卡尔曼滤波分成两步:观测更新 + 运动预测

观测更新
先验分布的均值、方差分别为μ,σ\mu, \sigmaμ,σ
观测分布的均值、方差分别为ν,γ\nu, \gammaν,γ
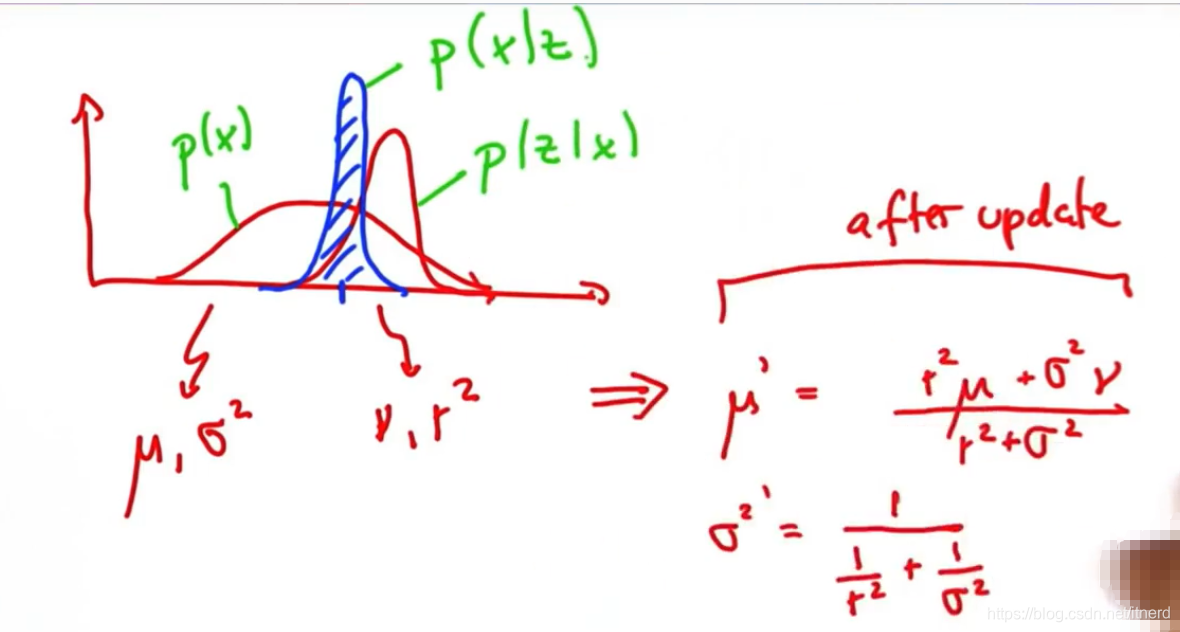
后验分布的均值介于 μ,ν\mu,\nuμ,ν之间,方差却比前两者要小。
运动更新(预测)
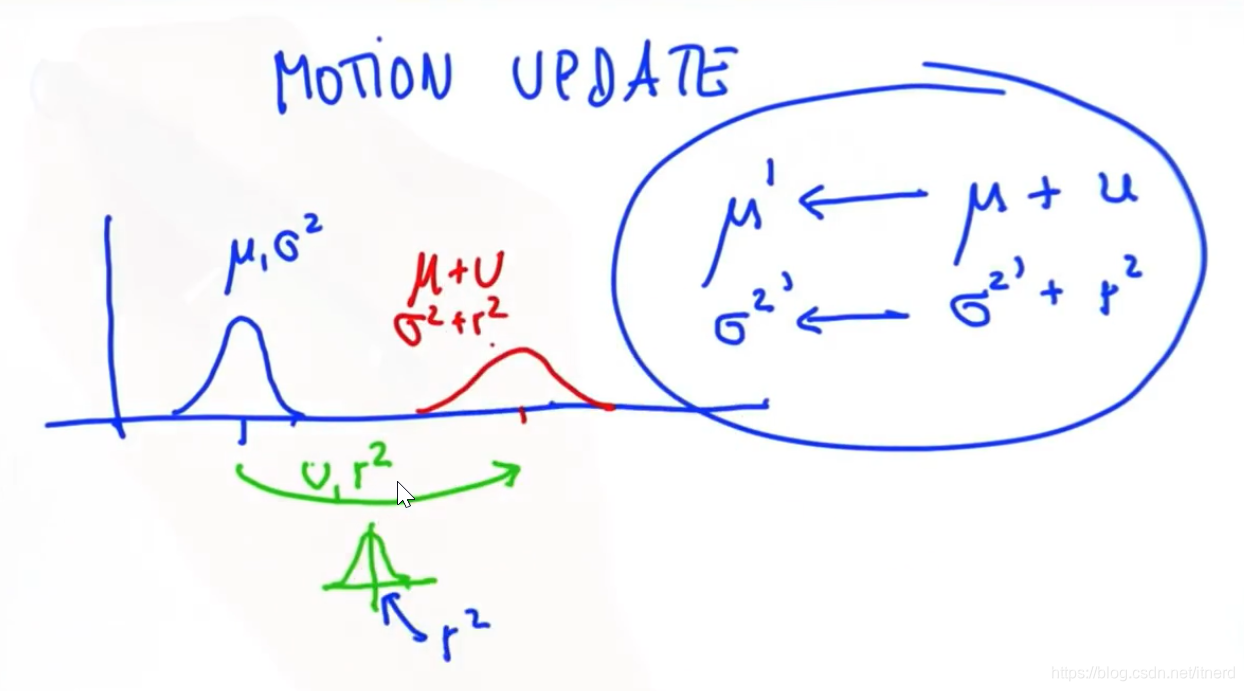
两个高斯分布相加(当前位置+位移量):均值相加,方差相加
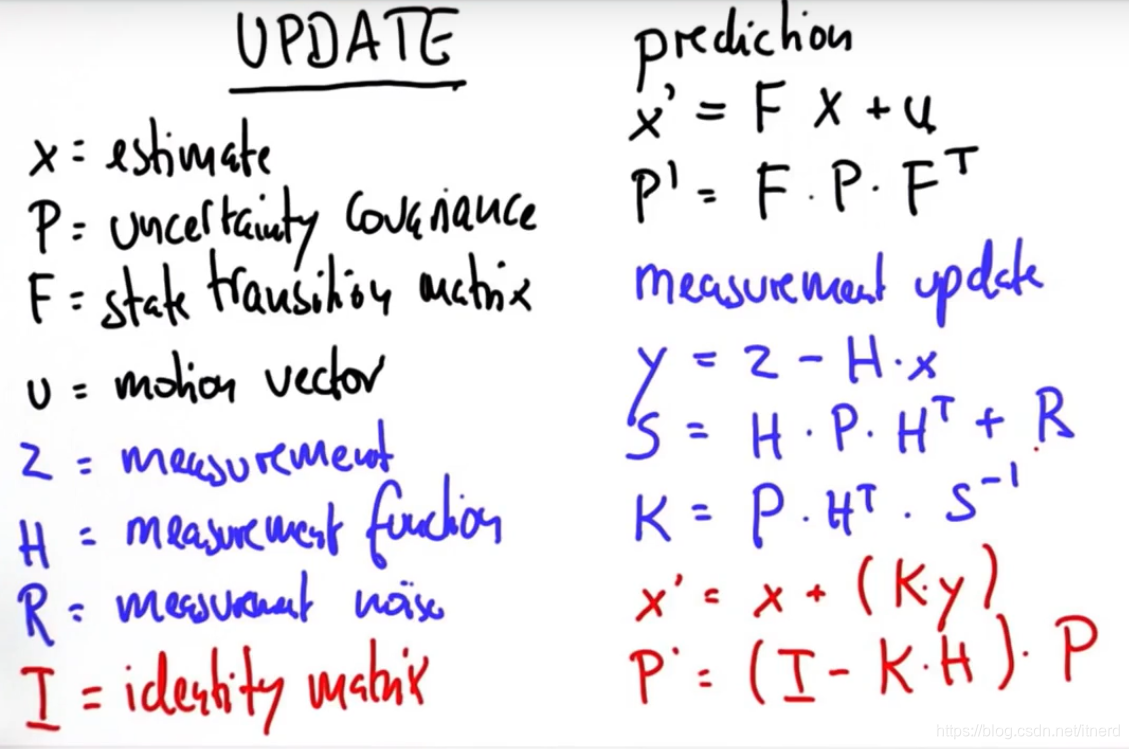
矩阵形式的 kalman 滤波方程
自定义矩阵类
# Write a function 'kalman_filter' that implements a multi-
# dimensional Kalman Filter for the example given
from math import *
class matrix:
# implements basic operations of a matrix class
def __init__(self, value):
self.value = value
self.dimx = len(value)
self.dimy = len(value[0])
if value == [[]]:
self.dimx = 0
def zero(self, dimx, dimy):
# check if valid dimensions
if dimx < 1 or dimy < 1:
raise ValueError, "Invalid size of matrix"
else:
self.dimx = dimx
self.dimy = dimy
self.value = [[0 for row in range(dimy)] for col in range(dimx)]
def identity(self, dim):
# check if valid dimension
if dim < 1:
raise ValueError, "Invalid size of matrix"
else:
self.dimx = dim
self.dimy = dim
self.value = [[0 for row in range(dim)] for col in range(dim)]
for i in range(dim):
self.value[i][i] = 1
def show(self):
for i in range(self.dimx):
print(self.value[i])
print(' ')
def __add__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimy != other.dimy:
raise ValueError, "Matrices must be of equal dimensions to add"
else:
# add if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] + other.value[i][j]
return res
