一、概要
点云特征提取是3D计算机视觉中的关键步骤,用于识别和描述点云中的显著特征。以下是几种常见的点云特征提取方法:
1.1 Harris
- Harris角点检测:最初用于2D图像,通过计算像素灰度变化来检测角点。在3D点云中,Harris通过分析点云曲率或法向量变化来检测角点。
- 应用:适用于需要高重复性和稳定性的场景,如物体识别和配准。
1.2 ISS (Intrinsic Shape Signatures)
- ISS特征点检测:基于点云的局部几何特性,通过计算每个点的邻域协方差矩阵,选择具有显著几何变化的点作为特征点。
- 应用:常用于3D物体识别和场景理解。
1.3 SIFT (Scale-Invariant Feature Transform)
- SIFT特征提取:最初用于2D图像,通过检测尺度空间中的极值点并生成描述符。在3D点云中,SIFT通过分析点云的多尺度表示来提取特征。
- 应用:适用于需要尺度不变性和旋转不变性的场景,如3D物体识别和配准。
1.4 Boundary
- 边界特征提取:通过检测点云中的边界点来提取特征,通常基于点云的法向量或曲率变化。
- 应用:适用于需要识别物体边界的场景,如场景分割和物体识别。
1.5 总结
- Harris:基于曲率或法向量变化检测角点。
- ISS:基于局部几何特性检测特征点。
- SIFT:基于多尺度表示提取特征。
- Boundary:基于法向量或曲率变化检测边界点。
2、代码和结果
2.1 PCL代码:
#include <pcl/point_types.h>
#include<pcl/common/common.h>
#include <pcl/io/ply_io.h>
#include<pcl/keypoints/harris_3d.h>
#include<pcl/keypoints/iss_3d.h>
#include<pcl/keypoints/sift_keypoint.h>
#include<pcl/features/pfh.h>
#include<pcl/features/fpfh.h>
#include<pcl/features/vfh.h>
#include<pcl/features/ppf.h>
#include <pcl/features/shot.h>
#include <pcl/features/normal_3d.h>
#include <pcl/visualization/pcl_visualizer.h>
#include <boost/thread/thread.hpp> // Include the Boost.Thread header
#include <boost/date_time/posix_time/posix_time.hpp> // Include for boost::posix_time
namespace pcl
{
template<>
struct SIFTKeypointFieldSelector<PointXYZ>
{
inline float
operator () (const PointXYZ &p) const
{
return p.z;
}
};
}
void computeNormal(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud_in, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr cloud_normals) {
pcl::NormalEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal> nores;
pcl::search::KdTree< pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree< pcl::PointXYZ>());
nores.setInputCloud(cloud_in);
nores.setSearchMethod(tree);
//nores.setKSearch(20);
nores.setRadiusSearch(0.02);
nores.compute(*cloud_normals);
}
void visualize(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr keypoint){
pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer viewer("3D Viewer");
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> cloud_h(cloud, 0, 0, 255);
pcl::visualization::PointCloudColorHandlerCustom<pcl::PointXYZ> keypoint_h(keypoint, 255, 0, 0);
viewer.addPointCloud(cloud, cloud_h, "cloud");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 2, "cloud");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 0, 0, 255, "cloud");
