目录
1. 前言
osg已经自己实现了很多操控器类,这些操控器类存放在osg源码目录下的src\osgGA目录。感兴趣的童鞋,可以自己去研究源码。下面两篇博文是我研究osg的键盘切换操控器和动画路径操控器之后写的,感兴趣的可以参考学习:
虽然说osg实现了很多常用的操控器类,但现实中的业务需求是各种各样的,当osg自己实现的操控器不能满足平时的业务需求时,就需要自己开发操控器,本博文通过实现一个简单的操控器,来说明如何定制开发自己的操控器类。
2. 操控器需求

图1
如上图,实现一个网格,网格在X、Y轴范围为[-5, 5],单元格的长宽都为0.5,网格颜色为白色,坐标轴位于(0, 0, 0)处,实现一个操控器,操控器功能必须满足如下要求:
- 按住键盘←键,能逆时针转动整个网格。
- 按住键盘→键,能顺时针转动整个网格。
- 起始时视点位于(0, -15, 15)处。
- 当鼠标滚轮朝向人的方向转动时,此时网格变大。
- 当鼠标滚轮背向人的方向转动,此时网格变小。
- 按住空格键,网格回到原始状态。
即操控器要能实现如下效果:
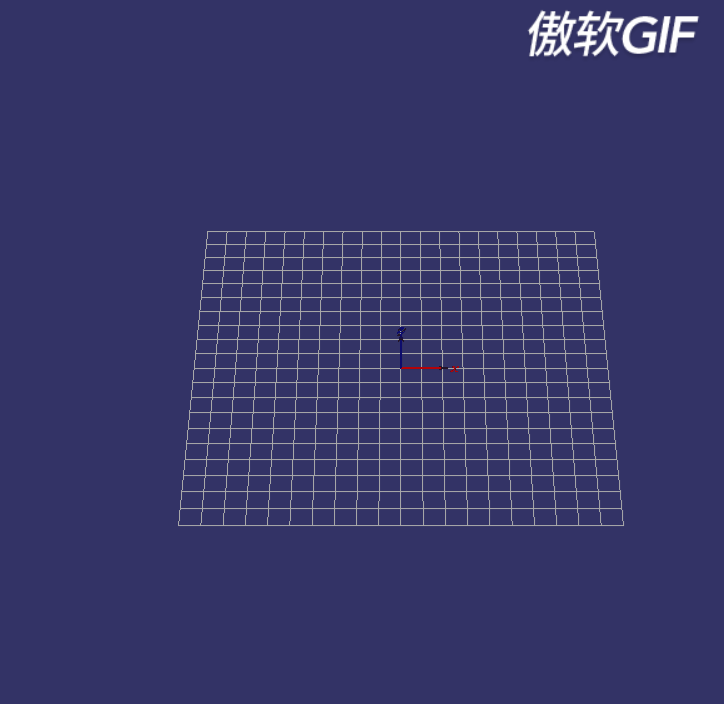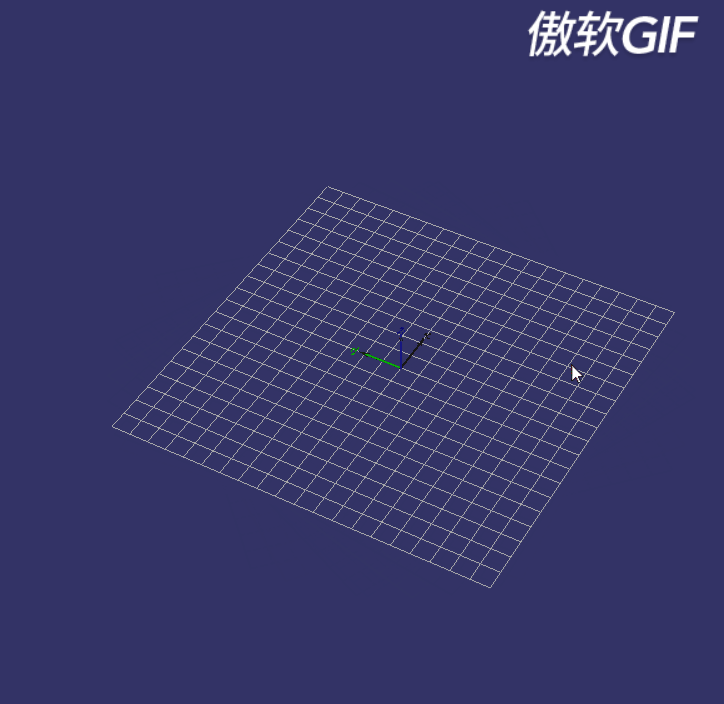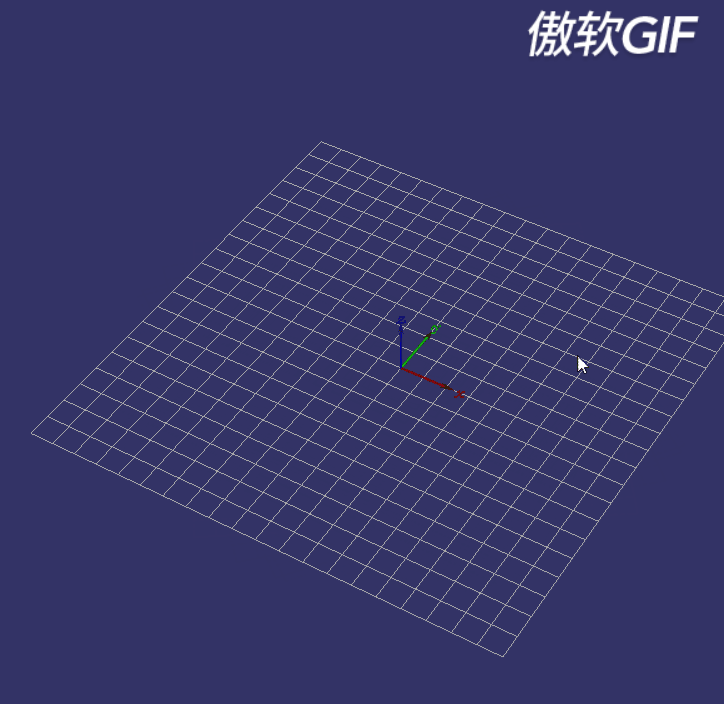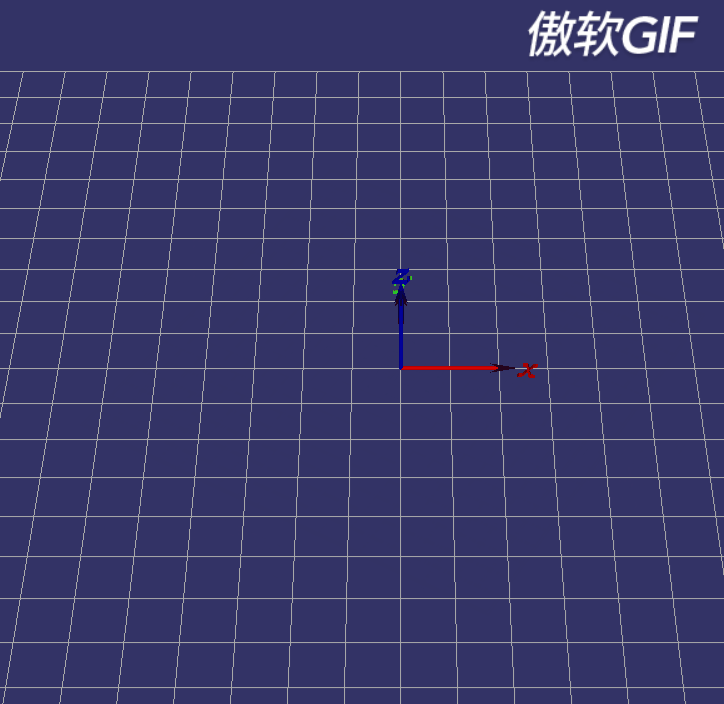
图2
3. 功能实现
3.1. 预备知识
三维场景中的操控器都有一个共同特点,即它们都采用实时修正观察矩阵(也就是观察者的观察位置和姿态)的方式实现平滑导航浏览。而此处又有一个重要的结论:相机在世界坐标中的位置姿态矩阵,等于观察者的观察位置和姿态的逆矩阵。假设相机在世界坐标系中的位置姿态矩阵为M,观察者在世界坐标系中的观察位置和姿态矩阵为V,则有:
M = V的逆根据物理学相对性原理很好理解这种互逆关系,相机向前(左)运动等同于观察点向后(右)运动,反之亦然。关于这一结论更详细的描述,请参见:浅谈在操控器类中,为何要通过osgGA::CameraManipulator的逆矩阵改变视点位置博文。
osg提供了操控器类的基类CameraManipulator,该基类定义了实现操控器的所有接口。如果要定制自己的操控器类,则必须根据自己的需求,重写CameraManipulator类的Virtual开头的函数。CameraManipulator存放在osg源码目录下的include\osgGA目录。
关于场景(本例是指网格)的拉近拉远,参见:osg下如何将物体拉近拉远博文。
3.2. 代码实现
main.cpp文件如下:
#include<osgViewer/Viewer>
#include<osgDB/readFile>
#include<osgDB/writeFile>
#include<osgDB/FileUtils>
#include "mySimpleManipulator.h"
// 创建地板网格
osg::Geode* createFloorGrid()
{
auto pGeode = new osg::Geode;
auto pQuardGeomery = new osg::Geometry();
pGeode->addDrawable(pQuardGeomery);
auto pCoordArray = new osg::Vec3dArray;
osg::DrawElementsUShort* pElementsUShort = new osg::DrawElementsUShort(GL_LINES, 84); // 共84个点
auto elementIndex = 0;
for (auto yIndex = -5.0; yIndex <= 5.0; yIndex += 0.5) // Y轴方向21条直线,42个点
{
pCoordArray->push_back(osg::Vec3d(-5.0, yIndex, 0.0));
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = pCoordArray->size() - 1; // 记录每个点的索引,下同
pCoordArray->push_back(osg::Vec3d(5.0, yIndex, 0.0));
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = pCoordArray->size() - 1 ;
