数据库对表的操作
1 内部表与外部表
1.1 内部表
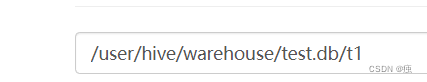
表目录hive会自动创建在默认的HDFS目录下/user/hive/warehouse/…
建表语句
create table t1(
id int,
name string,
sex string
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by " ";
1.2 外部表
创建的时候,需要使用external关键字,并指定表对应hdfs上的目录/work
建表语句
create external table t2(id int,
name string,
sex string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ' '
location '/work';

1.3 内部表和外部表的差别
1.删除一个内部表时,表的元信息和表数据目录都会被删除
2.删除一个外部表时,只删除表的元信息,表的数据目录不会被删除
2 数据的导入导出
数据准备
新建t1.txt文件

上传的到虚拟机上
2.1 数据导入
2.1.1 将hive服务器运行所在节点的本地磁盘上的文件导入表中
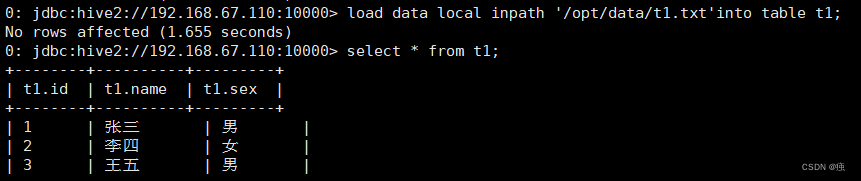
load data local inpath '/opt/data/t1.txt'into table t1;
load data local inpath '/opt/data/t1.txt' overwrite into table t1;
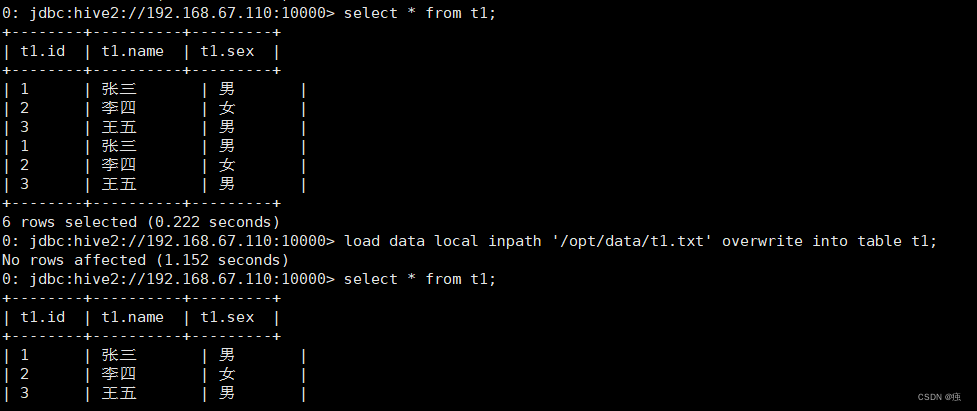
加上overwrite会实现数据的覆盖,不加overwrite是追加到原有数据的后面
2.1.2 将hdfs上的文件导入表中
上传文件到HDFS

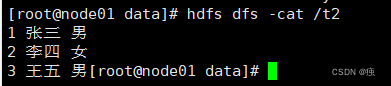
load data inpath'/t2' into table t2;

