文章目录
Problem
Find a rigid transformation to align two point clouds
Papers
The Normal Distributions Transform: A New Approach to Laser Scan Matching (2003)
- 首次提出NDT(2D)
The Three-Dimensional Normal-Distributions Transform— an Efficient Representation for Registration,Surface Analysis, and Loop Detection (2009)
- 一篇博士论文,对NDT 进行了总结
- pcl中的实现主要是参考该论文6.2 和 6.2.2
pcl implenmentation:
registration/include/pcl/registration/impl/ndt.hpp
Cost Function
核心思想:使用PDF 来表示点云
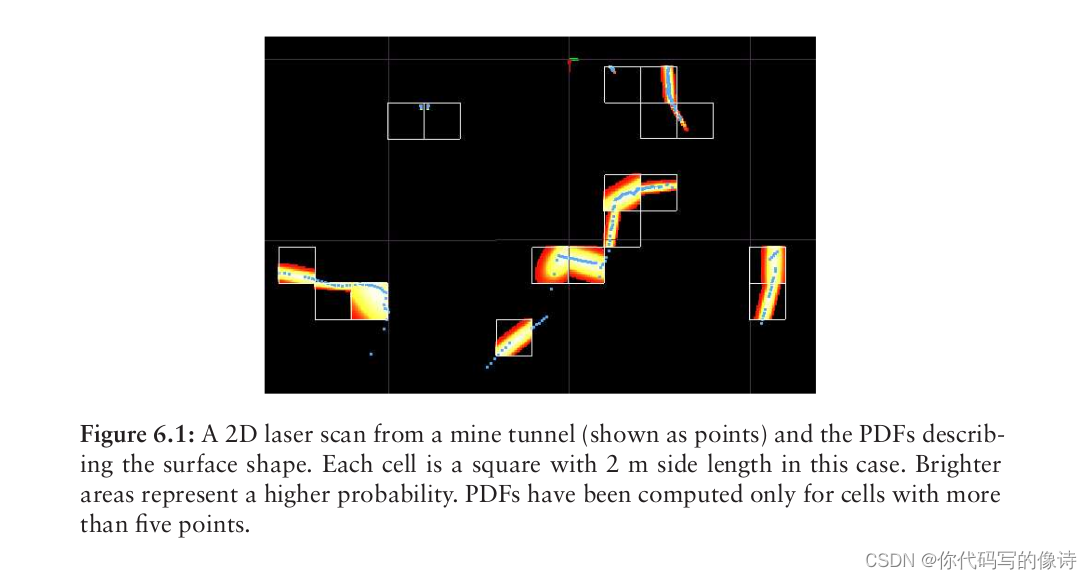
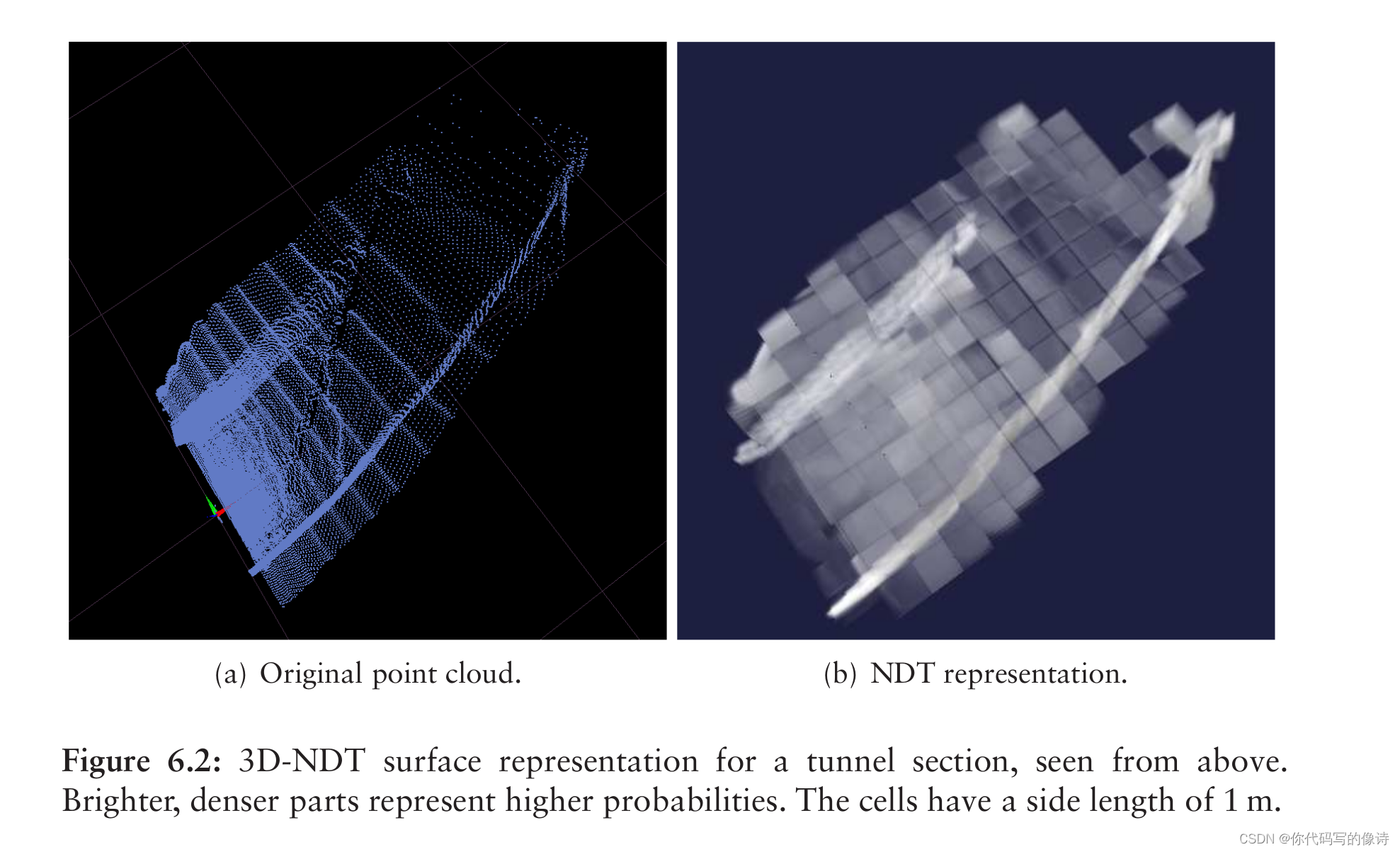
把点云分成多个cell,每个cell内使用概率密度函数(PDF) 来表示点云,该概率密度函数可以描述点云的局部形状。
注意:PDF 不一定非要选择正态分布,只要能表征局部形状,且对于outliers是鲁棒的,都可以拿来做PDF。正态分布的优点是光滑,可导。
The PDF is not necessarily restricted to be a normal distribution. Any PDF that locally captures the structure of the surface points and is robust to outliers is suitable.
怎么理解PDF的表示方法?
