如果是单变量时间序列,已知的只有 datetime 信息,怎么从中提取特征呢?
可以将一个日期拆分出多维信息,比如:是否是周末?是上旬中旬还是下旬?是否是节假日?是春是夏是秋还是冬?
人类活动和这些因素有着很强的联系,但是如果只将时间编码成一个日期的字符串,机器学习算法是无法提取到有效信息的。
下面就来将上图中的 datetime 列拆分成高维特征
def half_month(day):
return 1 if day < 15 else 2
temp.loc[:,'year'] = temp['datetime'].apply(lambda x:x.year)
temp.loc[:,'month'] = temp['datetime'].apply(lambda x:x.month)
temp.loc[:,'day'] = temp['datetime'].apply(lambda x: x.day)
temp.loc[:,'day_of_week'] = temp['datetime'].apply(lambda x: x.dayofweek)
temp.loc[:,'weekend'] = temp['datetime'].apply(lambda x:x.dayofweek>4)
temp.loc[:,'half_month'] = temp['datetime'].apply(lambda x: half_month(x.day))
temp.columns
'''
Index(['datetime', 'TEMP', 'year', 'month', 'day', 'day_of_week', 'weekend', 'half_month'],
dtype='object')
'''
temp.head()
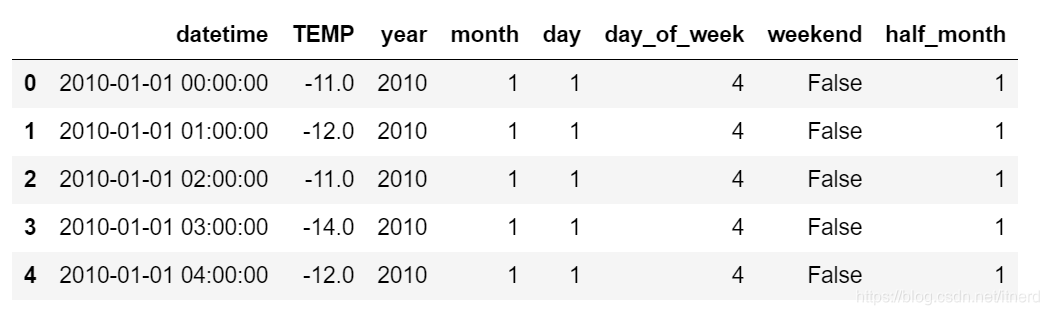
使用 pandas.get_dummies 函数把指定列编码成 onehot 形式
columns2onehot = ['year','month','day','day_of_week','half_month']
onehot = pd.get_dummies(temp, columns=columns2onehot)
onehot.columns
'''
Index(['datetime', 'TEMP', 'weekend', 'year_2010', 'year_2011', 'year_2012',
'year_2013', 'year_2014', 'month_1', 'month_2', 'month_3', 'month_4',
'month_5', 'month_6', 'month_7', 'month_8', 'month_9', 'month_10',
'month_11', 'month_12', 'day_1', 'day_2', 'day_3', 'day_4', 'day_5',
'day_6', 'day_7', 'day_8', 'day_9', 'day_10', 'day_11', 'day_12',
'day_13', 'day_14', 'day_15', 'day_16', 'day_17', 'day_18', 'day_19',
'day_20', 'day_21', 'day_22', 'day_23', 'day_24', 'day_25', 'day_26',
'day_27', 'day_28', 'day_29', 'day_30', 'day_31', 'day_of_week_0',
'day_of_week_1', 'day_of_week_2', 'day_of_week_3', 'day_of_week_4',
'day_of_week_5', 'day_of_week_6', 'half_month_1', 'half_month_2'],
dtype='object')
'''
onehot.head()
| datetime | TEMP | weekend | half_month | year_2010 | year_2011 | year_2012 | year_2013 | year_2014 | month_1 | … | day_29 | day_30 | day_31 | day_of_week_0 | day_of_week_1 | day_of_week_2 | day_of_week_3 | day_of_week_4 | day_of_week_5 | day_of_week_6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010-01-01 00:00:00 | -11.0 | False | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | … | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2010-01-01 01:00:00 | -12.0 | False | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | … | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2010-01-01 02:00:00 | -11.0 | False | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | … | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2010-01-01 03:00:00 | -14.0 | False | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | … | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2010-01-01 04:00:00 | -12.0 | False | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | … | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
然后就可以将原来非独热编码的列删掉,就可以用机器学习模型训练了!








 本文介绍如何从单变量时间序列的datetime信息中提取特征,包括日期的年、月、日、周几、是否周末及上旬中旬下旬等,并通过one-hot编码转换为机器学习模型可用的高维特征。
本文介绍如何从单变量时间序列的datetime信息中提取特征,包括日期的年、月、日、周几、是否周末及上旬中旬下旬等,并通过one-hot编码转换为机器学习模型可用的高维特征。

















 17万+
17万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