发现hdfs上的/t2被移动到外部表目录下
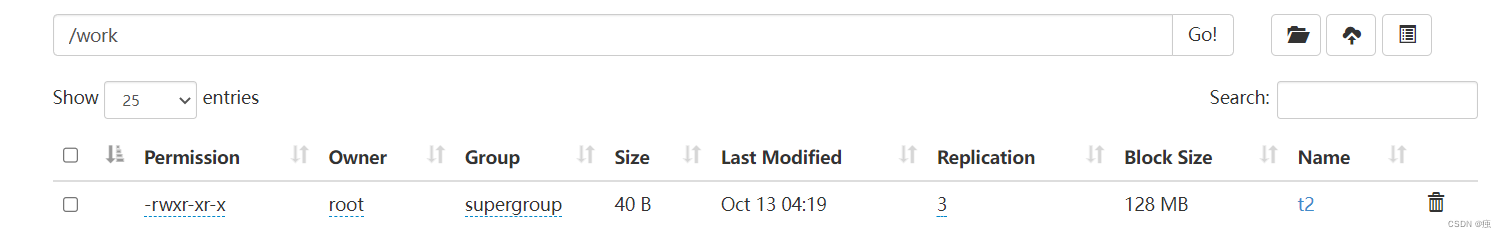
注意:如果加上local是复制,不是移动
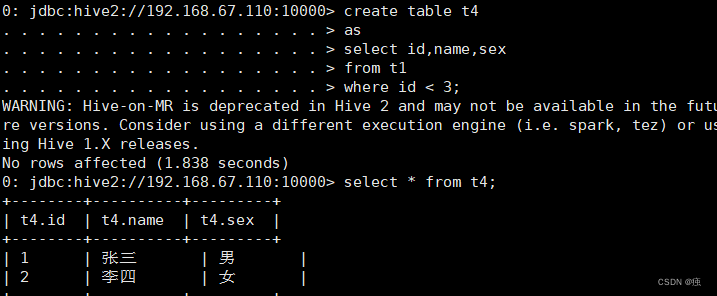
2.1.3 从别的表查询数据后插入到一张新建的表中
create table t4
as
select id,name,sex
from t1
where id < 3;
2.1.4 从别的表查询数据后插入到一张已经存在的表中
insert into table t3
select id,name,sex
from t1;
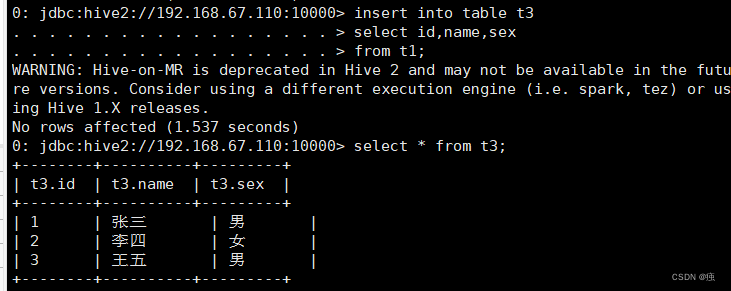
into替换为overwrite,会覆盖掉原表得数据
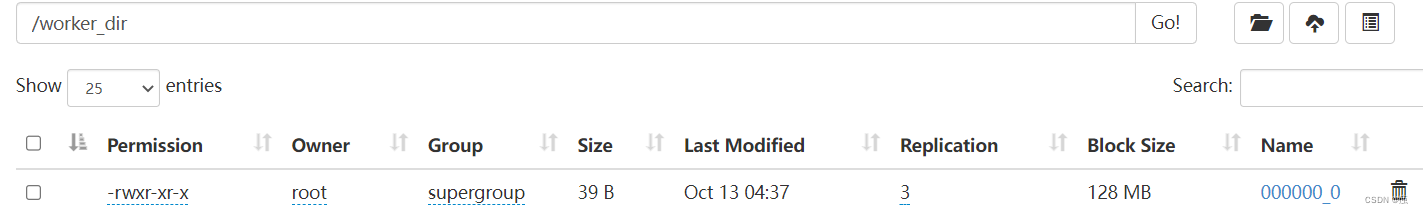
2.2 数据导出
将数据从hive的表中导出到hdfs的目录中
insert overwrite directory '/worker_dir'
select * from t1;
insert overwrite directory '/opt/data/aa.log'
select * from t1;
3 Hive的复杂数据类型 array、map、struct
3.1 数据准备

