1. 引言:单元测试在软件开发中的核心价值
在现代软件开发实践中,单元测试早已不再是可选的附加项,而是保障代码质量、确保系统稳定性的必备实践。想象一下,你正在构建一个复杂的金融交易系统,每次代码修改都可能影响核心业务流程。如果没有完善的测试套件,如何确保修改不会引入新的缺陷?如何保证重构不会破坏现有功能?
Spring框架对测试提供了全方位的支持,通过一系列专门的测试注解和工具类,让编写单元测试和集成测试变得简单而高效。良好的测试覆盖率不仅能减少bug,更能提升开发信心,促进代码重构,最终形成正向开发循环。
比喻:单元测试就像建筑物的结构安全检测系统。每个测试用例如同一个传感器,实时监测着代码的各个组件。当你进行修改或重构时,这个检测系统会立即发出警报,确保你的每一次"施工"都不会破坏整体的结构安全。
2. Spring测试框架核心组件
2.1 测试框架架构
Spring测试框架构建在JUnit和TestNG之上,提供了丰富的注解和工具类:
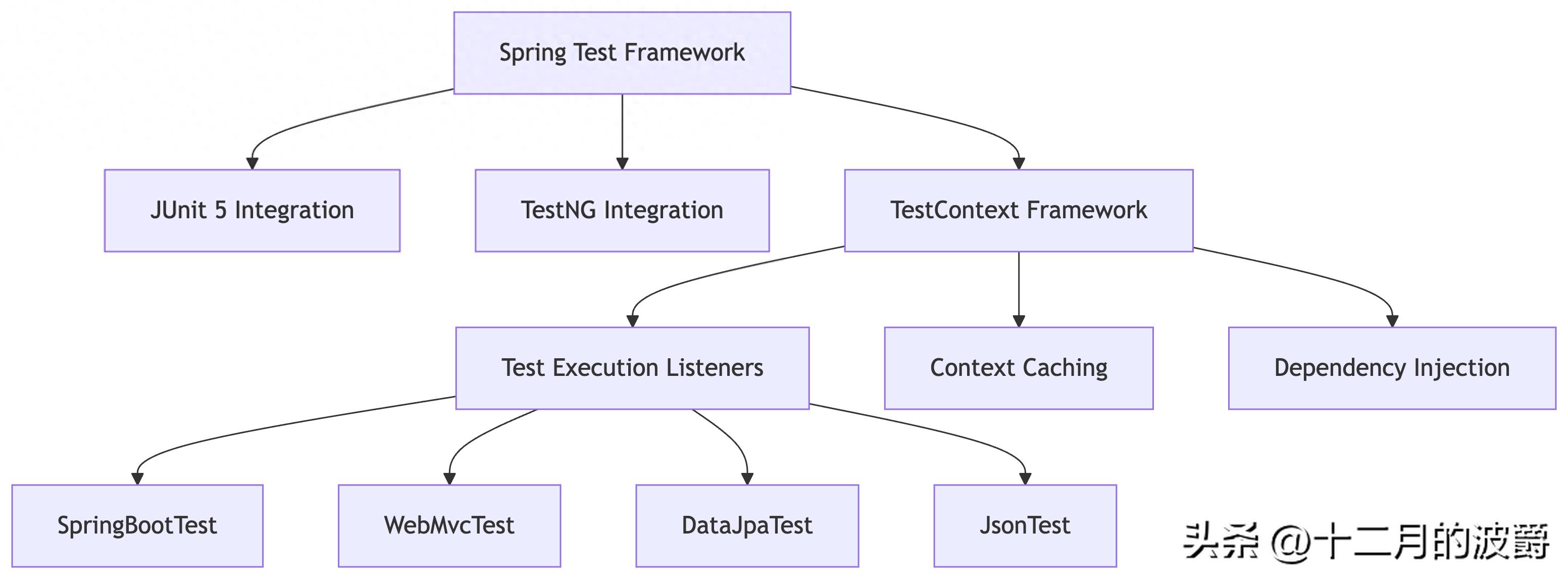
2.2 核心注解概览
Spring测试提供了分层级的测试注解,针对不同测试场景进行优化:
|
注解 |
用途 |
测试层级 |
|
@SpringBootTest |
完整集成测试 |
集成测试 |
|
@WebMvcTest |
MVC控制器测试 |
切片测试 |
|
@DataJpaTest |
数据层测试 |
切片测试 |
|
@JsonTest |
JSON序列化测试 |
切片测试 |
|
@RestClientTest |
REST客户端测试 |
切片测试 |
3. 环境搭建与基础配置
3.1 依赖配置
在Maven项目中添加测试依赖:
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Test Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.junit.vintage</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-vintage-engine</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<!-- 测试所需其他依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.h2database</groupId>
<artifactId>h2</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3.2 测试配置类
创建专门的测试配置文件:
// src/test/resources/application-test.yml
spring:
datasource:
url: jdbc:h2:mem:testdb;DB_CLOSE_DELAY=-1;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE
driver-class-name: org.h2.Driver
username: sa
password:
jpa:
hibernate:
ddl-auto: create-drop
show-sql: true
properties:
hibernate:
dialect: org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect
h2:
console:
enabled: true
4. 实战演练:编写Spring单元测试
4.1 服务层单元测试
使用Mockito进行依赖隔离测试:
@ExtendWith(MockitoExtension.class)
class UserServiceTest {
@Mock
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Mock
private EmailService emailService;
@InjectMocks
private UserService userService;
@Test
void createUser_WithValidData_ShouldReturnUser() {
// Arrange
UserCreateRequest request = new UserCreateRequest("john@example.com", "John", "Doe");
User expectedUser = new User(1L, "john@example.com", "John", "Doe");
when(userRepository.findByEmail(anyString())).thenReturn(Optional.empty());
when(userRepository.save(any(User.class))).thenReturn(expectedUser);
doNothing().when(emailService).sendWelcomeEmail(anyString());
// Act
User result = userService.createUser(request);
// Assert
assertNotNull(result);
assertEquals("john@example.com", result.getEmail());
assertEquals("John", result.getFirstName());