- PDF 可被解释为一种“生成过程”(generative process)。假设我们选择正态分布作为PDF,那么真实世界中surface上的某个点,其位置的测量值为x 的概率是:
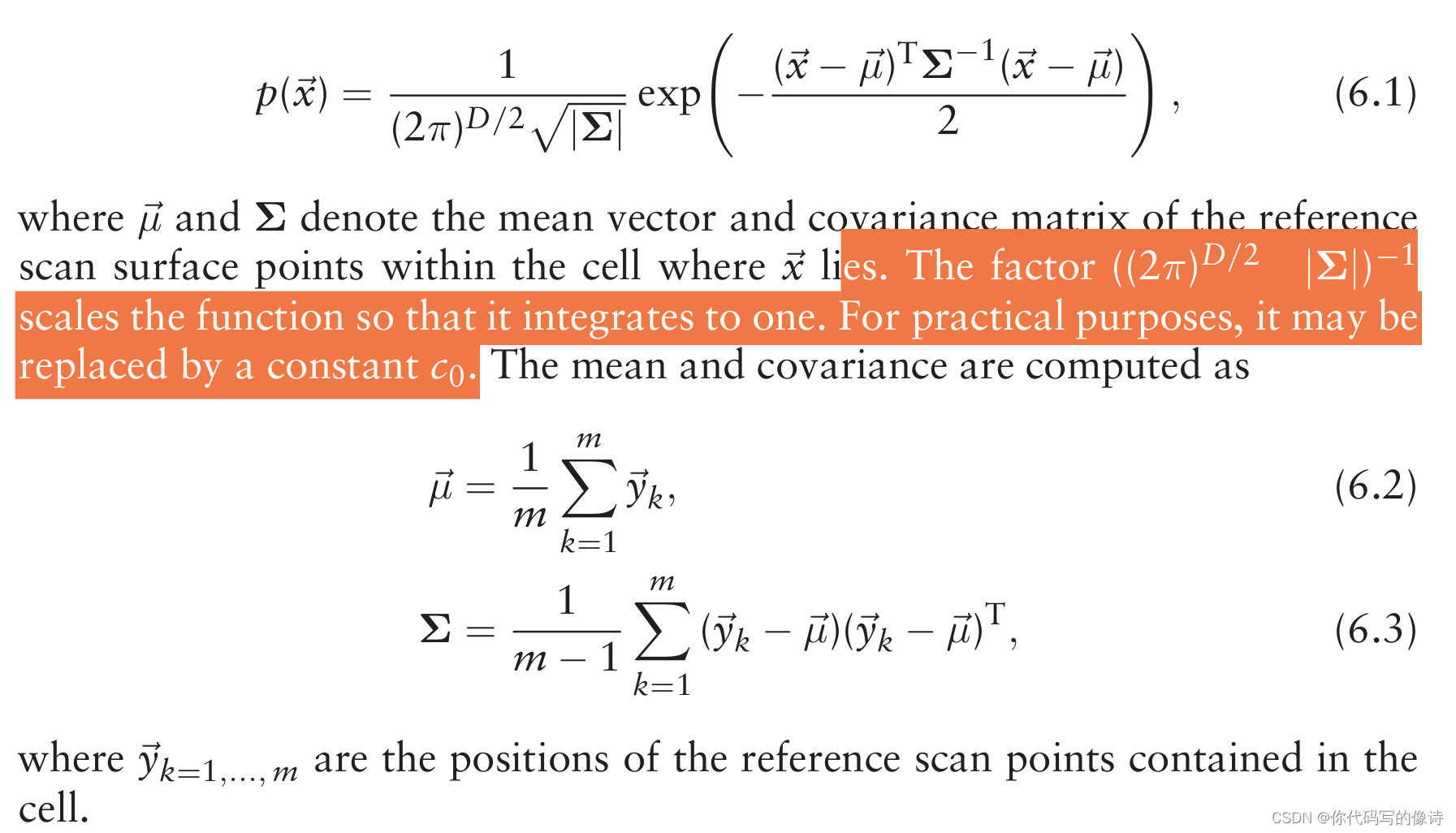
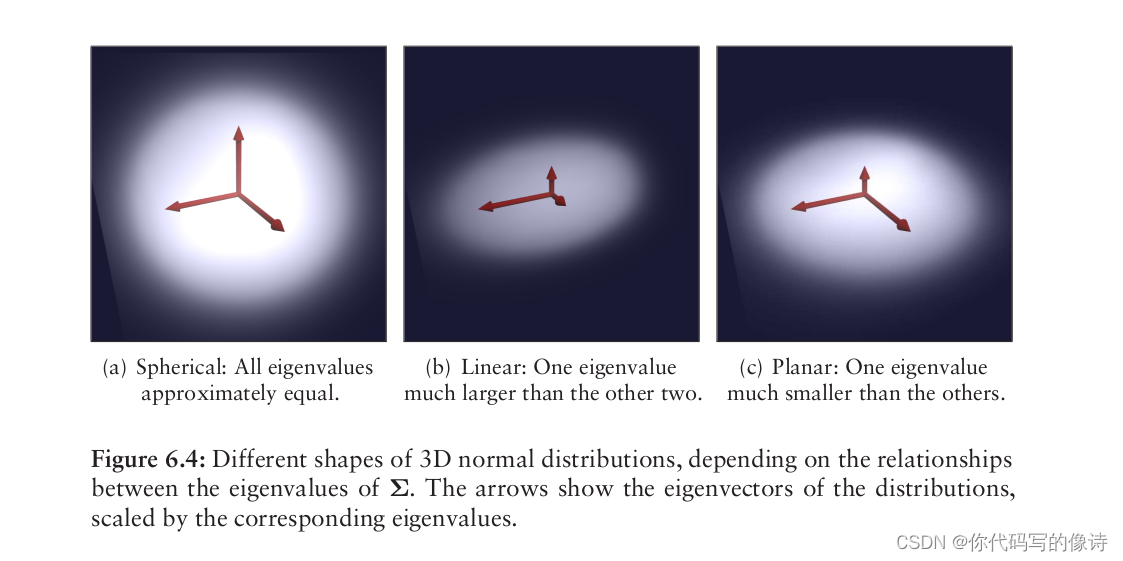
- PDF 可以看成局部表面(local surface)的近似,描述了它的位置,方向以及平滑度(position,orientation and smoothness)。方向和平滑度可以由正态分布协方差矩阵的特征值和特征向量表示。
Cost Function
目标:寻找一个rigid transfromation,可以最大化source 中的点,落在target表面的似然概率(likelihood)
When using NDT for scan registration, the goal is to find the pose of the current scan that maximises the likelihood that the points of the current scan lie on the reference scan surface.
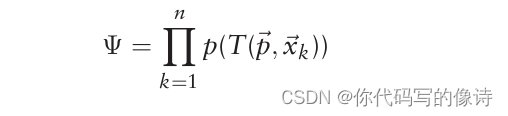