建表语句
create table demo(
id int,
name string,
work_location array<string>,
piaofang map<string,bigint>,
address struct<location:string,zipcode:int,phone:string,value:int>)
row format delimited
fields terminated by " "
collection items terminated by ","
map keys terminated by ":" ;
导入数据
load data local inpath "/opt/data/demo.txt" into table demo;
查询语句
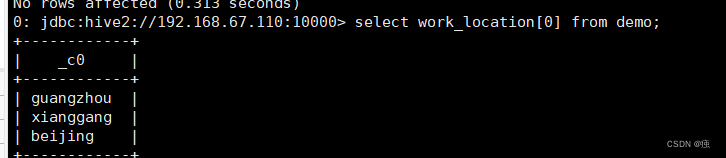
array:select work_location[0] from demo;
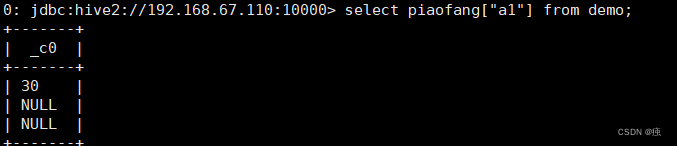
map:select piaofang[“a1”] from demo;
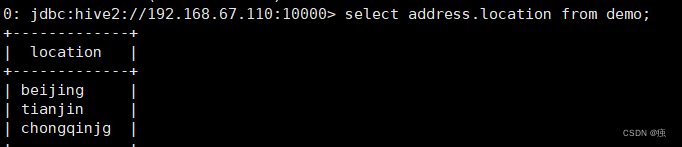
struct:select address.location from demo;
4 Hive的文件存储格式
Hive支持多种文件格式:sequence file、text file、parquet file、rc file、orc file
- TextFile
存储方式:行存储。默认格式,如果建表时不指定默认为此格式 - Sequence File
SequenceFile是一种二进制文件,以<key,value>的形式序列化到文件中。存储方式:行存储; - RC File
存储方式:数据按行分块,每块按照列存储 。 - ORC File
存储方式:数据按行分块,每块按照列存储 - Parquet File
存储方式:列式存储
5 查看表信息
以ti表为例
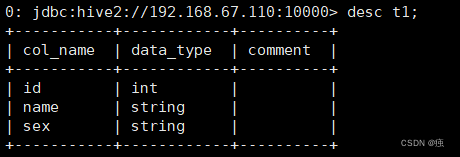
5.1 查看表信息
desc t1
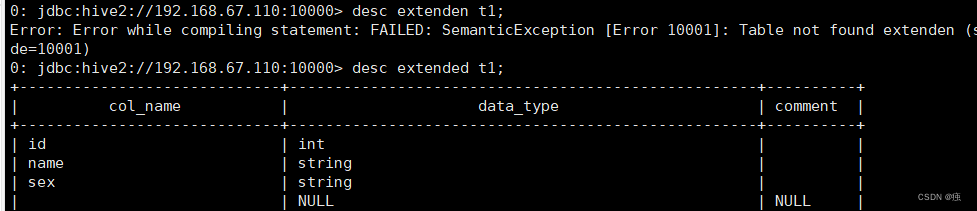
5.2 查看表的详细信息
desc extended t1;
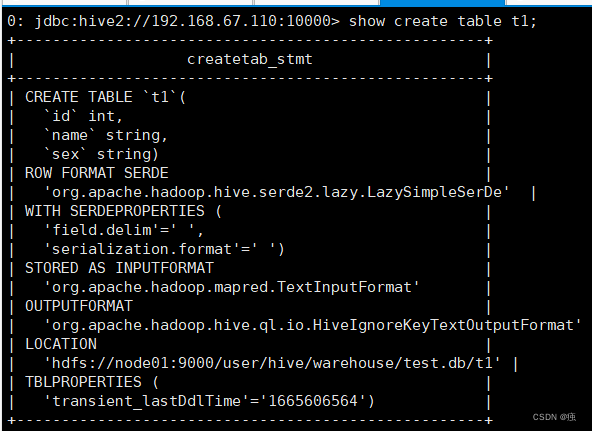
5.3 查看表的详细建表语句
show create table t1;
6 修改表
6.1 修改表名
alter table student rename to new_student;

