1. 引言:性能优化在现代应用中的重要性
在当今高速发展的数字时代,应用性能直接影响用户体验、业务转化率和系统可靠性。一个响应缓慢的应用不仅会导致用户流失,还可能造成巨大的商业损失。研究表明,页面加载时间每增加1秒,转化率就会下降7%,而超过3秒的延迟会导致40%的用户放弃使用。
Spring生态系统提供了一套完整的性能监控和优化解决方案,从代码级别的优化建议到生产环境的实时监控,帮助开发者构建高性能、高可用的应用程序。
比喻:应用性能优化就像F1赛车的调校过程。监控系统(如Actuator)是车上的传感器和仪表盘,实时收集各项数据;优化技巧则是工程师根据数据进行的精准调校,包括发动机调优(代码优化)、空气动力学改进(架构优化)和轮胎选择(资源配置),最终目标是让赛车在赛道上发挥最佳性能。
2. Spring性能监控体系
2.1 Spring Boot Actuator:应用监控的核心
Spring Boot Actuator是Spring生态中最重要的监控工具,它提供了丰富的生产就绪特性:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId>
</dependency>
基础配置:
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: health, info, metrics, prometheus
endpoint:
health:
show-details: always
metrics:
enabled: true
metrics:
export:
prometheus:
enabled: true
tags:
application: ${spring.application.name}
2.2 监控体系架构
Spring性能监控体系采用分层架构,如下图所示:
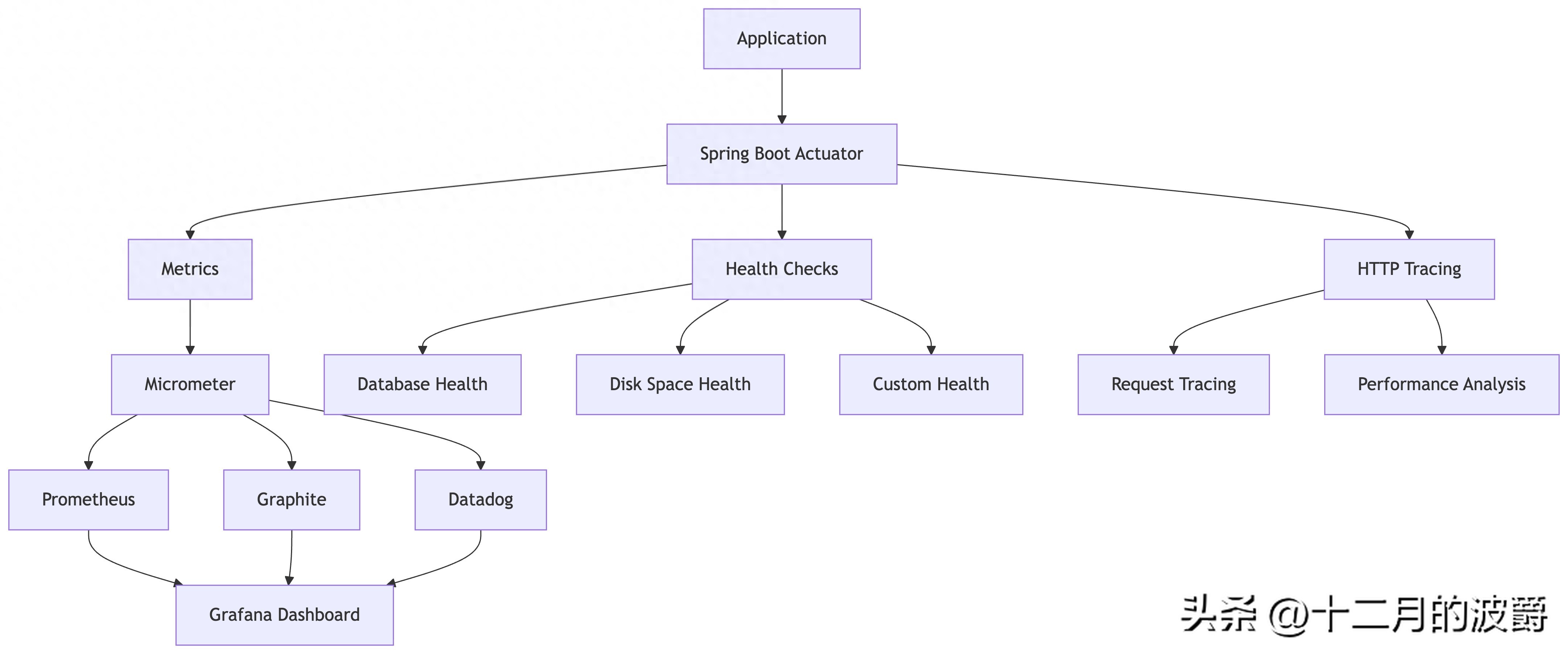
3. 实战演练:构建完整的监控体系
3.1 应用健康监控
自定义健康检查指示器:
@Component
public class CustomHealthIndicator extends AbstractHealthIndicator {
private final DatabaseService databaseService;
private final CacheService cacheService;
public CustomHealthIndicator(DatabaseService databaseService, CacheService cacheService) {
this.databaseService = databaseService;
this.cacheService = cacheService;
}
@Override
protected void doHealthCheck(Health.Builder builder) throws Exception {
// 检查数据库连接
boolean dbHealthy = databaseService.isConnected();
// 检查缓存状态
boolean cacheHealthy = cacheService.isAvailable();
if (dbHealthy && cacheHealthy) {
builder.up()
.withDetail("database", "connected")
.withDetail("cache", "available")
.withDetail("timestamp", Instant.now());
} else {
builder.down()
.withDetail("database", dbHealthy ? "connected" : "disconnected")
.withDetail("cache", cacheHealthy ? "available" : "unavailable")
.withException(new RuntimeException("Service degradation"));
}
}
}
3.2 指标收集与暴露
自定义业务指标:
@Service
public class OrderService {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final Timer orderProcessingTimer;
private final Counter failedOrderCounter;
private final DistributionSummary orderAmountSummary;
public OrderService(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.orderProcessingTimer = Timer.builder("order.processing.time")
.description("订单处理时间")
.tags("service", "order")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.failedOrderCounter = Counter.builder("order.failed.count")
.description("失败订单数量")
.tags("service", "order")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.orderAmountSummary = DistributionSummary.builder("order.amount.summary")
.description("订单金额分布")
.baseUnit("USD")
.register(meterRegistry);
}
@Transactional
public Order processOrder(OrderRequest request) {
return orderProcessingTimer.record(() -> {
try {
// 业务处理逻辑
validateOrder(request);
Order order = createOrder(request);
processPayment(order);
// 记录订单金额
orderAmountSummary.record(order.getAmount().doubleValue());
return order;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 记录失败指标
failedOrderCounter.increment();
