DecidePathBounds函数
InitPathBoundary函数
bool PathBoundsDeciderUtil::InitPathBoundary(
const ReferenceLineInfo& reference_line_info,
PathBoundary* const path_bound, SLState init_sl_state)
reference_line_info:参考线信息
path_bound:路径边界(出参)
init_sl_state_ = reference_line.ToFrenetFrame(planning_start_point);
init_sl_state:上一篇中planning模块(10)-路径规划(笛卡尔坐标转Frenet坐标) 获取到的 l l l, l ′ {l}' l′, l ′ ′ {l}'' l′′, s s s, s ˙ \dot{s} s˙, s ¨ \ddot{s} s¨
path_bound->set_delta_s(FLAGS_path_bounds_decider_resolution);
设置路径边界采样步长
const auto& vehicle_config =
common::VehicleConfigHelper::Instance()->GetConfig();
const double ego_front_to_center =
vehicle_config.vehicle_param().front_edge_to_center();
从modules/common/data/vehicle_param.pb.txt配置文件中,获取车辆最前边缘到后轴中心的距离
const auto& reference_line_towing_l =
reference_line_info.reference_line_towing_l();
上面变量,没有使用
for (double curr_s = init_sl_state.first[0];
curr_s < std::fmin(init_sl_state.first[0] +
std::fmax(FLAGS_path_bounds_horizon,
reference_line_info.GetCruiseSpeed() *
FLAGS_trajectory_time_length),
reference_line.Length() - ego_front_to_center);
curr_s += FLAGS_path_bounds_decider_resolution) {
path_bound->emplace_back(curr_s, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
if (index < reference_line_towing_l.size()) {
path_bound->back().towing_l = reference_line_towing_l.at(index);
}
index++;
}
curr_s:自车所匹配的参考点的纵向距离
循环终止条件:规划终点

FLAGS_path_bounds_decider_resolution:循环步长
path_bound->emplace_back(curr_s, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
根据上面步长对规划轨迹进行采样,初始化路径边界点路径边界为[lowest(), max()]
GetBoundaryFromSelfLane函数
double adc_lane_width =
GetADCLaneWidth(reference_line, init_sl_state.first[0]);
根据自车所对应的参考点的s值,从map中获取到此位置的车道宽度,作为路径边界采样点位置的默认路径边界
double offset_to_map = 0.0;
reference_line.GetOffsetToMap(curr_s, &offset_to_map);
通过当前s值获取到当前位置平滑参考线与粗糙参考线的横向偏移
double curr_left_bound = 0.0;
double curr_right_bound = 0.0;
curr_left_bound = curr_lane_left_width - offset_to_map;
curr_right_bound = -curr_lane_right_width - offset_to_map;
curr_left_bound/curr_right_bound:获取到的是以平滑后的参考线为中心线的左右路径边界
UpdateLeftPathBoundaryWithBuffer函数
double adc_half_width =
VehicleConfigHelper::GetConfig().vehicle_param().width() / 2.0;
从modules/common/data/vehicle_param.pb.txt配置中获取车辆宽度的一半
path_bound->emplace_back(curr_s, std::numeric_limits<double>::lowest(),
std::numeric_limits<double>::max());
在上面介绍中,路径边界都被初始化为了[lowest(), max()]
PathBoundPoint new_point = *bound_point;
if (new_point.l_upper.l > left_bound) {
new_point.l_upper.l = left_bound;
new_point.l_upper.type = left_type;
new_point.l_upper.id = left_id;
}
上面逻辑,会把路径边界点最大值更新为以平滑后的参考线为中心线的左边界减去自车宽度的一半得到[lowest(), left_bound]
UpdateRightPathBoundaryWithBuffer函数同理
会把路径边界点最小值更新为以平滑后的参考线为中心线的右边界加上自车宽度的一半得到[right_bound, left_bound].
left_bound = left_bound - adc_half_width;
right_bound = right_bound + adc_half_width;
在Frenet坐标系下,沿着车辆行驶的方向为s方向,垂直于s的方向为l方向,并且l方向是参考线左侧为正值,参考线右侧为负值.