6.2. 修改字段
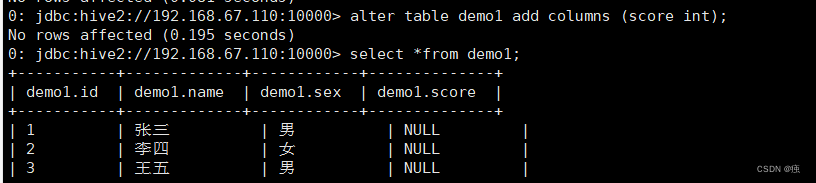
6.2.1 增加一个字段
alter table demo1 add columns (score int);
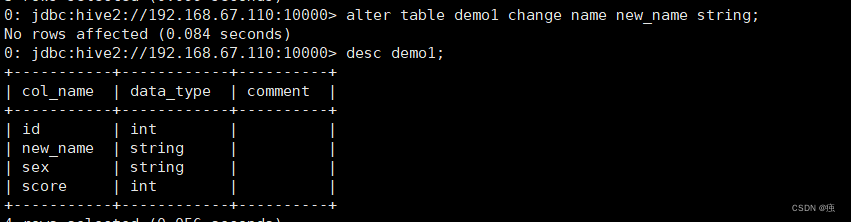
6.2.2修改一个字段的定义
alter table demo1 change name new_name string;
7 删除和清空表
7.1 删除表
drop table (表名);
7.2 清空表
truncate table (表名);
8 Hive的分区表
8.1 分区表的创建
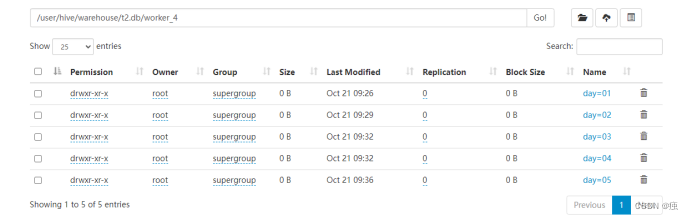
分区就是表目录中的一个子目录。
建表
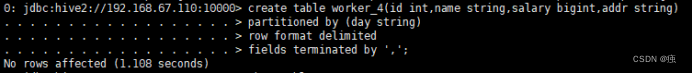
create table worker_4(id int,name string,salary bigint,addr string)
partitioned by (day string)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ‘,’;
注意:分区的字段一定不能在定义的字段里
8.2 导入数据到分区
load data local inpath '/opt/testData/hive/worker_1.txt' into table worker_4 partition(day='01');
load data local inpath '/opt/testData/hive/worker_1.txt' into table worker_4 partition(day='02');

它会将day这个分区条件也当成了一个字段。
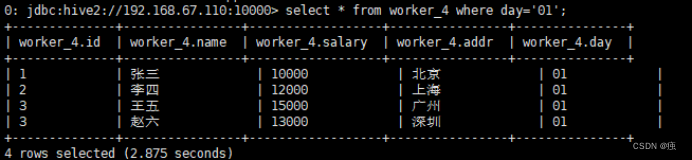
如果只查询worker_4下day=01目录下的信息,可以用:
select * from worker_4 where day=’01’;
8.3 增删分区
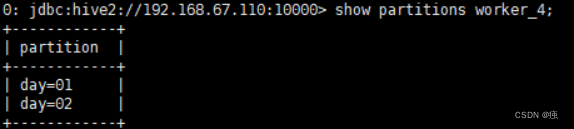
8.3.1查看分区信息
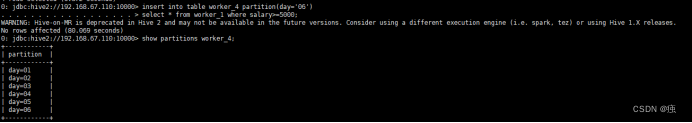
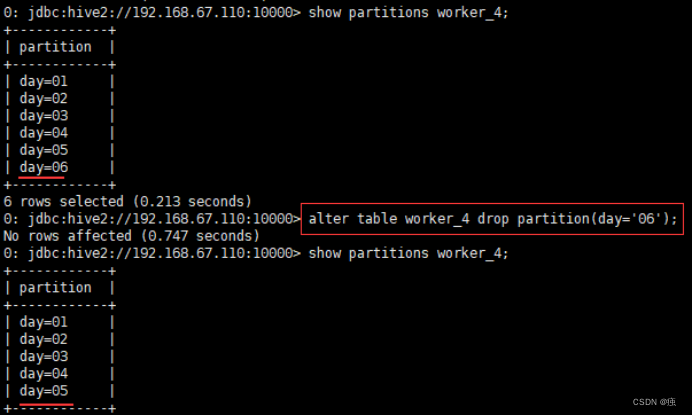
show partitions worker_4;
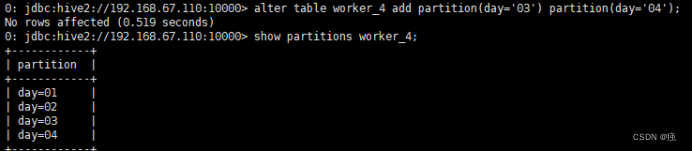
8.3.2 增加分区
alter table worker_4 add partition(day='03') partition(day='04');
通过加载数据实现添加分区
load data local inpath '/usr/datadir/worker_3.txt' into table worker_4 partition(day='05');
每个分区都对应一个表目录下的子目录
还可以使用insert实现分区
insert into table worker_4 partition(day='06')
select * from worker_1 where salary>=5000;
8.3.3删除分区
alter table worker_4 drop partition(day='06');
8.4 动态分区
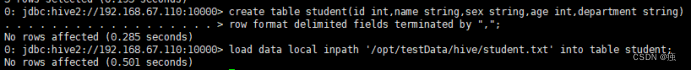
新建表
create table student(id int,name string,sex string,age int,department string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ",";
load data local inpath '/usr/datadir/student.txt' into table student;
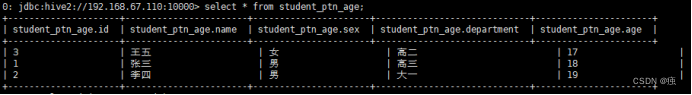
把这一张表的内容直接插入到另一张表student_ptn_age中,并实现age为动态分区(不指定到底是哪种年龄,让系统自己分配决定)
创建分区表
create table student_ptn_age(id int,name string,sex string,department string)
partitioned by (age int);

