从相关到精确的差距
目前利用vector DB和嵌入技术,我们能够有效地识别最相关的内容,以响应用户的查询。然而,在这个框架内精确定位相关答案是一个重大挑战。例如,当呈现三个不同的内容时 —— 一个图像文件(ultipa-logo. jpg);关于提供图解决方案的公司嬴图的信息;以及关于嬴图名为 SP 的合作伙伴的详细信息 —— 传统的问答系统通常很难解决诸如 “SP 的合作伙伴的标志是什么?” 或 “SP 如何制定图解决方案?”
传统的 QA 系统在面对分散在各种来源中的多格式数据时会遇到限制,阻碍了它们发现隐藏在不同数据关系互连性中的答案的能力。
一种利用图获得更多上下文的解决方案
这篇文章旨在展示 OpenAI、LangChain、Chroma Vector DB 和 嬴图的战略集成,以实现 QA 系统(称为嬴图-GraphBot)的最佳性能。在这种方法中,我们利用嬴图Graph 从寻路查询和节点属性中收集知识,通过深入研究可用数据来回答问题。
准备工作:
要设置基本组件,请安装 scikit-learn、嬴图、LangChain 和 OpenAI 软件包。
pip install scikit-learn ultipa langchain openai
导入演示数据集:使用嬴图-Transtor 将数据集导入嬴图Graph。配置服务器和图集信息,并在 import. yml 文件中指定节点 / 边缘模式和属性。

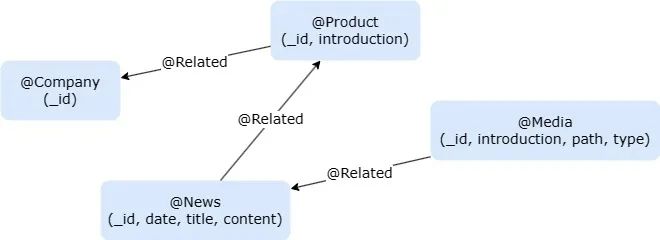
通过 Python SDK 连接到嬴图Graph:通过 Python SDK 连接到嬴图Graph,并为所有节点创建一个名为 “embedding” (嵌入)的新属性。
import os
Utilizing Ultipa-Transporter to Import all demo data
# Create the connection to Ultipa
from ultipa import Connection, UltipaConfig
from ultipa.types import ULTIPA
from ultipa import structs, ULTIPA_REQUEST
from ultipa.structs.Path import Path
ultipaConfig = UltipaConfig()
ultipaConfig.hosts = [os.getenv("HOST")]
ultipaConfig.username = os.getenv("USER")
ultipaConfig.password = os.getenv("PASS")
ultipaConfig.defaultGraph = os.getenv("GRAPH")
ultipaConfig.heartbeat = 0 # disable heartbeat
conn = Connection.NewConnection(defaultConfig=ultipaConfig)
conn.test().Print()
# Create the property embedding for all nodes
conn.uql("create().node_propery(@*,'embedding',float[],'vectors')")
配置 OpenAI 和其他:要继续,您需要一个 OPENAI_API_KEY。如果您没有,请按照此处列出的步骤申请一个。
导入必要的库:
from typing import List
from IPython.display import display, clear_output
from IPython.display import HTML
# Initialize OpenAI
OPENAI_API_KEY = os.getenv("OPENAI_API_KEY")
from openai import OpenAI
client = OpenAI()
# Import all dependence
from sklearn.metrics.pairwise import cosine_similarity
from langchain.chat_models import ChatOpenAI
from langchain.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
我们的主要任务是从图数据中提取有价值的上下文信息,包括节点属性(例如新闻内容)以及关系和路径,然后将其传递给大语言模型(LLM)以生成问题的答案。
提取的上下文将存储在两个变量中:
1、FinalGraphContext:存储关系和路径
2、FinalDetailContext:存储节点属性的详细信息
生成节点向量:
OpenAI text-embedding-ada-002 模型使我们能够将任何文本转换为一组高维向量,这些向量作为节点的表示,便于以后计算相似性。
为此,我们建立了三个函数:
1、嵌入:专用于将文本嵌入向量的函数。
2、UpdateEmbedding:更新一个节点向量的函数。
3、UpdateAllNodesEmbeddings:更新所有节点向量的函数,这个函数应该只调用一次。
# Get str embedding from OpenAI, you can also use LangChain do the same thing
def Embed(str:str):
res = client.embeddings.create(
model="text-embedding-ada-002",
input=str,
encoding_format="float"
)
return [float(x) for x in res.data[0].embedding]
# Update the embedding of node with an id
def UpdateEmbedding(id: str, vectors: List[float]):
uql = "update().nodes({{ _id == `{}` }}).set({{ embedding: {} }})".format(id, vectors)
return conn.uql(uql)