def __sub__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimx != other.dimx or self.dimy != other.dimy:
raise ValueError, "Matrices must be of equal dimensions to subtract"
else:
# subtract if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] = self.value[i][j] - other.value[i][j]
return res
def __mul__(self, other):
# check if correct dimensions
if self.dimy != other.dimx:
raise ValueError, "Matrices must be m*n and n*p to multiply"
else:
# multiply if correct dimensions
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, other.dimy)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(other.dimy):
for k in range(self.dimy):
res.value[i][j] += self.value[i][k] * other.value[k][j]
return res
def transpose(self):
# compute transpose
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimy, self.dimx)
for i in range(self.dimx):
for j in range(self.dimy):
res.value[j][i] = self.value[i][j]
return res
# Thanks to Ernesto P. Adorio for use of Cholesky and CholeskyInverse functions
def Cholesky(self, ztol=1.0e-5):
# Computes the upper triangular Cholesky factorization of
# a positive definite matrix.
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx)
for i in range(self.dimx):
S = sum([(res.value[k][i])**2 for k in range(i)])
d = self.value[i][i] - S
if abs(d) < ztol:
res.value[i][i] = 0.0
else:
if d < 0.0:
raise ValueError, "Matrix not positive-definite"
res.value[i][i] = sqrt(d)
for j in range(i+1, self.dimx):
S = sum([res.value[k][i] * res.value[k][j] for k in range(self.dimx)])
if abs(S) < ztol:
S = 0.0
try:
res.value[i][j] = (self.value[i][j] - S)/res.value[i][i]
except:
raise ValueError, "Zero diagonal"
return res
def CholeskyInverse(self):
# Computes inverse of matrix given its Cholesky upper Triangular
# decomposition of matrix.
res = matrix([[]])
res.zero(self.dimx, self.dimx)
# Backward step for inverse.
for j in reversed(range(self.dimx)):
tjj = self.value[j][j]
S = sum([self.value[j][k]*res.value[j][k] for k in range(j+1, self.dimx)])
res.value[j][j] = 1.0/tjj**2 - S/tjj
for i in reversed(range(j)):
res.value[j][i] = res.value[i][j] = -sum([self.value[i][k]*res.value[k][j] for k in range(i+1, self.dimx)])/self.value[i][i]
return res
def inverse(self):
aux = self.Cholesky()
res = aux.CholeskyInverse()
return res
def __repr__(self):
return repr(self.value)
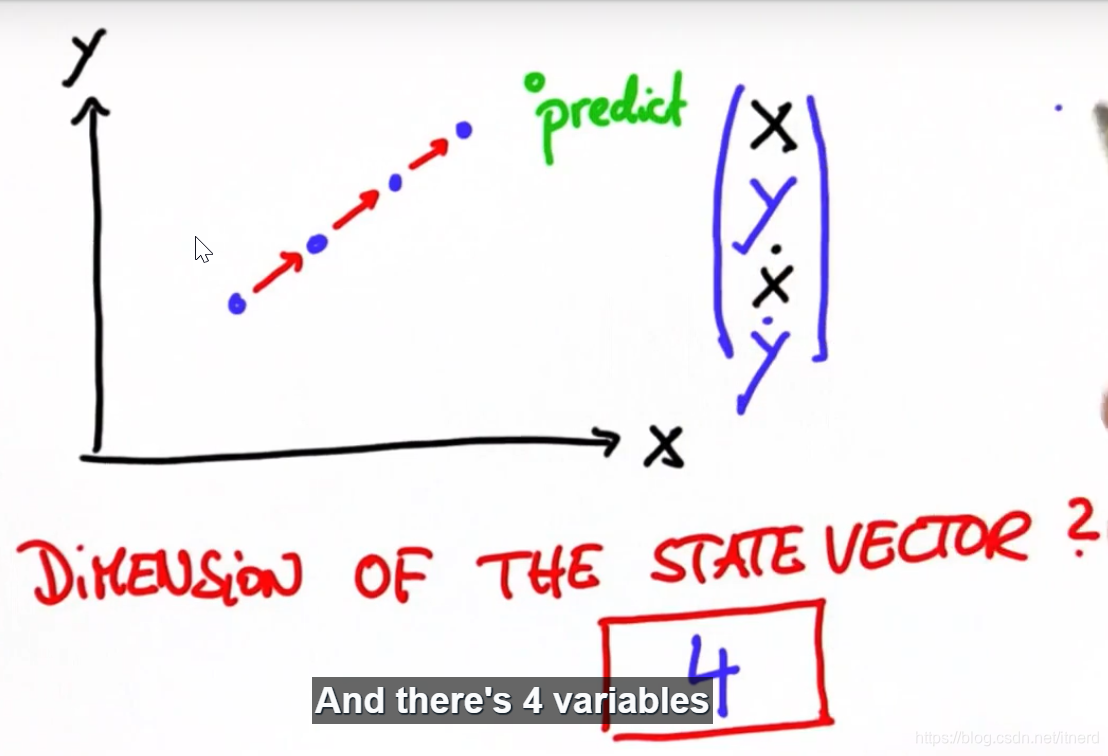
一维情形
# Implement the filter function below
def kalman_filter(x, P):
for n in range(len(measurements)):
# measurement update
z = matrix([[measurements[n]]])
y = z - H*x
S = H*P*H.transpose() + R
K = P*H.transpose()*S.inverse()
x = x + K*y
P = (I-K*H)*P
# prediction
x = F*x + u
P = F*P*F.transpose()
return x,P
############################################