// Verify interactions
verify(userRepository).findByEmail("john@example.com");
verify(userRepository).save(any(User.class));
verify(emailService).sendWelcomeEmail("john@example.com");
}
@Test
void createUser_WithExistingEmail_ShouldThrowException() {
// Arrange
UserCreateRequest request = new UserCreateRequest("existing@example.com", "John", "Doe");
User existingUser = new User(1L, "existing@example.com", "Existing", "User");
when(userRepository.findByEmail("existing@example.com"))
.thenReturn(Optional.of(existingUser));
// Act & Assert
assertThrows(DuplicateEmailException.class, () -> {
userService.createUser(request);
});
verify(userRepository, never()).save(any(User.class));
verify(emailService, never()).sendWelcomeEmail(anyString());
}
}
4.2 数据层单元测试
使用@DataJpaTest进行仓库层测试:
@DataJpaTest
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase(replace = AutoConfigureTestDatabase.Replace.NONE)
class UserRepositoryTest {
@Autowired
private TestEntityManager entityManager;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@Test
void findByEmail_WhenUserExists_ShouldReturnUser() {
// Arrange
User user = new User(null, "test@example.com", "Test", "User");
entityManager.persistAndFlush(user);
// Act
Optional<User> found = userRepository.findByEmail("test@example.com");
// Assert
assertTrue(found.isPresent());
assertEquals("test@example.com", found.get().getEmail());
}
@Test
void findByEmail_WhenUserNotExists_ShouldReturnEmpty() {
// Act
Optional<User> found = userRepository.findByEmail("nonexistent@example.com");
// Assert
assertFalse(found.isPresent());
}
@Test
void existsByEmail_WhenEmailExists_ShouldReturnTrue() {
// Arrange
User user = new User(null, "exists@example.com", "Exists", "User");
entityManager.persistAndFlush(user);
// Act
boolean exists = userRepository.existsByEmail("exists@example.com");
// Assert
assertTrue(exists);
}
}
4.3 Web层单元测试
使用@WebMvcTest进行控制器测试:
@WebMvcTest(UserController.class)
class UserControllerTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean
private UserService userService;
@Autowired
private ObjectMapper objectMapper;
@Test
void createUser_WithValidRequest_ShouldReturnCreated() throws Exception {
// Arrange
UserCreateRequest request = new UserCreateRequest("john@example.com", "John", "Doe");
UserResponse response = new UserResponse(1L, "john@example.com", "John", "Doe");
when(userService.createUser(any(UserCreateRequest.class))).thenReturn(response);
// Act & Assert