# Update the embeddings of all nodes
def UpdateAllNodesEmbeddings():
res = conn.uql("find().nodes() return nodes{*} limit 100")
for node in res.alias("nodes").asNodes():
content = node.getID()
content += {
"News": node.get("content") or "",
"Media": node.get("path") or "",
"Product": node.get("introduction") or ""
}.get(node.getSchema(), "")
# Display(content, node.getSchema())
vectors = Embed(content)
res = UpdateEmbedding(node.getID(), vectors)
if res.status.code != ULTIPA.Code.SUCCESS:
res.Print()
else:
clear_output()
display("finished embed: " + node.getID())
为问题查找相似的节点:
Option 1 - 嬴图: 当用户提出问题时,我们可以应用相同的文本到向量嵌入技术将问题转换为向量。随后,我们将问题向量与嬴图中的节点向量进行比较,以识别最相似的节点。
# Calc the most similar nodes for the question, you can also use a vector DB to do the same thing
def FindSimilarNodes(question="", min=0.8)->List[dict]:
res = conn.uql("find().nodes({}) return nodes{*} limit 100")
embed2 = Embed(question)
results = []
for node in res.alias("nodes").asNodes():
embeddings = []
embeddings.append(embed2)
embeddings.append(node.get("embedding"))
res = cosine_similarity(embeddings)
results.append({
"id": node.getID(),
"similarity": res.min()
})
results = [x for x in results if x.get("similarity") > min]
return results
Option 2 - Vector DB: 为了识别相似的节点,利用向量数据库被证明是有用的。VectorDB 提供了一系列为人工智能操作定制的服务,促进了向量、文档、元数据等的存储。利用图数据库和 VectorDB 的功能开创了质量保证系统的新时代。
在此示例中,我们将使用开源矢量数据库 chromaDB。
# Use data via a Vector DB - ChromaDB for example
import chromadb
# Create a temporary db
vDB = chromadb.Client()
# Get or create collection to store vector and ids
try:
vDB.delete_collection("graph-qa")
except:
pass
vCollection = vDB.get_or_create_collection(name="graph-qa")
def UpdateVectorDB():
res = conn.uql("n(as nodes) return nodes{_id, embedding}")
nodes = res.alias("nodes").asNodes()
for node in nodes:
exist = vCollection.get(ids=node.getID())
if exist.get("embeddings") is None:
vCollection.add(
ids=[node.getID()],
embeddings=[node.get("embedding")]
)
def FindSimilarNodesFromVectorDB(question = "") -> List[dict]:
results = vCollection.query(query_embeddings=[Embed(question)], n_results=3)
ids = results.get("ids")[0]
resp = conn.uql("n({_id in [\"%s\"]} as nodes) return nodes{*}" % '","'.join(ids))
return [{"id": n.getID()} for n in resp.alias("nodes").asNodes()]
寻路查询:
一旦确定了最相似的节点,我们就可以继续执行路径查询,以发现可能有助于回答提出的问题的深入信息。
为了检索图数据,我们将使用autonet(组网)和 path 模板查询。 【此处更多了解,关注嬴图文档库:https://www.ultipa.cn/document/ultipa-graph-query-language/autonet/】
# Make the path string
def MakePathStrings(paths: List[Path]) -> (List[str], List[List[str]]):
strs = []
pathNodes:List[List[str]] = []
for path in paths:
pathString: List[str] = []
nodes = path.getNodes()
edges = path.getEdges()
for index, node in enumerate(nodes):
if(index > 0):
