AlexNet
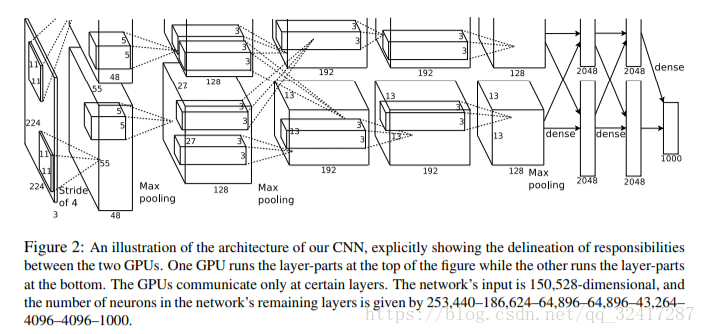
AlexNet 包含有5个卷积层,其中3个卷积层之后有pooling层,最后有3层全连接层,2012年 ILSVRC 比赛上 top-5的错误率为16.4%。
新技术
- 使用ReLU作为激励函数,来代替sigmoid函数,消除了sigmoid函数在网络较深的时候的梯度弥散的问题。
- 训练过程中在最后的全连接层使用了dropout 随机忽略一些神经元,避免了模型的过拟合,这也是dropout的作用。
- CNN中使用了重叠的最大池化,避免了平均池化的模糊化效果。重叠:步长比池化核小
- 提出LRN层,对局部神经元的活动创建竞争机制,使其响应比较大的值变得更大,并抑制其他比较小的神经元,增强模型的泛化能力
- 使用CUDA加速深度CNN的训练,使用GPU并行能力,处理神经网络训练时大量的矩阵计算;作者将AlexNet分布在两个GPU上,每个GPU的显存中存储一半的神经元的参数。让GPU之间的通信只在网络的某些层进行。
- 数据增强。随机从 256×256 256 × 256 的原始图像中截取 224×224 224 × 224 的区域(以及水平反转的镜像),相当于加入了 (256−224)2×2=2048 ( 256 − 224 ) 2 × 2 = 2048 的数据量。如果没有数据增强,参数众多的CNN则会出现过拟合现象。在AlexNet中,测试的时候,取图片的 四个角加上中间共5个位置 来进行左右反转,得到10个图像,对他们进行预测并对结果取平均值;同时,AlexNet论文中提到对RGB图像进行PAC处理,并对主成分增加标准差为 0.1 的高斯扰动, 可以让错误里再下降 1%
输入
224×224
224
×
224
输出
1000
1000
类
最后一层输出1000类 softmax层。
LRN出现在第一个、第二个卷积层后,最大池化层出现在两个LRN层以及最后一个卷积层之后。
ReLU 用在所有的卷积层以及全连接层之后。
网络结构
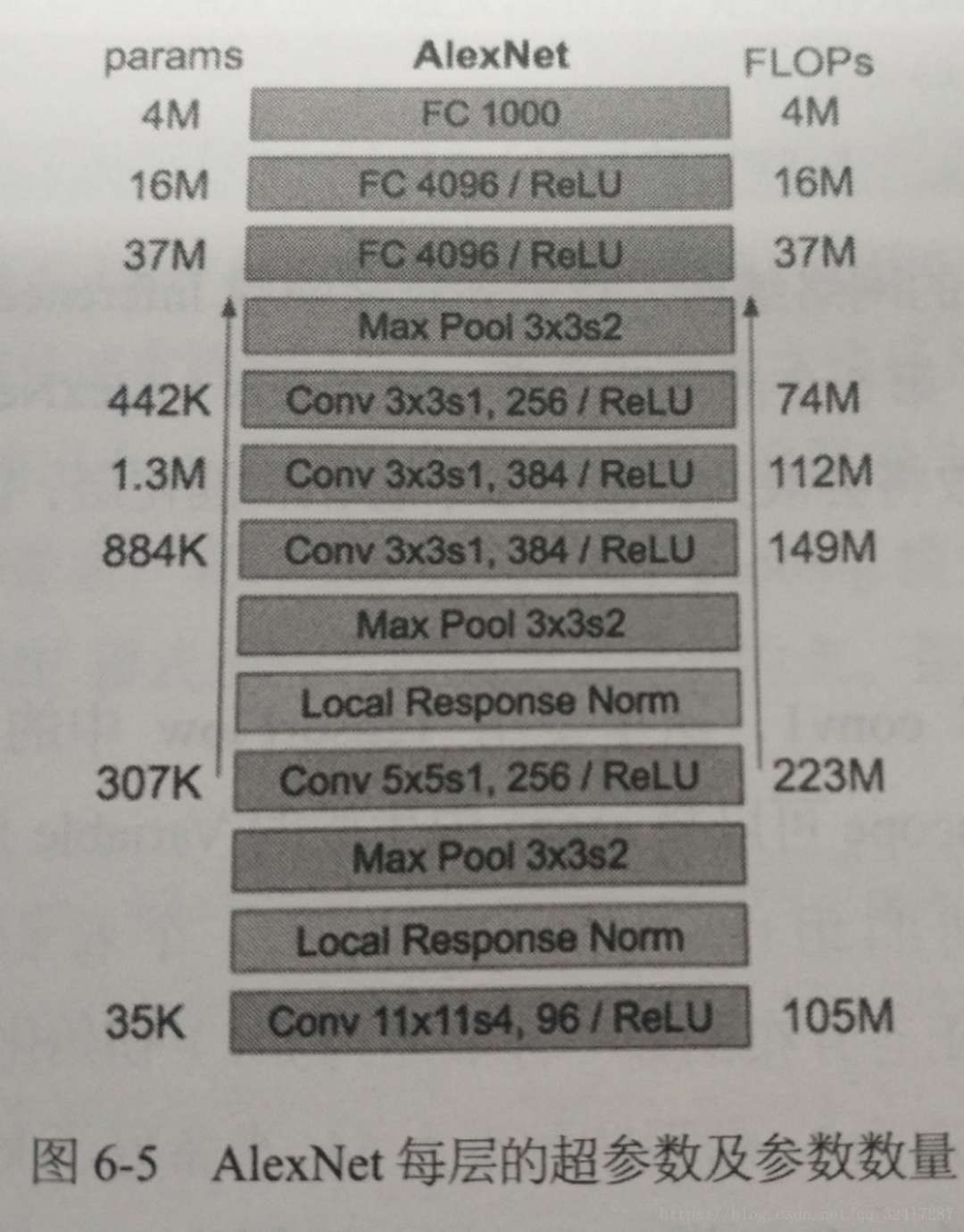
每层的超参数以及参数数量
实现
remain
如何设定filter个数,每一层的步长
何时使用pooling
如何确定使用多少层
refer:
# coding:utf-8
'''
refer: https://github.com/tensorflow/models/blob/master/tutorials/image/alexnet/alexnet_benchmark.py
主要实现的是AlexNet的卷积层,但是貌似没有按照论文上的参数来
'''
from datetime import datetime
import math
import time
import tensorflow as tf
# 共测试100个batch的数据
batch_size = 1
num_batches = 100
# 显示每一层的结构,结构的是tensor输入,显示名称和尺寸
def print_activations(t):
print(t.op.name, '', t.get_shape().as_list())
'''
定义Alex net网络,接受image 输入,返回最后一层 pool5 以及 parameters
'''
def inference(images):
parameters = []
# 第一层 conv1
with tf.name_scope('conv1') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([11, 11, 3, 64], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights') # 这里为什么是64,而不是 96个核
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(images, kernel, [1, 4, 4, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[64], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv1 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv1)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
# 在第一层之后加入LRN,最大支池化层,但是LRN的效果不是很明显,可以选择去掉
with tf.name_scope('lrn1') as scope:
lrn1 = tf.nn.lrn(conv1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9, beta=0.75, name='lrn1')
