自定义矩阵
from math import *
import random
class matrix:
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.dimx = len(value)
self.dimy = len(value[0])
if value == [[]]:
self.dimx = 0
def zero(self, dimx, dimy):
# check if valid dimensions
if dimx < 1 or dimy < 1:
raise ValueError("Invalid size of matrix")
else:
self.dimx = dimx
self.dimy = dimy
self.value = [[0 for row in range(dimy)] for col in range(dimx)]
def identity(self, dim):
# check if valid dimension
if dim < 1:
raise ValueError("Invalid size of matrix")
else:
self.dimx = dim
self.dimy = dim
self.value = [[0 for row in range(dim)] for col in range(dim)]
for i in range(dim):
self.value[i][i] = 1
def __add__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimy != other.dimy:
raise ValueError("Matrices must be of equal dimension to add")
else:
# add if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] + other.value[i][j]
return res
def __sub__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimy != other.dimy:
raise ValueError("Matrices must be of equal dimension to subtract")
else:
# subtract if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] - other.value[i][j]
return res
def __mul__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimy != other.dimx:
raise ValueError("Matrices must be m*n and n*p to multiply")
else:
# multiply if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, other.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(other.dimy):
for k in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] += self.value[i][k] * other.value[k][j]
return res
def transpose(self):
# compute transpose
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimy, self.dimx)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[j][i] = self.value[i][j]
return res
def Cholesky(self, ztol=1.0e-5):
# Computes the upper triangular Cholesky factorization of
# a positive definite matrix.
# This code is based on http://adorio-research.org/wordpress/?p=4560
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx)
for i in range(self.dimx):
S = sum([(res.value[k][i]) ** 2 for k in range(i)])
d = self.value[i][i] - S
if abs(d) < ztol:
res.value[i][i] = 0.0
else:
if d < 0.0:
raise ValueError("Matrix not positive-definite")
res.value[i][i] = sqrt(d)
for j in range(i + 1, self.dimx):
S = sum([res.value[k][i] * res.value[k][j] for k in range(i)])
if abs(S) < ztol:
S = 0.0
try:
res.value[i][j] = (self.value[i][j] - S) / res.value[i][i]
except:
raise ValueError("Zero diagonal")
return res
def CholeskyInverse(self):
# Computes inverse of matrix given its Cholesky upper Triangular
# decomposition of matrix.
# This code is based on http://adorio-research.org/wordpress/?p=4560
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx)
# Backward step for inverse.
for j in reversed(list(range(self.dimx))):
tjj = self.value[j][j]
S = sum([self.value[j][k] * res.value[j][k] for k in range(j + 1, self.dimx)])
res.value[j][j] = 1.0 / tjj ** 2 - S / tjj
for i in reversed(list(range(j))):
res.value[j][i] = res.value[i][j] = -sum(
[self.value[i][k] * res.value[k][j] for k in range(i + 1, self.dimx)]) / self.value[i][i]
return res
def inverse(self):
aux = self.Cholesky()
res = aux.CholeskyInverse()
return res
def __repr__(self):
return repr(self.value)
自定义 robot
质点模型:x、y 坐标 + 方向
from math import *
import random
class robot:
def __init__(self, x = 0.0, y = 0.0, heading = 0.0, turning = 2*pi/10, distance = 1.0):
"""This function is called when you create a new robot. It sets some of
the attributes of the robot, either to their default values or to the values
specified when it is created."""
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.heading = heading
self.turning = turning # only applies to target robots who constantly move in a circle
self.distance = distance # only applies to target bot, who always moves at same speed.
self.turning_noise = 0.0
self.distance_noise = 0.0
self.measurement_noise = 0.0
def set_noise(self, new_t_noise, new_d_noise, new_m_noise):
"""This lets us change the noise parameters, which can be very
helpful when using particle filters."""
self.turning_noise = float(new_t_noise)
self.distance_noise = float(new_d_noise)
self.measurement_noise = float(new_m_noise)
def move(self, turning, distance, tolerance = 0.001, max_turning_angle = pi/4):
"""This function turns the robot and then moves it forward."""
# apply noise, this doesn't change anything if turning_noise
# and distance_noise are zero.
turning = random.gauss(turning, self.turning_noise)
distance = random.gauss(distance, self.distance_noise)
# truncate to fit physical limitations
turning = max(-max_turning_angle, turning)
turning = min( max_turning_angle, turning)
distance = max(0.0, distance)
# Execute motion
self.heading += turning
self.heading = angle_trunc(self.heading)
self.x += distance * cos(self.heading)
self.y += distance * sin(self.heading)
def move_in_circle(self):
"""This function is used to advance the runaway target bot."""
self.move(self.turning, self.distance)
def sense(self):
"""This function represents the robot sensing its location. When
measurements are noisy, this will return a value that is close to,
but not necessarily equal to, the robot's (x, y) position."""