}
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = 0; // (-5.0, -5.0, 0.0)点的索引为0
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = pCoordArray->size() - 2;// (-5.0, 5.0, 0.0)点的索引
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = pCoordArray->size() - 1;// (5.0, 5.0, 0.0)点的索引
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = 1;// (5.0, -5.0, 0.0)点的索引为0
for (auto xIndex = -4.5; xIndex <= 4.5; xIndex += 0.5) // X轴方向有19条直线,38个点
{
pCoordArray->push_back(osg::Vec3d(xIndex, -5.0, 0.0));
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = pCoordArray->size() - 1 ;
pCoordArray->push_back(osg::Vec3d(xIndex, 5.0, 0.0));
(*pElementsUShort)[elementIndex++] = pCoordArray->size() - 1;
}
pQuardGeomery->setVertexArray(pCoordArray);
// 使格子线颜色为白色
auto pColorArray = new osg::Vec4Array;
pColorArray->push_back(osg::Vec4(1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0));
pQuardGeomery->setColorArray(pColorArray, osg::Array::Binding::BIND_OVERALL);
auto pNormalArray = new osg::Vec3Array();
pNormalArray->push_back(osg::Vec3(0, 0, 1));
pQuardGeomery->setNormalArray(pNormalArray, osg::Array::Binding::BIND_OVERALL);
pQuardGeomery->addPrimitiveSet(pElementsUShort);
return pGeode;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
osgViewer::Viewer viewer;
auto pAxis = osgDB::readRefNodeFile(R"(E:\osg\OpenSceneGraph-Data\axes.osgt)");
if (nullptr == pAxis)
{
OSG_WARN << "axes node is nullpr!";
return 1;
}
auto pRoot = new osg::Group();
pRoot->addChild(pAxis);
viewer.setSceneData(pRoot);
auto pFloorGrid = createFloorGrid();
pRoot->addChild(pFloorGrid);
// 创建一个自定义的操控器对象
auto pMySimpleManipulator = new CMySimpleManipulator();
pMySimpleManipulator->setNode(pRoot);
viewer.setCameraManipulator(pMySimpleManipulator);
// 设置相机位置,注意:最开始时相机和观察点是重合的
pMySimpleManipulator->setHomePosition(osg::Vec3d(0.0, -15.0, 15.0), osg::Vec3d(0.0, 0.0, 0.0), osg::Vec3(0, 0, 1));
viewer.run();
}
mySimpleManipulator.h文件如下:
#pragma once
#include<osgGA/CameraManipulator>
using namespace osgGA;
class CMySimpleManipulator :
public CameraManipulator
{
public:
CMySimpleManipulator();
~CMySimpleManipulator();
public:
/** set the position of the matrix manipulator using a 4x4 Matrix.*/
virtual void setByMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix) override;
/** set the position of the matrix manipulator using a 4x4 Matrix.*/
virtual void setByInverseMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix) override;
/** get the position of the manipulator as 4x4 Matrix.*/
virtual osg::Matrixd getMatrix() const override;
/** get the position of the manipulator as a inverse matrix of the manipulator, typically used as a model view matrix.*/
virtual osg::Matrixd getInverseMatrix() const override;
/** Handle events, return true if handled, false otherwise. */
virtual bool handle(const GUIEventAdapter& ea, GUIActionAdapter& us) override;
/**
Move the camera to the default position.
May be ignored by manipulators if home functionality is not appropriate.
*/
virtual void home(const GUIEventAdapter&, GUIActionAdapter&) override;
/** Manually set the home position, and set the automatic compute of home position. */
virtual void setHomePosition(const osg::Vec3d& eye,
const osg::Vec3d& center,
const osg::Vec3d& up,
bool autoComputeHomePosition = false) override;
virtual void setNode(osg::Node*) override;
private:
void setTransformation(const osg::Vec3d& eye, const osg::Vec3d& center, const osg::Vec3d& up);
// 更新观察点位置
void updateEyePos(const GUIEventAdapter& ea, GUIActionAdapter& us);
private:
osg::ref_ptr<osg::Node> _spNode;
osg::Vec3d _center;
double _distance;
osg::Quat _rotation;
float _rotateZAngle{0};
osg::Vec3d _initEye;
float _sina{0.0};
float _cosa{ 0.0 };
};
mySimpleManipulator.cpp文件如下:
#include "mySimpleManipulator.h"
#include<osgViewer/Viewer>
#include<iostream>
//#include <math.h>
CMySimpleManipulator::CMySimpleManipulator()