所以左边界left_bound是正数要减去adc_half_width才是左侧车辆空余的空间
右边界right_bound是负数要加上adc_half_width才是右侧车辆空余的空间
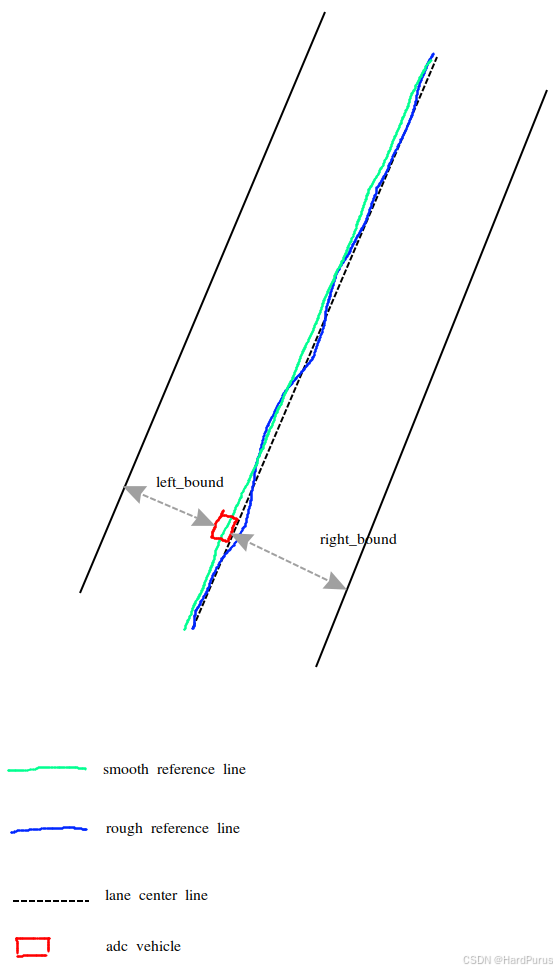
TrimPathBounds函数
如果发现路径边界点对应的可行驶范围,车辆无法通过,就会把这个路径边界点及之后的路径边界点都裁剪掉.
if (is_include_adc) {
PathBoundsDeciderUtil::ExtendBoundaryByADC(
*reference_line_info_, init_sl_state_, config_.extend_buffer(),
&path_bound);
}
上面是借道逻辑,先暂时不考虑,在介绍lane borrow task的时候再进行介绍
auto indexed_obstacles = reference_line_info_->path_decision()->obstacles();
这里需要先介绍一下reference_line_info信息的构建函数
modules/planning/planning_base/common/frame.cc
CreateReferenceLineInfo函数
忽略的逻辑,我觉得如果认真看,是可以理解的,所以就不介绍了.
for (auto iter = reference_line_info_.begin();
iter != reference_line_info_.end();) {
if (!iter->Init(obstacles(), target_speed)) {
reference_line_info_.erase(iter++);
} else {
has_valid_reference_line = true;
iter->set_index(ref_line_index);
AINFO << "get referenceline: index: " << iter->index()
<< ", id: " << iter->id() << ", key: " << iter->key();
ref_line_index++;
iter++;
}
}
这里要介绍一下obstacles()函数,在Frame类中有两处可以向obstacles_变量中加入障碍物
第一处
void Frame::AddObstacle(const Obstacle &obstacle) {
obstacles_.Add(obstacle.Id(), obstacle);
}
第二处
const Obstacle *Frame::CreateStaticVirtualObstacle(const std::string &id,
const Box2d &box) {
const auto *object = obstacles_.Find(id);
if (object) {
AWARN << "obstacle " << id << " already exist.";
return object;
}
auto *ptr =
obstacles_.Add(id, *Obstacle::CreateStaticVirtualObstacles(id, box));
if (!ptr) {
AERROR << "Failed to create virtual obstacle " << id;
}
return ptr;
}
第一处障碍物的来源是prediction,prediction的来源是perception
第二处障碍物是根据需求可以通过规则的配置文件进行配置的,比如你想在某个位置停下来,那么就可以通过配置设置虚拟障碍物来实现
本专栏目的是快速入门pnc算法,所以只介绍来自perception的障碍物.