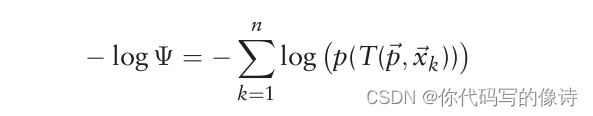
本文使用的PDF:正态分布+ 均匀分布
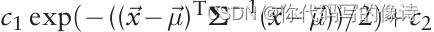
原因:对于离中心太远的outliers, 仅使用正态分布,负log函数会变得无界
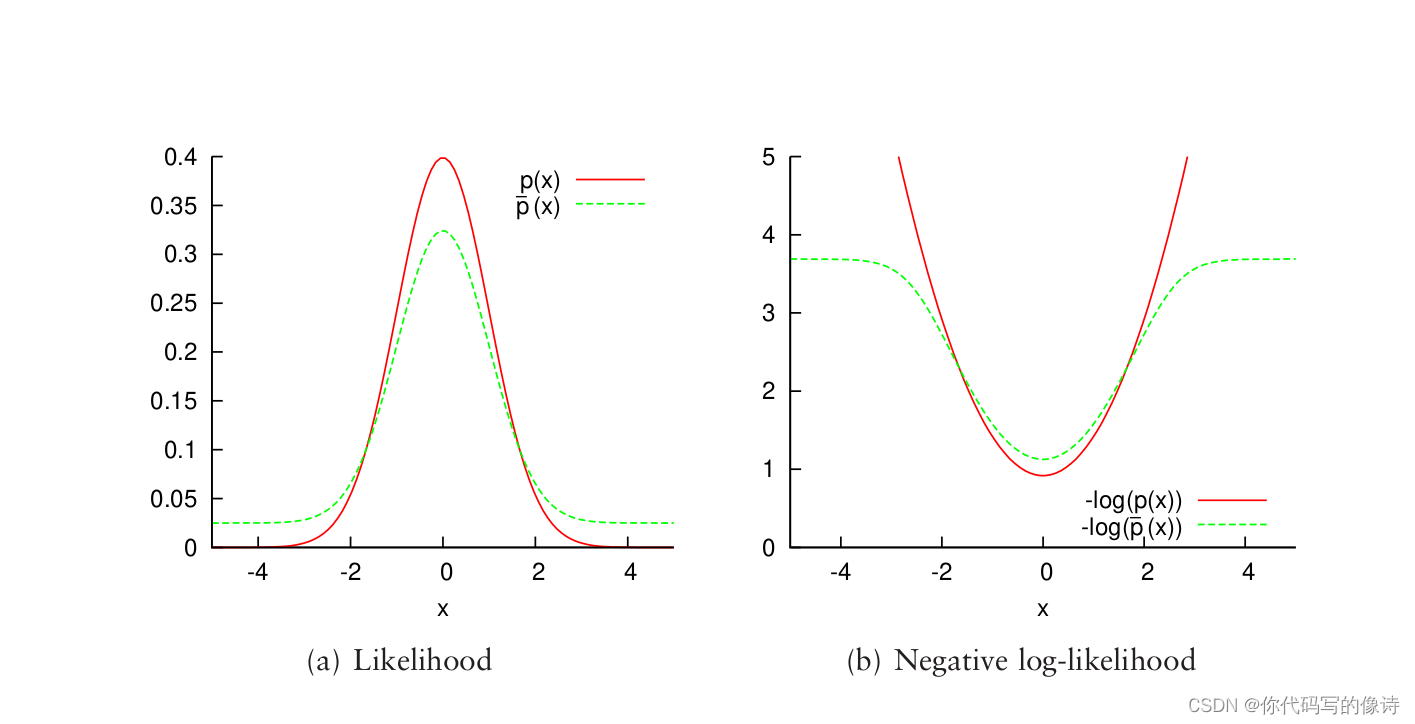
c1, c2 求解: 利用概率密度函数在cell内,概率积分为1。其中c2项的积分,应该等于outlier ratio,这是一个算法的超参数, pcl 默认设为0.55,一般不做修改。
// Initializes the gaussian fitting parameters (eq. 6.8) [Magnusson 2009]
const double gauss_c1 = 10 * (1 - outlier_ratio_); //这部分积分并不是严格等于1-outliers_ratio的
const double gauss_c2 = outlier_ratio_ / pow(resolution_, 3);
但该函数的负log函数,一阶,二阶导数不好求。又用另一个Gauss函数来近似它。
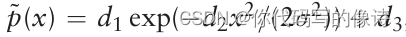
d1,d2,d3 求解:





 本文深入探讨了点云配准中的NDT(Normal Distributions Transform)方法,包括其基本思想、代价函数、优化过程和评估指标。NDT通过使用概率密度函数表示点云,寻找最佳刚性变换以最大化源点云在目标点云表面的似然概率。在优化过程中,采用牛顿法结合线搜索策略,并对比了不同的线搜索准则。同时,文章还讨论了鲁棒性问题以及如何处理异常值。最后,提出了几种衡量配准效果的指标,如NDT分数、Hessian逆和均方误差,并分析了它们的优缺点。
本文深入探讨了点云配准中的NDT(Normal Distributions Transform)方法,包括其基本思想、代价函数、优化过程和评估指标。NDT通过使用概率密度函数表示点云,寻找最佳刚性变换以最大化源点云在目标点云表面的似然概率。在优化过程中,采用牛顿法结合线搜索策略,并对比了不同的线搜索准则。同时,文章还讨论了鲁棒性问题以及如何处理异常值。最后,提出了几种衡量配准效果的指标,如NDT分数、Hessian逆和均方误差,并分析了它们的优缺点。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 7720
7720

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








