:
数据加载
网络构建(self.network = self.build_network_architecture())
损失函数
优化器
验证、保存、学习率调度等
其中:
nnUNetTrainer:原始 v1 版本
nnUNetTrainerV2_CascadeFullRes:v2 改进版,支持 cascade + 更好默认设置
替换网络模型正确做法:
继承 nnUNetTrainerV2(或类似)并重写网络构建方法,新建一个 Python 文件,比如 nnunet/training/network_training/MyCustomTrainer.py,继承 nnUNetTrainerV2(推荐)。
default_configuration.py
代码如下:
# Copyright 2020 Division of Medical Image Computing, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import nnunet
from nnunet.paths import network_training_output_dir, preprocessing_output_dir, default_plans_identifier
from batchgenerators.utilities.file_and_folder_operations import *
from nnunet.experiment_planning.summarize_plans import summarize_plans
from nnunet.training.model_restore import recursive_find_python_class
def get_configuration_from_output_folder(folder):
# split off network_training_output_dir
folder = folder[len(network_training_output_dir):]
if folder.startswith("/"):
folder = folder[1:]
configuration, task, trainer_and_plans_identifier = folder.split("/")
trainer, plans_identifier = trainer_and_plans_identifier.split("__")
return configuration, task, trainer, plans_identifier
def get_default_configuration(network, task, network_trainer, plans_identifier=default_plans_identifier,
search_in=(nnunet.__path__[0], "training", "network_training"),
base_module='nnunet.training.network_training'):
assert network in ['2d', '3d_lowres', '3d_fullres', '3d_cascade_fullres'], \
"network can only be one of the following: \'2d\', \'3d_lowres\', \'3d_fullres\', \'3d_cascade_fullres\'"
dataset_directory = join(preprocessing_output_dir, task)
if network == '2d':
plans_file = join(preprocessing_output_dir, task, plans_identifier + "_plans_2D.pkl")
else:
plans_file = join(preprocessing_output_dir, task, plans_identifier + "_plans_3D.pkl")
plans = load_pickle(plans_file)
possible_stages = list(plans['plans_per_stage'].keys())
if (network == '3d_cascade_fullres' or network == "3d_lowres") and len(possible_stages) == 1:
raise RuntimeError("3d_lowres/3d_cascade_fullres only applies if there is more than one stage. This task does "
"not require the cascade. Run 3d_fullres instead")
if network == '2d' or network == "3d_lowres":
stage = 0
else:
stage = possible_stages[-1]
trainer_class = recursive_find_python_class([join(*search_in)], network_trainer,
current_module=base_module)
output_folder_name = join(network_training_output_dir, network, task, network_trainer + "__" + plans_identifier)
print("###############################################")
print("I am running the following nnUNet: %s" % network)
print("My trainer class is: ", trainer_class)
print("For that I will be using the following configuration:")
summarize_plans(plans_file)
print("I am using stage %d from these plans" % stage)
if (network == '2d' or len(possible_stages) > 1) and not network == '3d_lowres':
batch_dice = True
print("I am using batch dice + CE loss")
else:
batch_dice = False
print("I am using sample dice + CE loss")
print("\nI am using data from this folder: ", join(dataset_directory, plans['data_identifier']))
print("###############################################")
return plans_file, output_folder_name, dataset_directory, batch_dice, stage, trainer_class
一般不用更改这个代码,逻辑不涉及网络架构,只做路径、配置、流程控制:
plans_file 路径构建(_plans_2D.pkl / _plans_3D.pkl)
stage 的选择逻辑(3d_lowres → stage 0,3d_fullres → 最后 stage)
batch_dice 的判断(基于是否多 stage 或 2D)
output_folder_name 的命名规则
summarize_plans 打印信息
第二部分:命令行参数解析
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument("network")
parser.add_argument("network_trainer")
parser.add_argument("task", help="can be task name or task id")
parser.add_argument("fold", help='0, 1, ..., 5 or \'all\'')
parser.add_argument("-val", "--validation_only", help="use this if you want to only run the validation",
action="store_true")
parser.add_argument("-c", "--continue_training", help="use this if you want to continue a training",
action="store_true")
parser.add_argument("-p", help="plans identifier. Only change this if you created a custom experiment planner",
default=default_plans_identifier, required=False)
parser.add_argument("--use_compressed_data", default=False, action="store_true",
help="If you set use_compressed_data, the training cases will not be decompressed. Reading compressed data "
"is much more CPU and RAM intensive and should only be used if you know what you are "
"doing", required=False)
parser.add_argument("--deterministic",
help="Makes training deterministic, but reduces training speed substantially. I (Fabian) think "
"this is not necessary. Deterministic training will make you overfit to some random seed. "
"Don't use that.",
required=False, default=False, action="store_true")
parser.add_argument("--npz", required=False, default=False, action="store_true", help="if set then nnUNet will "
"export npz files of "
"predicted segmentations "
"in the validation as well. "
"This is needed to run the "
"ensembling step so unless "
"you are developing nnUNet "
"you should enable this")
parser.add_argument("--find_lr", required=False, default=False, action="store_true",
help="not used here, just for fun")
parser.add_argument("--valbest", required=False, default=False, action="store_true",
help="hands off. This is not intended to be used")
parser.add_argument("--fp32", required=False, default=False, action="store_true",
help="disable mixed precision training and run old school fp32")
parser.add_argument("--val_folder", required=False, default="validation_raw",
help="name of the validation folder. No need to use this for most people")
parser.add_argument("--disable_saving", required=False, action='store_true',
help="If set nnU-Net will not save any parameter files (except a temporary checkpoint that "
"will be removed at the end of the training). Useful for development when you are "
"only interested in the results and want to save some disk space")
parser.add_argument("--disable_postprocessing_on_folds", required=False, action='store_true',
help="Running postprocessing on each fold only makes sense when developing with nnU-Net and "
"closely observing the model performance on specific configurations. You do not need it "
"when applying nnU-Net because the postprocessing for this will be determined only once "
"all five folds have been trained and nnUNet_find_best_configuration is called. Usually "
"running postprocessing on each fold is computationally cheap, but some users have "
"reported issues with very large images. If your images are large (>600x600x600 voxels) "
"you should consider setting this flag.")
parser.add_argument("--disable_validation_inference", required=False, action="store_true",
help="If set nnU-Net will not run inference on the validation set. This is useful if you are "
"only interested in the test set results and want to save some disk space and time.")
# parser.add_argument("--interp_order", required=False, default=3, type=int,
# help="order of interpolation for segmentations. Testing purpose only. Hands off")
# parser.add_argument("--interp_order_z", required=False, default=0, type=int,
# help="order of interpolation along z if z is resampled separately. Testing purpose only. "
# "Hands off")
# parser.add_argument("--force_separate_z", required=False, default="None", type=str,
# help="force_separate_z resampling. Can be None, True or False. Testing purpose only. Hands off")
parser.add_argument('--val_disable_overwrite', action='store_false', default=True,
help='Validation does not overwrite existing segmentations')
parser.add_argument('--disable_next_stage_pred', action='store_true', default=False,
help='do not predict next stage')
parser.add_argument('-pretrained_weights', type=str, required=False, default=None,
help='path to nnU-Net checkpoint file to be used as pretrained model (use .model '
'file, for example model_final_checkpoint.model). Will only be used when actually training. '
'Optional. Beta. Use with caution.')
args = parser.parse_args() 位置参数(无 -) 表示必须提供。
可选参数(有 -) 控制行为细节(如是否验证、是否继续训练等)。
| 参数名 | 命令行形式 | 是否必填 | 默认值 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
"network" | 无(位置参数第1个) | ✅ 是 | 预处理决定了哪些 network 类型是可用的,在训练时选择其中一个。 | 网络类型:2d, 3d_lowres, 3d_fullres, 3d_cascade_fullres |
"network_trainer" | 无(位置参数第2个) | ✅ 是 | — | 训练器类名,如 nnUNetTrainerV2 |
"task" | 无(位置参数第3个) | ✅ 是 | — | 任务ID(如 500)或任务名(如 Task500_Synapse) |
"fold" | 无(位置参数第4个) | ✅ 是 | — | 折数:0–4 或 'all' |
--validation_only / -val | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 仅验证,不训练 |
--continue_training / -c | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 从最近 checkpoint 继续训练 |
--plans_identifier / -p | 可选 | ❌ 否 | "nnUNetPlans" | 预处理计划标识符 |
--use_compressed_data | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 直接读取 .npz 压缩数据(节省磁盘,慢速) |
--deterministic | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 启用确定性模式(可复现,但慢) |
--npz | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 验证时保存 softmax 为 .npz(用于集成) |
--find_lr | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 学习率搜索(作者称“just for fun”) |
--valbest | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 验证时加载 model_best.model |
--fp32 | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 禁用混合精度,使用 FP32 |
--val_folder | 可选 | ❌ 否 | "validation_raw" | 验证结果保存子目录名 |
--disable_saving | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 禁止保存模型(除临时文件) |
--disable_postprocessing_on_folds | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 不对每个 fold 运行后处理 |
--disable_validation_inference | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | 跳过验证集推理 |
--val_disable_overwrite | 可选 | ❌ 否 | True(注意:action='store_false') | 若已存在预测结果,不覆盖 |
--disable_next_stage_pred | 可选 | ❌ 否 | False | (仅用于级联)跳过生成下一阶段输入 |
--pretrained_weights | 可选 | ❌ 否 | None | 指定预训练权重路径(迁移学习) |
训练命令中必须包含的参数(即位置参数)
| 顺序 | 参数含义 | 命令中的值 | 是否必须 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 第1个 | network | 3d_fullres | 必须 |
| 第2个 | network_trainer | nnUNetTrainerV2 | 必须 |
| 第3个 | task | 500 | 必须 |
| 第4个 | fold | all | 必须 |
例如我的命名为Task500_Synapse(数据集)的任务的训练命令如下:
export nnUNet_raw_data_base="/xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_raw" && export nnUNet_preprocessed="/xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_preprocessed" && export RESULTS_FOLDER="/xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_trained_models" && python /xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnunet/run/run_training.py 3d_fullres nnUNetTrainerV2 500 all第三部分:参数标准化
if not task.startswith("Task"):
task_id = int(task)
task = convert_id_to_task_name(task_id)
# e.g., 500 → "Task500_Synapse"
if fold == 'all':
pass
else:
fold = int(fold)确保 task 是标准格式 "TaskXXX_Name"(如"Task500_Synapse");fold='all' 表示训练所有 5 折(用于最终模型集成)。
第四部分:获取默认配置(核心!)
plans_file, output_folder_name, dataset_directory, batch_dice, stage, \
trainer_class = get_default_configuration(network, task, network_trainer, plans_identifier)get_default_configuration 做了什么?(函数在 nnunet/run/default_configuration.py中 )
(1)根据 network 判断是 2D 还是 3D
(2)构造 plans_file 路径(如 .../nnUNetPlansv2.1_plans_3D.pkl)
(3)读取 plans.pkl,检查是否启用 cascade(决定 stage)
(4)动态导入 network_trainer 字符串对应的 Python 类
例如 "nnUNetTrainerV2" → from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainerV2 import nnUNetTrainerV2
(5)返回所有必要信息
!这是 nnUNet 插件化设计的核心:通过字符串名动态加载任意Trainer。
第五部分:Trainer 类型校验(安全检查)
if network == "3d_cascade_fullres":
assert issubclass(trainer_class, (nnUNetTrainerCascadeFullRes, nnUNetTrainerV2CascadeFullRes))
else:
assert issubclass(trainer_class, nnUNetTrainer)(1)防止用户错误地用普通 Trainer 跑 cascade 任务
(2)确保类型安全
第六部分:实例化 Trainer
trainer = trainer_class(plans_file, fold, output_folder=output_folder_name, dataset_directory=dataset_directory,
batch_dice=batch_dice, stage=stage, unpack_data=decompress_data,
deterministic=deterministic,
fp16=run_mixed_precision)参数:
| 参数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
plans_file | 包含 patch size、spacing、normalization 等 |
stage | 0(lowres)或 1(fullres in cascade) |
unpack_data | 是否解压 .npz 数据(节省 RAM vs 节省 CPU) |
fp16 | 是否启用混合精度训练 |
此时网络尚未构建,数据加载器也未创建 —— 这些都在
initialize()中完成。
第七部分:初始化 Trainer
if args.disable_saving:
trainer.save_final_checkpoint = False # 是否保存最终 epoch 的模型(model_final_checkpoint.model)
trainer.save_best_checkpoint = False # 是否保存验证指标最好的模型(model_best.model)
trainer.save_intermediate_checkpoints = True # 是否保存中间检查点(如 checkpoint_latest.model)
trainer.save_latest_only = True # 是否只保留最新的中间检查点(避免存多个)
trainer.initialize(not validation_only)initialize(training=True) 做了什么?(以 nnUNetTrainerV2 为例)
(1)加载 plans → 设置 self.plans
(2)确定输入通道数、类别数
(3)构建网络 → self.network = self.build_network_architecture()
默认是 Generic_UNet
(4)设置 optimizer / lr scheduler
(5)设置数据增强 pipeline
(6)创建 dataloader(训练集 + 验证集)
(7)设置 loss function(通常为 DC+CE)
这是替换网络结构的关键入口点!
第八部分:训练 / 验证主逻辑
情况 1:找学习率(调试用)
if find_lr:
trainer.find_lr()情况 2:正常训练
if not validation_only:
if args.continue_training:
trainer.load_latest_checkpoint() # 继续训练
elif args.pretrained_weights is not None:
load_pretrained_weights(trainer.network, args.pretrained_weights) # 加载预训练
else:
pass # 从头训练
trainer.run_training() # ← 主训练循环!trainer.run_training() :把控制权完全交给 Trainer。下面会紧接着讲解一下trainer,也就是主训练循环流程。
情况 3:仅验证
else:
if valbest: trainer.load_best_checkpoint()
else: trainer.load_final_checkpoint()
trainer.validate(...) # 推理 + 评估第九部分:Cascade 特殊处理
if network == '3d_lowres' and not args.disable_next_stage_pred:
predict_next_stage(trainer, join(dataset_directory, ... "_stage1"))predict_next_stage 做了什么?
(1)用刚训练好的 3d_lowres 模型对训练集 + 验证集做推理
(2)将预测的概率图(softmax 输出)保存为 .npz 文件,这些概率图会在 3d_cascade_fullres 训练时作为额外输入通道
这就是 cascade 的“桥梁”:stage0 的输出 → stage1 的输入
Trainer(最重要!最关键!)