modules/planning/planning_base/common/frame.cc
Status Frame::InitFrameData(
const common::VehicleStateProvider *vehicle_state_provider,
const EgoInfo *ego_info) {
...
for (auto &ptr :
Obstacle::CreateObstacles(*local_view_.prediction_obstacles)) {
AddObstacle(*ptr);
}
CreateObstacles函数
IsValidPerceptionObstacle函数对感知障碍物数据做合法性校验,主要是验证障碍物的长宽高,在x方向上的速度,在y方向上的速度,障碍物几何图形各点的合理性
然后会根据障碍物是否有预测轨迹线并通过障碍物id来区分,构建Obstacle
然后通过Frame::AddObstacle函数将障碍物添加到obstacles_中.
现在,在回到Frame::CreateReferenceLineInfo函数
iter->Init(obstacles(), target_speed)
obstacles()就是从Frame类obstacles_中获取到所有的障碍物,然后在ReferenceLineInfo::Init函数中通过AddObstacles函数调用AddObstacle函数将障碍物信息传入到ReferenceLineInfo::path_decision_中
ReferenceLineInfo::AddObstacle函数
Obstacle* ReferenceLineInfo::AddObstacle(const Obstacle* obstacle) {
...
auto* mutable_obstacle = path_decision_.AddObstacle(*obstacle);
SLBoundary perception_sl;
if (!reference_line_.GetSLBoundary(obstacle->PerceptionPolygon(),
&perception_sl)) {
AERROR << "Failed to get sl boundary for obstacle: " << obstacle->Id();
return mutable_obstacle;
}
ReferenceLine::GetSLBoundary函数
corners:规划模块只用障碍物在地面上的投影,所以角点的个数一般是4个
int first_index = 0;
double min_dist = std::numeric_limits<double>::max();
for (int i = 0; i < obs_corners.size(); ++i) {
double ego_dist = ego_position_.DistanceTo(obs_corners[i]);
if (ego_dist < min_dist) {
min_dist = ego_dist;
first_index = i;
}
}
获取到离自车最近的角点
std::rotate(obs_corners.begin(), obs_corners.begin() + first_index,
obs_corners.end());
const common::math::Vec2d& first_point = obs_corners.front();
ADEBUG << "first_point: " << std::setprecision(9) << first_point.x() << ", "
<< first_point.y();
SLPoint first_sl_point;
if (!XYToSL(first_point, &first_sl_point, warm_start_s)) {
AERROR << "Failed to get projection for point: "
<< first_point.DebugString() << " on reference line.";
return false;
}
sl_corners.push_back(std::move(first_sl_point));
}
根据粗糙参考线获取离自车最近角点的横纵距离
double hueristic_start_s = 0.0;
double hueristic_end_s = 0.0;
double distance = 0.0;
SLPoint sl_point;
for (size_t i = 1; i < obs_corners.size(); ++i) {
distance = obs_corners[i].DistanceTo(obs_corners[i - 1]);
hueristic_start_s = sl_corners.back().s() - 2.0 * distance;
hueristic_end_s = sl_corners.back().s() + 2.0 * distance;
if (!XYToSL(obs_corners[i], &sl_point, hueristic_start_s,
hueristic_end_s)) {
AERROR << "Failed to get projection for point: "
<< obs_corners[i].DebugString() << " on reference line.";
return false;
}
sl_corners.push_back(std::move(sl_point));
}
上面逻辑主要是根据已经计算了s的角点,再结合两个角点之间的distance,可以限定出来一个搜索范围,这样在求其它角点的s,l时,不用搜索整条粗糙参考线,而是只在这个限定范围内做投影计算s,l就可以了,减少计算量.