插入数据,实现动态分区
动态分区需要设置set hive.exec.dynamic.partition.mode=nonstrict;不然会报错


insert overwrite table student_ptn_age partition(age)
select id,name,sex,department,age from student;

查询的分区字段要写在最后
9 Hive的分区桶
9.1 什么是分桶
分桶是相对分区进行更细粒度的划分(数据取样更高效)。分桶将整个数据内容按照某列属性值的hash值进行区分,如要安装name属性分为3个桶,就是对name属性值的hash 值对3取摸,按照取模结果对数据分桶。如取模结果为0的数据记录存放到一个文件,取模为1的数据存放到一个文件,取模为2的数据存放到一个文件
9.2 分桶操作
创建分通表
create table student_bck(id int, name string)
clustered by (id) into 3 buckets
row format delimited fields
terminated by ",";
向桶中插入数据
insert overwrite table student_bck
select id,name from t2;
查看存储的信息
查看分桶数据
select * from student_bck tablesample(bucket 1 out of 3 on id);
10 视图
create view v_name(字段)
as
select * from t_student;
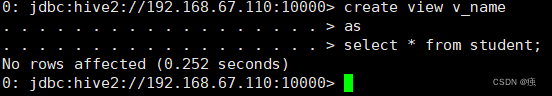
视图不能load数据,也不能insert。只能用来进行查询。
视图是一个逻辑的概念,并不是物理上存在的。
11 Hive的表关联操作
11.1 join操作
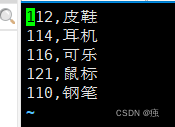
准备需要的数据
创建表t_order
create table t_order(
orderid int,
name string
)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ",";
导入数据
load data local inpath '/opt/testData/hive/order.txt' into table t_order;

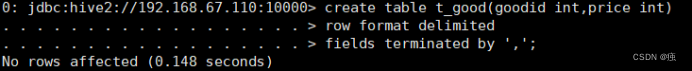
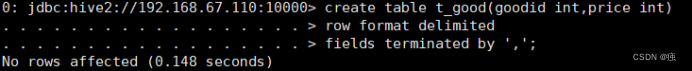
创建表t_good
create table t_good(goodid int,price int)
row format delimited
fields terminated by ',';
导入数据
load data local inpath '/opt/testData/hive/order.txt' into table t_goodr;