edge = edges[index - 1]
if edge.to_id != node.getID():
pathString += [" <- ", edge.getSchema(), " - "]
else:
pathString += [" - ", edge.getSchema(), " -> "]
nodeStr = node.getID()
if nodeStr.startswith(("media-")):
nodeStr = nodeStr.replace("media-", "(%s)" % node.get("type"))
pathString.append(nodeStr)
strs.append(" ".join(pathString))
pathNodes.append([ node.getID() for node in path.getNodes()])
return (strs, pathNodes)
# Find relations and paths by the autonet and template queries
def FindRelationsAndPaths(starts: List[dict])->(List[str], List[List[str]]):
res = conn.uql("""autonet().src({_id in %s}).depth(2).shortest() as paths return paths{*}""" % ([x.get("id") or "" for x in starts]))
paths = res.alias("paths").asPaths()
contextAutoNet, ids1 = MakePathStrings(paths)
res = conn.uql("""n({_id in %s} as start).e()[:3].n() as paths return paths{*} limit 10""" % ([x.get("id") or "" for x in starts]))
paths = res.alias("paths").asPaths()
contextPathFinding, ids2 = MakePathStrings(paths)
context = contextAutoNet + contextPathFinding
PathIds = ids1 + ids2
return (context, PathIds)
路径过滤:
FindRelationsAndPaths()函数发现的路径可能包含模糊或不清楚的数据。为了改进,我们使用 LLM 来识别最有用的路径。
这次我们使用 LangChain 而不是 OpenAI API,因为前者提供了提示模板、模型创建、结果输出和更多功能。
def LLMFindRelatedGraphInfo(question="", pathContext: List[str] = [], pathIDs = []) -> List[str]:
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Recommend up to 10 paths related to the question or containing words related to the question, -- PATHS -- \n {context} \n -- END -- \n Question: {question}\n path indices split by `,`:")
model = ChatOpenAI(model = "gpt-4")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
res = chain.invoke({
"context": "\n".join(pathContext),
"question": question
})
nodeIDs = set()
print("pathIDs", res, pathIDs)
for i in res.split(","):
index = int(i.strip()) -1
nodeIDs = nodeIDs.union(pathIDs[index])
FinalGraphContext.append(pathContext[index])
return nodeIDs
在这个代码片段中,我们已经为 FinalGraphContext 变量分配了所有有用的关系和路径!
来自图表的更多上下文:
我们认为仅仅依靠这些路径仍然是不够的,为了给 LLM 提供更丰富的上下文,我们希望从每个模式的属性中提取额外的信息,具体来说,我们的重点是找到图像路径和新闻内容,这可以通过带有_id 过滤器的节点查询来实现。
def FindDetailContext(nodeIDs) -> (List[str],List[str]):
uql = "find().nodes({_id in %s}) return nodes{*}" % list(nodeIDs)
print(uql)
res = conn.uql(uql)
details = []
medias = []
for node in res.alias("nodes").asNodes():
if node.getSchema() == "News":
details.append("--- (Knowledge) %s ---\n %s \n--- Article END ---\n" % (node.getID(), node.get("content")))
elif node.getSchema() == "Media":
details.append("--- (%s) ---\nName:[%s]\nURL[%s]\n--- Media END ---\n" % (node.get("type"),node.getID(), node.get("path")))
medias += [node]
return (details, medias)
这是使用 FinalDetailContext 变量的地方。
将上下文传递给 LLM 以获得答案!