throw new OrderProcessingException("订单处理失败", e);
}
});
}
// 方法级别的监控
@Timed(value = "order.validation.time", description = "订单验证时间")
private void validateOrder(OrderRequest request) {
// 验证逻辑
}
@Timed(value = "order.creation.time", description = "订单创建时间")
private Order createOrder(OrderRequest request) {
// 创建逻辑
return new Order();
}
}
3.3 分布式追踪集成
集成Micrometer Tracing:
management:
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.0
zipkin:
base-url: http://localhost:9411
@Configuration
public class TracingConfig {
@Bean
public ObservationHandler<Observation.Context> customObservationHandler() {
return new ObservationHandler<>() {
@Override
public boolean supportsContext(Observation.Context context) {
return true;
}
@Override
public void onStart(Observation.Context context) {
context.put("startTime", System.currentTimeMillis());
log.info("Starting observation: {}", context.getName());
}
@Override
public void onStop(Observation.Context context) {
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - (Long) context.get("startTime");
log.info("Completed observation: {} in {}ms", context.getName(), duration);
}
};
}
}
4. 性能优化实战技巧
4.1 数据库性能优化
JPA/Hibernate优化:
@Configuration
public class JpaOptimizationConfig {
@Bean
public LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean em = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
em.setDataSource(dataSource);
em.setPackagesToScan("com.example.entity");
JpaVendorAdapter vendorAdapter = new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter();
em.setJpaVendorAdapter(vendorAdapter);
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto", "validate");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.dialect", "org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL8Dialect");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.show_sql", "false");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.format_sql", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.use_sql_comments", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.jdbc.batch_size", "50");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.order_inserts", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.order_updates", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.jdbc.fetch_size", "100");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.default_batch_fetch_size", "16");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.cache.use_second_level_cache", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.cache.use_query_cache", "true");
properties.setProperty("hibernate.cache.region.factory_class",
"org.hibernate.cache.ehcache.EhCacheRegionFactory");
em.setJpaProperties(properties);
return em;
}
}
查询优化示例:
@Repository
@Slf4j
public class OptimizedUserRepository {
@PersistenceContext
private EntityManager entityManager;
// 使用DTO投影减少数据传输
public List<UserDTO> findActiveUsersWithProjection() {
return entityManager.createQuery(
"SELECT new com.example.dto.UserDTO(u.id, u.username, u.email) " +