mockMvc.perform(post("/api/users")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(request)))
.andExpect(status().isCreated())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.id").value(1L))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email").value("john@example.com"))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.firstName").value("John"))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.lastName").value("Doe"));
}
@Test
void createUser_WithInvalidEmail_ShouldReturnBadRequest() throws Exception {
// Arrange
UserCreateRequest request = new UserCreateRequest("invalid-email", "John", "Doe");
// Act & Assert
mockMvc.perform(post("/api/users")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(request)))
.andExpect(status().isBadRequest())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.errors[0].field").value("email"))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.errors[0].message").value("必须是合法的电子邮件地址"));
}
@Test
void getUser_WhenUserExists_ShouldReturnUser() throws Exception {
// Arrange
UserResponse response = new UserResponse(1L, "john@example.com", "John", "Doe");
when(userService.getUserById(1L)).thenReturn(response);
// Act & Assert
mockMvc.perform(get("/api/users/{id}", 1L))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.id").value(1L))
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.email").value("john@example.com"));
}
@Test
void getUser_WhenUserNotExists_ShouldReturnNotFound() throws Exception {
// Arrange
when(userService.getUserById(999L))
.thenThrow(new UserNotFoundException("用户不存在"));
// Act & Assert
mockMvc.perform(get("/api/users/{id}", 999L))
.andExpect(status().isNotFound())
.andExpect(jsonPath("$.message").value("用户不存在"));
}
}
4.4 集成测试
使用@SpringBootTest进行完整集成测试:
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@Testcontainers
@ActiveProfiles("test")
class UserIntegrationTest {
@Container
static PostgreSQLContainer<?> postgreSQL = new PostgreSQLContainer<>("postgres:13")
.withDatabaseName("testdb")
.withUsername("test")
.withPassword("test");
@DynamicPropertySource
static void configureProperties(DynamicPropertyRegistry registry) {
registry.add("spring.datasource.url", postgreSQL::getJdbcUrl);
registry.add("spring.datasource.username", postgreSQL::getUsername);
registry.add("spring.datasource.password", postgreSQL::getPassword);
}
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
@AfterEach
void tearDown() {