为了显示结果,我们将 FinalGraphContext 和 FinalDetailContext 传递给 LLM 并请求它返回超文本标记语言进行显示。
# Answer question based on context
def LLMAnswer(question = "") -> str:
prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_template("Answer the question as an expert with comprehensive knowledge of the given context: \n {context} \n !!CONTEXT END!! \n Question: {question}\n Answer(Ensure the output is rich, including media and styles, in HTML format):")
model = ChatOpenAI(model = "gpt-4")
output_parser = StrOutputParser()
chain = prompt | model | output_parser
res = chain.invoke({
"context": "\n".join(FinalGraphContext + FinalDetailContext),
"question": question
})
return res
把所有放在一起:
# Step 0, set embeddings/vectors to each nodes
# UpdateAllNodesEmbeddings()
# question = "what is the logo of SP's partner?"
# question = "What is the advantages about Ultipa?"
vectorDB = True
question = "How can SP build an architecture design for graph databases using Ultipa?"
if vectorDB == False:
# Step 1, find similar nodes by cosine similarity
display("FindSimilarNodes")
starts = FindSimilarNodes(question, 0.8)
else:
UpdateVectorDB()
# Step 1.1, find similar nodes by vectorDB chroma
display("Find Similar Nodes by VectorDB")
starts = FindSimilarNodesFromVectorDB(question=question)
# display(starts)
# Step 2, find relations entities
display("FindRelationsAndPaths")