"FROM User u WHERE u.active = true", UserDTO.class)
.setHint("org.hibernate.readOnly", true)
.getResultList();
}
// 批量处理优化
@Transactional
public void batchInsertUsers(List<User> users) {
for (int i = 0; i < users.size(); i++) {
entityManager.persist(users.get(i));
if (i % 50 == 0) { // 每50条刷新一次
entityManager.flush();
entityManager.clear();
}
}
}
// 使用EntityGraph解决N+1问题
public List<User> findUsersWithOrders() {
EntityGraph<User> graph = entityManager.createEntityGraph(User.class);
graph.addSubgraph("orders");
return entityManager.createQuery("SELECT u FROM User u", User.class)
.setHint("javax.persistence.fetchgraph", graph)
.getResultList();
}
}
4.2 缓存优化策略
多级缓存配置:
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class CacheConfig {
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager() {
CaffeineCacheManager cacheManager = new CaffeineCacheManager();
cacheManager.setCaffeine(caffeineCacheBuilder());
cacheManager.setCacheNames(Arrays.asList("users", "products", "orders"));
return cacheManager;
}
Caffeine<Object, Object> caffeineCacheBuilder() {
return Caffeine.newBuilder()
.initialCapacity(100)
.maximumSize(500)
.expireAfterAccess(10, TimeUnit.MINUTES)
.recordStats();
}
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager redisCacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofHours(1))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair
.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(redisConnectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.transactionAware()
.build();
}
}
缓存使用最佳实践:
@Service
@Slf4j
public class CachedUserService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
public CachedUserService(UserRepository userRepository) {
this.userRepository = userRepository;
}
@Cacheable(value = "users", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
log.info("Fetching user from database: {}", id);
return userRepository.findById(id).orElse(null);
}
@CacheEvict(value = "users", key = "#user.id")
public User updateUser(User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
@Caching(evict = {
@CacheEvict(value = "users", key = "#id"),
@CacheEvict(value = "userLists", allEntries = true)
})
public void deleteUser(Long id) {
userRepository.deleteById(id);
}
@Cacheable(value = "userLists", keyGenerator = "customKeyGenerator")
public List<User> getActiveUsers() {
return userRepository.findByActiveTrue();
}
}
4.3 线程池与异步处理优化
线程池精细化配置:
@Configuration
@EnableAsync
public class AsyncConfig implements AsyncConfigurer {
@Override
public Executor getAsyncExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(10);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(50);
executor.setQueueCapacity(100);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("async-");
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
executor.setWaitForTasksToCompleteOnShutdown(true);
executor.setAwaitTerminationSeconds(60);
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Bean("ioExecutor")
