Configure C/C++ IntelliSense
This article is about configuring the C/C++ extension to provide C++ specific IntelliSense suggestions in Visual Studio Code. IntelliSense is a helpful tool built into VS Code that provides various code editing features to help you code faster and more efficiently. For example, code completion, parameter info, syntax highlighting, Code Actions (light bulbs), and member lists are all generated using IntelliSense.
C/C++ IntelliSense only requires a C/C++ compiler to be installed on your system. The C/C++ compiler provides C++ specific information to IntelliSense, such as the locations of system include paths and other settings. For project level configurations, reference Project level IntelliSense configuration section.
When will the C/C++ extension configure core IntelliSense features for me?
A compiler is the only requirement to configure core IntelliSense functionality. To identify a compiler for IntelliSense, the C/C++ extension scans common paths on your machine for compilers such as Clang, GCC, MinGW, cygwin, cygwin64, and MSVC. If any of these compilers are identified and in a secure location, they are automatically configured for IntelliSense. Otherwise, a notification is displayed asking you to confirm that this compiler should be configured for IntelliSense. In either of these scenarios, the compiler selected is also set as the default compiler.
How to check whether IntelliSense is configured
If you don't have IntelliSense configured, the C/C++ extension shows a yellow indicator in the status bar with a warning sign labeled Configure IntelliSense.

To configure, select the status bar indicator, which brings up the configuration Quick Pick. The Quick Pick can help you select or install a C/C++ compiler.
If you do not see a status bar indicator, you can also check your project's c_cpp_properties.json file. This file stores all of your IntelliSense configuration settings. Navigate to this file by selecting C/C++: Edit Configurations (UI) from the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P). Check the IntelliSense mode to find your configuration. To learn more about the c_cpp_properties.json file, you can review the schema reference.
How to configure IntelliSense
IntelliSense configuration is stored in the c_cpp_properties.json file, which is automatically created in your workspace. All three of the following options are different ways of editing the c_cpp_properties.json file:
Option 1. Select a configuration option through the configuration Quick Pick
Open the Quick Pick by entering Select IntelliSense Configuration in the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), which shows you a dropdown with all of the configuration options found by the C/C++ extension on your machine.
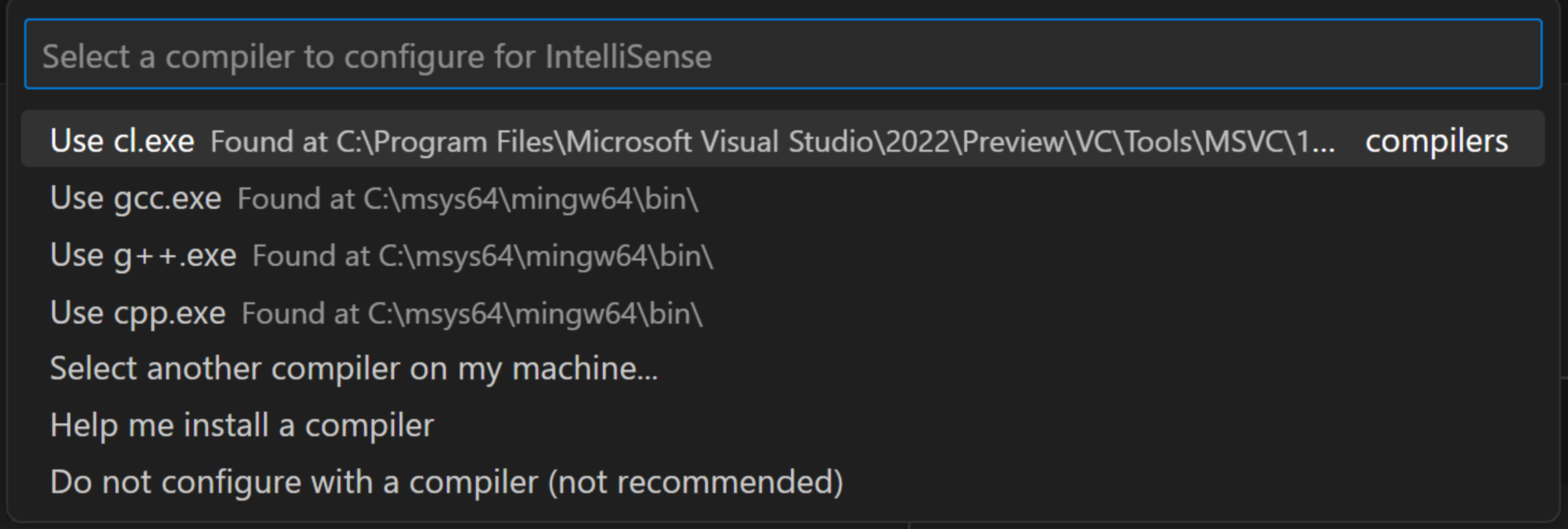
Select one of the options available. If you select a compiler, this compiler is used by IntelliSense by default. You can return to the Configure IntelliSense Quick Pick at any point to change which option is used to configure IntelliSense.
