英文是纯手打的!论文原文的summarizing and paraphrasing。可能会出现难以避免的拼写错误和语法错误,若有发现欢迎评论指正!文章偏向于笔记,谨慎食用
目录
2.3.1. YOLO Series Object Detectors
2.3.2. DETR Series Object Detectors
2.3.3. Hypergraph Learning Methods
2.4. Hypergraph Computation Empowered Semantic Collecting and Scattering Framework
2.5.3. Mixed Aggregation Network
2.5.4. Hypergraph-Based Cross-Level and Cross-Position Representation Network
2.5.5. Comparison and Analysis
2.6.2. Results and Discussions
2.6.3. Ablation Studies on Backbone
2.6.4. Ablation Studies on Neck
2.6.6. More Evaluation on Instance Segmentation Task
2.6.7. Visualization of High-Order Learning in Object Detection
1. 心得
(1)省流,清华佬的
(2)重要的图片补药放在补充材料里面啊我们看不到!!!

好想看wwwwww
2. 论文逐段精读
2.1. Abstract
①Limitations of traditional YOLO: neck can not efficiently aggregate cross-level feature or utilize the correlation of high order features
②Thus, they proposed Hypergraph Computation Empowered Semantic Collecting and Scattering (HGC-SCS)
2.2. Introduction
①Most of existing works fail to explore the high order relationship between features
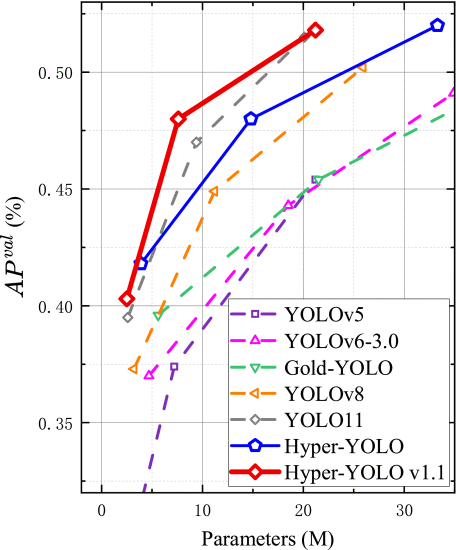
②Performance:
2.3. Related Work
2.3.1. YOLO Series Object Detectors
①List different versions of YOLO and mention that they proposed an improved version
2.3.2. DETR Series Object Detectors
①DERT, which based on Transformer, is faster and more accurate than YOLO. However, it has plenty of parameters and performs worse on small object detection
②Transformer is similar to graph(感觉有点小共识怎么回事)
③Hyper-graph is able to solve the problem of Transformer
2.3.3. Hypergraph Learning Methods
①超图捕获高阶关系然后超图在计算机视觉还没有充分探索哈哈哈哈哈哈哈哈
2.4. Hypergraph Computation Empowered Semantic Collecting and Scattering Framework
①For feature map , hyper graph will construct it to
. Then get the hyper feature map
.