Trainer 是 nnUNet 的核心训练引擎类,所有训练行为都通过 Trainer 实例完成,它封装了:
网络初始化
数据加载(dataloader)
优化器 & 学习率调度
训练循环(epoch + iteration)
验证与指标计算
模型保存与恢复
我的训练命令里指定了nnUNetTrainerV2,对应着nnUNetTrainerV2.py文件,下面就这个代码讲解一下它的流程。
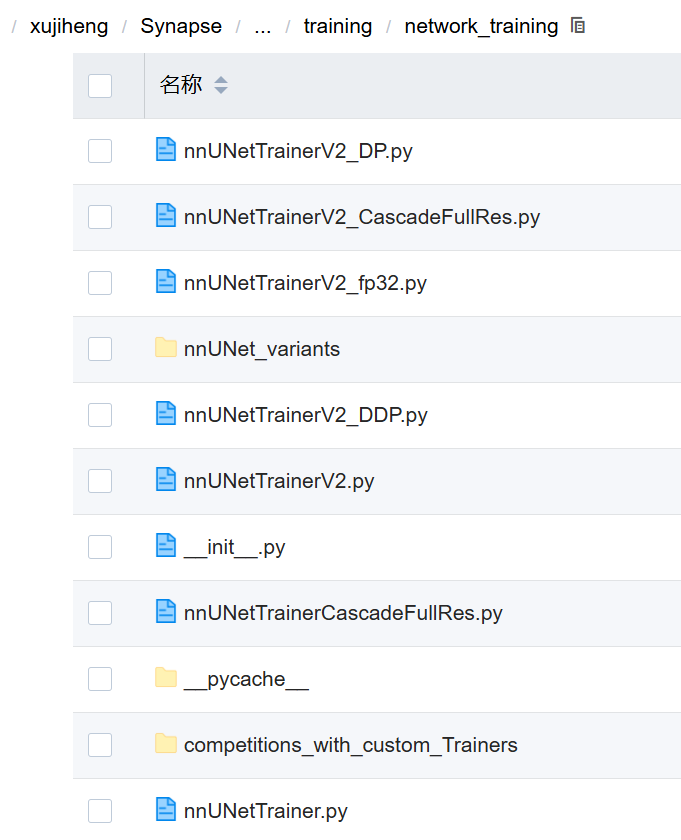
| 文件名 | 类型 | 是否常用 | 作用说明 | 是否可被继承? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
nnUNetTrainer.py | Python 文件 | ❌ 已废弃 | 最早版本的 Trainer,已不再推荐使用 | ❌ 不建议 |
nnUNetTrainerV2.py | 核心文件 | 主要使用 | 当前主流的训练器,支持 3D/2D、FP16、DDP、数据增强等 | 可继承(最常用) |
nnUNetTrainerV2_DP.py | Python 文件 | ⚠️ 较少 | 支持 Data Parallel(DP)模式的 V2 版本 | ✅ 可继承 |
nnUNetTrainerV2_fp32.py | Python 文件 | ⚠️ 较少 | 使用 FP32 精度的 V2 版本(默认是混合精度) | ✅ 可继承 |
nnUNetTrainerV2_DDP.py | Python 文件 | ✅ 中等 | 支持 Distributed Data Parallel(DDP)的 V2 版本。DDP是一种用于分布式训练深度学习模型的技术,它在多个设备(如GPU)上并行化训练过程 | ✅ 可继承 |
nnUNetTrainerV2_CascadeFullRes.py | Python 文件 | ✅ 中等 | 用于 Cascade Training 的 FullRes 阶段(低分辨率训练后继续高分辨率) | ✅ 可继承 |
nnUNetTrainerCascadeFullRes.py | Python 文件 | ✅ 中等 | 旧版 Cascade 的 FullRes 版本(已被新版替代) | ✅ 可继承 |
nnUNet_variants | 文件夹 | ✅ 常见 | 存放各种变体 Trainer(如不同 loss、不同 optimizer) | ✅ 包含多个子类 |
__init__.py | Python 文件 | ✅ 必须 | 使该目录成为 Python 包,允许 from network_training import xxx | ❌ 不需修改 |
__pycache__ | 文件夹 | ❌ 系统生成 | Python 缓存文件,无需关心 | ❌ 不要动 |
competitions_with_custom_Trainers | 文件夹 | ⚠️ 特殊用途 | 一些竞赛专用的自定义 Trainer 示例 | ✅ 可参考 |
_init_.py:
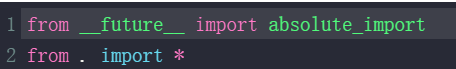
python的绝对导入机制, from . import * 是明确地从当前包中导入所有公开内容,而不会和同名的标准库模块冲突(包就是一个包含 __init__.py 文件的目录)。
下面是nnUNetTrainerV2的代码:
# Copyright 2020 Division of Medical Image Computing, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from collections import OrderedDict
from typing import Tuple
import numpy as np
import torch
from nnunet.training.data_augmentation.data_augmentation_moreDA import get_moreDA_augmentation
from nnunet.training.loss_functions.deep_supervision import MultipleOutputLoss2
from nnunet.utilities.to_torch import maybe_to_torch, to_cuda
from nnunet.network_architecture.generic_UNet import Generic_UNet
from nnunet.network_architecture.initialization import InitWeights_He
from nnunet.network_architecture.neural_network import SegmentationNetwork
from nnunet.training.data_augmentation.default_data_augmentation import default_2D_augmentation_params, \
get_patch_size, default_3D_augmentation_params
from nnunet.training.dataloading.dataset_loading import unpack_dataset
from nnunet.training.network_training.nnUNetTrainer import nnUNetTrainer
from nnunet.utilities.nd_softmax import softmax_helper
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from torch import nn
from torch.cuda.amp import autocast
from nnunet.training.learning_rate.poly_lr import poly_lr
from batchgenerators.utilities.file_and_folder_operations import *
class nnUNetTrainerV2(nnUNetTrainer):
"""
Info for Fabian: same as internal nnUNetTrainerV2_2
"""
def __init__(self, plans_file, fold, output_folder=None, dataset_directory=None, batch_dice=True, stage=None,
unpack_data=True, deterministic=True, fp16=False):
super().__init__(plans_file, fold, output_folder, dataset_directory, batch_dice, stage, unpack_data,
deterministic, fp16)
self.max_num_epochs = 1000
self.initial_lr = 1e-2
self.deep_supervision_scales = None
self.ds_loss_weights = None
self.pin_memory = True
def initialize(self, training=True, force_load_plans=False):
"""
- replaced get_default_augmentation with get_moreDA_augmentation
- enforce to only run this code once
- loss function wrapper for deep supervision
:param training:
:param force_load_plans:
:return:
"""
if not self.was_initialized:
maybe_mkdir_p(self.output_folder)
if force_load_plans or (self.plans is None):
self.load_plans_file()
self.process_plans(self.plans)
self.setup_DA_params()
################# Here we wrap the loss for deep supervision ############
# we need to know the number of outputs of the network
net_numpool = len(self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes)
# we give each output a weight which decreases exponentially (division by 2) as the resolution decreases
# this gives higher resolution outputs more weight in the loss
weights = np.array([1 / (2 ** i) for i in range(net_numpool)])
# we don't use the lowest 2 outputs. Normalize weights so that they sum to 1
mask = np.array([True] + [True if i < net_numpool - 1 else False for i in range(1, net_numpool)])
weights[~mask] = 0
weights = weights / weights.sum()
self.ds_loss_weights = weights
# now wrap the loss
self.loss = MultipleOutputLoss2(self.loss, self.ds_loss_weights)
################# END ###################
self.folder_with_preprocessed_data = join(self.dataset_directory, self.plans['data_identifier'] +
"_stage%d" % self.stage)
if training:
self.dl_tr, self.dl_val = self.get_basic_generators()
if self.unpack_data:
print("unpacking dataset")
unpack_dataset(self.folder_with_preprocessed_data)
print("done")
else:
print(
"INFO: Not unpacking data! Training may be slow due to that. Pray you are not using 2d or you "
"will wait all winter for your model to finish!")
self.tr_gen, self.val_gen = get_moreDA_augmentation(
self.dl_tr, self.dl_val,
self.data_aug_params[
'patch_size_for_spatialtransform'],
self.data_aug_params,
deep_supervision_scales=self.deep_supervision_scales,
pin_memory=self.pin_memory,
use_nondetMultiThreadedAugmenter=False
)
self.print_to_log_file("TRAINING KEYS:\n %s" % (str(self.dataset_tr.keys())),
also_print_to_console=False)
self.print_to_log_file("VALIDATION KEYS:\n %s" % (str(self.dataset_val.keys())),
also_print_to_console=False)
else:
pass
self.initialize_network()
self.initialize_optimizer_and_scheduler()
assert isinstance(self.network, (SegmentationNetwork, nn.DataParallel))
else:
self.print_to_log_file('self.was_initialized is True, not running self.initialize again')
self.was_initialized = True
def initialize_network(self):
"""
- momentum 0.99
- SGD instead of Adam
- self.lr_scheduler = None because we do poly_lr
- deep supervision = True
- i am sure I forgot something here
Known issue: forgot to set neg_slope=0 in InitWeights_He; should not make a difference though
:return:
"""
if self.threeD:
conv_op = nn.Conv3d
dropout_op = nn.Dropout3d
norm_op = nn.InstanceNorm3d
else:
conv_op = nn.Conv2d
dropout_op = nn.Dropout2d
norm_op = nn.InstanceNorm2d
norm_op_kwargs = {'eps': 1e-5, 'affine': True}
dropout_op_kwargs = {'p': 0, 'inplace': True}
net_nonlin = nn.LeakyReLU
net_nonlin_kwargs = {'negative_slope': 1e-2, 'inplace': True}
self.network = Generic_UNet(self.num_input_channels, self.base_num_features, self.num_classes,
len(self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes),
self.conv_per_stage, 2, conv_op, norm_op, norm_op_kwargs, dropout_op,
dropout_op_kwargs,
net_nonlin, net_nonlin_kwargs, True, False, lambda x: x, InitWeights_He(1e-2),
self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes, self.net_conv_kernel_sizes, False, True, True)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
self.network.cuda()
self.network.inference_apply_nonlin = softmax_helper
def initialize_optimizer_and_scheduler(self):
assert self.network is not None, "self.initialize_network must be called first"
self.optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(self.network.parameters(), self.initial_lr, weight_decay=self.weight_decay,
momentum=0.99, nesterov=True)
self.lr_scheduler = None
def run_online_evaluation(self, output, target):
"""
due to deep supervision the return value and the reference are now lists of tensors. We only need the full
resolution output because this is what we are interested in in the end. The others are ignored
:param output:
:param target:
:return:
"""
target = target[0]
output = output[0]
return super().run_online_evaluation(output, target)
def validate(self, do_mirroring: bool = True, use_sliding_window: bool = True,
step_size: float = 0.5, save_softmax: bool = True, use_gaussian: bool = True, overwrite: bool = True,
validation_folder_name: str = 'validation_raw', debug: bool = False, all_in_gpu: bool = False,
segmentation_export_kwargs: dict = None, run_postprocessing_on_folds: bool = True):
"""
We need to wrap this because we need to enforce self.network.do_ds = False for prediction
"""
ds = self.network.do_ds
self.network.do_ds = False
ret = super().validate(do_mirroring=do_mirroring, use_sliding_window=use_sliding_window, step_size=step_size,
save_softmax=save_softmax, use_gaussian=use_gaussian,
overwrite=overwrite, validation_folder_name=validation_folder_name, debug=debug,
all_in_gpu=all_in_gpu, segmentation_export_kwargs=segmentation_export_kwargs,
run_postprocessing_on_folds=run_postprocessing_on_folds)
self.network.do_ds = ds
return ret
def predict_preprocessed_data_return_seg_and_softmax(self, data: np.ndarray, do_mirroring: bool = True,
mirror_axes: Tuple[int] = None,
use_sliding_window: bool = True, step_size: float = 0.5,
use_gaussian: bool = True, pad_border_mode: str = 'constant',
pad_kwargs: dict = None, all_in_gpu: bool = False,
verbose: bool = True, mixed_precision=True) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""
We need to wrap this because we need to enforce self.network.do_ds = False for prediction
"""
ds = self.network.do_ds
self.network.do_ds = False
ret = super().predict_preprocessed_data_return_seg_and_softmax(data,
do_mirroring=do_mirroring,
mirror_axes=mirror_axes,
use_sliding_window=use_sliding_window,
step_size=step_size, use_gaussian=use_gaussian,
pad_border_mode=pad_border_mode,
pad_kwargs=pad_kwargs, all_in_gpu=all_in_gpu,
verbose=verbose,
mixed_precision=mixed_precision)
self.network.do_ds = ds
return ret
def run_iteration(self, data_generator, do_backprop=True, run_online_evaluation=False):
"""
gradient clipping improves training stability
:param data_generator:
:param do_backprop:
:param run_online_evaluation:
:return:
"""
data_dict = next(data_generator)
data = data_dict['data']
target = data_dict['target']
data = maybe_to_torch(data)
target = maybe_to_torch(target)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
data = to_cuda(data)
target = to_cuda(target)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
if self.fp16:
with autocast():
output = self.network(data)
del data
l = self.loss(output, target)
if do_backprop:
self.amp_grad_scaler.scale(l).backward()
self.amp_grad_scaler.unscale_(self.optimizer)
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.network.parameters(), 12)
self.amp_grad_scaler.step(self.optimizer)
self.amp_grad_scaler.update()
else:
output = self.network(data)
del data
l = self.loss(output, target)
if do_backprop:
l.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.network.parameters(), 12)
self.optimizer.step()
if run_online_evaluation:
self.run_online_evaluation(output, target)
del target
return l.detach().cpu().numpy()
def do_split(self):
"""
The default split is a 5 fold CV on all available training cases. nnU-Net will create a split (it is seeded,
so always the same) and save it as splits_final.pkl file in the preprocessed data directory.
Sometimes you may want to create your own split for various reasons. For this you will need to create your own
splits_final.pkl file. If this file is present, nnU-Net is going to use it and whatever splits are defined in
it. You can create as many splits in this file as you want. Note that if you define only 4 splits (fold 0-3)
and then set fold=4 when training (that would be the fifth split), nnU-Net will print a warning and proceed to
use a random 80:20 data split.
:return:
"""
if self.fold == "all":
# if fold==all then we use all images for training and validation
tr_keys = val_keys = list(self.dataset.keys())
else:
splits_file = join(self.dataset_directory, "splits_final.pkl")
# if the split file does not exist we need to create it
if not isfile(splits_file):
self.print_to_log_file("Creating new 5-fold cross-validation split...")
splits = []
all_keys_sorted = np.sort(list(self.dataset.keys()))
kfold = KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=12345)
for i, (train_idx, test_idx) in enumerate(kfold.split(all_keys_sorted)):
train_keys = np.array(all_keys_sorted)[train_idx]
test_keys = np.array(all_keys_sorted)[test_idx]
splits.append(OrderedDict())
splits[-1]['train'] = train_keys
splits[-1]['val'] = test_keys
save_pickle(splits, splits_file)
else:
self.print_to_log_file("Using splits from existing split file:", splits_file)
splits = load_pickle(splits_file)
self.print_to_log_file("The split file contains %d splits." % len(splits))
self.print_to_log_file("Desired fold for training: %d" % self.fold)
if self.fold < len(splits):
tr_keys = splits[self.fold]['train']
val_keys = splits[self.fold]['val']
self.print_to_log_file("This split has %d training and %d validation cases."
% (len(tr_keys), len(val_keys)))
else:
self.print_to_log_file("INFO: You requested fold %d for training but splits "
"contain only %d folds. I am now creating a "
"random (but seeded) 80:20 split!" % (self.fold, len(splits)))
# if we request a fold that is not in the split file, create a random 80:20 split
rnd = np.random.RandomState(seed=12345 + self.fold)
keys = np.sort(list(self.dataset.keys()))
idx_tr = rnd.choice(len(keys), int(len(keys) * 0.8), replace=False)
idx_val = [i for i in range(len(keys)) if i not in idx_tr]
tr_keys = [keys[i] for i in idx_tr]
val_keys = [keys[i] for i in idx_val]
self.print_to_log_file("This random 80:20 split has %d training and %d validation cases."