If no options are available in the Quick Pick, no compiler could be identified in your system. You can browse your machine manually or install a C/C++ compiler. To install on a Windows machine, select the Help me install a compiler option that redirects you to the step-by-step walkthrough of how to install a C/C++ compiler. On a macOS or Linux machine, select Install a compiler and navigate through the prompts to have a C++ compiler installed on your machine.
Option 2. Edit your IntelliSense configurations through the UI
Open your IntelliSense configuration by selecting C/C++: Edit Configurations (UI) from the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P). This view is a user interface for the c_cpp_properties.json file.
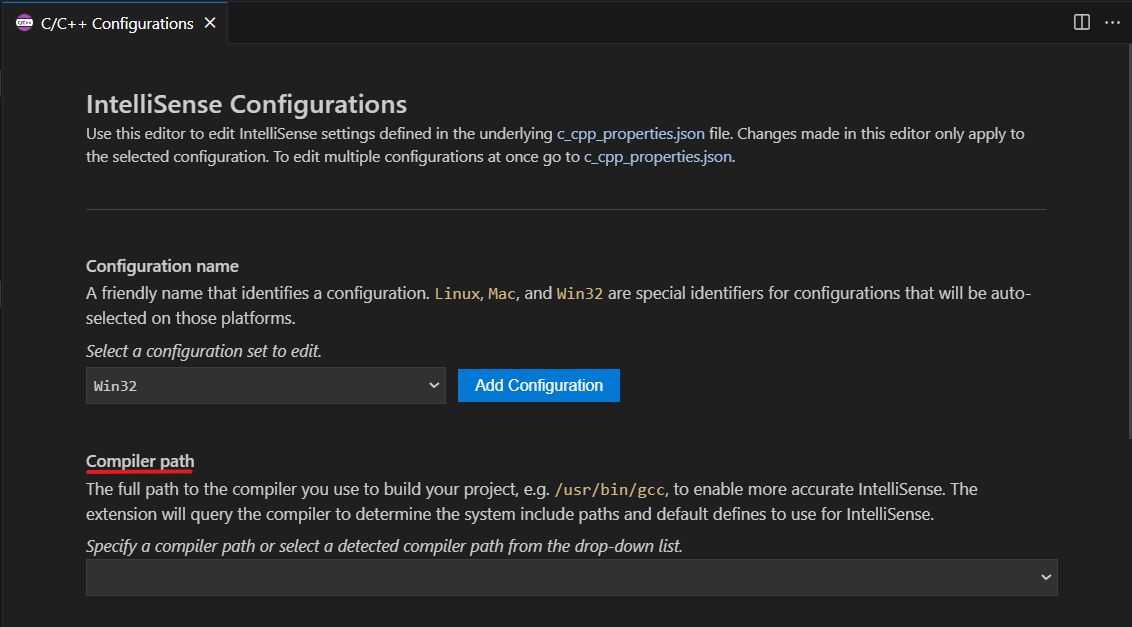
Set the Compiler path field to the full path of the compiler you're using to build your project. For example, when using the default install path for GCC on Linux, the compiler path is /usr/bin/gcc. Set the IntelliSense mode to the architecture-specific variant of the compiler you're using.
Option 3. Edit the c_cpp_properties.json file directly
You can edit the c_cpp_properties.json file directly to customize your configuration. Use the C/C++ Edit Configurations (JSON) command from the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P), then the c_cpp_properties.json file is created in the .vscode folder of your workspace.
Use the compilerPath variable to add a compiler. This variable is the full path of the compiler you're using to build your project. For example, when using the default install path for GCC on Linux, the compiler path is /usr/bin/gcc.
For more information about the c_cpp_properties.json file, review the schema reference.
