✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,修心和技术同步精进,matlab项目合作可私信。
🍎个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知。
更多Matlab仿真内容点击👇
⛄ 内容介绍
The cosmic ray muon (CRM) simulator provides stochastic results based on the two semi-empirical models: (1) muon energy distribution and (2) zenith angle distribution. Both energy and zenith angle distribution models are developed based on analytical studies and experimental data.
⛄ 部分代码
%___________________________________________________________
%
% MuSpect.m
%___________________________________________________________
% "MuSpect.m" provides a cosmic ray muon (CRM) energy distribution with a
% ragne from 0.2 GeV to the user-defiend maximum energy, MaxE (< 2,000 GeV).
% The maximum muon energy is limited upto 2,000 [GeV] or 2 [TeV] because
% the uncertainty level of CRM count rate is too high. Very high CRM
% energy, > 2 TeV, is extremely rare event, especially at sea level.
% Details for the model, please read:
% [1] Cosmic Rays and Particle Physics, 2nd Ed., (2016), T. Gaisser, R. Engel, E. Resconi
% [2] Review of Particle Physics, (2022), R.L. Workman et al (PDG), Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys.
%
% Inputs:
% (1) MaxE: Maximum CRM energy to simulate [GeV]
% (2) ZenAngle: Zenith angle (pointing angle of a detector surface) [deg]
% (3) iffig: show (=1) or suppress (=0) figures.
% For example,
% >> [dNdE, E_mu, sigma_E, ZenAngle] = MuSpect(1000,10,1)
%
%================================================================
if MaxE > 2000
disp('Please adjust your input, Maximum Energy');
return ;
end
sigma_E = 0.1;
E_mu = linspace(0.2 + sigma_E/2, MaxE-sigma_E/2, 1E5); %[GeV]
% Minimun and maximum degrees are slightly adjusted to take into account
% +-0.05 GeV uncertainty during the random generation process.
ZenAng = ZenAngle * (pi/180); % Degree -> radian
% Total atmospheric depth at sea level
X0 = 1030; % [g/cm2]
% Energy loss rate of muon through the atmosphere
alpha = 2E-3; % [GeV/g/cm2]
% Integral spectral index of the cosmic-ray spectrum
Gamma = 1.7;
% Spectrum-weighted moment for a "i" to produce "j" when Z_ji
Z_NN = 0.3;
Z_Npi = 0.08;
Z_Nkp = 0.15 * Z_Npi;
% Mass ratio, muon to pion/kaon
r_pi = 0.573; % (m_mu/m_pi)^2
r_kp = 0.046; % (m_mu/m_kp)^2
% Characteristic length for exponential attenuation in the atmosphere.
% Char lengths depend on particle energy as shown in data set below.
Lambda_N_data = [120 115 106 97]; % [g/cm2] When E = [1E2 1E3 1E4 1E5] GeV
Lambda_pi_data = [155 148 135 114];
Lambda_kp_data = [160 147 133 114];
% Critical energy
epsilon_pi = 115; % [GeV]
epsilon_kp = 850;
epsilon_mu = 1;
% Energy dependent numerical values
% Boundary condition, the initial flux of CRM at the slant depth is X
% in the atmosphere with energies in the interval E to E+dE
N0 = 1.7*E_mu.^(-2.7);
%
p1 = epsilon_mu./(E_mu.*cos(ZenAng)+alpha*X0);
% Lambdas depend on E_mu. Curve-fitting for the approximation.
Lambda_N = -13.31.*E_mu.^(0.1061)+142;
Lambda_pi = -3.714.*E_mu.^(0.2289)+165.8;
Lambda_kp = -36.28.*E_mu.^(0.08816)+214.2;
%
A_pimu = Z_Npi*(1-(r_pi).^(Gamma+1))./((1-r_pi).*(Gamma+1));
B_pimu = (1+(Gamma+1)^-1).*((1-(r_pi).^(Gamma+1))./(1-(r_pi).^(Gamma+2))).* ((Lambda_pi - Lambda_N)./(Lambda_pi.*log(Lambda_pi./Lambda_N)));
A_kpmu = Z_Nkp*(1-(r_kp).^(Gamma+1))./((1-r_kp).*(Gamma+1));
B_kpmu = (1+(Gamma+1)^-1).*((1-(r_kp).^(Gamma+1))./(1-(r_kp).^(Gamma+2))).* ((Lambda_kp - Lambda_N)./(Lambda_kp.*log(Lambda_kp./Lambda_N)));
% Suppression Factor
S = (Lambda_N.* cos(ZenAng)./X0).^p1 .* (E_mu./(E_mu+(alpha*X0./cos(ZenAng)))).^(p1+Gamma+1).* gamma(p1+1);
% Differential muon flux [cm-2 sr-1 sec-1 GeV-1]
dNdE = (S.*(N0./(1-Z_NN))).*((A_pimu./(1+B_pimu.*cos(ZenAng).*(E_mu./epsilon_pi)))...