# lrn1 = tf.nn.local_response_normalization(conv1, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001 / 9, beta=0.75, name='lrn1')
pool1 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn1, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name="pool1")
print_activations(pool1)
# 第二层 conv2
with tf.name_scope('conv2') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([5, 5, 64, 192], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool1, kernel, [1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[192], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv2 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
print_activations(conv2)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
# 加入LRN、最大池化层
with tf.name_scope('lrn2') as scope:
lrn2 = tf.nn.lrn(conv2, 4, bias=1.0, alpha=0.001/9, beta=0.75, name='lrn2')
pool2 = tf.nn.max_pool(lrn2, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool2')
print_activations(pool2)
# 第三层
with tf.name_scope('conv3') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 192, 384], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(pool2, kernel, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[384]), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv3 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv3)
# 第四层
with tf.name_scope('conv4') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 384, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv3, kernel, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, dtype=tf.float32, shape=[256]), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv4 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv4)
# 第五层
with tf.name_scope('conv5') as scope:
kernel = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 256], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
conv = tf.nn.conv2d(conv4, kernel, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[256], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
bias = tf.nn.bias_add(conv, biases)
conv5 = tf.nn.relu(bias, name=scope)
parameters += [kernel, biases]
print_activations(conv5)
# 池化层,最后的输出结果pool5
pool5 = tf.nn.max_pool(conv5, ksize=[1, 3, 3, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='VALID', name='pool5')
print_activations(pool5)
# 当正式训练或者预测时,需要添加3个全连接层,4096、4096、1000
# 全连接层的添加类似于感知机
# with tf.name_scope('dense1') as scope:
# weights = tf.Variable(tf.truncated_normal([3, 3, 256, 4096], dtype=tf.float32, stddev=1e-1), name='weights')
# biases = tf.Variable(tf.constant(0.0, shape=[4096], dtype=tf.float32), trainable=True, name='biases')
# dense1 = tf.add(tf.matmul(pool5, weights), biases)
return pool5, parameters
'''
计算每轮所需时间
session: Session
target: 需要评测的运算算子
info_string: 测试的名称
'''
def time_tensorflow_run(session, target, info_string):
num_steps_burn_in = 10 # 考虑10次迭代之后的计算时间
total_duration = 0.0
total_duration_squared = 0.0
for i in range(num_batches + num_steps_burn_in):
start_time = time.time()
_ = session.run(target)
duration = time.time() - start_time
if i >= num_steps_burn_in:
if not i % 10:
print('%s: step %d, duration = %.3f' % (datetime.now(), i - num_steps_burn_in, duration))
total_duration += duration
total_duration_squared += duration * duration
mn = total_duration / num_batches
vr = total_duration_squared /num_batches - mn * mn
sd = math.sqrt(vr)
print('%s: %s across %d steps, %.3f +/- %.3f sec / batch' % (datetime.now(), info_string, num_batches, mn, sd))
# 主函数
def run_benchmark():
with tf.Graph().as_default():
image_size = 224
# 构造图像
images = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([batch_size,
image_size,
image_size,
3],
dtype=tf.float32,
stddev=1e-1))
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
pool5, parameters = inference(images)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, pool5, 'Forward')
objective = tf.nn.l2_loss(pool5)
grad = tf.gradients(objective, parameters)
time_tensorflow_run(sess, grad, 'Forward-backward')
run_benchmark()








 本文详细介绍了AlexNet网络结构,包括5个卷积层、3个全连接层及其实现细节。探讨了ReLU、Dropout等技术的应用,以及如何通过数据增强避免过拟合。
本文详细介绍了AlexNet网络结构,包括5个卷积层、3个全连接层及其实现细节。探讨了ReLU、Dropout等技术的应用,以及如何通过数据增强避免过拟合。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