### use the code below to test your filter!
############################################
measurements = [1, 2, 3]
x = matrix([[0.], [0.]]) # initial state (location and velocity)
P = matrix([[1000., 0.], [0., 1000.]]) # initial uncertainty
u = matrix([[0.], [0.]]) # external motion
F = matrix([[1., 1.], [0, 1.]]) # next state function
H = matrix([[1., 0.]]) # measurement function
R = matrix([[1.]]) # measurement uncertainty
I = matrix([[1., 0.], [0., 1.]]) # identity matrix
print(kalman_filter(x, P))
# output should be:
# x: [[3.9996664447958645], [0.9999998335552873]]
# P: [[2.3318904241194827, 0.9991676099921091], [0.9991676099921067, 0.49950058263974184]]
二维情形
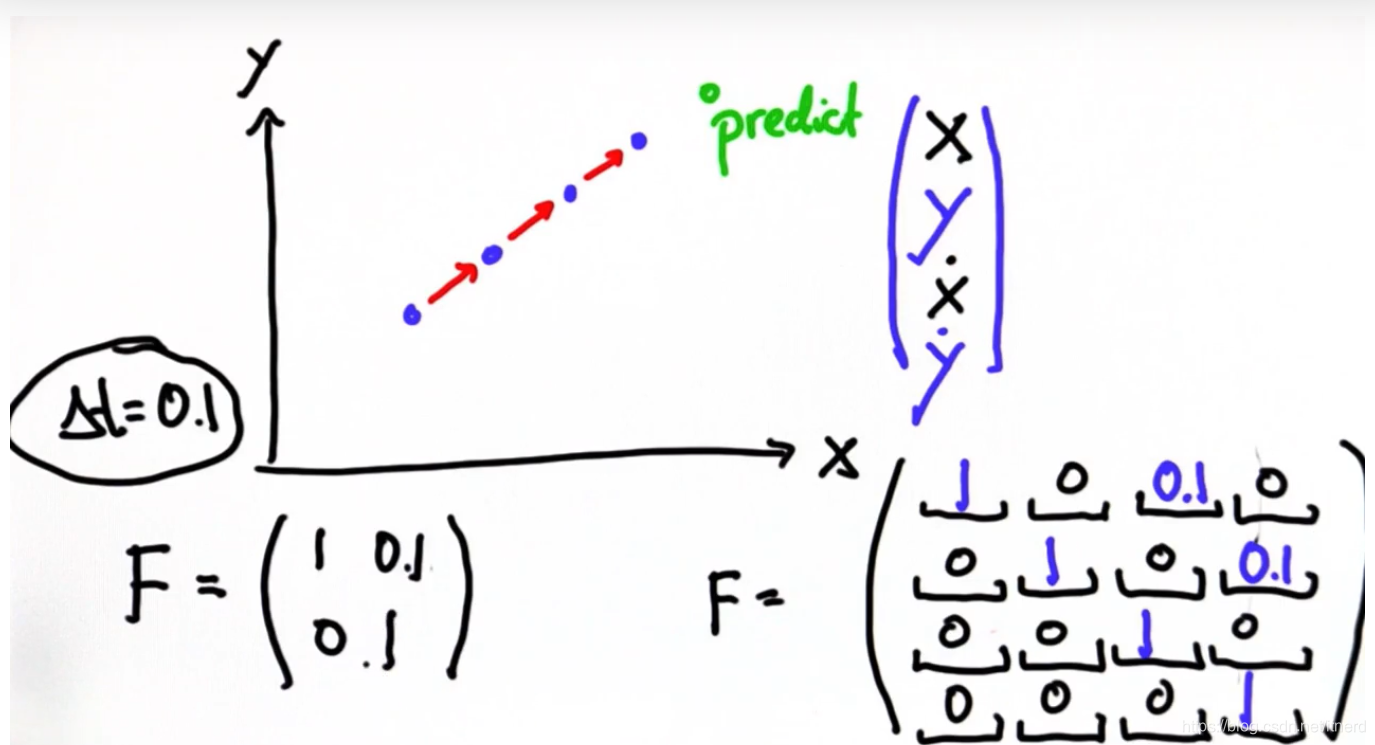
########################################
def filter(x, P):
for n in range(len(measurements)):
# prediction
x = (F * x) + u
P = F * P * F.transpose()
# measurement update
Z = matrix([measurements[n]])
y = Z.transpose() - (H * x)
S = H * P * H.transpose() + R
K = P * H.transpose() * S.inverse()
x = x + (K * y)
P = (I - (K * H)) * P
print 'x= '
x.show()
print 'P= '
P.show()
########################################
print "### 4-dimensional example ###"
measurements = [[5., 10.], [6., 8.], [7., 6.], [8., 4.], [9., 2.], [10., 0.]]
initial_xy = [4., 12.]
# measurements = [[1., 4.], [6., 0.], [11., -4.], [16., -8.]]
# initial_xy = [-4., 8.]
# measurements = [[1., 17.], [1., 15.], [1., 13.], [1., 11.]]
# initial_xy = [1., 19.]
dt = 0.1