+ (0.635.*A_kpmu./(1+B_kpmu.*cos(ZenAng).*(E_mu./epsilon_kp))));
if iffig == 1
plot(E_mu,dNdE.*(E_mu.^3),'LineWidth', 2)
% ^^^
% Exponent can be adjusted for user's preference to display the figure.
hold on
set(gca, 'XScale', 'log')
set(gca, 'YScale', 'log')
ax = gca;
ax.YGrid = 'on';
ax.GridLineStyle = '-';
xlabel('Muon Energy [GeV]')
ylabel('E^3{\mu} dN{\mu}/dE{\mu} [cm^{-2}sr^{-1}sec^{-1}GeV^2]')
end
end
%===========================================================
%
% END
%
%===========================================================
⛄ 运行结果
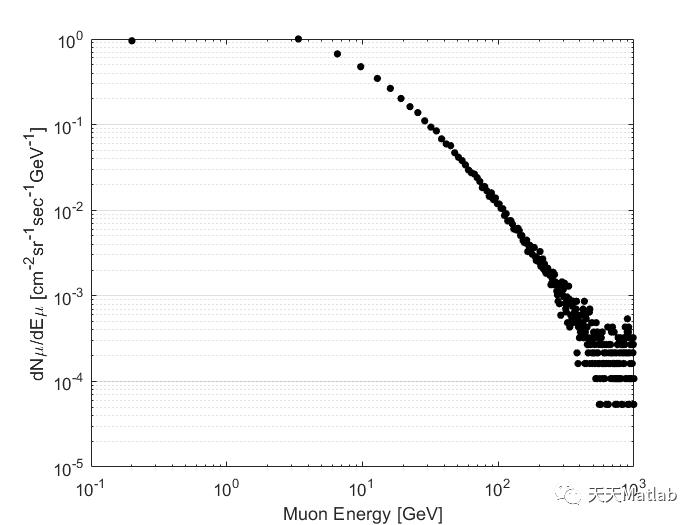
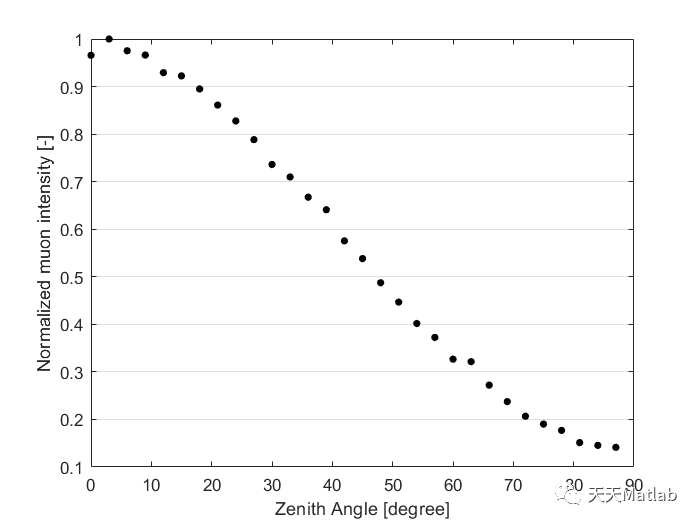
⛄ 参考文献
[1] Cosmic Rays and Particle Physics, 2nd Ed., (2016), T. Gaisser, R. Engel, E. Resconi.
[2] Review of Particle Physics, (2022), R.L. Workman et al (PDG), Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys.
[3] A New Semi-Empirical Model for Cosmic Ray Muon Flux Estimation, (2022) J.Bae, S. Chatzidakis, Prog. Theor. Exp. Phys.
⛄ 完整代码
❤️部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
❤️ 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料






















 2593
2593

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