public Executor ioIntensiveExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(20);
executor.setMaxPoolSize(100);
executor.setQueueCapacity(200);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("io-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
@Bean("cpuExecutor")
public Executor cpuIntensiveExecutor() {
ThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
executor.setCorePoolSize(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
executor.setMaxPoolSize(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 2);
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("cpu-");
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
}
异步处理示例:
@Service
@Slf4j
public class AsyncProcessingService {
@Async("ioExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<String> processImageAsync(String imagePath) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
// 模拟耗时IO操作
Thread.sleep(1000);
return "Processed: " + imagePath;
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
throw new RuntimeException("Processing interrupted", e);
}
});
}
@Async("cpuExecutor")
public CompletableFuture<BigDecimal> calculateAsync(BigDecimal input) {
return CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
// CPU密集型计算
BigDecimal result = input;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
result = result.multiply(BigDecimal.valueOf(1.01));
}
return result;
});
}
@Async
@Timed(value = "async.operation.time", description = "异步操作时间")
public void asyncOperationWithMonitoring() {
// 带有监控的异步操作
}
}
5. 高级监控与诊断
5.1 APM集成(Application Performance Monitoring)
集成New Relic或AppDynamics:
# application.yml
newrelic:
config:
app_name: ${spring.application.name}
license_key: ${NEW_RELIC_LICENSE_KEY}
自定义APM指标:
@Component
public class CustomAPMAgent {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final NewRelic newRelic;
public CustomAPMAgent(MeterRegistry meterRegistry, NewRelic newRelic) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.newRelic = newRelic;
}
public void recordBusinessTransaction(String name, long duration) {
// Micrometer记录
Timer.builder("business.transaction")
.tags("name", name)
.register(meterRegistry)
.record(duration, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
// New Relic记录
newRelic.recordMetric("Custom/BusinessTransaction/" + name, duration);
}
}
5.2 内存分析与GC调优
JVM参数优化:
# 启动参数示例 java -jar application.jar \ -Xms2g -Xmx2g \ -XX:+UseG1GC \ -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200 \ -XX:InitiatingHeapOccupancyPercent=35 \ -XX:+ExplicitGCInvokesConcurrent \ -XX:+PrintGC \ -XX:+PrintGCDetails \ -XX:+PrintGCTimeStamps \ -XX:+PrintGCDateStamps \ -XX:+PrintGCApplicationStoppedTime \ -Xloggc:gc.log \ -XX:+UseStringDeduplication \ -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError \ -XX:HeapDumpPath=./heapdump.hprof
内存监控端点:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/diagnostics")
public class DiagnosticsController {
@GetMapping("/memory")
public Map<String, Object> memoryInfo() {