% (len(tr_keys), len(val_keys)))
tr_keys.sort()
val_keys.sort()
self.dataset_tr = OrderedDict()
for i in tr_keys:
self.dataset_tr[i] = self.dataset[i]
self.dataset_val = OrderedDict()
for i in val_keys:
self.dataset_val[i] = self.dataset[i]
def setup_DA_params(self):
"""
- we increase roation angle from [-15, 15] to [-30, 30]
- scale range is now (0.7, 1.4), was (0.85, 1.25)
- we don't do elastic deformation anymore
:return:
"""
self.deep_supervision_scales = [[1, 1, 1]] + list(list(i) for i in 1 / np.cumprod(
np.vstack(self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes), axis=0))[:-1]
if self.threeD:
self.data_aug_params = default_3D_augmentation_params
self.data_aug_params['rotation_x'] = (-30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
self.data_aug_params['rotation_y'] = (-30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
self.data_aug_params['rotation_z'] = (-30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
if self.do_dummy_2D_aug:
self.data_aug_params["dummy_2D"] = True
self.print_to_log_file("Using dummy2d data augmentation")
self.data_aug_params["elastic_deform_alpha"] = \
default_2D_augmentation_params["elastic_deform_alpha"]
self.data_aug_params["elastic_deform_sigma"] = \
default_2D_augmentation_params["elastic_deform_sigma"]
self.data_aug_params["rotation_x"] = default_2D_augmentation_params["rotation_x"]
else:
self.do_dummy_2D_aug = False
if max(self.patch_size) / min(self.patch_size) > 1.5:
default_2D_augmentation_params['rotation_x'] = (-15. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 15. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
self.data_aug_params = default_2D_augmentation_params
self.data_aug_params["mask_was_used_for_normalization"] = self.use_mask_for_norm
if self.do_dummy_2D_aug:
self.basic_generator_patch_size = get_patch_size(self.patch_size[1:],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_x'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_y'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_z'],
self.data_aug_params['scale_range'])
self.basic_generator_patch_size = np.array([self.patch_size[0]] + list(self.basic_generator_patch_size))
else:
self.basic_generator_patch_size = get_patch_size(self.patch_size, self.data_aug_params['rotation_x'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_y'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_z'],
self.data_aug_params['scale_range'])
self.data_aug_params["scale_range"] = (0.7, 1.4)
self.data_aug_params["do_elastic"] = False
self.data_aug_params['selected_seg_channels'] = [0]
self.data_aug_params['patch_size_for_spatialtransform'] = self.patch_size
self.data_aug_params["num_cached_per_thread"] = 2
def maybe_update_lr(self, epoch=None):
"""
if epoch is not None we overwrite epoch. Else we use epoch = self.epoch + 1
(maybe_update_lr is called in on_epoch_end which is called before epoch is incremented.
herefore we need to do +1 here)
:param epoch:
:return:
"""
if epoch is None:
ep = self.epoch + 1
else:
ep = epoch
self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] = poly_lr(ep, self.max_num_epochs, self.initial_lr, 0.9)
self.print_to_log_file("lr:", np.round(self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'], decimals=6))
def on_epoch_end(self):
"""
overwrite patient-based early stopping. Always run to 1000 epochs
:return:
"""
super().on_epoch_end()
continue_training = self.epoch < self.max_num_epochs
# it can rarely happen that the momentum of nnUNetTrainerV2 is too high for some dataset. If at epoch 100 the
# estimated validation Dice is still 0 then we reduce the momentum from 0.99 to 0.95
if self.epoch == 100:
if self.all_val_eval_metrics[-1] == 0:
self.optimizer.param_groups[0]["momentum"] = 0.95
self.network.apply(InitWeights_He(1e-2))
self.print_to_log_file("At epoch 100, the mean foreground Dice was 0. This can be caused by a too "
"high momentum. High momentum (0.99) is good for datasets where it works, but "
"sometimes causes issues such as this one. Momentum has now been reduced to "
"0.95 and network weights have been reinitialized")
return continue_training
def run_training(self):
"""
if we run with -c then we need to set the correct lr for the first epoch, otherwise it will run the first
continued epoch with self.initial_lr
we also need to make sure deep supervision in the network is enabled for training, thus the wrapper
:return:
"""
self.maybe_update_lr(self.epoch) # if we dont overwrite epoch then self.epoch+1 is used which is not what we
# want at the start of the training
ds = self.network.do_ds
self.network.do_ds = True
ret = super().run_training()
self.network.do_ds = ds
return ret
第一部分:__init__ —— 构造函数
def __init__(self, plans_file, fold, output_folder=None, dataset_directory=None, batch_dice=True, stage=None,
unpack_data=True, deterministic=True, fp16=False):
super().__init__(plans_file, fold, output_folder, dataset_directory, batch_dice, stage, unpack_data,
deterministic, fp16)
self.max_num_epochs = 1000
self.initial_lr = 1e-2
self.deep_supervision_scales = None
self.ds_loss_weights = None
self.pin_memory = True作用:接收配置参数,但不创建网络、不加载数据
关键点:
(1)调用父类 nnUNetTrainer 初始化(处理 plans、fold、路径等)
(2)定义训练超参数:
最大 epoch:1000
初始学习率:1e-2
Deep Supervision 相关变量(稍后填充)
(3)启用 pin_memory=True(加速 GPU 数据传输)
此时网络、数据、优化器都还没创建,只是设定了“计划”。
第二部分:主入口 —— run_training()
def run_training(self):
self.maybe_update_lr(self.epoch) # 确保继续训练时 lr 正确
ds = self.network.do_ds
self.network.do_ds = True # 开启 deep supervision
ret = super().run_training() # 调用父类训练主循环
self.network.do_ds = ds # 恢复原状态
return ret说明:
(1)如果是 断点续训(-c),需手动更新当前 epoch 的 lr(避免从 initial_lr 重新开始)
(2)训练时必须开启 deep supervision(do_ds = True),因为损失函数依赖多尺度输出
(3)实际训练逻辑在父类 nnUNetTrainer.run_training() 中(包含 epoch 循环、保存 checkpoint 等)
重点讲一下(3),它的流程如下:
第一步:nnUNetTrainerV2.run_training() 被调用
第二步:进入 nnUNetTrainer.run_training()
def run_training(self):
self.save_debug_information() # 保存调试信息(如超参、路径等)
super(nnUNetTrainer, self).run_training() # 调用更上层的 run_training()(1)保存一份 debug.json 和 plans.pkl 到输出目录,便于复现实验。
(2)向上委托给 network_trainer.run_training() (真正的训练主循环)。
代码如下:
# Copyright 2020 Division of Medical Image Computing, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from _warnings import warn
from typing import Tuple
import matplotlib
from batchgenerators.utilities.file_and_folder_operations import *
from nnunet.network_architecture.neural_network import SegmentationNetwork
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from torch import nn
from torch.cuda.amp import GradScaler, autocast
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import _LRScheduler
matplotlib.use("agg")
from time import time, sleep
import torch
import numpy as np
from torch.optim import lr_scheduler
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
from collections import OrderedDict
import torch.backends.cudnn as cudnn
from abc import abstractmethod
from datetime import datetime
from tqdm import trange
from nnunet.utilities.to_torch import maybe_to_torch, to_cuda
class NetworkTrainer(object):
def __init__(self, deterministic=True, fp16=False):
"""
A generic class that can train almost any neural network (RNNs excluded). It provides basic functionality such
as the training loop, tracking of training and validation losses (and the target metric if you implement it)
Training can be terminated early if the validation loss (or the target metric if implemented) do not improve
anymore. This is based on a moving average (MA) of the loss/metric instead of the raw values to get more smooth
results.
What you need to override:
- __init__
- initialize
- run_online_evaluation (optional)
- finish_online_evaluation (optional)
- validate
- predict_test_case
"""
self.fp16 = fp16
self.amp_grad_scaler = None
if deterministic:
np.random.seed(12345)
torch.manual_seed(12345)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(12345)
cudnn.deterministic = True
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = False
else:
cudnn.deterministic = False
torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark = True
################# SET THESE IN self.initialize() ###################################
self.network: Tuple[SegmentationNetwork, nn.DataParallel] = None
self.optimizer = None
self.lr_scheduler = None
self.tr_gen = self.val_gen = None
self.was_initialized = False
################# SET THESE IN INIT ################################################
self.output_folder = None
self.fold = None
self.loss = None
self.dataset_directory = None
################# SET THESE IN LOAD_DATASET OR DO_SPLIT ############################
self.dataset = None # these can be None for inference mode
self.dataset_tr = self.dataset_val = None # do not need to be used, they just appear if you are using the suggested load_dataset_and_do_split
################# THESE DO NOT NECESSARILY NEED TO BE MODIFIED #####################
self.patience = 50
self.val_eval_criterion_alpha = 0.9 # alpha * old + (1-alpha) * new
# if this is too low then the moving average will be too noisy and the training may terminate early. If it is
# too high the training will take forever
self.train_loss_MA_alpha = 0.93 # alpha * old + (1-alpha) * new
self.train_loss_MA_eps = 5e-4 # new MA must be at least this much better (smaller)
self.max_num_epochs = 1000
self.num_batches_per_epoch = 250
self.num_val_batches_per_epoch = 50
self.also_val_in_tr_mode = False
self.lr_threshold = 1e-6 # the network will not terminate training if the lr is still above this threshold
################# LEAVE THESE ALONE ################################################
self.val_eval_criterion_MA = None
self.train_loss_MA = None
self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA = None
self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience = None
self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss = None
self.all_tr_losses = []
self.all_val_losses = []
self.all_val_losses_tr_mode = []
self.all_val_eval_metrics = [] # does not have to be used
self.epoch = 0
self.log_file = None
self.deterministic = deterministic
self.use_progress_bar = False
if 'nnunet_use_progress_bar' in os.environ.keys():
self.use_progress_bar = bool(int(os.environ['nnunet_use_progress_bar']))
################# Settings for saving checkpoints ##################################
self.save_every = 50
self.save_latest_only = True # if false it will not store/overwrite _latest but separate files each
# time an intermediate checkpoint is created
self.save_intermediate_checkpoints = True # whether or not to save checkpoint_latest
self.save_best_checkpoint = True # whether or not to save the best checkpoint according to self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA
self.save_final_checkpoint = True # whether or not to save the final checkpoint
@abstractmethod
def initialize(self, training=True):
"""
create self.output_folder
modify self.output_folder if you are doing cross-validation (one folder per fold)
set self.tr_gen and self.val_gen
call self.initialize_network and self.initialize_optimizer_and_scheduler (important!)
finally set self.was_initialized to True
:param training:
:return:
"""
@abstractmethod
def load_dataset(self):
pass
def do_split(self):
"""
This is a suggestion for if your dataset is a dictionary (my personal standard)
:return:
"""
splits_file = join(self.dataset_directory, "splits_final.pkl")
if not isfile(splits_file):
self.print_to_log_file("Creating new split...")
splits = []
all_keys_sorted = np.sort(list(self.dataset.keys()))
kfold = KFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=12345)
for i, (train_idx, test_idx) in enumerate(kfold.split(all_keys_sorted)):
train_keys = np.array(all_keys_sorted)[train_idx]
test_keys = np.array(all_keys_sorted)[test_idx]
splits.append(OrderedDict())
splits[-1]['train'] = train_keys
splits[-1]['val'] = test_keys
save_pickle(splits, splits_file)
splits = load_pickle(splits_file)
if self.fold == "all":
tr_keys = val_keys = list(self.dataset.keys())
else:
tr_keys = splits[self.fold]['train']
val_keys = splits[self.fold]['val']
tr_keys.sort()
val_keys.sort()
self.dataset_tr = OrderedDict()
for i in tr_keys:
self.dataset_tr[i] = self.dataset[i]
self.dataset_val = OrderedDict()
for i in val_keys:
self.dataset_val[i] = self.dataset[i]
def plot_progress(self):
"""
Should probably by improved
:return:
"""
try:
font = {'weight': 'normal',
'size': 18}
matplotlib.rc('font', **font)
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(30, 24))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111)
ax2 = ax.twinx()
x_values = list(range(self.epoch + 1))
ax.plot(x_values, self.all_tr_losses, color='b', ls='-', label="loss_tr")
ax.plot(x_values, self.all_val_losses, color='r', ls='-', label="loss_val, train=False")
if len(self.all_val_losses_tr_mode) > 0:
ax.plot(x_values, self.all_val_losses_tr_mode, color='g', ls='-', label="loss_val, train=True")
if len(self.all_val_eval_metrics) == len(x_values):
ax2.plot(x_values, self.all_val_eval_metrics, color='g', ls='--', label="evaluation metric")
ax.set_xlabel("epoch")
ax.set_ylabel("loss")
ax2.set_ylabel("evaluation metric")
ax.legend()
ax2.legend(loc=9)
fig.savefig(join(self.output_folder, "progress.png"))
plt.close()
except IOError:
self.print_to_log_file("failed to plot: ", sys.exc_info())
def print_to_log_file(self, *args, also_print_to_console=True, add_timestamp=True):
timestamp = time()
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp)
if add_timestamp:
args = ("%s:" % dt_object, *args)
if self.log_file is None:
maybe_mkdir_p(self.output_folder)
timestamp = datetime.now()
self.log_file = join(self.output_folder, "training_log_%d_%d_%d_%02.0d_%02.0d_%02.0d.txt" %
(timestamp.year, timestamp.month, timestamp.day, timestamp.hour, timestamp.minute,
timestamp.second))
with open(self.log_file, 'w') as f:
f.write("Starting... \n")
successful = False
max_attempts = 5
ctr = 0
while not successful and ctr < max_attempts:
try:
with open(self.log_file, 'a+') as f:
for a in args:
f.write(str(a))
f.write(" ")
f.write("\n")
successful = True
except IOError:
print("%s: failed to log: " % datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp), sys.exc_info())
sleep(0.5)
ctr += 1
if also_print_to_console:
print(*args)
def save_checkpoint(self, fname, save_optimizer=True):
start_time = time()
state_dict = self.network.state_dict()
for key in state_dict.keys():
state_dict[key] = state_dict[key].cpu()
lr_sched_state_dct = None
if self.lr_scheduler is not None and hasattr(self.lr_scheduler,
'state_dict'): # not isinstance(self.lr_scheduler, lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau):
lr_sched_state_dct = self.lr_scheduler.state_dict()
# WTF is this!?
# for key in lr_sched_state_dct.keys():
# lr_sched_state_dct[key] = lr_sched_state_dct[key]
if save_optimizer:
optimizer_state_dict = self.optimizer.state_dict()
else:
optimizer_state_dict = None
self.print_to_log_file("saving checkpoint...")