PathContext, PathIDs = FindRelationsAndPaths(starts)
# display(PathContext)
# display(PathIDs)
# Step 3, ask LLM to filter the good infos
display("LLMFindRelatedGraphInfo")
nodeIDs = LLMFindRelatedGraphInfo(question=question, pathContext=PathContext, pathIDs= PathIDs)
# clear_output()
# display(nodeIDs)
# Step 4, find more details from the properties
display("FindDetailContext")
FinalDetailContext, medias = FindDetailContext(nodeIDs)
# Step 4, answer the question
display("LLMAnswer")
answer = LLMAnswer(question=question)
clear_output()
display("Question: %s" % question)
display("Answer:")
display(HTML("<style> .ultipa-answer {background: black; color: white; max-width: 600px; font-size: 14px; line-height:1.5;} img {max-width: 100px; } </style> <div class='ultipa-answer'>%s</div>" % answer))
#print("Related Path", PathContext)
#print("Detail Nodes", nodeIDs)
#print("Medias", [node.getID() for node in medias])
#print("Context", FinalGraphContext)
#print("Context", FinalDetailContext)
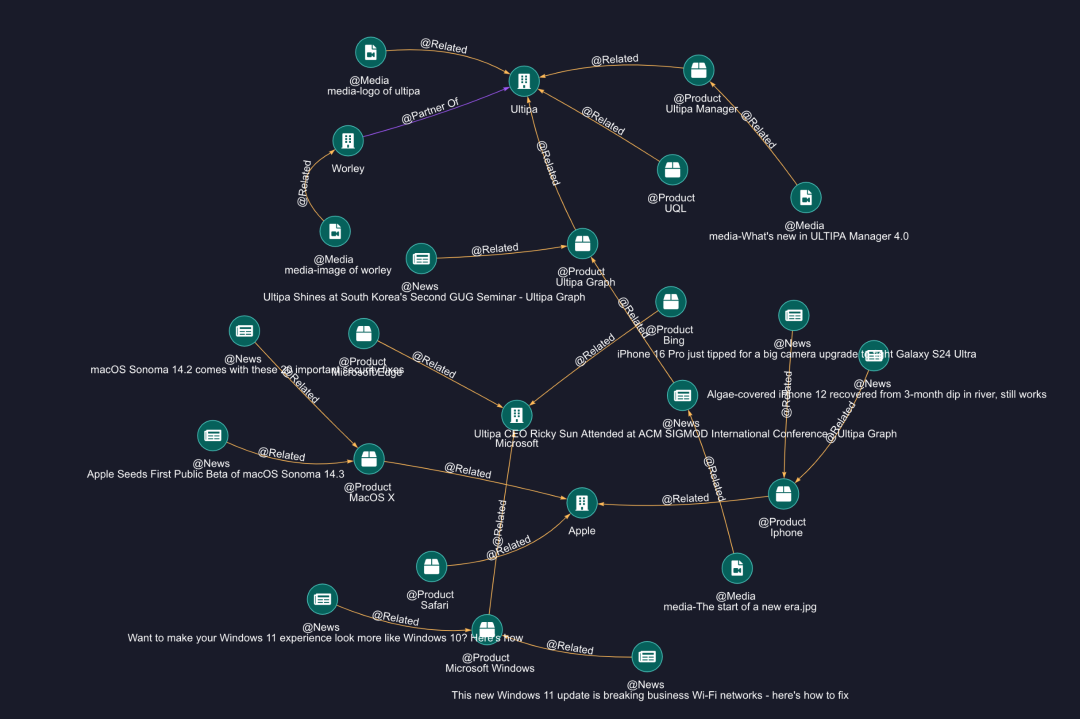
以下是一些测试结果的截图:
QA - 1
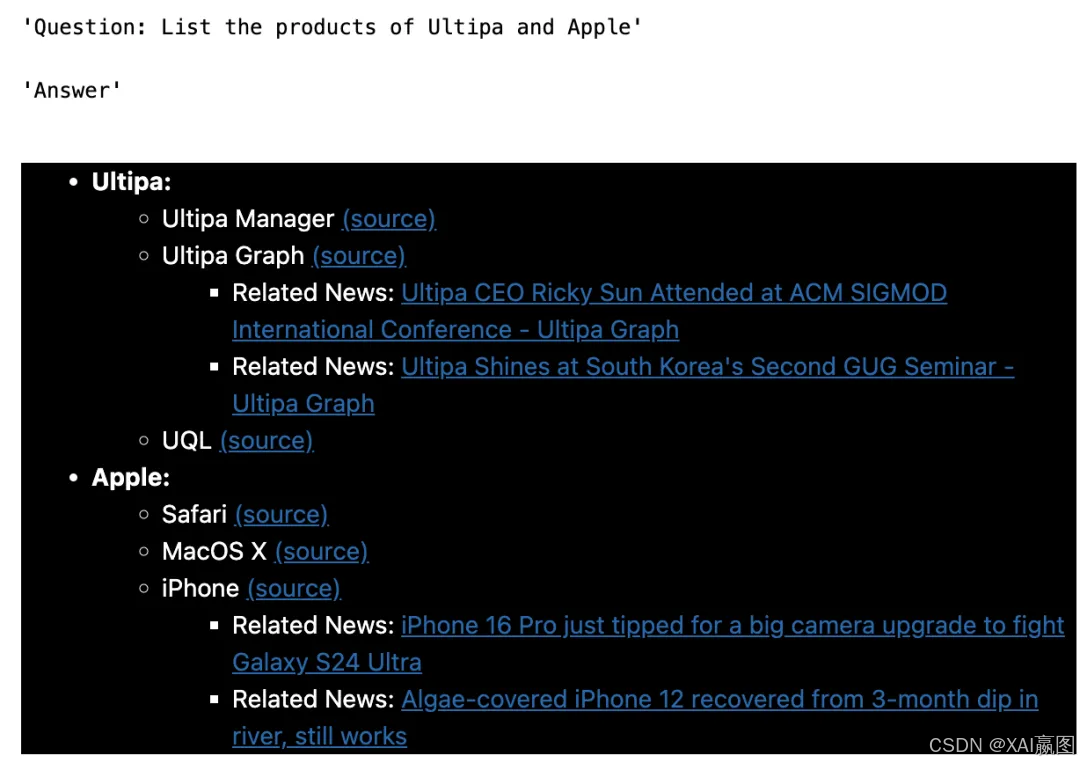
QA - 2

还有一件事——
嬴图-Graphbot 现在作为一个小部件发布,可在 嬴图-Manager 中使用。
(文/ Jason · Z)
· END ·






















 602
602

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








