说在前面
我第一次接触堆这个东西是在做堆排序的时候。这玩意还不错,难度也不大,可以用的地方很多,值得玩一玩。
前置知识:
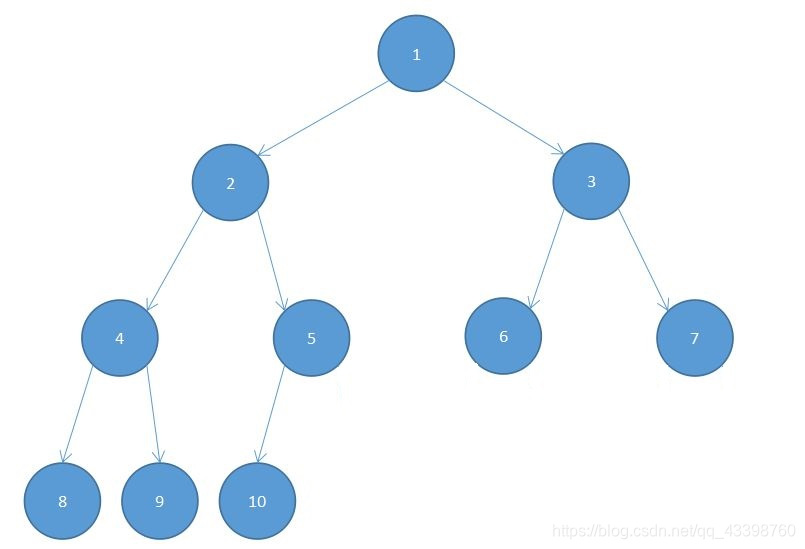
完全二叉树
完全二叉树 ,顾名思义是一种二叉树就是说 (假设树根深度为1 )深度为k的二叉树 ,第1至第k-1层的结
点都是满的,也就是说 ,如果一颗二叉树满足第i(1<=i<=K-1)层的结点数为2 * i-1 ,0<第K层的结点数
<=2 * k-1 ,并且最下面一层的结点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置 ,那么它就是一颗完全二叉树。
like this:
堆的性质及其基本操作:
堆的性质
1.编号为i的结点的左二子的编号为2 * i ,右儿子编号为2 * i + 1 ,父结点编号为i / 2 (假设有)
2.n个结点的堆的高度为log2(n + 1)的对数
3.h[i] <= h[2 * i], h[i] <= h[2 * i + 1] (或者 h[i] >= h[2 * i], h[i] >= h[2 * i + 1] )ps:前面那个是小
根堆 ,即h[1]是最小值 ;而后者为大根堆 ,即h[1]是最大值。
基本操作
1.上浮(up)
void up(int x) { //h[x]上浮
while(x > 1 && h[x] < h[x >> 1]) {
swap(h[x], h[x >> 1]);
x >>= 1;
}
}
2.下沉(down)
void down(int x) { //h[x]下沉,len是堆中元素个数
int y = x << 1;
while(y <= len) {
if(y + 1 <= len && h[y + 1] < h[y]) y++;
if(h[y] < h[x]) {
swap(h[x], h[y]);
x = y;
y = x << 1;
} else break;
}
}3.读入(insert)
void insert(int x) {
h[++len] = x;
up(len);
}4.删除(delete)
void del(int x) { //删除元素h[x]
h[x] = h[len--];
up(x);
down(x);
}下面放一个模板(小根堆):
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n, k;
int a[100010], h[100010];
int b[100010];
int cnt, len;
void up(int x) {
while (x > 1 && h[x] < h[x >> 1]) {
swap(h[x], h[x >> 1]);
x >>= 1;
}
}
void down(int x) {
int y = x << 1;
while (y <= len) {
if (y + 1 <= len && h[y + 1] < h[y]) y++;
if (h[y] < h[x]) {
swap(h[x], h[y]);
x = y;
y = x << 1;
}
else break;
}
}
void insert(int x) {
h[++len] = x;
up(len);
}
int solve() {
int d = h[1];
h[1] = h[len--];
down(1);
return d;
}
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
insert(a[i]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cout << solve() << " ";
}
}
/*
13
19 17 16 12 9 15 1 2 11 7 3 10 14
*/几个题目:








 本文介绍了堆的概念,特别是完全二叉树的定义,并详细阐述了堆的性质,包括左、右子节点的编号规则和高度计算。此外,讨论了堆的基本操作,如上浮、下沉、插入和删除,并提供了小根堆的模板。还推荐了几道入门级的在线编程题目以巩固理解。
本文介绍了堆的概念,特别是完全二叉树的定义,并详细阐述了堆的性质,包括左、右子节点的编号规则和高度计算。此外,讨论了堆的基本操作,如上浮、下沉、插入和删除,并提供了小根堆的模板。还推荐了几道入门级的在线编程题目以巩固理解。
















 731
731

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