viewer.addPointCloud(keypoint, keypoint_h, "keypoints");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_POINT_SIZE, 7, "keypoints");
viewer.setPointCloudRenderingProperties(pcl::visualization::PCL_VISUALIZER_COLOR, 255, 0, 0, "keypoints");
/*viewer.addCoordinateSystem(1.0);*/
while (!viewer.wasStopped())
{
viewer.spinOnce(100);
boost::this_thread::sleep(boost::posix_time::microseconds(100000));
}
}
void harris3d(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr keypoints) {
pcl::HarrisKeypoint3D<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZI, pcl::Normal> harris;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>::Ptr keypoints_(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZI>());
harris.setInputCloud(cloud);
harris.setNonMaxSupression(true);
harris.setRadius(0.005f);
harris.setThreshold(0.005f);
harris.compute(*keypoints_);
pcl::PointXYZ temp;
for (int i = 0; i < keypoints_->points.size(); i++) {
temp.x = keypoints_->points[i].x;
temp.y = keypoints_->points[i].y;
temp.z = keypoints_->points[i].z;
keypoints->points.push_back(temp);
}
}
void iss3d(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr keypoints) {
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::ISSKeypoint3D<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointXYZ> iss_detector;
iss_detector.setSearchMethod(tree);
iss_detector.setSalientRadius(0.005);
iss_detector.setNonMaxRadius(0.005);
iss_detector.setThreshold21(0.975);
iss_detector.setThreshold32(0.975);
iss_detector.setMinNeighbors(5);
iss_detector.setNumberOfThreads(64);
iss_detector.setInputCloud(cloud);
iss_detector.compute(*keypoints);
}
void sift3d(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr keypoints) {
const float min_scale = 0.0005f;
const int n_octaves = 6;
const int n_scales_per_octave = 4;
const float min_contrast = 0.0005f;
pcl::SIFTKeypoint<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::PointWithScale> sift;
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointWithScale> result;
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr tree(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>());
sift.setSearchMethod(tree);
sift.setScales(min_scale, n_octaves, n_scales_per_octave);
sift.setMinimumContrast(min_contrast);
sift.setInputCloud(cloud);
sift.compute(result);
pcl::copyPointCloud(result, *keypoints);
}
void acBoundary(pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud, pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr boundarys) {