save_this = {
'epoch': self.epoch + 1,
'state_dict': state_dict,
'optimizer_state_dict': optimizer_state_dict,
'lr_scheduler_state_dict': lr_sched_state_dct,
'plot_stuff': (self.all_tr_losses, self.all_val_losses, self.all_val_losses_tr_mode,
self.all_val_eval_metrics),
'best_stuff' : (self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss, self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience, self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA)}
if self.amp_grad_scaler is not None:
save_this['amp_grad_scaler'] = self.amp_grad_scaler.state_dict()
torch.save(save_this, fname)
self.print_to_log_file("done, saving took %.2f seconds" % (time() - start_time))
def load_best_checkpoint(self, train=True):
if self.fold is None:
raise RuntimeError("Cannot load best checkpoint if self.fold is None")
if isfile(join(self.output_folder, "model_best.model")):
self.load_checkpoint(join(self.output_folder, "model_best.model"), train=train)
else:
self.print_to_log_file("WARNING! model_best.model does not exist! Cannot load best checkpoint. Falling "
"back to load_latest_checkpoint")
self.load_latest_checkpoint(train)
def load_latest_checkpoint(self, train=True):
if isfile(join(self.output_folder, "model_final_checkpoint.model")):
return self.load_checkpoint(join(self.output_folder, "model_final_checkpoint.model"), train=train)
if isfile(join(self.output_folder, "model_latest.model")):
return self.load_checkpoint(join(self.output_folder, "model_latest.model"), train=train)
if isfile(join(self.output_folder, "model_best.model")):
return self.load_best_checkpoint(train)
raise RuntimeError("No checkpoint found")
def load_final_checkpoint(self, train=False):
filename = join(self.output_folder, "model_final_checkpoint.model")
if not isfile(filename):
raise RuntimeError("Final checkpoint not found. Expected: %s. Please finish the training first." % filename)
return self.load_checkpoint(filename, train=train)
def load_checkpoint(self, fname, train=True):
self.print_to_log_file("loading checkpoint", fname, "train=", train)
if not self.was_initialized:
self.initialize(train)
# saved_model = torch.load(fname, map_location=torch.device('cuda', torch.cuda.current_device()))
#saved_model = torch.load(fname, map_location=torch.device('cpu'), weights_only=False)
saved_model = torch.load(fname, map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
self.load_checkpoint_ram(saved_model, train)
@abstractmethod
def initialize_network(self):
"""
initialize self.network here
:return:
"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def initialize_optimizer_and_scheduler(self):
"""
initialize self.optimizer and self.lr_scheduler (if applicable) here
:return:
"""
pass
def load_checkpoint_ram(self, checkpoint, train=True):
"""
used for if the checkpoint is already in ram
:param checkpoint:
:param train:
:return:
"""
if not self.was_initialized:
self.initialize(train)
new_state_dict = OrderedDict()
curr_state_dict_keys = list(self.network.state_dict().keys())
# if state dict comes from nn.DataParallel but we use non-parallel model here then the state dict keys do not
# match. Use heuristic to make it match
for k, value in checkpoint['state_dict'].items():
key = k
if key not in curr_state_dict_keys and key.startswith('module.'):
key = key[7:]
new_state_dict[key] = value
if self.fp16:
self._maybe_init_amp()
if train:
if 'amp_grad_scaler' in checkpoint.keys():
self.amp_grad_scaler.load_state_dict(checkpoint['amp_grad_scaler'])
self.network.load_state_dict(new_state_dict)
self.epoch = checkpoint['epoch']
if train:
optimizer_state_dict = checkpoint['optimizer_state_dict']
if optimizer_state_dict is not None:
self.optimizer.load_state_dict(optimizer_state_dict)
if self.lr_scheduler is not None and hasattr(self.lr_scheduler, 'load_state_dict') and checkpoint[
'lr_scheduler_state_dict'] is not None:
self.lr_scheduler.load_state_dict(checkpoint['lr_scheduler_state_dict'])
if issubclass(self.lr_scheduler.__class__, _LRScheduler):
self.lr_scheduler.step(self.epoch)
self.all_tr_losses, self.all_val_losses, self.all_val_losses_tr_mode, self.all_val_eval_metrics = checkpoint[
'plot_stuff']
# load best loss (if present)
if 'best_stuff' in checkpoint.keys():
self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss, self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience, self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA = checkpoint[
'best_stuff']
# after the training is done, the epoch is incremented one more time in my old code. This results in
# self.epoch = 1001 for old trained models when the epoch is actually 1000. This causes issues because
# len(self.all_tr_losses) = 1000 and the plot function will fail. We can easily detect and correct that here
if self.epoch != len(self.all_tr_losses):
self.print_to_log_file("WARNING in loading checkpoint: self.epoch != len(self.all_tr_losses). This is "
"due to an old bug and should only appear when you are loading old models. New "
"models should have this fixed! self.epoch is now set to len(self.all_tr_losses)")
self.epoch = len(self.all_tr_losses)
self.all_tr_losses = self.all_tr_losses[:self.epoch]
self.all_val_losses = self.all_val_losses[:self.epoch]
self.all_val_losses_tr_mode = self.all_val_losses_tr_mode[:self.epoch]
self.all_val_eval_metrics = self.all_val_eval_metrics[:self.epoch]
self._maybe_init_amp()
def _maybe_init_amp(self):
if self.fp16 and self.amp_grad_scaler is None:
self.amp_grad_scaler = GradScaler()
def plot_network_architecture(self):
"""
can be implemented (see nnUNetTrainer) but does not have to. Not implemented here because it imposes stronger
assumptions on the presence of class variables
:return:
"""
pass
def run_training(self):
if not torch.cuda.is_available():
self.print_to_log_file("WARNING!!! You are attempting to run training on a CPU (torch.cuda.is_available() is False). This can be VERY slow!")
_ = self.tr_gen.next()
_ = self.val_gen.next()
if torch.cuda.is_available():
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
self._maybe_init_amp()
maybe_mkdir_p(self.output_folder)
self.plot_network_architecture()
if cudnn.benchmark and cudnn.deterministic:
warn("torch.backends.cudnn.deterministic is True indicating a deterministic training is desired. "
"But torch.backends.cudnn.benchmark is True as well and this will prevent deterministic training! "
"If you want deterministic then set benchmark=False")
if not self.was_initialized:
self.initialize(True)
while self.epoch < self.max_num_epochs:
self.print_to_log_file("\nepoch: ", self.epoch)
epoch_start_time = time()
train_losses_epoch = []
# train one epoch
self.network.train()
if self.use_progress_bar:
with trange(self.num_batches_per_epoch) as tbar:
for b in tbar:
tbar.set_description("Epoch {}/{}".format(self.epoch+1, self.max_num_epochs))
l = self.run_iteration(self.tr_gen, True)
tbar.set_postfix(loss=l)
train_losses_epoch.append(l)
else:
for _ in range(self.num_batches_per_epoch):
l = self.run_iteration(self.tr_gen, True)
train_losses_epoch.append(l)
self.all_tr_losses.append(np.mean(train_losses_epoch))
self.print_to_log_file("train loss : %.4f" % self.all_tr_losses[-1])
with torch.no_grad():
# validation with train=False
self.network.eval()
val_losses = []
for b in range(self.num_val_batches_per_epoch):
l = self.run_iteration(self.val_gen, False, True)
val_losses.append(l)
self.all_val_losses.append(np.mean(val_losses))
self.print_to_log_file("validation loss: %.4f" % self.all_val_losses[-1])
if self.also_val_in_tr_mode:
self.network.train()
# validation with train=True
val_losses = []
for b in range(self.num_val_batches_per_epoch):
l = self.run_iteration(self.val_gen, False)
val_losses.append(l)
self.all_val_losses_tr_mode.append(np.mean(val_losses))
self.print_to_log_file("validation loss (train=True): %.4f" % self.all_val_losses_tr_mode[-1])
self.update_train_loss_MA() # needed for lr scheduler and stopping of training
continue_training = self.on_epoch_end()
epoch_end_time = time()
if not continue_training:
# allows for early stopping
break
self.epoch += 1
self.print_to_log_file("This epoch took %f s\n" % (epoch_end_time - epoch_start_time))
self.epoch -= 1 # if we don't do this we can get a problem with loading model_final_checkpoint.
if self.save_final_checkpoint: self.save_checkpoint(join(self.output_folder, "model_final_checkpoint.model"))
# now we can delete latest as it will be identical with final
if isfile(join(self.output_folder, "model_latest.model")):
os.remove(join(self.output_folder, "model_latest.model"))
if isfile(join(self.output_folder, "model_latest.model.pkl")):
os.remove(join(self.output_folder, "model_latest.model.pkl"))
def maybe_update_lr(self):
# maybe update learning rate
if self.lr_scheduler is not None:
assert isinstance(self.lr_scheduler, (lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau, lr_scheduler._LRScheduler))
if isinstance(self.lr_scheduler, lr_scheduler.ReduceLROnPlateau):
# lr scheduler is updated with moving average val loss. should be more robust
self.lr_scheduler.step(self.train_loss_MA)
else:
self.lr_scheduler.step(self.epoch + 1)
self.print_to_log_file("lr is now (scheduler) %s" % str(self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr']))
def maybe_save_checkpoint(self):
"""
Saves a checkpoint every save_ever epochs.
:return:
"""
if self.save_intermediate_checkpoints and (self.epoch % self.save_every == (self.save_every - 1)):
self.print_to_log_file("saving scheduled checkpoint file...")
if not self.save_latest_only:
self.save_checkpoint(join(self.output_folder, "model_ep_%03.0d.model" % (self.epoch + 1)))
self.save_checkpoint(join(self.output_folder, "model_latest.model"))
self.print_to_log_file("done")
def update_eval_criterion_MA(self):
"""
If self.all_val_eval_metrics is unused (len=0) then we fall back to using -self.all_val_losses for the MA to determine early stopping
(not a minimization, but a maximization of a metric and therefore the - in the latter case)
:return:
"""
if self.val_eval_criterion_MA is None:
if len(self.all_val_eval_metrics) == 0:
self.val_eval_criterion_MA = - self.all_val_losses[-1]
else:
self.val_eval_criterion_MA = self.all_val_eval_metrics[-1]
else:
if len(self.all_val_eval_metrics) == 0:
"""
We here use alpha * old - (1 - alpha) * new because new in this case is the vlaidation loss and lower
is better, so we need to negate it.
"""
self.val_eval_criterion_MA = self.val_eval_criterion_alpha * self.val_eval_criterion_MA - (
1 - self.val_eval_criterion_alpha) * \
self.all_val_losses[-1]
else:
self.val_eval_criterion_MA = self.val_eval_criterion_alpha * self.val_eval_criterion_MA + (
1 - self.val_eval_criterion_alpha) * \
self.all_val_eval_metrics[-1]
def manage_patience(self):
# update patience
continue_training = True
if self.patience is not None:
# if best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience and best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss were not yet initialized,
# initialize them
if self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience is None:
self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience = self.train_loss_MA
if self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss is None:
self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss = self.epoch
if self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA is None:
self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA = self.val_eval_criterion_MA
# check if the current epoch is the best one according to moving average of validation criterion. If so
# then save 'best' model
# Do not use this for validation. This is intended for test set prediction only.
#self.print_to_log_file("current best_val_eval_criterion_MA is %.4f0" % self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA)
#self.print_to_log_file("current val_eval_criterion_MA is %.4f" % self.val_eval_criterion_MA)
if self.val_eval_criterion_MA > self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA:
self.best_val_eval_criterion_MA = self.val_eval_criterion_MA
#self.print_to_log_file("saving best epoch checkpoint...")
if self.save_best_checkpoint: self.save_checkpoint(join(self.output_folder, "model_best.model"))
# Now see if the moving average of the train loss has improved. If yes then reset patience, else
# increase patience
if self.train_loss_MA + self.train_loss_MA_eps < self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience:
self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience = self.train_loss_MA
self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss = self.epoch
#self.print_to_log_file("New best epoch (train loss MA): %03.4f" % self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience)
else:
pass
#self.print_to_log_file("No improvement: current train MA %03.4f, best: %03.4f, eps is %03.4f" %
# (self.train_loss_MA, self.best_MA_tr_loss_for_patience, self.train_loss_MA_eps))
# if patience has reached its maximum then finish training (provided lr is low enough)
if self.epoch - self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss > self.patience:
if self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] > self.lr_threshold:
#self.print_to_log_file("My patience ended, but I believe I need more time (lr > 1e-6)")
self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss = self.epoch - self.patience // 2
else:
#self.print_to_log_file("My patience ended")
continue_training = False
else:
pass
#self.print_to_log_file(
# "Patience: %d/%d" % (self.epoch - self.best_epoch_based_on_MA_tr_loss, self.patience))
return continue_training
def on_epoch_end(self):
self.finish_online_evaluation() # does not have to do anything, but can be used to update self.all_val_eval_
# metrics
self.plot_progress()
self.maybe_update_lr()
self.maybe_save_checkpoint()
self.update_eval_criterion_MA()
continue_training = self.manage_patience()
return continue_training
def update_train_loss_MA(self):
if self.train_loss_MA is None:
self.train_loss_MA = self.all_tr_losses[-1]
else:
self.train_loss_MA = self.train_loss_MA_alpha * self.train_loss_MA + (1 - self.train_loss_MA_alpha) * \
self.all_tr_losses[-1]
def run_iteration(self, data_generator, do_backprop=True, run_online_evaluation=False):
data_dict = next(data_generator)
data = data_dict['data']
target = data_dict['target']
data = maybe_to_torch(data)
target = maybe_to_torch(target)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
data = to_cuda(data)
target = to_cuda(target)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
if self.fp16:
with autocast():
output = self.network(data)
del data
l = self.loss(output, target)
if do_backprop:
self.amp_grad_scaler.scale(l).backward()
self.amp_grad_scaler.step(self.optimizer)
self.amp_grad_scaler.update()
else:
output = self.network(data)
del data
l = self.loss(output, target)
if do_backprop:
l.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
if run_online_evaluation:
self.run_online_evaluation(output, target)
del target
return l.detach().cpu().numpy()
def run_online_evaluation(self, *args, **kwargs):
"""
Can be implemented, does not have to
:param output_torch:
:param target_npy:
:return:
"""
pass
def finish_online_evaluation(self):
"""
Can be implemented, does not have to
:return:
"""
pass
@abstractmethod
def validate(self, *args, **kwargs):
pass
def find_lr(self, num_iters=1000, init_value=1e-6, final_value=10., beta=0.98):
"""
stolen and adapted from here: https://sgugger.github.io/how-do-you-find-a-good-learning-rate.html
:param num_iters:
:param init_value:
:param final_value:
:param beta:
:return:
"""
import math
self._maybe_init_amp()
mult = (final_value / init_value) ** (1 / num_iters)
lr = init_value
self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] = lr
avg_loss = 0.
best_loss = 0.
losses = []
log_lrs = []
for batch_num in range(1, num_iters + 1):
# +1 because this one here is not designed to have negative loss...
loss = self.run_iteration(self.tr_gen, do_backprop=True, run_online_evaluation=False).data.item() + 1
# Compute the smoothed loss
avg_loss = beta * avg_loss + (1 - beta) * loss
smoothed_loss = avg_loss / (1 - beta ** batch_num)
# Stop if the loss is exploding
if batch_num > 1 and smoothed_loss > 4 * best_loss:
break
# Record the best loss
if smoothed_loss < best_loss or batch_num == 1:
best_loss = smoothed_loss
# Store the values
losses.append(smoothed_loss)
log_lrs.append(math.log10(lr))
# Update the lr for the next step
lr *= mult
self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] = lr
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
lrs = [10 ** i for i in log_lrs]
fig = plt.figure()
plt.xscale('log')
plt.plot(lrs[10:-5], losses[10:-5])
plt.savefig(join(self.output_folder, "lr_finder.png"))
plt.close()
return log_lrs, losses
on_epoch_end() 做了什么?
这个函数在每个 epoch 结束时被调用,负责:
| 功能 | 方法 |
|---|---|
| 📈 画 loss/metric 曲线 | plot_progress() |
| 🔁 更新学习率 | maybe_update_lr() → 调用 scheduler.step() |
| 💾 保存 checkpoint | maybe_save_checkpoint()(每 save_every 轮) |
| 📊 更新验证指标 MA | update_eval_criterion_MA()(默认用 -val_loss 作为指标) |
| ⏸️ 判断是否早停 | manage_patience():- 如果 train_loss_MA 长时间没 improvement- 且 LR 已低于阈值( 1e-6)→ 停止训练 |
📌 注意:
ReduceLROnPlateau是基于 平滑后的训练 loss (train_loss_MA) 来调整 LR 的,不是原始 loss。
run_iteration() 如何工作?