return (random.gauss(self.x, self.measurement_noise),
random.gauss(self.y, self.measurement_noise))
def __repr__(self):
"""This allows us to print a robot's position"""
return '[%.5f, %.5f]' % (self.x, self.y)
跟踪环形轨道上的目标
绿色为目标的轨迹, 红色为每个时间间隔的带有高斯误差的目标位置,需要根据历史的目标位置,预测下一时刻的目标位置并将其捕获
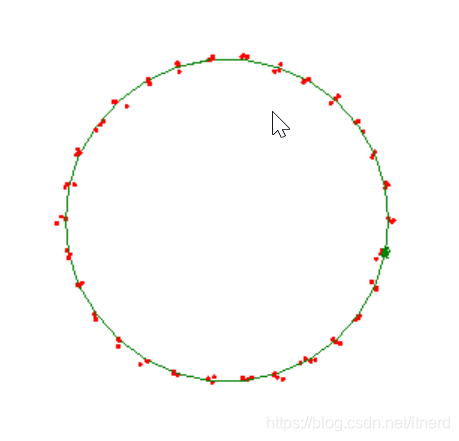
预测目标位置时另辟蹊径,假设目标在 N 个单位时间后会出现在原来某个相同位置上,即具有周期 N,先把周期求出来。
然后得到同一位置在不同时刻的数据,取平均消去高斯误差,得到更准确的位置估计。
# 环形轨道上预测 K 个单位时间后的目标位置
def estimate_next_k_pos(measurement, K, OTHER=None):
"""Estimate the next (x, y) position of the wandering Traxbot
based on noisy (x, y) measurements."""
def find_nearist(hist, target):
nearist = 0
min_dist = distance_between(hist[nearist], target)
for i in range(len(hist)):
dist = distance_between(hist[i], target)
if dist < min_dist:
nearist = i
min_dist = dist
return nearist
def next_k_pos(history, period, K):
estimate = history[-1]
if period == int(period):
aver_x, aver_y = 0, 0
count = 0
for i in range(len(history)):
if i%period == (len(history)+K)%period:
count += 1
aver_x += history[i][0]
aver_y += history[i][1]
if count > 0:
estimate = (aver_x/count, aver_y/count)
return estimate
next_estimate = measurement # 返回下一时刻的目标位置
next_k_estimate = measurement # 返回下K个时刻的目标位置
if not OTHER: # 第一次执行时的初始化
OTHER = [[measurement], [[0, pi]]]
else:
history = OTHER[0]
period_support_list = OTHER[1]
period_list = [i[1] for i in period_support_list]
nearist = find_nearist(history, measurement)
if not nearist == len(history)-1:
p = len(history)- nearist
if sum([p%x==0 for x in period_list]) == 0:
period_support_list.append([1, p])
else:
for i in range(len(period_list)):
if p%period_list[i] == 0:
period_support_list[i][0] += 1
period_support_list.sort()
period = period_support_list[-1][1]
next_estimate = next_k_pos(history, period, 1)
next_k_estimate = next_k_pos(history, period, K)
history.append(measurement)
OTHER = [history, period_support_list]
return next_estimate, next_k_estimate, OTHER
# 给出 hunter 的下一步动作
def next_move(hunter_position, hunter_heading, target_measurement, max_distance, OTHER = None):
# This function will be called after each time the target moves.
# The OTHER variable is a place for you to store any historical information about
# the progress of the hunt (or maybe some localization information). Your return format
# must be as follows in order to be graded properly.
next_estimate, next_k_estimate, OTHER = estimate_next_k_pos(target_measurement, 3, OTHER)
if distance_between(next_estimate, hunter_position) < 0.9*max_distance:
estimate = next_estimate
else:
estimate = next_k_estimate
heading_to_target = get_heading(hunter_position, estimate)
heading_difference = heading_to_target - hunter_heading
turning = angle_trunc(heading_difference) # turn towards the target
distance = distance_between(hunter_position, estimate) # full speed ahead!
return turning, distance, OTHER
def distance_between(point1, point2):
"""Computes distance between point1 and point2. Points are (x, y) pairs."""
x1, y1 = point1
x2, y2 = point2
return sqrt((x2 - x1) ** 2 + (y2 - y1) ** 2)
def get_heading(hunter_position, target_position):
"""Returns the angle, in radians, between the target and hunter positions"""
hunter_x, hunter_y = hunter_position
target_x, target_y = target_position
heading = atan2(target_y - hunter_y, target_x - hunter_x)
return angle_trunc(heading)
可视化跟踪过程
You got it right! It took you 158 steps to catch the target.