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>::Ptr normal(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Normal>);
computeNormal(cloud, normal);
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>::Ptr boundaries(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::Boundary>); //声明一个boundary类指针,作为返回值
boundaries->resize(cloud->size()); //初始化大小
pcl::BoundaryEstimation<pcl::PointXYZ, pcl::Normal, pcl::Boundary> boundary_estimation; //声明一个BoundaryEstimation类
boundary_estimation.setInputCloud(cloud); //设置输入点云
boundary_estimation.setInputNormals(normal); //设置输入法线
pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr kdtree_ptr(new pcl::search::KdTree<pcl::PointXYZ>);
boundary_estimation.setSearchMethod(kdtree_ptr); //设置搜寻k近邻的方式
boundary_estimation.setKSearch(30); //设置k近邻数量
boundary_estimation.setAngleThreshold(M_PI * 0.6); //设置角度阈值,大于阈值为边界
boundary_estimation.compute(*boundaries); //计算点云边界,结果保存在boundaries中
for (int i = 0; i < cloud->size(); i++)
{
if (boundaries->points[i].boundary_point != 0)
{
boundarys->points.emplace_back(cloud->points[i]);
}
}
}
int main() {
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr cloud(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>::Ptr keypoint(new pcl::PointCloud<pcl::PointXYZ>());
pcl::io::loadPLYFile("../../../data/monkey.ply", *cloud);
sift3d(cloud, keypoint);
visualize(cloud, keypoint);
iss3d(cloud, keypoint);
visualize(cloud, keypoint);
harris3d(cloud, keypoint);
visualize(cloud, keypoint);
acBoundary(cloud, keypoint);
visualize(cloud, keypoint);
return 0;
}
2.3 CMakeList.txt:
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.10 FATAL_ERROR)
project(cloud_viewer)
find_package(PCL 1.14 REQUIRED)
find_package(Boost REQUIRED COMPONENTS thread) # 查找 Boost 并指定需要链接的组件(thread)
# 添加头文件路径
include_directories(${PCL_INCLUDE_DIRS} ${Boost_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${PCL_LIBRARY_DIRS})
add_definitions(${PCL_DEFINITIONS})
add_executable (demo demo .cpp)
target_link_libraries(demo ${PCL_LIBRARIES})
target_link_libraries(demo Boost::thread) # 链接 Boost.Thread 库
2.3 代码运行结果
-
Harris:
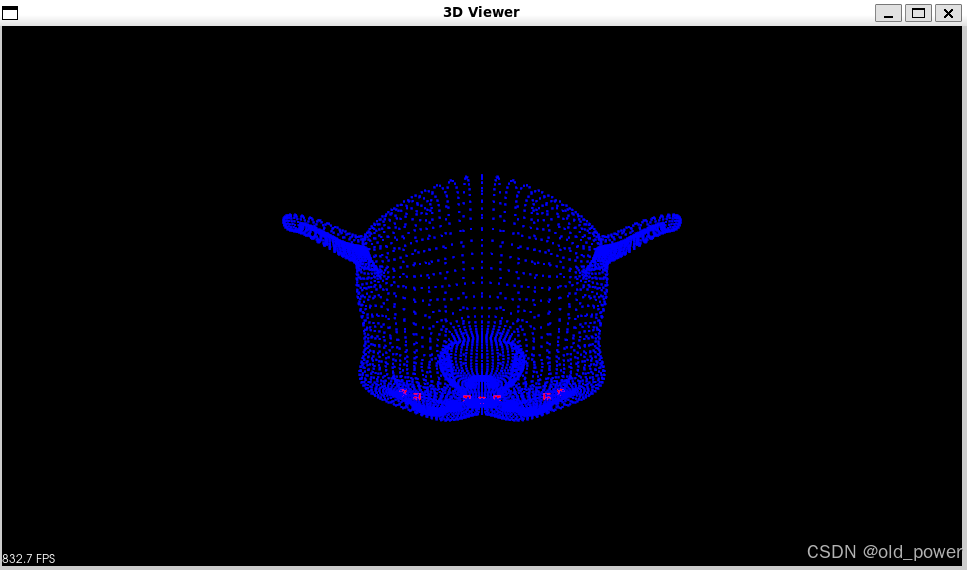
-
ISS
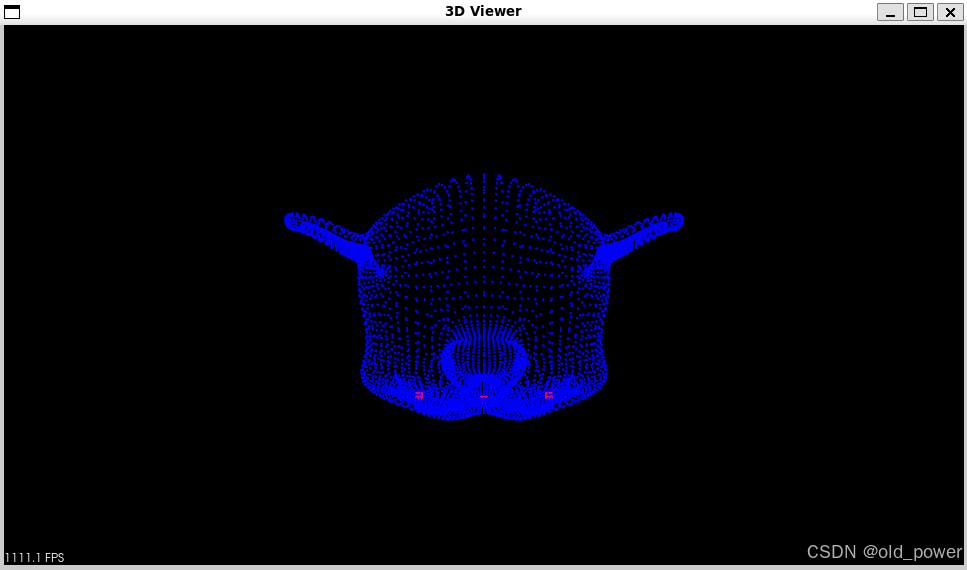
-
SIFT
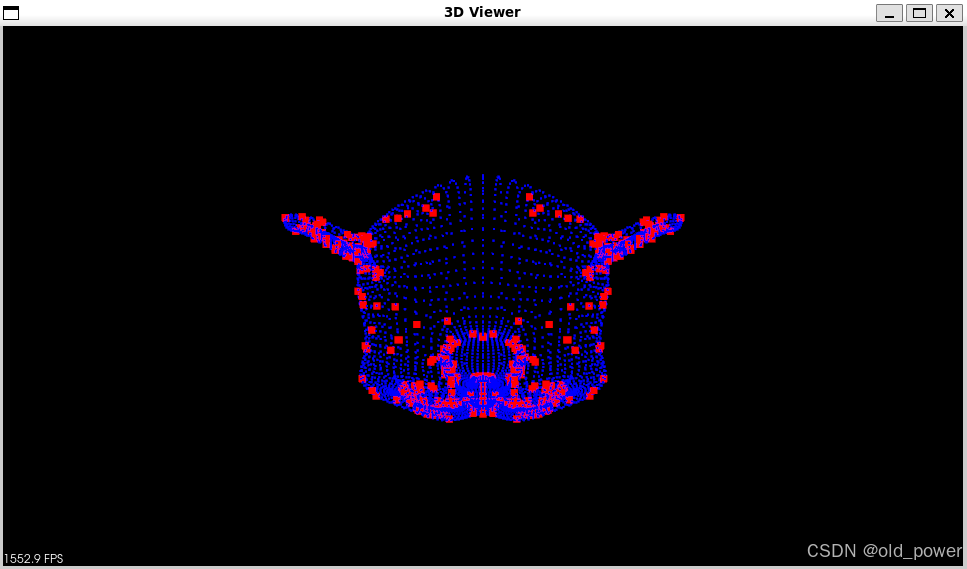
-
Boundary:






















 662
662

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