userRepository.deleteAll();
}
@Test
void fullUserWorkflow_ShouldWorkCorrectly() {
// Create user
UserCreateRequest createRequest = new UserCreateRequest(
"integration@test.com", "Integration", "Test");
ResponseEntity<UserResponse> createResponse = restTemplate.postForEntity(
"/api/users", createRequest, UserResponse.class);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.CREATED, createResponse.getStatusCode());
assertNotNull(createResponse.getBody());
assertNotNull(createResponse.getBody().getId());
// Get user
Long userId = createResponse.getBody().getId();
ResponseEntity<UserResponse> getResponse = restTemplate.getForEntity(
"/api/users/" + userId, UserResponse.class);
assertEquals(HttpStatus.OK, getResponse.getStatusCode());
assertNotNull(getResponse.getBody());
assertEquals("integration@test.com", getResponse.getBody().getEmail());
// Verify user exists in database
Optional<User> dbUser = userRepository.findById(userId);
assertTrue(dbUser.isPresent());
assertEquals("Integration", dbUser.get().getFirstName());
}
}
5. 高级测试技巧与最佳实践
5.1 自定义测试注解
创建组合注解简化测试配置:
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@SpringBootTest
@ActiveProfiles("test")
@ExtendWith(SpringExtension.class)
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
@Transactional
public @interface SpringUnitTest {
}
// 使用自定义注解
@SpringUnitTest
class CustomAnnotationTest {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@Test
void testWithCustomAnnotation() throws Exception {
mockMvc.perform(get("/api/test"))
.andExpect(status().isOk());
}
}
5.2 数据库测试优化
使用测试数据工厂:
class TestDataFactory {
static User createUser() {
return createUser("test@example.com");
}
static User createUser(String email) {
return new User(null, email, "Test", "User");
}
static UserCreateRequest createUserRequest() {
return new UserCreateRequest("test@example.com", "Test", "User");
}
}
// 在测试中使用
@Test
void testWithFactoryData() {
User user = TestDataFactory.createUser("specific@test.com");
// 测试逻辑
}
5.3 性能测试
使用@Timed进行执行时间验证:
@SpringBootTest
class PerformanceTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
@Timed(millis = 100) // 要求方法在100ms内完成
void userCreation_ShouldBePerformant() {
UserCreateRequest request = TestDataFactory.createUserRequest();
userService.createUser(request);
}
}
6. 测试覆盖率与质量保障
6.1 配置Jacoco测试覆盖率
在pom.xml中配置Jacoco:
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.8.8</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-agent</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>report</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>check</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>check</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<rules>
<rule>
<element>BUNDLE</element>
<limits>
<limit>
<counter>INSTRUCTION</counter>
<value>COVEREDRATIO</value>
<minimum>0.80</minimum>
</limit>
</limits>
</rule>
</rules>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
6.2 生成测试报告
运行测试并生成报告:
# 运行测试并生成覆盖率报告 mvn clean test jacoco:report # 查看报告 open target/site/jacoco/index.html
7. 常见问题与解决方案
7.1 测试上下文缓存问题
问题:多个测试类重复加载应用上下文,导致测试速度变慢。
解决方案:合理组织测试类,共享测试配置
// 基础测试类,定义共享配置
@SpringBootTest
@ContextConfiguration(classes = TestConfig.class)
@ActiveProfiles("test")
public abstract class BaseIntegrationTest {
@Autowired
protected TestEntityManager entityManager;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
// 共享的初始化逻辑
}
}
// 具体测试类继承基础类
class UserServiceIntegrationTest extends BaseIntegrationTest {
// 自动继承所有配置
}
7.2 异步测试处理
测试异步代码:
@SpringBootTest
class AsyncServiceTest {
@Autowired
private AsyncService asyncService;
@Test
void asyncOperation_ShouldComplete() throws Exception {
// Arrange
CompletableFuture<String> future = asyncService.asyncOperation("test");
// Act & Assert
String result = future.get(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
assertEquals("processed-test", result);
}
}
7.3 环境隔离问题
使用Testcontainers进行隔离测试:
@Testcontainers
@SpringBootTest
class IsolationTest {
@Container
static MySQLContainer<?> mysql = new MySQLContainer<>("mysql:8.0");
@DynamicPropertySource
static void configureProperties(DynamicPropertyRegistry registry) {
registry.add("spring.datasource.url", mysql::getJdbcUrl);
registry.add("spring.datasource.username", mysql::getUsername);
registry.add("spring.datasource.password", mysql::getPassword);
}
@Test
void testWithRealDatabase() {
// 使用真实的MySQL数据库进行测试
}
}
8. 总结:构建有效的测试策略
Spring测试框架提供了全面的工具支持,帮助开发者构建高质量的测试套件:
8.1 测试金字塔实践
遵循测试金字塔原则,构建健康的测试体系:
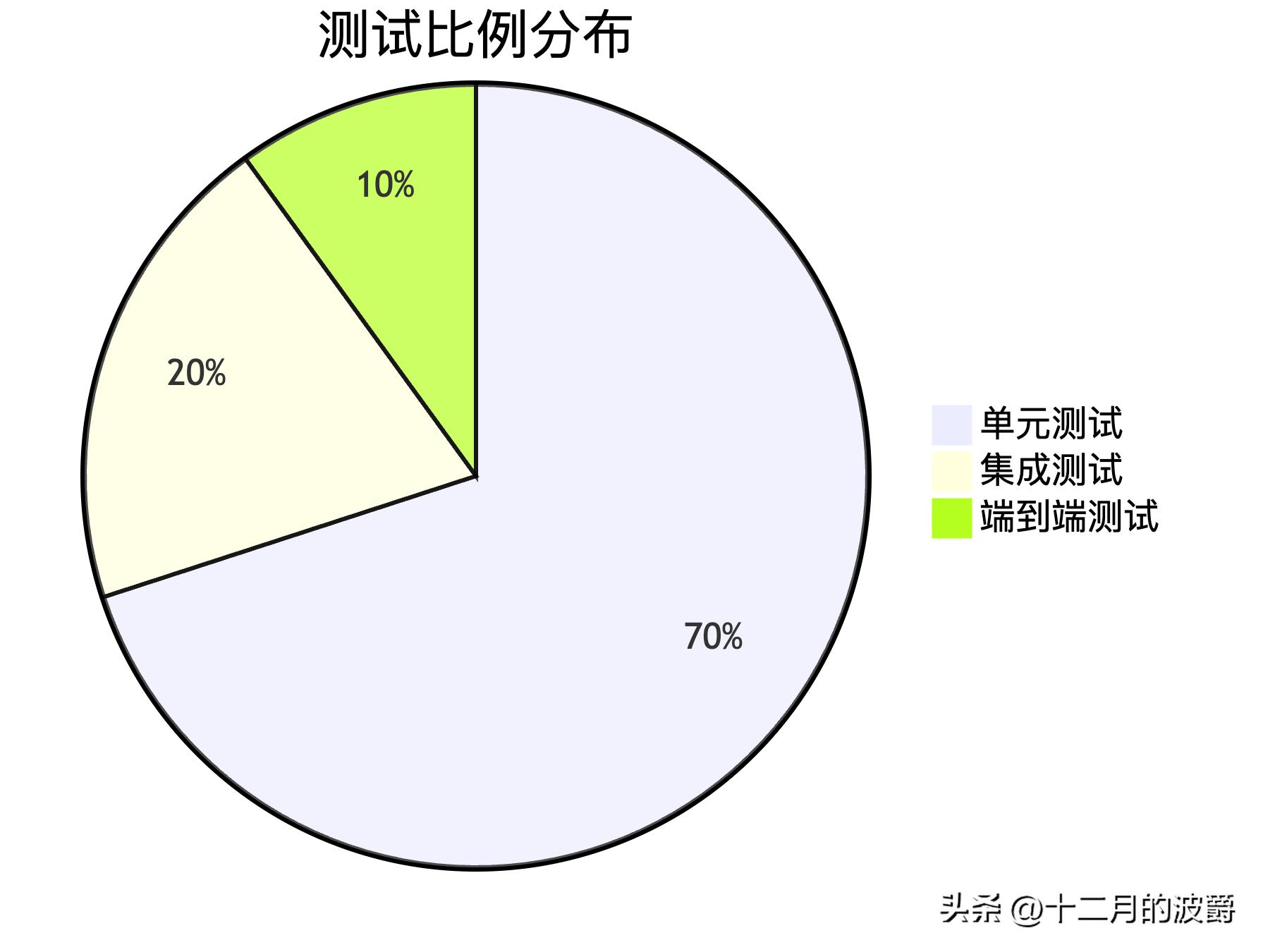
8.2 最佳实践总结
- 分层测试:按照金字塔模型组织测试,大量单元测试+适量集成测试
- 测试隔离:每个测试应该独立运行,不依赖其他测试的状态
- 快速反馈:保持测试快速执行,促进TDD实践
- 覆盖率导向:追求有意义的覆盖率,而不是盲目追求100%
- 持续维护:将测试作为代码的一部分进行维护和重构
8.3 测试心态培养
记住:好的测试不是负担,而是开发者的安全网。它们让你能够:
自信地进行重构
快速发现回归缺陷
理解代码的预期行为
提供活生生的文档示例
通过系统性地应用Spring测试框架,你将能够构建出更加健壮、可维护的应用程序,真正实现"质量内建"的开发理念。





















 9022
9022

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