这样障碍物所有投影点我们认为是4个投影点的s,l都已经计算出来了,存到了sl_corners中 .
for (size_t i = 0; i < obs_corners.size(); ++i) {
auto index0 = i;
auto index1 = (i + 1) % obs_corners.size();
const auto& p0 = obs_corners[index0];
const auto& p1 = obs_corners[index1];
const auto p_mid = (p0 + p1) * 0.5;
distance = obs_corners[index0].DistanceTo(p_mid);
hueristic_start_s = sl_corners[index0].s() - 2.0 * distance;
hueristic_end_s = sl_corners[index0].s() + 2.0 * distance;
SLPoint sl_point_mid;
if (!XYToSL(p_mid, &sl_point_mid, hueristic_start_s, hueristic_end_s)) {
AERROR << "Failed to get projection for point: " << p_mid.DebugString()
<< " on reference line.";
return false;
}
Vec2d v0(sl_corners[index1].s() - sl_corners[index0].s(),
sl_corners[index1].l() - sl_corners[index0].l());
Vec2d v1(sl_point_mid.s() - sl_corners[index0].s(),
sl_point_mid.l() - sl_corners[index0].l());
*sl_boundary->add_boundary_point() = sl_corners[index0];
// sl_point is outside of polygon; add to the vertex list
if (v0.CrossProd(v1) < 0.0) {
*sl_boundary->add_boundary_point() = sl_point_mid;
}
}
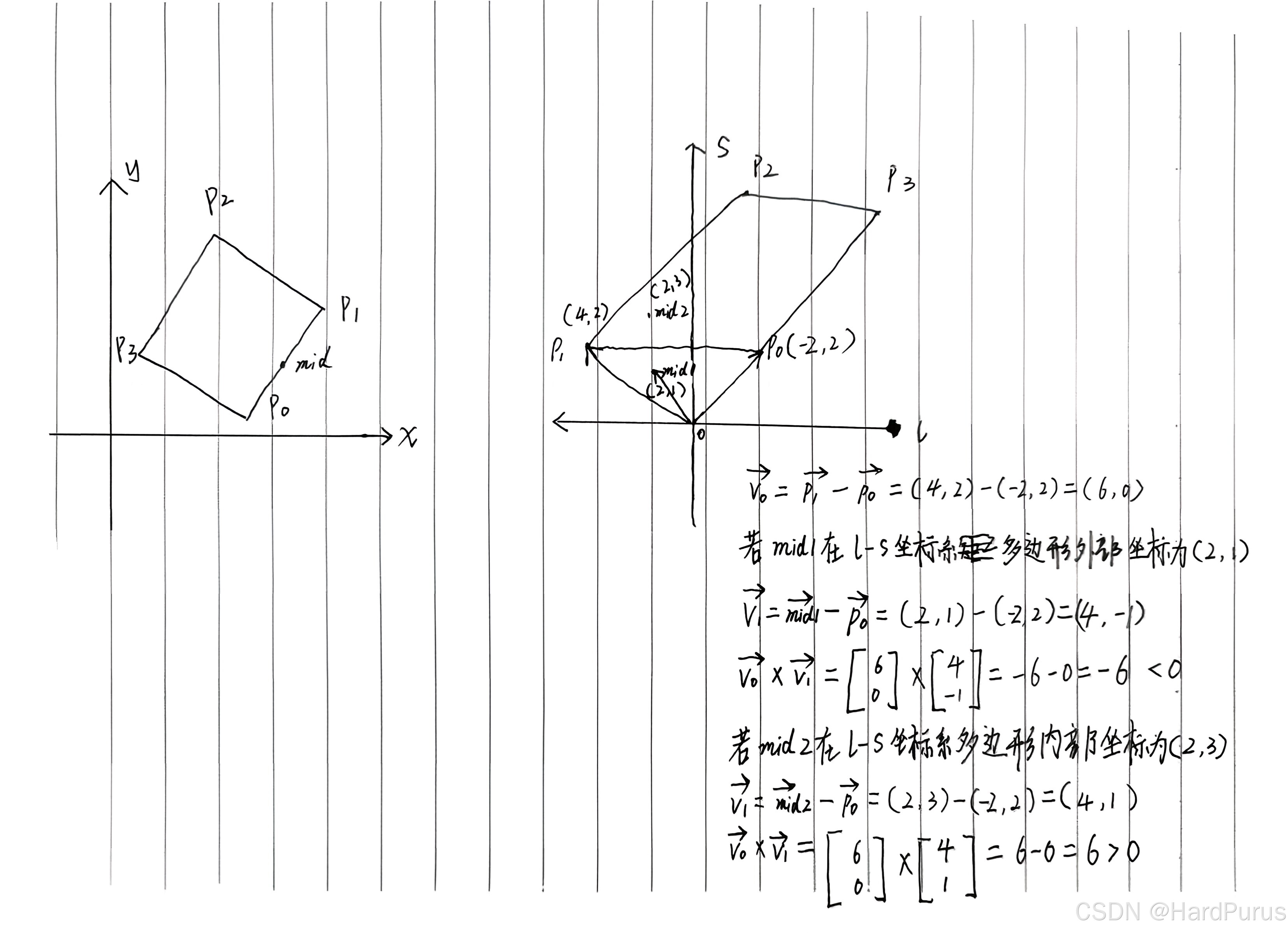
上面代码逻辑,是在判断障碍物每条边的中点在l-s坐标系上的投影点是在多边形内部还是外部,如果在外部,也会把这个在l-s坐标系下的投影点加入到sl_boundary中
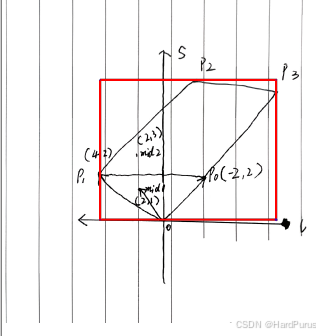
推导过程可以参看上面图示,左侧是笛卡尔坐标系,右侧是投影到l-s坐标系下的对应投影点.
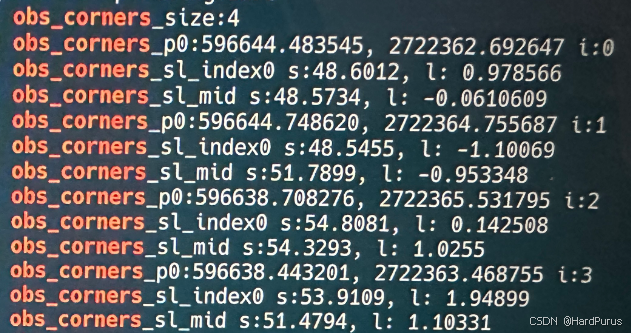
也可以根据日志自己画一下,一共四个角点_p0是从p0开始的四个笛卡尔坐标系下的角点坐标,sl_index0是l-s坐标系的投影点坐标,sl_mid是每条边中点投影点的坐标.