这是单次前向+反向传播的核心:
def run_iteration(self, data_generator, do_backprop=True, ...):
data_dict = next(data_generator)
data, target = data_dict['data'], data_dict['target']
output = self.network(data)
loss = self.loss(output, target) # DC_and_CE_loss
if do_backprop:
loss.backward()
self.optimizer.step()
if run_online_evaluation: # 验证时计算 Dice
self.run_online_evaluation(output, target)
return loss.item()训练时:do_backprop=True,执行反向传播。
验证时:do_backprop=False,只计算 loss 和指标。
补充:print_to_log_file()这个函数,是日志上输出的主要来源:
def print_to_log_file(self, *args, also_print_to_console=True, add_timestamp=True):
timestamp = time()
dt_object = datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp)
if add_timestamp:
args = ("%s:" % dt_object, *args)
if self.log_file is None:
maybe_mkdir_p(self.output_folder)
timestamp = datetime.now()
self.log_file = join(self.output_folder, "training_log_%d_%d_%d_%02.0d_%02.0d_%02.0d.txt" %
(timestamp.year, timestamp.month, timestamp.day, timestamp.hour, timestamp.minute,
timestamp.second))
with open(self.log_file, 'w') as f:
f.write("Starting... \n")
successful = False
max_attempts = 5
ctr = 0
while not successful and ctr < max_attempts:
try:
with open(self.log_file, 'a+') as f:
for a in args:
f.write(str(a))
f.write(" ")
f.write("\n")
successful = True
except IOError:
print("%s: failed to log: " % datetime.fromtimestamp(timestamp), sys.exc_info())
sleep(0.5)
ctr += 1
if also_print_to_console:
print(*args)第三部分:initialize(training=True) —— 真正的初始化阶段
加载 plans 并设置基本属性
self.load_plans_file()
self.process_plans(self.plans)(1)设置self.num_input_channels, self.num_classes, self.patch_size, self.batch_size 等。
(2)plans.pkl 包含:图像尺寸、类别数、patch size、网络结构建议等
(3)process_plans() 设置:
self.num_input_channels
self.num_classes
self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes(决定下采样次数)
self.patch_size
self.threeD(2D or 3D)
设置数据增强参数 (setup_DA_params())
self.setup_DA_params()主要改动(相比默认):
旋转角度:±30°(原来是 ±15°)
缩放范围:(0.7, 1.4)(原来是 (0.85, 1.25))
关闭 elastic deformation(弹性形变)
计算 deep_supervision_scales(用于多尺度监督)
def setup_DA_params(self):
"""
- we increase roation angle from [-15, 15] to [-30, 30]
- scale range is now (0.7, 1.4), was (0.85, 1.25)
- we don't do elastic deformation anymore
:return:
"""
self.deep_supervision_scales = [[1, 1, 1]] + list(list(i) for i in 1 / np.cumprod(
np.vstack(self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes), axis=0))[:-1]
if self.threeD:
self.data_aug_params = default_3D_augmentation_params
self.data_aug_params['rotation_x'] = (-30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
self.data_aug_params['rotation_y'] = (-30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
self.data_aug_params['rotation_z'] = (-30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 30. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
if self.do_dummy_2D_aug:
self.data_aug_params["dummy_2D"] = True
self.print_to_log_file("Using dummy2d data augmentation")
self.data_aug_params["elastic_deform_alpha"] = \
default_2D_augmentation_params["elastic_deform_alpha"]
self.data_aug_params["elastic_deform_sigma"] = \
default_2D_augmentation_params["elastic_deform_sigma"]
self.data_aug_params["rotation_x"] = default_2D_augmentation_params["rotation_x"]
else:
self.do_dummy_2D_aug = False
if max(self.patch_size) / min(self.patch_size) > 1.5:
default_2D_augmentation_params['rotation_x'] = (-15. / 360 * 2. * np.pi, 15. / 360 * 2. * np.pi)
self.data_aug_params = default_2D_augmentation_params
self.data_aug_params["mask_was_used_for_normalization"] = self.use_mask_for_norm
if self.do_dummy_2D_aug:
self.basic_generator_patch_size = get_patch_size(self.patch_size[1:],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_x'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_y'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_z'],
self.data_aug_params['scale_range'])
self.basic_generator_patch_size = np.array([self.patch_size[0]] + list(self.basic_generator_patch_size))
else:
self.basic_generator_patch_size = get_patch_size(self.patch_size, self.data_aug_params['rotation_x'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_y'],
self.data_aug_params['rotation_z'],
self.data_aug_params['scale_range'])
self.data_aug_params["scale_range"] = (0.7, 1.4)
self.data_aug_params["do_elastic"] = False
self.data_aug_params['selected_seg_channels'] = [0]
self.data_aug_params['patch_size_for_spatialtransform'] = self.patch_size
self.data_aug_params["num_cached_per_thread"] = 2构建 Deep Supervision 损失函数
net_numpool = len(self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes) # 下采样层数
weights = np.array([1 / (2 ** i) for i in range(net_numpool)])
mask = [True] + [i < net_numpool - 1 for i in range(1, net_numpool)] # 忽略最后两层
weights[~mask] = 0
weights = weights / weights.sum()
self.ds_loss_weights = weights
self.loss = MultipleOutputLoss2(self.loss, self.ds_loss_weights)作用:
损失函数接收多个分辨率的输出(如 4 个尺度)
高分辨率输出权重更大(1, 0.5, 0.25, ...)
最低的两个尺度被忽略(mask 掉),避免噪声干扰
加载数据集 & 数据生成器
self.dl_tr, self.dl_val = self.get_basic_generators()
if self.unpack_data: unpack_dataset(...)
self.tr_gen, self.val_gen = get_moreDA_augmentation(...)get_basic_generators():从预处理数据中读取原始样本
unpack_dataset():将 .npz 解压到内存(加速 IO)
get_moreDA_augmentation():应用更强的数据增强(旋转、缩放等)
tr_gen是一个无限生成器,每次next(tr_gen)返回一个 batch 的(data, target)
初始化网络 (initialize_network())
def initialize_network(self):
"""
- momentum 0.99
- SGD instead of Adam
- self.lr_scheduler = None because we do poly_lr
- deep supervision = True
- i am sure I forgot something here
Known issue: forgot to set neg_slope=0 in InitWeights_He; should not make a difference though
:return:
"""
if self.threeD:
conv_op = nn.Conv3d
dropout_op = nn.Dropout3d
norm_op = nn.InstanceNorm3d
else:
conv_op = nn.Conv2d
dropout_op = nn.Dropout2d
norm_op = nn.InstanceNorm2d
norm_op_kwargs = {'eps': 1e-5, 'affine': True}
dropout_op_kwargs = {'p': 0, 'inplace': True}
net_nonlin = nn.LeakyReLU
net_nonlin_kwargs = {'negative_slope': 1e-2, 'inplace': True}
self.network = Generic_UNet(self.num_input_channels, self.base_num_features, self.num_classes,
len(self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes),
self.conv_per_stage, 2, conv_op, norm_op, norm_op_kwargs, dropout_op,
dropout_op_kwargs,
net_nonlin, net_nonlin_kwargs, True, False, lambda x: x, InitWeights_He(1e-2),
self.net_num_pool_op_kernel_sizes, self.net_conv_kernel_sizes, False, True, True)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
self.network.cuda()
self.network.inference_apply_nonlin = softmax_helper网络特点:
使用 LeakyReLU (slope=1e-2)
InstanceNorm
He 初始化
启用 deep supervision → 输出为 list: [full_res, half_res, quarter_res, ...]
初始化优化器 (initialize_optimizer_and_scheduler()
def initialize_optimizer_and_scheduler(self):
assert self.network is not None, "self.initialize_network must be called first"
self.optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(self.network.parameters(), self.initial_lr, weight_decay=self.weight_decay,
momentum=0.99, nesterov=True)
self.lr_scheduler = NonennUNet 不用 Adam,而用高 momentum SGD(0.99),这对医学图像分割更稳定。
第四部分:每个 epoch 的训练循环 (run_iteration())
这是单次迭代(一个 batch)的核心逻辑。
def run_iteration(self, data_generator, do_backprop=True, run_online_evaluation=False):
"""
gradient clipping improves training stability
:param data_generator:
:param do_backprop:
:param run_online_evaluation:
:return:
"""
data_dict = next(data_generator)
data = data_dict['data']
target = data_dict['target']
data = maybe_to_torch(data)
target = maybe_to_torch(target)
if torch.cuda.is_available():
data = to_cuda(data)
target = to_cuda(target)
self.optimizer.zero_grad()
if self.fp16:
with autocast():
output = self.network(data)
del data
l = self.loss(output, target)
if do_backprop:
self.amp_grad_scaler.scale(l).backward()
self.amp_grad_scaler.unscale_(self.optimizer)
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.network.parameters(), 12)
self.amp_grad_scaler.step(self.optimizer)
self.amp_grad_scaler.update()
else:
output = self.network(data)
del data
l = self.loss(output, target)
if do_backprop:
l.backward()
torch.nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(self.network.parameters(), 12)
self.optimizer.step()
if run_online_evaluation:
self.run_online_evaluation(output, target)
del target
return l.detach().cpu().numpy()关键细节:
梯度裁剪(clip_grad_norm_=12):防止梯度爆炸,提升稳定性
FP16 支持:通过 autocast() 和 amp_grad_scaler 实现混合精度
在线评估:只用最高分辨率输出(output[0])计算 Dice
第五部分:学习率调度 (maybe_update_lr())
def maybe_update_lr(self, epoch=None):
"""
if epoch is not None we overwrite epoch. Else we use epoch = self.epoch + 1
(maybe_update_lr is called in on_epoch_end which is called before epoch is incremented.
herefore we need to do +1 here)
:param epoch:
:return:
"""
if epoch is None:
ep = self.epoch + 1
else:
ep = epoch
self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'] = poly_lr(ep, self.max_num_epochs, self.initial_lr, 0.9)
self.print_to_log_file("lr:", np.round(self.optimizer.param_groups[0]['lr'], decimals=6))
每个 epoch 结束时调用(on_epoch_end() → maybe_update_lr())。
第六部分:验证与预测(关闭 Deep Supervision)
训练时用 deep supervision,但推理时只需最终输出。
def validate(self, do_mirroring: bool = True, use_sliding_window: bool = True,
step_size: float = 0.5, save_softmax: bool = True, use_gaussian: bool = True, overwrite: bool = True,
validation_folder_name: str = 'validation_raw', debug: bool = False, all_in_gpu: bool = False,
segmentation_export_kwargs: dict = None, run_postprocessing_on_folds: bool = True):
"""
We need to wrap this because we need to enforce self.network.do_ds = False for prediction
"""
ds = self.network.do_ds
self.network.do_ds = False
ret = super().validate(do_mirroring=do_mirroring, use_sliding_window=use_sliding_window, step_size=step_size,
save_softmax=save_softmax, use_gaussian=use_gaussian,
overwrite=overwrite, validation_folder_name=validation_folder_name, debug=debug,
all_in_gpu=all_in_gpu, segmentation_export_kwargs=segmentation_export_kwargs,
run_postprocessing_on_folds=run_postprocessing_on_folds)
self.network.do_ds = ds
return retGeneric_UNet 的 do_ds=False 时,只返回 [full_res_output]
验证、测试、推理都必须关闭 deep supervision
第七部分:交叉验证拆分 (do_split())
默认使用 5-fold CV
若 splits_final.pkl 不存在,则用 KFold(random_state=12345) 生成并保存
支持 fold="all"(全量训练)
若指定 fold 超出范围,自动创建 80:20 随机划分
第八部分:特殊保护机制 (on_epoch_end())
def on_epoch_end(self):
"""
overwrite patient-based early stopping. Always run to 1000 epochs
:return:
"""
super().on_epoch_end()
continue_training = self.epoch < self.max_num_epochs
# it can rarely happen that the momentum of nnUNetTrainerV2 is too high for some dataset. If at epoch 100 the
# estimated validation Dice is still 0 then we reduce the momentum from 0.99 to 0.95
if self.epoch == 100:
if self.all_val_eval_metrics[-1] == 0:
self.optimizer.param_groups[0]["momentum"] = 0.95
self.network.apply(InitWeights_He(1e-2))
self.print_to_log_file("At epoch 100, the mean foreground Dice was 0. This can be caused by a too "
"high momentum. High momentum (0.99) is good for datasets where it works, but "
"sometimes causes issues such as this one. Momentum has now been reduced to "
"0.95 and network weights have been reinitialized")
return continue_training在每个训练周期(epoch)结束时执行。
(1)调用父类的on_epoch_end() 方法:
def on_epoch_end(self):
self.finish_online_evaluation() # does not have to do anything, but can be used to update self.all_val_eval_
# metrics
self.plot_progress()
self.maybe_update_lr()
self.maybe_save_checkpoint()
self.update_eval_criterion_MA()
continue_training = self.manage_patience()
return continue_training每个 epoch 结束时执行以下关键任务:
完成验证评估;
绘制训练曲线;
动态调整学习率;
有条件地保存模型;
更新评估指标的平滑值;
判断是否应提前终止训练。
(2)检测训练是否“卡住”
如果到了第 100 个 epoch,验证集上的平均前景 Dice 系数仍然是 0,说明模型完全没有学会分割目标(预测全是背景)。
可能原因:动量(momentum)太高(默认 0.99)导致优化过程不稳定或陷入不良局部极小值。
应对措施:
(1)降低动量:从 0.99 改为 0.95,使优化更稳定。
(2)重新初始化网络权重:使用 He 初始化(带缩放因子 1e-2),相当于“重启”训练。
(3)记录日志:通知用户发生了这种情况及采取的措施。
第九部分:run_online_evaluation
def run_online_evaluation(self, output, target):
"""
due to deep supervision the return value and the reference are now lists of tensors. We only need the full
resolution output because this is what we are interested in in the end. The others are ignored
:param output:
:param target:
:return:
"""
target = target[0]
output = output[0]
return super().run_online_evaluation(output, target)父类中的:
def run_online_evaluation(self, output, target):
with torch.no_grad():
num_classes = output.shape[1]
output_softmax = softmax_helper(output)
output_seg = output_softmax.argmax(1)
target = target[:, 0]
axes = tuple(range(1, len(target.shape)))
tp_hard = torch.zeros((target.shape[0], num_classes - 1)).to(output_seg.device.index)
fp_hard = torch.zeros((target.shape[0], num_classes - 1)).to(output_seg.device.index)
fn_hard = torch.zeros((target.shape[0], num_classes - 1)).to(output_seg.device.index)
for c in range(1, num_classes):
tp_hard[:, c - 1] = sum_tensor((output_seg == c).float() * (target == c).float(), axes=axes)
fp_hard[:, c - 1] = sum_tensor((output_seg == c).float() * (target != c).float(), axes=axes)
fn_hard[:, c - 1] = sum_tensor((output_seg != c).float() * (target == c).float(), axes=axes)
tp_hard = tp_hard.sum(0, keepdim=False).detach().cpu().numpy()
fp_hard = fp_hard.sum(0, keepdim=False).detach().cpu().numpy()
fn_hard = fn_hard.sum(0, keepdim=False).detach().cpu().numpy()
self.online_eval_foreground_dc.append(list((2 * tp_hard) / (2 * tp_hard + fp_hard + fn_hard + 1e-8)))
self.online_eval_tp.append(list(tp_hard))
self.online_eval_fp.append(list(fp_hard))
self.online_eval_fn.append(list(fn_hard))在验证过程中,对每个 batch 的预测结果计算各类别的 TP/FP/FN 和 Dice 系数,并缓存起来,以便在整个验证集上求平均指标。
总结:nnUNetTrainerV2 的流程(以及替换网络结构继承重写时注意点)
| 阶段 | 方法 | 是否可重写 | 是否需要关注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 构造 | __init__ | ⚠️ 少量 | ❌ 一般不用动 |
| 初始化 | initialize() | ❌(但调用下面的方法) | ✅ 看整体流程 |
| 网络创建 | initialize_network() | ✅ 是 | ✅✅✅ 重点! |
| 优化器 | initialize_optimizer_and_scheduler() | ✅ 是 | ⚠️ 按需 |
| 数据加载 | initialize_data_loader() | ⚠️ 很少 | ❌ |
| 训练循环 | run_training() | ⚠️ 不推荐 | ❌ |
| 单步训练 | run_iteration() | ✅ 是 | ⚠️ 高级定制 |
| 验证 | validate() | ✅ 是 | ⚠️ 如需改评估逻辑 |
网络
网络结构的文件目录:
| 文件名 | 功能简述 | 是否默认使用 | 核心特点 | 适用场景 | 学习优先级 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
generic_UNet.py | 实现标准的 2D/3D U-Net 网络结构 | ✅ 是(默认主干) | - 支持动态深度 - 深度监督 - 跳跃连接 - 自动适配 patch size | 所有 nnUNet 默认训练任务 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐(最高) |
generic_UNet_DP.py | 支持数据并行(Data Parallel)的 U-Net | ❌ 否(仅多 GPU 时调用) | 继承自 Generic_UNet,添加多卡支持 | 多 GPU 训练 | ⭐⭐ |
generic_modular_UNet.py | 模块化通用 U-Net 基础类 | ❌ 否 | 可插拔 block 设计,结构灵活 | 研究或自定义网络 | ⭐⭐⭐ |
generic_modular_residual_UNet.py | 基于残差块的模块化 U-Net | ❌ 否 | 使用标准 residual blocks(Conv → BN → ReLU + skip) | 需要更强梯度传播的任务 | ⭐⭐ |
generic_modular_preact_residual_UNet.py | 预激活残差模块化 U-Net | ❌ 否 | 使用 pre-activation 残差块(BN → ReLU → Conv) | 更深网络、避免梯度爆炸 | ⭐⭐ |
下面讲解一下generic_UNet.py:
# Copyright 2020 Division of Medical Image Computing, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
from copy import deepcopy
from nnunet.utilities.nd_softmax import softmax_helper
from torch import nn
import torch
import numpy as np
from nnunet.network_architecture.initialization import InitWeights_He
from nnunet.network_architecture.neural_network import SegmentationNetwork
import torch.nn.functional
class ConvDropoutNormNonlin(nn.Module):
"""
fixes a bug in ConvDropoutNormNonlin where lrelu was used regardless of nonlin. Bad.