通过goodid = orderid 建立内连接
select *
from t_order inner join t_goods
on orderid = goodid;
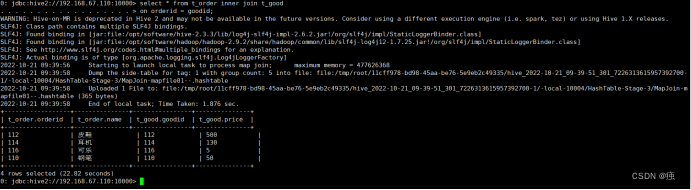
左外连接
select *
from t_order left join t_goods
on orderid = goodid;
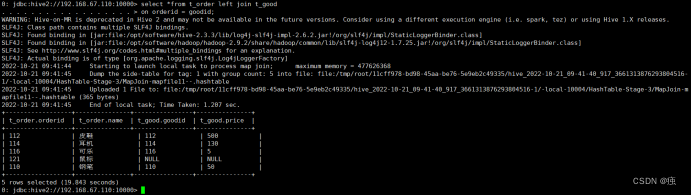
右外连接
select *
from t_order right join t_goods
on orderid = goodid;
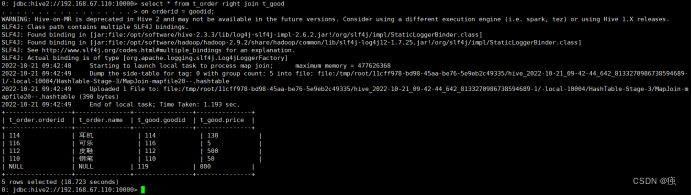
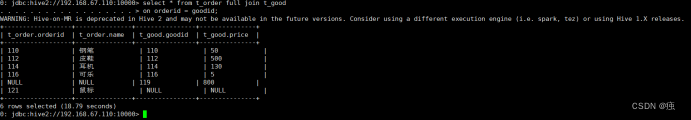
全外连接
select *
from t_order full join t_goods
on orderid = goodid;
11.2 笛卡尔积
笛卡尔积:假设集合A={a, b},集合B={0, 1, 2},则两个集合的笛卡尔积为{(a, 0), (a, 1), (a, 2), (b, 0), (b, 1), (b, 2)}
两张表没有关联条件,但是需要关联的时候,就可以使用笛卡尔积
create table doctor_info(name string,second_dep string,illness string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ",";
load data local inpath '/usr/datadir/doctor.txt' into table doctor_info;
create table department_info(first_dep string,keyword string)
row format delimited fields terminated by ",";
load data local inpath '/usr/datadir/department.txt' into table department_info;
set hive.mapred.mode=nonstrict;
create table hospital_info
as
select *
from doctor_info
join department_info
on 1=1;
select *
from hospital_info
where second_dep regexp keyword;
11.3 union和union all
11.3.1 数据准备
首先在good.txt 中加入三行数据
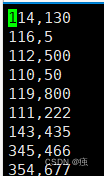
创建表t_good1 并将good.txt 数据导入
load data local inpath '/opt/testData/hive/good.txt' into table t_good1;
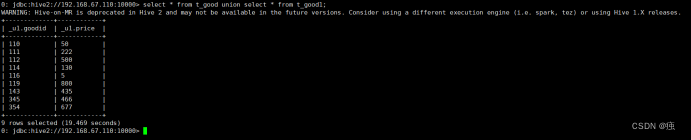
11.3.2 Union关联(Union 关联会对数据进行去重)
select * from t_good union select * from t_good1;
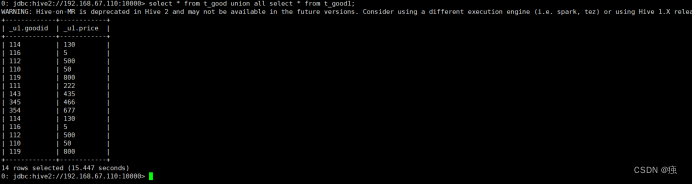
11.3.3 Union all 关联 不会对数据进行去重操作
select * from t_good union all select * from t_good1;




 本文详细介绍了Hive中的表操作,包括内部表与外部表的创建和区别,数据的导入导出,复杂数据类型如array、map、struct的使用,以及文件存储格式。此外,还讲解了查看和修改表信息、分区表和动态分区的概念,以及Hive的视图、表关联操作如join、笛卡尔积和union。内容深入浅出,适合大数据领域的Hive学习者参考。
本文详细介绍了Hive中的表操作,包括内部表与外部表的创建和区别,数据的导入导出,复杂数据类型如array、map、struct的使用,以及文件存储格式。此外,还讲解了查看和修改表信息、分区表和动态分区的概念,以及Hive的视图、表关联操作如join、笛卡尔积和union。内容深入浅出,适合大数据领域的Hive学习者参考。
















 1152
1152

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