x = matrix([[initial_xy[0]], [initial_xy[1]], [0.], [0.]]) # initial state (location and velocity)
u = matrix([[0.], [0.], [0.], [0.]]) # external motion
#### DO NOT MODIFY ANYTHING ABOVE HERE ####
#### fill this in, remember to use the matrix() function!: ####
P = matrix([[0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0],[0,0,1000,0],[0,0,0,1000]])# initial uncertainty: 0 for positions x and y, 1000 for the two velocities
F = matrix([[1,0,0.1,0],[0,1,0,0.1],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]])# next state function: generalize the 2d version to 4d
H = matrix([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0]])# measurement function: reflect the fact that we observe x and y but not the two velocities
R = matrix([[0.1,0.],[0.,0.1]])# measurement uncertainty: use 2x2 matrix with 0.1 as main diagonal
I = matrix([[1,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0],[0,0,1,0],[0,0,0,1]])# 4d identity matrix
###### DO NOT MODIFY ANYTHING HERE #######
filter(x, P)







 博客介绍卡尔曼滤波,其分为观测更新和运动预测两步。观测更新中,后验分布均值介于先验和观测分布均值之间,方差更小;运动预测是两个高斯分布相加,均值和方差分别相加。还提及矩阵形式的卡尔曼滤波方程,包括自定义矩阵类及一、二维情形。
博客介绍卡尔曼滤波,其分为观测更新和运动预测两步。观测更新中,后验分布均值介于先验和观测分布均值之间,方差更小;运动预测是两个高斯分布相加,均值和方差分别相加。还提及矩阵形式的卡尔曼滤波方程,包括自定义矩阵类及一、二维情形。


















 1409
1409

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