{
}
CMySimpleManipulator::~CMySimpleManipulator()
{
}
/** set the position of the matrix manipulator using a 4x4 Matrix.*/
void CMySimpleManipulator::setByMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix)
{
}
/** set the position of the matrix manipulator using a 4x4 Matrix.*/
void CMySimpleManipulator::setByInverseMatrix(const osg::Matrixd& matrix)
{
}
/** get the position of the manipulator as 4x4 Matrix.*/
osg::Matrixd CMySimpleManipulator::getMatrix() const
{
return osg::Matrixd::translate(0., 0., _distance) *
osg::Matrixd::rotate(_rotation) *
osg::Matrixd::translate(_center);
}
/** get the position of the manipulator as a inverse matrix of the manipulator, typically used as a model view matrix.*/
osg::Matrixd CMySimpleManipulator::getInverseMatrix() const
{
return osg::Matrixd::translate(-_center) *
osg::Matrixd::rotate(_rotation.inverse()) *
osg::Matrixd::translate(0.0, 0.0, -_distance);
}
/** Handle events, return true if handled, false otherwise. */
bool CMySimpleManipulator::handle(const GUIEventAdapter& ea, GUIActionAdapter& us)
{
auto pViewer = (osgViewer::Viewer*)(&us);
switch (ea.getEventType())
{
case GUIEventAdapter::KEYDOWN:
{
int nKeyCode = ea.getKey();
if (GUIEventAdapter::KEY_Left == nKeyCode)
{
_rotateZAngle += 1.0;
updateEyePos(ea, us);
}
else if (GUIEventAdapter::KEY_Right == nKeyCode)
{
_rotateZAngle -= 1.0;
updateEyePos(ea, us);
}
else if (GUIEventAdapter::KEY_Space == nKeyCode)
{
_homeEye = _initEye;
_rotateZAngle = 0.0;
home(ea, us);
}
}
break;
case GUIEventAdapter::SCROLL:
{
auto center = _spNode->getBound().center();
auto scrollingMotion = ea.getScrollingMotion();
auto scrollingIsMotion = false;
if (GUIEventAdapter::SCROLL_DOWN == scrollingMotion) // 滚轮朝向人的方向转动
{
if (3 < _distance) // 防止拉得过近
{
scrollingIsMotion = true;
_distance -= 0.5;
}
}
else if (GUIEventAdapter::SCROLL_UP == scrollingMotion)// 滚轮背向人的方向转动
{
if (_distance < 50) // 防止拉得过远
{
scrollingIsMotion = true;