"""
def __init__(self, input_channels, output_channels,
conv_op=nn.Conv2d, conv_kwargs=None,
norm_op=nn.BatchNorm2d, norm_op_kwargs=None,
dropout_op=nn.Dropout2d, dropout_op_kwargs=None,
nonlin=nn.LeakyReLU, nonlin_kwargs=None):
super(ConvDropoutNormNonlin, self).__init__()
if nonlin_kwargs is None:
nonlin_kwargs = {'negative_slope': 1e-2, 'inplace': True}
if dropout_op_kwargs is None:
dropout_op_kwargs = {'p': 0.5, 'inplace': True}
if norm_op_kwargs is None:
norm_op_kwargs = {'eps': 1e-5, 'affine': True, 'momentum': 0.1}
if conv_kwargs is None:
conv_kwargs = {'kernel_size': 3, 'stride': 1, 'padding': 1, 'dilation': 1, 'bias': True}
self.nonlin_kwargs = nonlin_kwargs
self.nonlin = nonlin
self.dropout_op = dropout_op
self.dropout_op_kwargs = dropout_op_kwargs
self.norm_op_kwargs = norm_op_kwargs
self.conv_kwargs = conv_kwargs
self.conv_op = conv_op
self.norm_op = norm_op
self.conv = self.conv_op(input_channels, output_channels, **self.conv_kwargs)
if self.dropout_op is not None and self.dropout_op_kwargs['p'] is not None and self.dropout_op_kwargs[
'p'] > 0:
self.dropout = self.dropout_op(**self.dropout_op_kwargs)
else:
self.dropout = None
self.instnorm = self.norm_op(output_channels, **self.norm_op_kwargs)
self.lrelu = self.nonlin(**self.nonlin_kwargs)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
if self.dropout is not None:
x = self.dropout(x)
return self.lrelu(self.instnorm(x))
class ConvDropoutNonlinNorm(ConvDropoutNormNonlin):
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv(x)
if self.dropout is not None:
x = self.dropout(x)
return self.instnorm(self.lrelu(x))
class StackedConvLayers(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_feature_channels, output_feature_channels, num_convs,
conv_op=nn.Conv2d, conv_kwargs=None,
norm_op=nn.BatchNorm2d, norm_op_kwargs=None,
dropout_op=nn.Dropout2d, dropout_op_kwargs=None,
nonlin=nn.LeakyReLU, nonlin_kwargs=None, first_stride=None, basic_block=ConvDropoutNormNonlin):
'''
stacks ConvDropoutNormLReLU layers. initial_stride will only be applied to first layer in the stack. The other parameters affect all layers
:param input_feature_channels:
:param output_feature_channels:
:param num_convs:
:param dilation:
:param kernel_size:
:param padding:
:param dropout:
:param initial_stride:
:param conv_op:
:param norm_op:
:param dropout_op:
:param inplace:
:param neg_slope:
:param norm_affine:
:param conv_bias:
'''
self.input_channels = input_feature_channels
self.output_channels = output_feature_channels
if nonlin_kwargs is None:
nonlin_kwargs = {'negative_slope': 1e-2, 'inplace': True}
if dropout_op_kwargs is None:
dropout_op_kwargs = {'p': 0.5, 'inplace': True}
if norm_op_kwargs is None:
norm_op_kwargs = {'eps': 1e-5, 'affine': True, 'momentum': 0.1}
if conv_kwargs is None:
conv_kwargs = {'kernel_size': 3, 'stride': 1, 'padding': 1, 'dilation': 1, 'bias': True}
self.nonlin_kwargs = nonlin_kwargs
self.nonlin = nonlin
self.dropout_op = dropout_op
self.dropout_op_kwargs = dropout_op_kwargs
self.norm_op_kwargs = norm_op_kwargs
self.conv_kwargs = conv_kwargs
self.conv_op = conv_op
self.norm_op = norm_op
if first_stride is not None:
self.conv_kwargs_first_conv = deepcopy(conv_kwargs)
self.conv_kwargs_first_conv['stride'] = first_stride
else:
self.conv_kwargs_first_conv = conv_kwargs
super(StackedConvLayers, self).__init__()
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(
*([basic_block(input_feature_channels, output_feature_channels, self.conv_op,
self.conv_kwargs_first_conv,
self.norm_op, self.norm_op_kwargs, self.dropout_op, self.dropout_op_kwargs,
self.nonlin, self.nonlin_kwargs)] +
[basic_block(output_feature_channels, output_feature_channels, self.conv_op,
self.conv_kwargs,
self.norm_op, self.norm_op_kwargs, self.dropout_op, self.dropout_op_kwargs,
self.nonlin, self.nonlin_kwargs) for _ in range(num_convs - 1)]))
def forward(self, x):
return self.blocks(x)
def print_module_training_status(module):
if isinstance(module, nn.Conv2d) or isinstance(module, nn.Conv3d) or isinstance(module, nn.Dropout3d) or \
isinstance(module, nn.Dropout2d) or isinstance(module, nn.Dropout) or isinstance(module, nn.InstanceNorm3d) \
or isinstance(module, nn.InstanceNorm2d) or isinstance(module, nn.InstanceNorm1d) \
or isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm2d) or isinstance(module, nn.BatchNorm3d) or isinstance(module,
nn.BatchNorm1d):
print(str(module), module.training)
class Upsample(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=False):
super(Upsample, self).__init__()
self.align_corners = align_corners
self.mode = mode
self.scale_factor = scale_factor
self.size = size
def forward(self, x):
return nn.functional.interpolate(x, size=self.size, scale_factor=self.scale_factor, mode=self.mode,
align_corners=self.align_corners)
class Generic_UNet(SegmentationNetwork):
DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE_3D = 2
DEFAULT_PATCH_SIZE_3D = (64, 192, 160)
SPACING_FACTOR_BETWEEN_STAGES = 2
BASE_NUM_FEATURES_3D = 30
MAX_NUMPOOL_3D = 999
MAX_NUM_FILTERS_3D = 320
DEFAULT_PATCH_SIZE_2D = (256, 256)
BASE_NUM_FEATURES_2D = 30
DEFAULT_BATCH_SIZE_2D = 50
MAX_NUMPOOL_2D = 999
MAX_FILTERS_2D = 480
use_this_for_batch_size_computation_2D = 19739648
use_this_for_batch_size_computation_3D = 520000000 # 505789440
def __init__(self, input_channels, base_num_features, num_classes, num_pool, num_conv_per_stage=2,
feat_map_mul_on_downscale=2, conv_op=nn.Conv2d,
norm_op=nn.BatchNorm2d, norm_op_kwargs=None,
dropout_op=nn.Dropout2d, dropout_op_kwargs=None,
nonlin=nn.LeakyReLU, nonlin_kwargs=None, deep_supervision=True, dropout_in_localization=False,
final_nonlin=softmax_helper, weightInitializer=InitWeights_He(1e-2), pool_op_kernel_sizes=None,
conv_kernel_sizes=None,
upscale_logits=False, convolutional_pooling=False, convolutional_upsampling=False,
max_num_features=None, basic_block=ConvDropoutNormNonlin,
seg_output_use_bias=False):
"""
basically more flexible than v1, architecture is the same
Does this look complicated? Nah bro. Functionality > usability
This does everything you need, including world peace.
Questions? -> f.isensee@dkfz.de
"""
super(Generic_UNet, self).__init__()
self.convolutional_upsampling = convolutional_upsampling
self.convolutional_pooling = convolutional_pooling
self.upscale_logits = upscale_logits
if nonlin_kwargs is None:
nonlin_kwargs = {'negative_slope': 1e-2, 'inplace': True}
if dropout_op_kwargs is None:
dropout_op_kwargs = {'p': 0.5, 'inplace': True}
if norm_op_kwargs is None:
norm_op_kwargs = {'eps': 1e-5, 'affine': True, 'momentum': 0.1}
self.conv_kwargs = {'stride': 1, 'dilation': 1, 'bias': True}
self.nonlin = nonlin
self.nonlin_kwargs = nonlin_kwargs
self.dropout_op_kwargs = dropout_op_kwargs
self.norm_op_kwargs = norm_op_kwargs
self.weightInitializer = weightInitializer
self.conv_op = conv_op
self.norm_op = norm_op
self.dropout_op = dropout_op
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.final_nonlin = final_nonlin
self._deep_supervision = deep_supervision
self.do_ds = deep_supervision
if conv_op == nn.Conv2d:
upsample_mode = 'bilinear'
pool_op = nn.MaxPool2d
transpconv = nn.ConvTranspose2d
if pool_op_kernel_sizes is None:
pool_op_kernel_sizes = [(2, 2)] * num_pool
if conv_kernel_sizes is None:
conv_kernel_sizes = [(3, 3)] * (num_pool + 1)
elif conv_op == nn.Conv3d:
upsample_mode = 'trilinear'
pool_op = nn.MaxPool3d
transpconv = nn.ConvTranspose3d
if pool_op_kernel_sizes is None:
pool_op_kernel_sizes = [(2, 2, 2)] * num_pool
if conv_kernel_sizes is None:
conv_kernel_sizes = [(3, 3, 3)] * (num_pool + 1)
else:
raise ValueError("unknown convolution dimensionality, conv op: %s" % str(conv_op))
self.input_shape_must_be_divisible_by = np.prod(pool_op_kernel_sizes, 0, dtype=np.int64)
self.pool_op_kernel_sizes = pool_op_kernel_sizes
self.conv_kernel_sizes = conv_kernel_sizes
self.conv_pad_sizes = []
for krnl in self.conv_kernel_sizes:
self.conv_pad_sizes.append([1 if i == 3 else 0 for i in krnl])
if max_num_features is None:
if self.conv_op == nn.Conv3d:
self.max_num_features = self.MAX_NUM_FILTERS_3D
else:
self.max_num_features = self.MAX_FILTERS_2D
else:
self.max_num_features = max_num_features
self.conv_blocks_context = []
self.conv_blocks_localization = []
self.td = []
self.tu = []
self.seg_outputs = []
output_features = base_num_features
input_features = input_channels
for d in range(num_pool):
# determine the first stride
if d != 0 and self.convolutional_pooling:
first_stride = pool_op_kernel_sizes[d - 1]
else:
first_stride = None
self.conv_kwargs['kernel_size'] = self.conv_kernel_sizes[d]
self.conv_kwargs['padding'] = self.conv_pad_sizes[d]
# add convolutions
self.conv_blocks_context.append(StackedConvLayers(input_features, output_features, num_conv_per_stage,
self.conv_op, self.conv_kwargs, self.norm_op,
self.norm_op_kwargs, self.dropout_op,
self.dropout_op_kwargs, self.nonlin, self.nonlin_kwargs,
first_stride, basic_block=basic_block))
if not self.convolutional_pooling:
self.td.append(pool_op(pool_op_kernel_sizes[d]))
input_features = output_features
output_features = int(np.round(output_features * feat_map_mul_on_downscale))
output_features = min(output_features, self.max_num_features)