Select the sample below based on your operating system for a c_cpp_configuration.json file:
Sample c_cpp_configuration.json on Windows
Using the default install path for MinGW:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Win32",
"includePath": ["${workspaceFolder}/**"],
"defines": ["_DEBUG", "UNICODE", "_UNICODE"],
"windowsSdkVersion": "10.0.22621.0",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "${default}",
"compilerPath": "C:/msys64/mingw64/bin/gcc.exe"
}
],
"version": 4
}
Sample c_cpp_configuration.json on macOS
Using the default install path for Clang:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Mac",
"includePath": ["${workspaceFolder}/**"],
"defines": [],
"macFrameworkPath": [
"/Library/Developer/CommandLineTools/SDKs/MacOSX.sdk/System/Library/Frameworks"
],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/clang",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "macos-clang-arm64"
}
],
"version": 4
}
Sample c_cpp_configuration.json on Linux
Using the default install path for GCC:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "Linux-GCC",
"includePath": ["${workspaceFolder}/**"],
"defines": [],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/g++",
"cStandard": "c17",
"cppStandard": "c++17",
"intelliSenseMode": "gcc-x64",
"browse": {
"path": ["${workspaceFolder}"],
"limitSymbolsToIncludedHeaders": true,
"databaseFilename": ""
}
}
],
"version": 4
}
Project level IntelliSense configuration
Configuring IntelliSense with a compiler provides you with core IntelliSense features. This setup is called the base configuration. For more complex usage scenarios, such as setting up a project that requires:
* Additional include paths, such as references to one or multiple different libraries
* Specific compiler arguments that influence the behavior of the language(and therefore IntelliSense)
There are multiple other ways to configure IntelliSense. You can provide these additional configurations either through:
* The c_cpp_properties.json file and related settings
* A custom configuration provider in the form of another VS Code extension (for example, the Makefile Tools or CMake Tools extensions)
* A compile_commands.json file
Configuration providers
A custom configuration provider is another extension in VS Code that can potentially provide more accurate C++ IntelliSense configuration than the C/C++ extension. For example, for the CMake or Make build systems, where the Makefile Tools or CMake Tools extensions can be configuration providers. To add an extension as a configuration provider, either select the extension through the configuration Quick Pick, add it to configuration UI by editing the Configuration provider field under Advanced Settings, or add the configurationProvider field to your c_cpp_properties.json file. For example, for the CMake extension, the path to add would be ms-vscode.cmake-tools.
The C/C++ extension scans your system for custom configuration providers. If it identifies only one custom configuration provider, this configuration provider is automatically configured for IntelliSense. If there are multiple configuration providers identified, you need to select which the extension should use by opening the configuration Quick Pick.
compile_commands.json file
Another option to provide IntelliSense configuration is a compile_commands.json file, which describes the exact compile commands used for every file in a project. This file is often generated by a build system, such as CMake or Bazel, by setting command line arguments when configuring your project. A compile_commands.json file can be selected for configuration through the same methods as discussed in the How to configure IntelliSense section via the configuration Quick Pick, editing configurations through the UI, or editing the c_cpp_properties.json file directly. In the configuration UI, the file can be added under Advanced Configurations and the Compile commands field. For example, if your compile_commands.json file is in the root of your workspace, enter ${workspaceFolder}/compile_commands.json in the Compile commands field. Otherwise, it can be added to the c_cpp_properties.json file directly using the compileCommands configuration property.
If the compile commands database does not contain an entry for the translation unit that corresponds to the file you opened in the editor, your base configuration (found in c_cpp_properties.json) is used instead (such as your includePath and defines). If the C/C++ extension reverts to the base configuration, the language status bar indicator shows you the label Configure IntelliSense in the status bar.
If you specified a custom configuration provider and a compile_commands.json file, the custom configuration provider is queried first for an IntelliSense configuration.
If your program includes header files that aren't in your workspace or that aren't in the standard library path, you can modify the Include Path. The C/C++ extension populates the include path by querying the compiler specified by Compiler path. If the extension can't find the path for the target system libraries, you can enter the include path manually.
Check IntelliSense activity using the language status bar
You can determine if IntelliSense is actively working on your file using the language status bar. To invoke the language status bar, open a C++ file. The status bar shows the text {} C++. Hover over the {} symbol to open the language status bar flyout. The top item in the flyout indicates the IntelliSense status. Here are the different statuses and their meanings:
* IntelliSense: Ready = IntelliSense is configured for the C/C++ extension and automatically activates if you interact with the editor, for example, by writing code.
* IntelliSense: Updating = IntelliSense is actively working to determine any code completions, syntax highlighting, etc. based on changes you're making to your code.