MemoryMXBean memoryMXBean = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean();
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
Map<String, Object> info = new HashMap<>();
info.put("heapUsed", memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getUsed());
info.put("heapMax", memoryMXBean.getHeapMemoryUsage().getMax());
info.put("nonHeapUsed", memoryMXBean.getNonHeapMemoryUsage().getUsed());
info.put("totalMemory", runtime.totalMemory());
info.put("freeMemory", runtime.freeMemory());
info.put("memoryUsage", (runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory()) * 100 / runtime.totalMemory());
return info;
}
@GetMapping("/gc")
public List<Map<String, Object>> gcInfo() {
List<GarbageCollectorMXBean> gcBeans = ManagementFactory.getGarbageCollectorMXBeans();
return gcBeans.stream().map(bean -> {
Map<String, Object> gcInfo = new HashMap<>();
gcInfo.put("name", bean.getName());
gcInfo.put("collectionCount", bean.getCollectionCount());
gcInfo.put("collectionTime", bean.getCollectionTime());
return gcInfo;
}).collect(Collectors.toList());
}
}
6. 性能测试与基准评估
6.1 JMH基准测试
集成JMH进行微基准测试:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId>
<artifactId>jmh-core</artifactId>
<version>1.35</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.openjdk.jmh</groupId>
<artifactId>jmh-generator-annprocess</artifactId>
<version>1.35</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
基准测试示例:
@BenchmarkMode(Mode.AverageTime)
@OutputTimeUnit(TimeUnit.MICROSECONDS)
@State(Scope.Benchmark)
@Warmup(iterations = 3, time = 1)
@Measurement(iterations = 5, time = 1)
@Fork(2)
public class ServiceBenchmark {
private UserService userService;
private OrderService orderService;
@Setup
public void setup() {
// 初始化测试环境
userService = new UserService();
orderService = new OrderService();
}
@Benchmark
public User benchmarkUserCreation() {
return userService.createUser("test@example.com");
}
@Benchmark
public Order benchmarkOrderProcessing() {
return orderService.processOrder(createTestOrder());
}
private OrderRequest createTestOrder() {
return new OrderRequest("test@example.com", BigDecimal.valueOf(100.0));
}
}
6.2 负载测试与压力测试
使用Gatling进行负载测试:
import io.gatling.core.Predef._
import io.gatling.http.Predef._
import scala.concurrent.duration._
class LoadTest extends Simulation {
val httpProtocol = http
.baseUrl("http://localhost:8080")
.acceptHeader("application/json")
val scn = scenario("User Load Test")
.exec(
http("Create User")
.post("/api/users")
.body(StringBody("""{"email": "test${randomInt()}@example.com", "name": "Test User"}"""))
.asJson
.check(status.is(201))
)
.pause(1)
.exec(
http("Get Users")
.get("/api/users")
.check(status.is(200))
)
setUp(
scn.inject(
rampUsersPerSec(10).to(100).during(1.minute),
constantUsersPerSec(100).during(5.minutes)
).protocols(httpProtocol)
)
}
7. 常见性能问题与解决方案
7.1 内存泄漏诊断
内存泄漏检测模式:
@Component
public class MemoryLeakDetector {
private final Map<String, byte[]> memoryMap = new HashMap<>();
private final ScheduledExecutorService scheduler = Executors.newScheduledThreadPool(1);