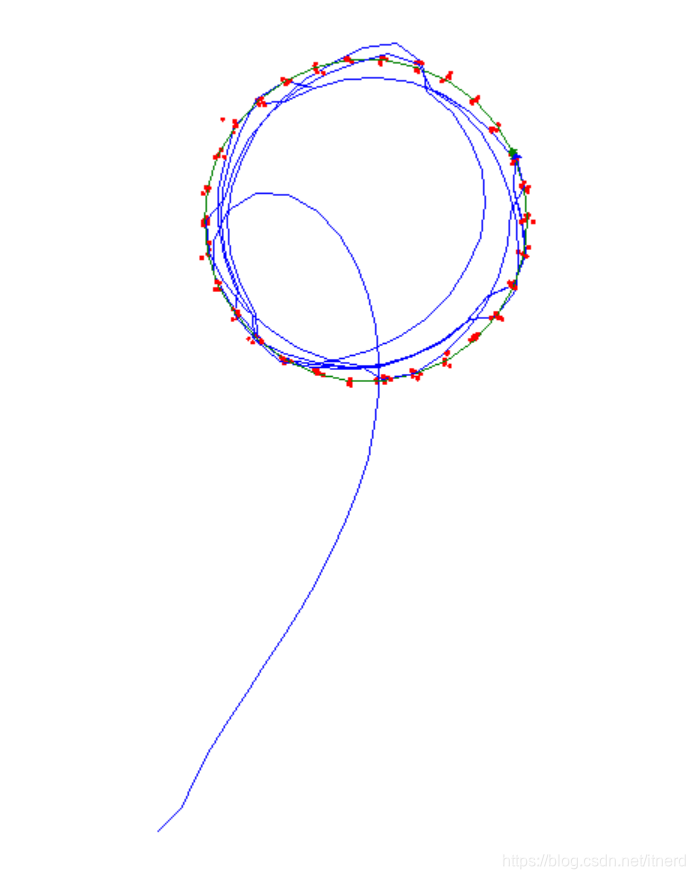
def demo_grading(hunter_bot, target_bot, next_move_fcn, OTHER = None):
"""Returns True if your next_move_fcn successfully guides the hunter_bot
to the target_bot. This function is here to help you understand how we
will grade your submission."""
max_distance = 0.98 * target_bot.distance
separation_tolerance = 0.02 * target_bot.distance # hunter must be within 0.02 step size to catch target
caught = False
ctr = 0
#For Visualization
import turtle
window = turtle.Screen()
window.bgcolor('white')
chaser_robot = turtle.Turtle()
chaser_robot.shape('arrow')
chaser_robot.color('blue')
chaser_robot.resizemode('user')
chaser_robot.shapesize(0.3, 0.3, 0.3)
broken_robot = turtle.Turtle()
broken_robot.shape('turtle')
broken_robot.color('green')
broken_robot.resizemode('user')
broken_robot.shapesize(0.3, 0.3, 0.3)
size_multiplier = 15.0 #change Size of animation
chaser_robot.hideturtle()
chaser_robot.penup()
chaser_robot.goto(hunter_bot.x*size_multiplier, hunter_bot.y*size_multiplier-100)
chaser_robot.showturtle()
broken_robot.hideturtle()
broken_robot.penup()
broken_robot.goto(target_bot.x*size_multiplier, target_bot.y*size_multiplier-100)
broken_robot.showturtle()
measuredbroken_robot = turtle.Turtle()
measuredbroken_robot.shape('circle')
measuredbroken_robot.color('red')
measuredbroken_robot.penup()
measuredbroken_robot.resizemode('user')
measuredbroken_robot.shapesize(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)
broken_robot.pendown()
chaser_robot.pendown()
#End of Visualization
# We will use your next_move_fcn until we catch the target or time expires.
while not caught and ctr < 1000:
# Check to see if the hunter has caught the target.
hunter_position = (hunter_bot.x, hunter_bot.y)
target_position = (target_bot.x, target_bot.y)
separation = distance_between(hunter_position, target_position)
if separation < separation_tolerance:
print("You got it right! It took you ", ctr, " steps to catch the target.")
caught = True
# The target broadcasts its noisy measurement
target_measurement = target_bot.sense()
# This is where YOUR function will be called.
turning, distance, OTHER = next_move_fcn(hunter_position, hunter_bot.heading, target_measurement, max_distance, OTHER)
# Don't try to move faster than allowed!
if distance > max_distance:
distance = max_distance
# We move the hunter according to your instructions
hunter_bot.move(turning, distance)
# The target continues its (nearly) circular motion.
target_bot.move_in_circle()
#Visualize it
measuredbroken_robot.setheading(target_bot.heading*180/pi)
measuredbroken_robot.goto(target_measurement[0]*size_multiplier, target_measurement[1]*size_multiplier-100)
measuredbroken_robot.stamp()
broken_robot.setheading(target_bot.heading*180/pi)
broken_robot.goto(target_bot.x*size_multiplier, target_bot.y*size_multiplier-100)
chaser_robot.setheading(hunter_bot.heading*180/pi)
chaser_robot.goto(hunter_bot.x*size_multiplier, hunter_bot.y*size_multiplier-100)
#End of visualization
ctr += 1
if ctr >= 1000:
print("It took too many steps to catch the target.")
turtle.done()
try:
turtle.bye()
except turtle.Terminator:
pass
return caught
























 1525
1525

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