# now the bottleneck.
# determine the first stride
if self.convolutional_pooling:
first_stride = pool_op_kernel_sizes[-1]
else:
first_stride = None
# the output of the last conv must match the number of features from the skip connection if we are not using
# convolutional upsampling. If we use convolutional upsampling then the reduction in feature maps will be
# done by the transposed conv
if self.convolutional_upsampling:
final_num_features = output_features
else:
final_num_features = self.conv_blocks_context[-1].output_channels
self.conv_kwargs['kernel_size'] = self.conv_kernel_sizes[num_pool]
self.conv_kwargs['padding'] = self.conv_pad_sizes[num_pool]
self.conv_blocks_context.append(nn.Sequential(
StackedConvLayers(input_features, output_features, num_conv_per_stage - 1, self.conv_op, self.conv_kwargs,
self.norm_op, self.norm_op_kwargs, self.dropout_op, self.dropout_op_kwargs, self.nonlin,
self.nonlin_kwargs, first_stride, basic_block=basic_block),
StackedConvLayers(output_features, final_num_features, 1, self.conv_op, self.conv_kwargs,
self.norm_op, self.norm_op_kwargs, self.dropout_op, self.dropout_op_kwargs, self.nonlin,
self.nonlin_kwargs, basic_block=basic_block)))
# if we don't want to do dropout in the localization pathway then we set the dropout prob to zero here
if not dropout_in_localization:
old_dropout_p = self.dropout_op_kwargs['p']
self.dropout_op_kwargs['p'] = 0.0
# now lets build the localization pathway
for u in range(num_pool):
nfeatures_from_down = final_num_features
nfeatures_from_skip = self.conv_blocks_context[
-(2 + u)].output_channels # self.conv_blocks_context[-1] is bottleneck, so start with -2
n_features_after_tu_and_concat = nfeatures_from_skip * 2
# the first conv reduces the number of features to match those of skip
# the following convs work on that number of features
# if not convolutional upsampling then the final conv reduces the num of features again
if u != num_pool - 1 and not self.convolutional_upsampling:
final_num_features = self.conv_blocks_context[-(3 + u)].output_channels
else:
final_num_features = nfeatures_from_skip
if not self.convolutional_upsampling:
self.tu.append(Upsample(scale_factor=pool_op_kernel_sizes[-(u + 1)], mode=upsample_mode))
else:
self.tu.append(transpconv(nfeatures_from_down, nfeatures_from_skip, pool_op_kernel_sizes[-(u + 1)],
pool_op_kernel_sizes[-(u + 1)], bias=False))
self.conv_kwargs['kernel_size'] = self.conv_kernel_sizes[- (u + 1)]
self.conv_kwargs['padding'] = self.conv_pad_sizes[- (u + 1)]
self.conv_blocks_localization.append(nn.Sequential(
StackedConvLayers(n_features_after_tu_and_concat, nfeatures_from_skip, num_conv_per_stage - 1,
self.conv_op, self.conv_kwargs, self.norm_op, self.norm_op_kwargs, self.dropout_op,
self.dropout_op_kwargs, self.nonlin, self.nonlin_kwargs, basic_block=basic_block),
StackedConvLayers(nfeatures_from_skip, final_num_features, 1, self.conv_op, self.conv_kwargs,
self.norm_op, self.norm_op_kwargs, self.dropout_op, self.dropout_op_kwargs,
self.nonlin, self.nonlin_kwargs, basic_block=basic_block)
))
for ds in range(len(self.conv_blocks_localization)):
self.seg_outputs.append(conv_op(self.conv_blocks_localization[ds][-1].output_channels, num_classes,
1, 1, 0, 1, 1, seg_output_use_bias))
self.upscale_logits_ops = []
cum_upsample = np.cumprod(np.vstack(pool_op_kernel_sizes), axis=0)[::-1]
for usl in range(num_pool - 1):
if self.upscale_logits:
self.upscale_logits_ops.append(Upsample(scale_factor=tuple([int(i) for i in cum_upsample[usl + 1]]),
mode=upsample_mode))
else:
self.upscale_logits_ops.append(lambda x: x)
if not dropout_in_localization:
self.dropout_op_kwargs['p'] = old_dropout_p
# register all modules properly
self.conv_blocks_localization = nn.ModuleList(self.conv_blocks_localization)
self.conv_blocks_context = nn.ModuleList(self.conv_blocks_context)
self.td = nn.ModuleList(self.td)
self.tu = nn.ModuleList(self.tu)
self.seg_outputs = nn.ModuleList(self.seg_outputs)
if self.upscale_logits:
self.upscale_logits_ops = nn.ModuleList(
self.upscale_logits_ops) # lambda x:x is not a Module so we need to distinguish here
if self.weightInitializer is not None:
self.apply(self.weightInitializer)
# self.apply(print_module_training_status)
def forward(self, x):
skips = []
seg_outputs = []
for d in range(len(self.conv_blocks_context) - 1):
x = self.conv_blocks_context[d](x)
skips.append(x)
if not self.convolutional_pooling:
x = self.td[d](x)
x = self.conv_blocks_context[-1](x)
for u in range(len(self.tu)):
x = self.tu[u](x)
x = torch.cat((x, skips[-(u + 1)]), dim=1)
x = self.conv_blocks_localization[u](x)
seg_outputs.append(self.final_nonlin(self.seg_outputs[u](x)))
if self._deep_supervision and self.do_ds:
return tuple([seg_outputs[-1]] + [i(j) for i, j in
zip(list(self.upscale_logits_ops)[::-1], seg_outputs[:-1][::-1])])
else:
return seg_outputs[-1]
@staticmethod
def compute_approx_vram_consumption(patch_size, num_pool_per_axis, base_num_features, max_num_features,
num_modalities, num_classes, pool_op_kernel_sizes, deep_supervision=False,
conv_per_stage=2):
"""
This only applies for num_conv_per_stage and convolutional_upsampling=True
not real vram consumption. just a constant term to which the vram consumption will be approx proportional
(+ offset for parameter storage)
:param deep_supervision:
:param patch_size:
:param num_pool_per_axis:
:param base_num_features:
:param max_num_features:
:param num_modalities:
:param num_classes:
:param pool_op_kernel_sizes:
:return:
"""
if not isinstance(num_pool_per_axis, np.ndarray):
num_pool_per_axis = np.array(num_pool_per_axis)
npool = len(pool_op_kernel_sizes)
map_size = np.array(patch_size)
tmp = np.int64((conv_per_stage * 2 + 1) * np.prod(map_size, dtype=np.int64) * base_num_features +
num_modalities * np.prod(map_size, dtype=np.int64) +
num_classes * np.prod(map_size, dtype=np.int64))
num_feat = base_num_features
for p in range(npool):
for pi in range(len(num_pool_per_axis)):
map_size[pi] /= pool_op_kernel_sizes[p][pi]
num_feat = min(num_feat * 2, max_num_features)
num_blocks = (conv_per_stage * 2 + 1) if p < (npool - 1) else conv_per_stage # conv_per_stage + conv_per_stage for the convs of encode/decode and 1 for transposed conv
tmp += num_blocks * np.prod(map_size, dtype=np.int64) * num_feat
if deep_supervision and p < (npool - 2):
tmp += np.prod(map_size, dtype=np.int64) * num_classes
# print(p, map_size, num_feat, tmp)
return tmp
| 模块/组件名称 | 功能说明 | 对应类/函数 | 关键参数/行为 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ConvDropoutNormNonlin | 基础卷积块:卷积 → (可选) Dropout → Batch/Instance Norm → 非线性激活(默认 LeakyReLU) | class ConvDropoutNormNonlin(nn.Module) | 支持 2D/3D;可配置 conv/norm/dropout/activation 类型及参数 |
| ConvDropoutNonlinNorm | 变体:卷积 → Dropout → 非线性 → Norm(顺序不同) | class ConvDropoutNonlinNorm(ConvDropoutNormNonlin) | 仅 forward 方法重写,其余继承 |
| StackedConvLayers | 多层卷积堆叠(如编码器/解码器中的 stage) | class StackedConvLayers(nn.Module) | 第一层可设不同 stride(用于下采样),其余层共享参数;支持自定义基础块(basic_block) |
| Upsample | 上采样操作封装(支持插值或转置卷积) | class Upsample(nn.Module) | 使用 torch.nn.functional.interpolate;支持 nearest/bilinear/trilinear 等模式 |
| Generic_UNet | 主干网络:U-Net 架构,支持 2D/3D、深度监督、卷积池化/上采样等 | class Generic_UNet(SegmentationNetwork) | 核心参数: • num_pool: 下采样次数• convolutional_pooling: 是否用 stride 卷积代替 MaxPool• convolutional_upsampling: 是否用转置卷积上采样• deep_supervision: 是否启用多尺度输出 |
| 编码器(Context Path) | 特征提取路径,逐级下采样 | self.conv_blocks_context + self.td(MaxPool) | 每级包含 num_conv_per_stage 个卷积块;特征图数量按 feat_map_mul_on_downscale=2 倍增(上限 max_num_features) |
| 瓶颈层(Bottleneck) | 最深层特征融合 | self.conv_blocks_context[-1] | 由两个 StackedConvLayers 组成;若使用卷积上采样,则输出通道数需匹配跳跃连接 |
| 解码器(Localization Path) | 逐级上采样 + 跳跃连接融合 | self.tu + self.conv_blocks_localization | 上采样方式由 convolutional_upsampling 决定:• False: 插值 + concat + 卷积 • True: 转置卷积直接上采样 |
| 分割头(Seg Outputs) | 每级解码器输出预测图(用于深度监督) | self.seg_outputs | 1×1 卷积映射到 num_classes;最终输出经 final_nonlin(默认 softmax_helper) |
| 深度监督(Deep Supervision) | 训练时输出多尺度预测,提升梯度传播 | forward() 中逻辑 | 返回 tuple:(final_pred, upsampled_pred_1, ..., upsampled_pred_{n-1});推理时仅用 final_pred |
| 初始化 | 权重初始化(He 初始化) | weightInitializer=InitWeights_He(1e-2) | 在 __init__ 末尾调用 self.apply(self.weightInitializer) |
| 辅助函数 | VRAM 估算、训练状态打印等 | compute_approx_vram_consumption, print_module_training_status | 用于自动规划 batch size 和调试 |
如果要写自己的网络结构以嵌入nnuent框架实现pipeline:
| 类别 | 功能/要求 | 是否必需 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基类继承 | 继承 nnunet.network_architecture.neural_network.SegmentationNetwork | ✅ 必需 | 这是 nnU-Net 对所有分割模型的抽象基类,确保兼容训练器和推理器。 |
构造函数 (__init__) | 接受标准参数如 input_channels, num_classes, num_pool, base_num_features 等 | ⚠️ 推荐 | 虽非强制,但 nnU-Net 的 plans 文件和训练脚本会按 Generic_UNet 的接口传参。建议保留相同签名或使用 **kwargs 兼容。 |
支持 2D/3D 切换(通过 conv_op=nn.Conv2d/Conv3d) | ❌ 可选 | 若只做 3D 可省略,但通用性更强的做法是支持维度自动适配。 | |
前向传播 (forward) | 输入:x(形状 [B, C, H, W] 或 [B, C, D, H, W]) | ✅ 必需 | 标准张量输入。 |
输出:若 self.do_ds == True,返回 tuple,第一个元素为最终预测,其余为低分辨率监督输出 | ✅ 必需(训练时) | nnU-Net 训练默认启用 deep supervision,loss 会遍历 tuple 中每个元素。 | |
输出:若 self.do_ds == False,返回单个 tensor(最终预测) | ✅ 必需(推理时) | 推理阶段通常关闭 deep supervision。 | |
| 输出为 raw logits(未经过 softmax/sigmoid) | ✅ 必需 | nnU-Net 使用 Dice+CrossEntropy 等 loss,需要未归一化的 logits。 | |
| 关键属性 | self.num_classes = num_classes | ✅ 必需 | 用于验证输出通道数是否匹配。 |
self.do_ds = deep_supervision(布尔值) | ✅ 必需 | 控制是否启用 deep supervision,训练/推理切换依赖此属性。 | |
| 模块注册 | 所有子模块(如卷积层、上采样层、输出头)必须用 nn.ModuleList 或直接作为 nn.Module 属性注册 | ✅ 必需 | 确保 state_dict 正确保存/加载,避免“missing keys”错误。 |
| 权重初始化 | 调用 self.apply(initializer)(如 InitWeights_He) | ⚠️ 推荐 | 保持与原版 nnU-Net 一致的初始化策略,有助于收敛。 |
| 显存估算(可选但重要) | 实现静态方法:@staticmethod compute_approx_vram_consumption(...) | ⚠️推荐 | 用于 nnU-Net 自动计算 batch size。若不实现,会 fallback 到保守值(可能浪费 GPU)。 |
| 输出通道数 | 最终分割头输出通道数 = num_classes | ✅ 必需 | 包括背景类(如 3 类任务 → 输出通道=3)。 |
| 设备与数据类型兼容 | 网络应能处理 float32 输入,并在 GPU/CPU 上正常运行 | ✅ 隐式必需 | PyTorch 默认要求,但需避免硬编码 .cuda() 等操作。 |
测试(评估)
我的推理与评估命令:
# 1. 设置 nnU-Net 所需的环境变量
export nnUNet_raw_data_base="/xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_raw"
export nnUNet_preprocessed="/xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_preprocessed"
export RESULTS_FOLDER="/xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_trained_models"
# 2. 设置预测结果保存目录
PRED_DIR="/xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_trained_models/test_predictions_Task500"
mkdir -p $PRED_DIR
# 3. 运行推理(使用 all fold + model_best)
nnUNet_predict \
-i $nnUNet_raw_data_base/nnUNet_raw_data/Task500_Synapse/imagesTs \
-o $PRED_DIR \
-t 500 \
-m 3d_fullres \
-tr nnUNetTrainerV2 \
-f all \
-chk model_best
nnUNet_evaluate_folder -ref /xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_raw/nnUNet_raw_data/Task500_Synapse/labelsTs -pred /xujiheng/Synapse/nnUNet/nnUNet/nnUNetFrame/DATASET/nnUNet_trained_models/test_predictions_Task500 -l 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
关键代码文件目录:
代码:
# Copyright 2020 Division of Medical Image Computing, German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ), Heidelberg, Germany
#
# Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
# you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
# You may obtain a copy of the License at
#
# http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
#
# Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
# distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
# WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
# limitations under the License.
import collections
import inspect
import json
import hashlib
from datetime import datetime
from multiprocessing.pool import Pool
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import SimpleITK as sitk
from nnunet.evaluation.metrics import ConfusionMatrix, ALL_METRICS
from batchgenerators.utilities.file_and_folder_operations import save_json, subfiles, join
from collections import OrderedDict
class Evaluator:
"""Object that holds test and reference segmentations with label information
and computes a number of metrics on the two. 'labels' must either be an
iterable of numeric values (or tuples thereof) or a dictionary with string
names and numeric values.
"""
default_metrics = [
"False Positive Rate",
"Dice",
"Jaccard",
"Precision",
"Recall",
"Accuracy",
"False Omission Rate",
"Negative Predictive Value",
"False Negative Rate",
"True Negative Rate",
"False Discovery Rate",
"Total Positives Test",
"Total Positives Reference"
]
default_advanced_metrics = [
#"Hausdorff Distance",
"Hausdorff Distance 95",
#"Avg. Surface Distance",
#"Avg. Symmetric Surface Distance"
]
def __init__(self,
test=None,
reference=None,
labels=None,
metrics=None,
advanced_metrics=None,
nan_for_nonexisting=True):
self.test = None
self.reference = None
self.confusion_matrix = ConfusionMatrix()
self.labels = None
self.nan_for_nonexisting = nan_for_nonexisting
self.result = None
self.metrics = []
if metrics is None:
for m in self.default_metrics:
self.metrics.append(m)
else:
for m in metrics:
self.metrics.append(m)
self.advanced_metrics = []
if advanced_metrics is None:
for m in self.default_advanced_metrics:
self.advanced_metrics.append(m)
else:
for m in advanced_metrics:
self.advanced_metrics.append(m)
self.set_reference(reference)
self.set_test(test)
if labels is not None:
self.set_labels(labels)
else:
if test is not None and reference is not None:
self.construct_labels()
def set_test(self, test):
"""Set the test segmentation."""
self.test = test
def set_reference(self, reference):
"""Set the reference segmentation."""
self.reference = reference
def set_labels(self, labels):
"""Set the labels.