@PostConstruct
public void startMonitoring() {
scheduler.scheduleAtFixedRate(this::checkMemoryUsage, 1, 1, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
}
private void checkMemoryUsage() {
MemoryUsage heapUsage = ManagementFactory.getMemoryMXBean().getHeapMemoryUsage();
long usedMemory = heapUsage.getUsed();
long maxMemory = heapUsage.getMax();
double usagePercentage = (double) usedMemory / maxMemory * 100;
if (usagePercentage > 80) {
log.warn("内存使用率过高: {}%", String.format("%.2f", usagePercentage));
// 触发内存分析或报警
analyzeMemoryUsage();
}
}
private void analyzeMemoryUsage() {
// 生成堆转储或执行内存分析
try {
String timestamp = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME);
String dumpFile = "heapdump-" + timestamp + ".hprof";
HotSpotDiagnosticMXBean diagnosticMXBean = ManagementFactory
.getPlatformMXBean(HotSpotDiagnosticMXBean.class);
diagnosticMXBean.dumpHeap(dumpFile, true);
log.info("堆转储已生成: {}", dumpFile);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("生成堆转储失败", e);
}
}
@PreDestroy
public void cleanup() {
scheduler.shutdown();
memoryMap.clear();
}
}
7.2 数据库连接池优化
HikariCP优化配置:
spring:
datasource:
hikari:
pool-name: MainPool
maximum-pool-size: 20
minimum-idle: 5
idle-timeout: 30000
connection-timeout: 20000
max-lifetime: 1800000
leak-detection-threshold: 5000
connection-test-query: SELECT 1
连接池监控:
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ConnectionPoolMonitor {
private final HikariDataSource dataSource;
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
public ConnectionPoolMonitor(HikariDataSource dataSource, MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.dataSource = dataSource;
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
}
@Scheduled(fixedRate = 30000)
public void monitorConnectionPool() {
HikariPoolMXBean poolMXBean = dataSource.getHikariPoolMXBean();
Gauge.builder("db.pool.active.connections", poolMXBean, HikariPoolMXBean::getActiveConnections)
.register(meterRegistry);
Gauge.builder("db.pool.idle.connections", poolMXBean, HikariPoolMXBean::getIdleConnections)
.register(meterRegistry);
Gauge.builder("db.pool.total.connections", poolMXBean, HikariPoolMXBean::getTotalConnections)
.register(meterRegistry);
Gauge.builder("db.pool.threads.awaiting", poolMXBean, HikariPoolMXBean::getThreadsAwaitingConnection)
.register(meterRegistry);
if (poolMXBean.getThreadsAwaitingConnection() > 10) {
log.warn("数据库连接池压力过大,等待线程: {}", poolMXBean.getThreadsAwaitingConnection());
}
}
}
8. 总结:性能优化最佳实践
8.1 性能优化生命周期
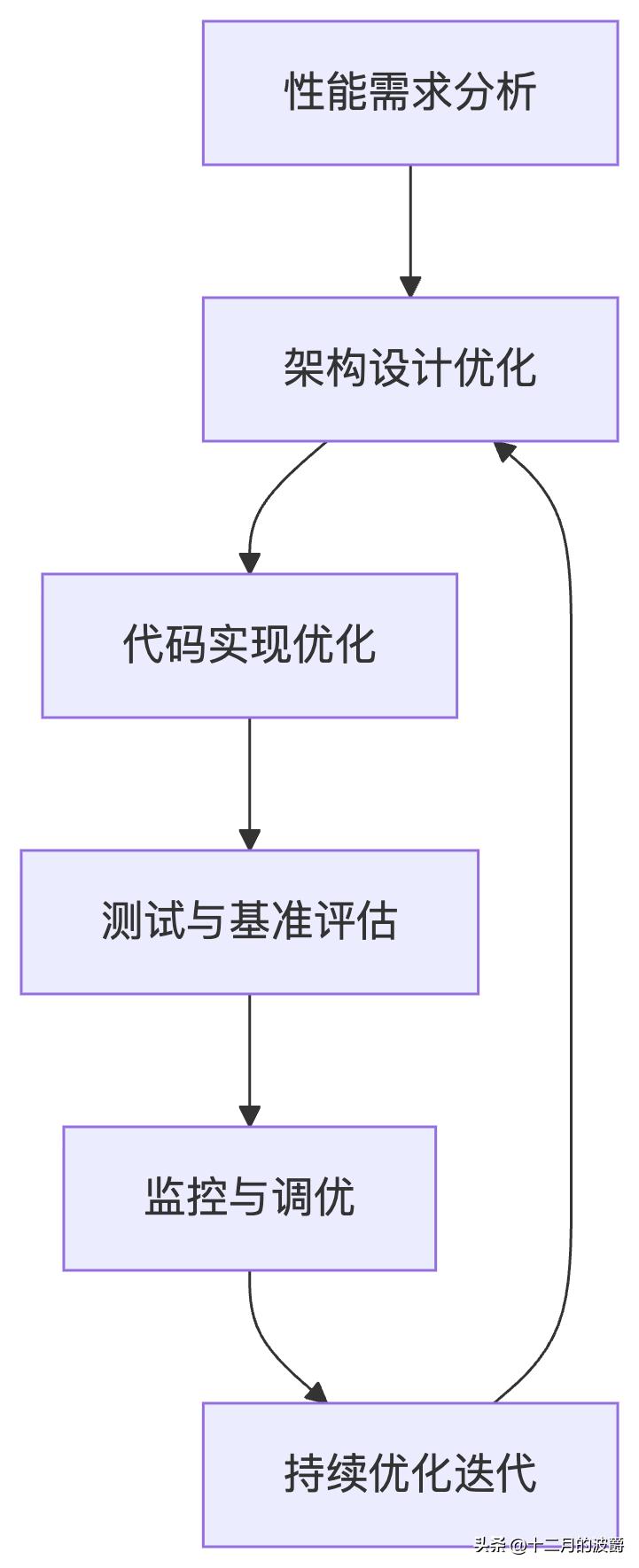
8.2 优化策略总结
- 监控先行:没有监控就没有优化,建立完善的监控体系
- 数据驱动:基于实际数据做出优化决策,避免盲目优化
- 分层优化:从架构、代码、数据库、JVM等多个层面系统优化
- 迭代改进:性能优化是一个持续的过程,不是一次性的任务
- 平衡取舍:在性能、可维护性、开发成本之间找到平衡点
8.3 持续性能文化
记住:性能优化不是项目最后阶段的补救措施,而应该是贯穿整个开发周期的持续实践。建立性能文化,让每个开发者都成为性能专家:
编写性能友好的代码
定期进行性能评审
建立性能基准和SLA
自动化性能测试
持续监控和优化
通过系统性地应用Spring性能监控和优化技术,你将能够构建出高性能、高可用的企业级应用,为用户提供卓越的使用体验。





















 1749
1749

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