_distance += 0.5;
}
}
if (scrollingIsMotion)
{
_homeEye = center + osg::Vec3d(0, 0, 1) * _distance;
pViewer->getCamera()->setViewMatrixAsLookAt(_homeEye, center, osg::Vec3(0, 0, 1));
}
pViewer->requiresRedraw();
pViewer->requestContinuousUpdate(false);
}
} // end switch
return CameraManipulator::handle(ea, us);
}
// 更新观察点位置
void CMySimpleManipulator::updateEyePos(const GUIEventAdapter& ea, GUIActionAdapter& us)
{
_homeEye.z() = _distance * _sina;
auto temp = _distance * _cosa;
auto radians = osg::DegreesToRadians(_rotateZAngle);
_homeEye.y() = -temp * std::cos(radians);
_homeEye.x() = -temp * std::sin(radians);
home(ea, us);
}
void CMySimpleManipulator::setHomePosition( const osg::Vec3d& eye,
const osg::Vec3d& center,
const osg::Vec3d& up,
bool autoComputeHomePosition /*= false*/)
{
_homeEye = eye;
_homeCenter = center;
_homeUp = up;
// 记录观察点初始位置,以便等下按空格键能重置会初始位姿
_initEye = _homeEye;
// 计算观察点即眼睛和物体中心即(0, 0, 0)点连线和Y轴负半轴的夹角的正弦值、余弦值
auto angle = std::atan2(std::fabs(eye.z()) / std::fabs(eye.y()), 1.0);
_sina = std::sinf(angle);
_cosa = std::cosf(angle);
}
void CMySimpleManipulator::home(const GUIEventAdapter&ea, GUIActionAdapter&aa)
{
setTransformation(_homeEye, _homeCenter, _homeUp);
auto pViewer = (osgViewer::Viewer*)(&aa);
pViewer->requiresRedraw();
pViewer->requestContinuousUpdate(false);
}
void CMySimpleManipulator::setNode(osg::Node*pNode)
{
_spNode = pNode;
}
void CMySimpleManipulator::setTransformation(const osg::Vec3d& eye, const osg::Vec3d& center, const osg::Vec3d& up)
{
osg::Vec3d lv(center - eye); // 相机指向物体中心(这里指世界坐标系中的原点)的向量
osg::Vec3d f(lv);
f.normalize();// 相机指向物体中心方向
// 计算相机其它两个轴的方向
osg::Vec3d s(f ^ up);
s.normalize();
osg::Vec3d u(s ^ f);
u.normalize();
// 计算相机姿态矩阵,即旋转矩阵
osg::Matrixd rotation_matrix(s[0], u[0], -f[0], 0.0f,
s[1], u[1], -f[1], 0.0f,
s[2], u[2], -f[2], 0.0f,
0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 1.0f);
_center = center;
_distance = lv.length(); // // 相机距离物体中心(这里指世界坐标系中的原点)的距离