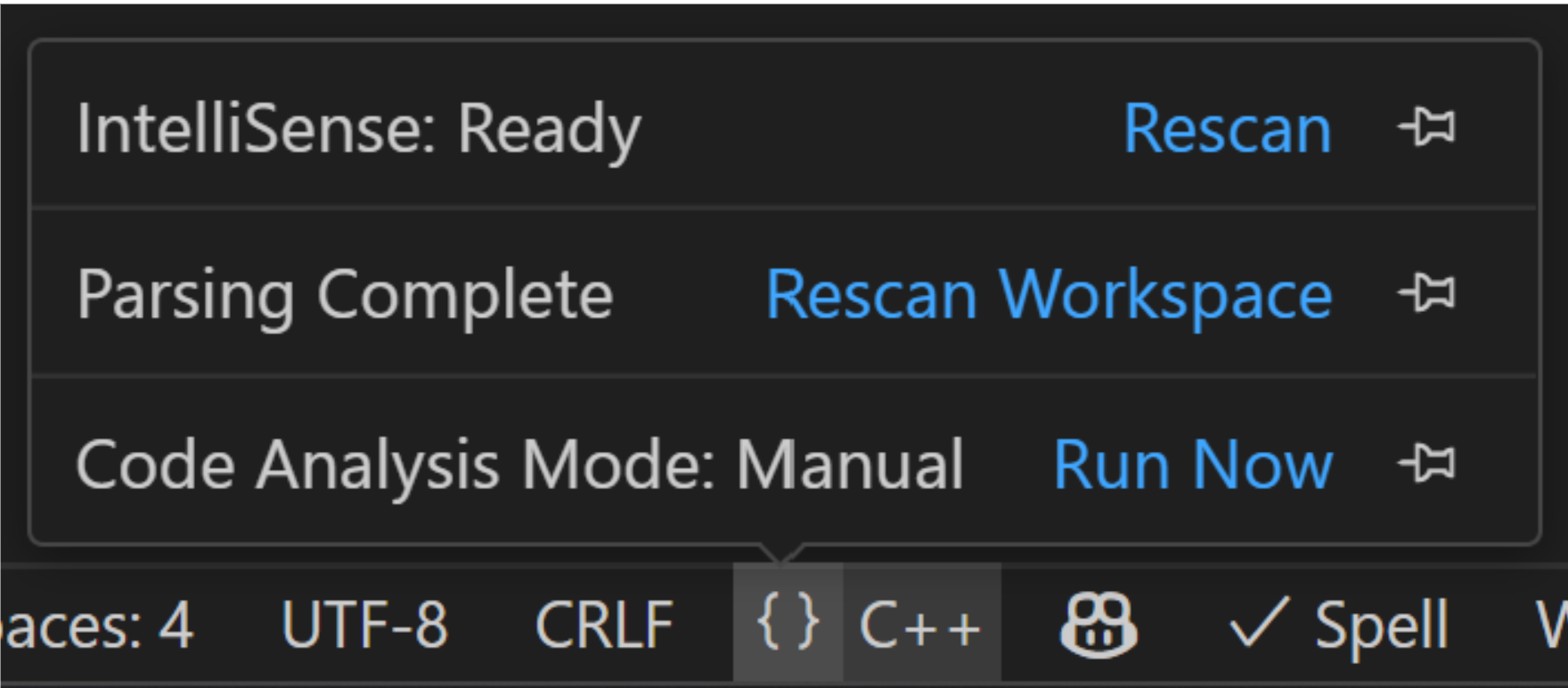
You can select the pin icon on the right of any item in the language status bar flyout to permanently pin it to your status bar.
IntelliSense for cross-compiling
IntelliSense for cross-compiling
These configuration settings are stored in your project's c_cpp_properties.json file. To edit this file, in VS Code, select C/C++: Edit Configurations (UI) from the Command Palette (Ctrl+Shift+P):
Example IntelliSense configuration
The following shows configuring the C/C++ extension for a Linux x64 host machine that targets Linux Arm. It configures the following IntelliSense settings:
* Compiler path: the extension queries your compiler at this location to retrieve system libraries and compiler defines.
* IntelliSense mode: emulates the target architecture and compiler so that the extension can provide correct IntelliSense and reflect the right sizes of data types such as pointer, size_t, long, and so on.
At a minimum, setting compiler path and IntelliSense mode provides enough information for the extension to emulate your project's target architecture, although setting IntelliSense mode may not be needed if the extension is able to choose it correctly based on the defines returned from querying the compiler path.
Compiler path
Set to the full path of the compiler you are using to build your project.
For example:

IntelliSense mode
Set to the architecture-specific variant of the compiler you are using.
For example:

Include path
You only need to modify the Include path if your program includes header files that aren't in your workspace or that are not in the standard library path.
The C/C++ extension populates the include path by querying the compiler specified by Compiler path. If the extension can't find the path for the target system libraries, you can enter the include path manually:
Given the settings above, your c_cpp_configuration.json file will look something like the following. You can open it by selecting C/C++: Edit Configurations (JSON) from the Command Palette:
{
"configurations": [
{
"name": "myConfigurationName",
"includePath": ["${workspaceFolder}/**"],
"defines": [],
"compilerPath": "/usr/bin/arm-none-eabi-g++",
"cStandard": "c11",
"cppStandard": "c++14",
"IntelliSenseMode": "gcc-arm"
}
],
"version": 4
}






















 6120
6120

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