:param labels= may be a dictionary (int->str), a set (of ints), a tuple (of ints) or a list (of ints). Labels
will only have names if you pass a dictionary"""
if isinstance(labels, dict):
self.labels = collections.OrderedDict(labels)
elif isinstance(labels, set):
self.labels = list(labels)
elif isinstance(labels, np.ndarray):
self.labels = [i for i in labels]
elif isinstance(labels, (list, tuple)):
self.labels = labels
else:
raise TypeError("Can only handle dict, list, tuple, set & numpy array, but input is of type {}".format(type(labels)))
def construct_labels(self):
"""Construct label set from unique entries in segmentations."""
if self.test is None and self.reference is None:
raise ValueError("No test or reference segmentations.")
elif self.test is None:
labels = np.unique(self.reference)
else:
labels = np.union1d(np.unique(self.test),
np.unique(self.reference))
self.labels = list(map(lambda x: int(x), labels))
def set_metrics(self, metrics):
"""Set evaluation metrics"""
if isinstance(metrics, set):
self.metrics = list(metrics)
elif isinstance(metrics, (list, tuple, np.ndarray)):
self.metrics = metrics
else:
raise TypeError("Can only handle list, tuple, set & numpy array, but input is of type {}".format(type(metrics)))
def add_metric(self, metric):
if metric not in self.metrics:
self.metrics.append(metric)
def evaluate(self, test=None, reference=None, advanced=False, **metric_kwargs):
"""Compute metrics for segmentations."""
if test is not None:
self.set_test(test)
if reference is not None:
self.set_reference(reference)
if self.test is None or self.reference is None:
raise ValueError("Need both test and reference segmentations.")
if self.labels is None:
self.construct_labels()
self.metrics.sort()
# get functions for evaluation
# somewhat convoluted, but allows users to define additonal metrics
# on the fly, e.g. inside an IPython console
_funcs = {m: ALL_METRICS[m] for m in self.metrics + self.advanced_metrics}
frames = inspect.getouterframes(inspect.currentframe())
for metric in self.metrics:
for f in frames:
if metric in f[0].f_locals:
_funcs[metric] = f[0].f_locals[metric]
break
else:
if metric in _funcs:
continue
else:
raise NotImplementedError(
"Metric {} not implemented.".format(metric))
# get results
self.result = OrderedDict()
eval_metrics = self.metrics
if advanced:
eval_metrics += self.advanced_metrics
if isinstance(self.labels, dict):
for label, name in self.labels.items():
k = str(name)
self.result[k] = OrderedDict()
if not hasattr(label, "__iter__"):
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(self.test == label)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(self.reference == label)
else:
current_test = 0
current_reference = 0
for l in label:
current_test += (self.test == l)
current_reference += (self.reference == l)
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(current_test)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(current_reference)
for metric in eval_metrics:
self.result[k][metric] = _funcs[metric](confusion_matrix=self.confusion_matrix,
nan_for_nonexisting=self.nan_for_nonexisting,
**metric_kwargs)
else:
for i, l in enumerate(self.labels):
k = str(l)
self.result[k] = OrderedDict()
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(self.test == l)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(self.reference == l)
for metric in eval_metrics:
self.result[k][metric] = _funcs[metric](confusion_matrix=self.confusion_matrix,
nan_for_nonexisting=self.nan_for_nonexisting,
**metric_kwargs)
return self.result
def to_dict(self):
if self.result is None:
self.evaluate()
return self.result
def to_array(self):
"""Return result as numpy array (labels x metrics)."""
if self.result is None:
self.evaluate
result_metrics = sorted(self.result[list(self.result.keys())[0]].keys())
a = np.zeros((len(self.labels), len(result_metrics)), dtype=np.float32)
if isinstance(self.labels, dict):
for i, label in enumerate(self.labels.keys()):
for j, metric in enumerate(result_metrics):
a[i][j] = self.result[self.labels[label]][metric]
else:
for i, label in enumerate(self.labels):
for j, metric in enumerate(result_metrics):
a[i][j] = self.result[label][metric]
return a
def to_pandas(self):
"""Return result as pandas DataFrame."""
a = self.to_array()
if isinstance(self.labels, dict):
labels = list(self.labels.values())
else:
labels = self.labels
result_metrics = sorted(self.result[list(self.result.keys())[0]].keys())
return pd.DataFrame(a, index=labels, columns=result_metrics)
class NiftiEvaluator(Evaluator):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.test_nifti = None
self.reference_nifti = None
super(NiftiEvaluator, self).__init__(*args, **kwargs)
def set_test(self, test):
"""Set the test segmentation."""
if test is not None:
self.test_nifti = sitk.ReadImage(test)
super(NiftiEvaluator, self).set_test(sitk.GetArrayFromImage(self.test_nifti))
else:
self.test_nifti = None
super(NiftiEvaluator, self).set_test(test)
def set_reference(self, reference):
"""Set the reference segmentation."""
if reference is not None:
self.reference_nifti = sitk.ReadImage(reference)
super(NiftiEvaluator, self).set_reference(sitk.GetArrayFromImage(self.reference_nifti))
else:
self.reference_nifti = None
super(NiftiEvaluator, self).set_reference(reference)
def evaluate(self, test=None, reference=None, voxel_spacing=None, **metric_kwargs):
if voxel_spacing is None:
voxel_spacing = np.array(self.test_nifti.GetSpacing())[::-1]
metric_kwargs["voxel_spacing"] = voxel_spacing
return super(NiftiEvaluator, self).evaluate(test, reference, **metric_kwargs)
def run_evaluation(args):
test, ref, evaluator, metric_kwargs = args
# evaluate
evaluator.set_test(test)
evaluator.set_reference(ref)
if evaluator.labels is None:
evaluator.construct_labels()
current_scores = evaluator.evaluate(**metric_kwargs)
if type(test) == str:
current_scores["test"] = test
if type(ref) == str:
current_scores["reference"] = ref
return current_scores
def aggregate_scores(test_ref_pairs,
evaluator=NiftiEvaluator,
labels=None,
nanmean=True,
json_output_file=None,
json_name="",
json_description="",
json_author="Fabian",
json_task="",
num_threads=2,
**metric_kwargs):
"""
test = predicted image
:param test_ref_pairs:
:param evaluator:
:param labels: must be a dict of int-> str or a list of int
:param nanmean:
:param json_output_file:
:param json_name:
:param json_description:
:param json_author:
:param json_task:
:param metric_kwargs:
:return:
"""
if type(evaluator) == type:
evaluator = evaluator()
if labels is not None:
evaluator.set_labels(labels)
all_scores = OrderedDict()
all_scores["all"] = []
all_scores["mean"] = OrderedDict()
test = [i[0] for i in test_ref_pairs]
ref = [i[1] for i in test_ref_pairs]
p = Pool(num_threads)
all_res = p.map(run_evaluation, zip(test, ref, [evaluator]*len(ref), [metric_kwargs]*len(ref)))
p.close()
p.join()
for i in range(len(all_res)):
all_scores["all"].append(all_res[i])
# append score list for mean
for label, score_dict in all_res[i].items():
if label in ("test", "reference"):
continue
if label not in all_scores["mean"]:
all_scores["mean"][label] = OrderedDict()
for score, value in score_dict.items():
if score not in all_scores["mean"][label]:
all_scores["mean"][label][score] = []
all_scores["mean"][label][score].append(value)
for label in all_scores["mean"]:
for score in all_scores["mean"][label]:
if nanmean:
all_scores["mean"][label][score] = float(np.nanmean(all_scores["mean"][label][score]))
else:
all_scores["mean"][label][score] = float(np.mean(all_scores["mean"][label][score]))
# save to file if desired
# we create a hopefully unique id by hashing the entire output dictionary
if json_output_file is not None:
json_dict = OrderedDict()
json_dict["name"] = json_name
json_dict["description"] = json_description
timestamp = datetime.today()
json_dict["timestamp"] = str(timestamp)
json_dict["task"] = json_task
json_dict["author"] = json_author
json_dict["results"] = all_scores
json_dict["id"] = hashlib.md5(json.dumps(json_dict).encode("utf-8")).hexdigest()[:12]
save_json(json_dict, json_output_file)
return all_scores
def aggregate_scores_for_experiment(score_file,
labels=None,
metrics=Evaluator.default_metrics,
nanmean=True,
json_output_file=None,
json_name="",
json_description="",
json_author="Fabian",
json_task=""):
scores = np.load(score_file)
scores_mean = scores.mean(0)
if labels is None:
labels = list(map(str, range(scores.shape[1])))
results = []
results_mean = OrderedDict()
for i in range(scores.shape[0]):
results.append(OrderedDict())
for l, label in enumerate(labels):
results[-1][label] = OrderedDict()
results_mean[label] = OrderedDict()
for m, metric in enumerate(metrics):
results[-1][label][metric] = float(scores[i][l][m])
results_mean[label][metric] = float(scores_mean[l][m])
json_dict = OrderedDict()
json_dict["name"] = json_name
json_dict["description"] = json_description
timestamp = datetime.today()
json_dict["timestamp"] = str(timestamp)
json_dict["task"] = json_task
json_dict["author"] = json_author
json_dict["results"] = {"all": results, "mean": results_mean}
json_dict["id"] = hashlib.md5(json.dumps(json_dict).encode("utf-8")).hexdigest()[:12]
if json_output_file is not None:
json_output_file = open(json_output_file, "w")
json.dump(json_dict, json_output_file, indent=4, separators=(",", ": "))
json_output_file.close()
return json_dict
def evaluate_folder(folder_with_gts: str, folder_with_predictions: str, labels: tuple, **metric_kwargs):
"""
writes a summary.json to folder_with_predictions
:param folder_with_gts: folder where the ground truth segmentations are saved. Must be nifti files.
:param folder_with_predictions: folder where the predicted segmentations are saved. Must be nifti files.
:param labels: tuple of int with the labels in the dataset. For example (0, 1, 2, 3) for Task001_BrainTumour.
:return:
"""
files_gt = subfiles(folder_with_gts, suffix=".nii.gz", join=False)
files_pred = subfiles(folder_with_predictions, suffix=".nii.gz", join=False)
assert all([i in files_pred for i in files_gt]), "files missing in folder_with_predictions"
assert all([i in files_gt for i in files_pred]), "files missing in folder_with_gts"
test_ref_pairs = [(join(folder_with_predictions, i), join(folder_with_gts, i)) for i in files_pred]
res = aggregate_scores(test_ref_pairs, json_output_file=join(folder_with_predictions, "summary.json"),
num_threads=8, labels=labels, **metric_kwargs)
return res
def nnunet_evaluate_folder():
import argparse
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser("Evaluates the segmentations located in the folder pred. Output of this script is "
"a json file. At the very bottom of the json file is going to be a 'mean' "
"entry with averages metrics across all cases")
parser.add_argument('-ref', required=True, type=str, help="Folder containing the reference segmentations in nifti "
"format.")
parser.add_argument('-pred', required=True, type=str, help="Folder containing the predicted segmentations in nifti "
"format. File names must match between the folders!")
parser.add_argument('-l', nargs='+', type=int, required=True, help="List of label IDs (integer values) that should "
"be evaluated. Best practice is to use all int "
"values present in the dataset, so for example "
"for LiTS the labels are 0: background, 1: "
"liver, 2: tumor. So this argument "
"should be -l 1 2. You can if you want also "
"evaluate the background label (0) but in "
"this case that would not give any useful "
"information.")
args = parser.parse_args()
return evaluate_folder(args.ref, args.pred, args.l)
if __name__ == '__main__':
evaluate_folder(
'/media/isensee/raw_data/nnUNet_raw/Dataset004_Hippocampus/labelsTr',
'/home/isensee/drives/checkpoints/nnUNet_results_remake/Dataset999_IntegrationTest_Hippocampus/ensembles/ensemble___nnUNetTrainer_5epochs__nnUNetPlans__3d_cascade_fullres___nnUNetTrainer_5epochs__nnUNetPlans__3d_fullres___0_1_2_3_4',
(1, 2), advanced=True
)
整体流程:
[预测文件夹] [真实标签文件夹]
↓ ↓
列出 .nii.gz 文件(名字必须匹配)
↓
构建 (pred, gt) 对
↓
多线程并行:每对 → NiftiEvaluator.evaluate()
↓
收集所有结果 → 计算 mean(按标签)
↓
保存为 summary.json这里主要讲一下指标计算:
指标函数的来源
首先,这段代码开头导入了:
from nnunet.evaluation.metrics import ConfusionMatrix, ALL_METRICSALL_METRICS 是一个字典,其键是字符串(如 "Dice"),值是可调用的函数对象。这些函数的具体实现在 nnunet/evaluation/metrics.py,但调用点在当前文件。
例如(这是 metrics.py 中典型的定义方式):
ALL_METRICS = {
"Dice": dice,
"Hausdorff Distance 95": hausdorff_distance_95,
...
}调用点一:构建指标函数映射表 _funcs
在 Evaluator.evaluate() 方法中,有如下完整代码:
def evaluate(self, test=None, reference=None, advanced=False, **metric_kwargs):
"""Compute metrics for segmentations."""
if test is not None:
self.set_test(test)
if reference is not None:
self.set_reference(reference)
if self.test is None or self.reference is None:
raise ValueError("Need both test and reference segmentations.")
if self.labels is None:
self.construct_labels()
self.metrics.sort()
# get functions for evaluation
# somewhat convoluted, but allows users to define additonal metrics
# on the fly, e.g. inside an IPython console
_funcs = {m: ALL_METRICS[m] for m in self.metrics + self.advanced_metrics}
frames = inspect.getouterframes(inspect.currentframe())
for metric in self.metrics:
for f in frames:
if metric in f[0].f_locals:
_funcs[metric] = f[0].f_locals[metric]
break
else:
if metric in _funcs:
continue
else:
raise NotImplementedError(
"Metric {} not implemented.".format(metric))
# get results
self.result = OrderedDict()
eval_metrics = self.metrics
if advanced:
eval_metrics += self.advanced_metrics
if isinstance(self.labels, dict):
for label, name in self.labels.items():
k = str(name)
self.result[k] = OrderedDict()
if not hasattr(label, "__iter__"):
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(self.test == label)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(self.reference == label)
else:
current_test = 0
current_reference = 0
for l in label:
current_test += (self.test == l)
current_reference += (self.reference == l)
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(current_test)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(current_reference)
for metric in eval_metrics:
self.result[k][metric] = _funcs[metric](confusion_matrix=self.confusion_matrix,
nan_for_nonexisting=self.nan_for_nonexisting,
**metric_kwargs)
else:
for i, l in enumerate(self.labels):
k = str(l)
self.result[k] = OrderedDict()
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(self.test == l)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(self.reference == l)
for metric in eval_metrics:
self.result[k][metric] = _funcs[metric](confusion_matrix=self.confusion_matrix,
nan_for_nonexisting=self.nan_for_nonexisting,
**metric_kwargs)
return self.result分析:
_funcs = {m: ALL_METRICS[m] for m in self.metrics + self.advanced_metrics}
直接从 ALL_METRICS 取出每个指标对应的函数。
如果 self.metrics 包含 "Dice",则 _funcs["Dice"] = ALL_METRICS["Dice"]
如果 self.advanced_metrics 包含 "Hausdorff Distance 95",则 _funcs["Hausdorff Distance 95"] = ALL_METRICS["Hausdorff Distance 95"]
调用点二:实际执行指标计算
继续看 Evaluator.evaluate() 中的循环部分:
if isinstance(self.labels, dict):
for label, name in self.labels.items():
k = str(name)
self.result[k] = OrderedDict()
if not hasattr(label, "__iter__"):
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(self.test == label)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(self.reference == label)
else:
current_test = 0
current_reference = 0
for l in label:
current_test += (self.test == l)
current_reference += (self.reference == l)
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(current_test)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(current_reference)
for metric in eval_metrics:
self.result[k][metric] = _funcs[metric](confusion_matrix=self.confusion_matrix,
nan_for_nonexisting=self.nan_for_nonexisting,
**metric_kwargs)
else:
for i, l in enumerate(self.labels):
k = str(l)
self.result[k] = OrderedDict()
self.confusion_matrix.set_test(self.test == l)
self.confusion_matrix.set_reference(self.reference == l)
for metric in eval_metrics:
self.result[k][metric] = _funcs[metric](confusion_matrix=self.confusion_matrix,
nan_for_nonexisting=self.nan_for_nonexisting,
**metric_kwargs)关键调用语句:
for metric in eval_metrics:
self.result[k][metric] = _funcs[metric](confusion_matrix=self.confusion_matrix,
nan_for_nonexisting=self.nan_for_nonexisting,
**metric_kwargs)对于 Dice:
metric == "Dice"
调用:_funcs["Dice"](confusion_matrix=..., nan_for_nonexisting=..., **metric_kwargs)
注意:Dice 函数通常只需要 confusion_matrix(内部有 TP, FP, FN 等),不需要 voxel_spacing,所以 **metric_kwargs 对它无影响。
对于 HD95:
metric == "Hausdorff Distance 95"
调用:_funcs["Hausdorff Distance 95"](confusion_matrix=..., nan_for_nonexisting=..., **metric_kwargs)
注意:HD95 的实现并不使用 confusion_matrix!
实际上,hausdorff_distance_95 函数需要原始的二值数组(test 和 reference)以及 voxel_spacing,所以在 nnunet/evaluation/metrics.py 中,该函数会忽略 confusion_matrix,而是通过其他方式获取 test/reference —— 这其实是设计上的一个“技巧”或“约定”




















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