_rotation = rotation_matrix.getRotate().inverse(); // 相机的位置姿态矩阵的逆是观察点位置姿态矩阵
}3.3. 代码难点说明
调用操控器的home函数后,相机将回到程序设置的相机初始位置,即调用操控器类的setHomePosition函数设置的位置。在home函数中调用setTransformation函数来计算相机的姿态矩阵,即朝向,也即旋转矩阵。因为观察点矩阵和相机矩阵互逆,所以可以根据互逆关系求出观察点矩阵。最开始时观察点和相机处于世界坐标系下的同一位置。观察点矩阵是通过操控器类的如下函数获取的:
/** get the position of the manipulator as 4x4 Matrix.*/
osg::Matrixd CMySimpleManipulator::getMatrix() const
{
return osg::Matrixd::translate(0., 0., _distance) *
osg::Matrixd::rotate(_rotation) *
osg::Matrixd::translate(_center);
}由线性代数矩阵方面的知识,我们知道:矩阵乘积的逆等于矩阵的逆的相反顺序的程序,即满足如下公式:

图3
所以将getMatrix函数中矩阵乘积求逆即为如下函数(注意:对于平移来说,直接将平移向量中的各个分量分别取反就取逆;对于矩阵来说就是取逆矩阵):
/** get the position of the manipulator as a inverse matrix of the manipulator, typically used as a model view matrix.*/
osg::Matrixd CMySimpleManipulator::getInverseMatrix() const
{
return osg::Matrixd::translate(-_center) *
osg::Matrixd::rotate(_rotation.inverse()) *
osg::Matrixd::translate(0.0, 0.0, -_distance);
}
而getInverseMatrix函数的返回值即为相机矩阵。当按住键盘←、→键或滚动鼠标滚轮,改变观察点位置和姿态时,需要将相机矩阵返回到外层。在viewer.cpp第1212行附近的更新阶段void Viewer::updateTraversal()中,会调用如下:
_cameraManipulator->updateCamera(*_camera);来更新相机位姿,其中_cameraManipulator为操控器类对象,也即main.cpp中的pMySimpleManipulator对象。上面代码的updateCamera函数在操控器基类CameraManipulator定义如下:
/** update the camera for the current frame, typically called by the viewer classes.
Default implementation simply set the camera view matrix. */
virtual void updateCamera(osg::Camera& camera) { camera.setViewMatrix(getInverseMatrix()); }即相机的位姿更新就在该处实现的,即前文说的操控器类将相机矩阵即getInverseMatrix()函数返回值返回到外层了。
代码中重写了setHomePosition函数,在该函数中算出了观察点和物体中心即(0, 0, 0)点连线与Y轴负半轴夹角的正弦值、余弦值,便于后面按下←、→键时实时更新观察点坐标。在转动网格时,始终保持观察点和物体中心即(0, 0, 0)点连线与网格所在平面夹角不变。
updateEyePos函数实时更新观察点坐标,需要说明的是:_rotateZAngle的0°位置和Y轴负半轴重合,由Y轴负半轴非0的某个点指向坐标原点(0, 0, 0),逆时针时,_rotateZAngle增加1°;顺时针时,_rotateZAngle减小1°。






















 1688
1688

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