for (const auto& sl_point : sl_boundary->boundary_point()) {
start_s = std::fmin(start_s, sl_point.s());
end_s = std::fmax(end_s, sl_point.s());
start_l = std::fmin(start_l, sl_point.l());
end_l = std::fmax(end_l, sl_point.l());
}
sl_boundary->set_start_s(start_s);
sl_boundary->set_end_s(end_s);
sl_boundary->set_start_l(start_l);
sl_boundary->set_end_l(end_l);
最后将障碍物的投影范围设置如下图AABB的矩形框形式
IsIrrelevantObstacle函数
判断一个障碍物,是否和当前参考线有关系,如果无关就不需要作为决策点,路径规划也不需要考虑此障碍物
AddLateralDecision函数
如果障碍物和当前参考线有关,则添加新的决策
bool PathDecision::AddLateralDecision(const std::string &tag,
const std::string &object_id,
const ObjectDecisionType &decision)
ObjectDecisionType类型如下:
核心设计原则
同一个障碍物:
可以同时有:
一个纵向决策
一个横向决策
但:
每个方向只有一个决策最终生效
message ObjectDecisionType {
oneof object_tag {
ObjectIgnore ignore = 1;
ObjectStop stop = 2;
ObjectFollow follow = 3;
ObjectYield yield = 4;
ObjectOvertake overtake = 5;
ObjectNudge nudge = 6;
ObjectAvoid avoid = 7;
ObjectSidePass side_pass = 8;
}
}
| 类型 | 含义 | 本质 | 决策类型 |
|---|---|---|---|
ignore | 忽略 | 对规划无影响 | 横向决策 |
stop | 停车 | 纵向强制约束 | 纵向决策 |
follow | 跟随 | 纵向控制(ACC) | 纵向决策 |
yield | 让行 | 减速让路 | 纵向决策 |
overtake | 超车 | 纵向 + 横向 | 纵向决策 |
nudge | 轻微横向避让 | 横向 | 横向决策 |
avoid | 避让 | 强避让(较少用) | |
side_pass | 侧向绕行 | 复杂横向 |
MergeLateralDecision函数
ObjectDecisionType Obstacle::MergeLateralDecision(
const ObjectDecisionType& lhs, const ObjectDecisionType& rhs) {
if (lhs.object_tag_case() == ObjectDecisionType::OBJECT_TAG_NOT_SET) {
return rhs;
}
if (rhs.object_tag_case() == ObjectDecisionType::OBJECT_TAG_NOT_SET) {
return lhs;
}
lhs:之前的决策
rhs:新的决策
const auto lhs_val =
FindOrDie(s_lateral_decision_safety_sorter_, lhs.object_tag_case());
const auto rhs_val =
FindOrDie(s_lateral_decision_safety_sorter_, rhs.object_tag_case());
Obstacle::s_lateral_decision_safety_sorter_ = {
{ObjectDecisionType::kIgnore, 0}, {ObjectDecisionType::kNudge, 100}};
s_lateral_decision_safety_sorter_:是决策安全等级,数值越大决策越强 / 越保守 / 越安全,这里apollo认为横向决策只用到了两个一个是nudge,一个是ignore.nudge就是如果自车前方有静止障碍物,如果条件满足,自车会稍微nudge一下,然后绕过障碍物,ignore就相当于认为前方静止障碍物不影响通行,就当它不存在.
else if (lhs.has_nudge()) {
DCHECK(lhs.nudge().type() == rhs.nudge().type())
<< "could not merge left nudge and right nudge";
return std::fabs(lhs.nudge().distance_l()) >
std::fabs(rhs.nudge().distance_l())
? lhs
: rhs;
}
message ObjectNudge {
enum Type {
LEFT_NUDGE = 1; // drive from the left side to nudge a static obstacle
RIGHT_NUDGE = 2; // drive from the right side to nudge a static obstacle
DYNAMIC_LEFT_NUDGE = 3; // drive from the left side to nudge a dynamic obstacle
DYNAMIC_RIGHT_NUDGE = 4; // drive from the right side to nudge a dynamic obstacle
};
optional Type type = 1;
// minimum lateral distance in meters. positive if type = LEFT_NUDGE
// negative if type = RIGHT_NUDGE
optional double distance_l = 2;
}
当新旧决策都是nudge时,并且nudge类型也相同时,比较nudge距离选择nudge大的决策,nudge距离,就是绕的距离.nudge会在介绍PATH_DECIDER时介绍.
最后MergeLateralDecision返回要执行的横向决策
AddLongitudinalDecision函数
和AddLateralDecision同理,是添加纵向决策
纵向决策安全等级:
Obstacle::s_longitudinal_decision_safety_sorter_ = {
{ObjectDecisionType::kIgnore, 0},
{ObjectDecisionType::kOvertake, 100},
{ObjectDecisionType::kFollow, 300},
{ObjectDecisionType::kYield, 400},
{ObjectDecisionType::kStop, 500}};

























 1389
1389

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