and
will be fused to construct the hybrid feature map
②Hypergraph Computation Empowered Semantic Collecting and Scattering (HGC-SCS) framework:
where denotes the feature fusion function
2.5. Methods
2.5.1. Preliminaries
①Three scale outputs of the neck: , which are small-scale, medium-scale, and large-scale feature map
②5 stages in backbone: , the higher number denotes the semantic feature at higher level and deeper layer
2.5.2. Hyper-YOLO Overview
①感觉把上一节的内容又说了一下,说自己在那些地方提取特征
2.5.3. Mixed Aggregation Network
①The schematic of Mixed Aggregation Network (MANet):
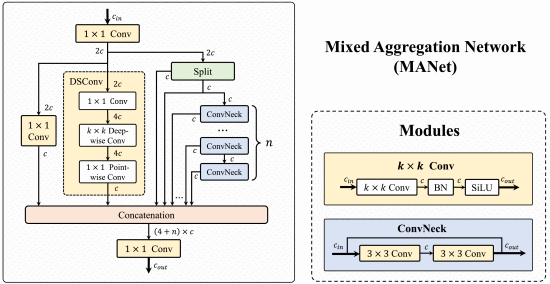
where in pictures denotes channel number
②The processes in MANet:
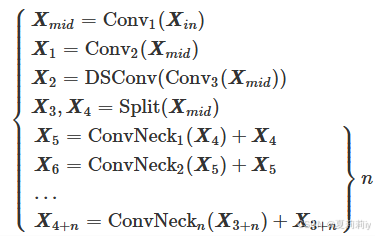
③The final output is fused by all of these feature:
prowess n.造诣;高超的技艺;非凡的技能
2.5.4. Hypergraph-Based Cross-Level and Cross-Position Representation Network
①Pipeline of proposed Hypergraph-Based Cross-Level and Cross-Position Representation Network (HyperC2Net):
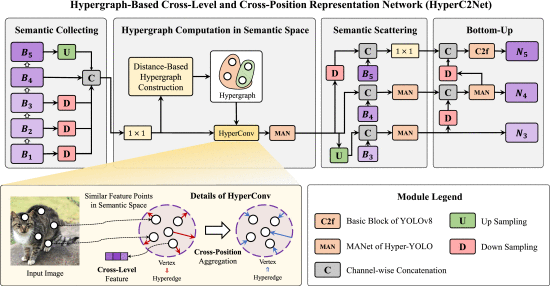
(1)Hypergraph Construction
①For hypergraph ,
denotes node set and
is hyperedge set
②How to build hypergraph:
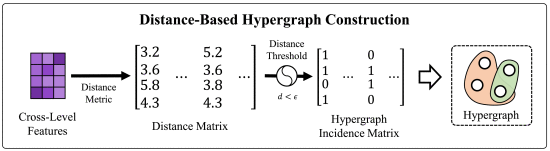
③Edges are screened by -ball from each feature point:
where
(2)Hypergraph Convolution
①Hypergraph conv: spatial-domain hypergraph convolution with residual connection:
where and
, where
is trainable parameter
②The fomular of hyper graph convolution:
where and
denote diagonal degree matrices of the vertices and hyperedges
(3)An Instance of HGC-SCS Framework
①Hypergraph-based cross-level and cross-position representation network (HyperC2Net):
where denotes concatenation,
denotes fusion function
2.5.5. Comparison and Analysis
①They change PANet/gather-distribute neck to HyperC2Net
2.6. Experiments
2.6.1. Experimental Setup
①Performance on Microsoft COCO dataset:
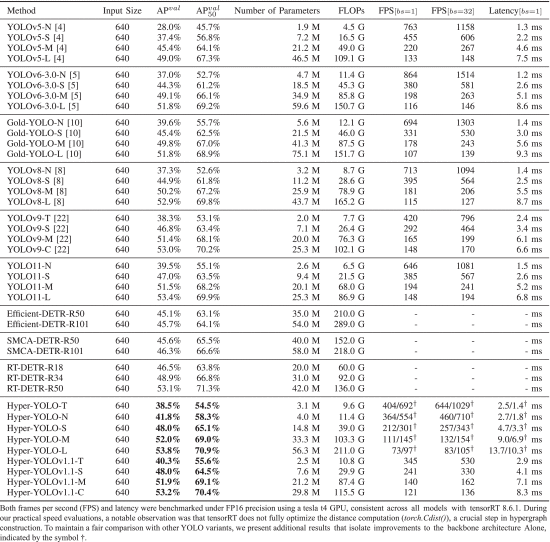
where different convolutional layers and feature dimension takes different model size, -T (the last C2F in Bottom-Up stage is changed to 1×1 Conv), -N, -S, -M, -L
②Fair comparison: no pretraining and self-distillation strategies for all methods
③Input of all these models: 640×640 pixels
2.6.2. Results and Discussions
①性能好,参数少,小参数模型上性能显著提升
2.6.3. Ablation Studies on Backbone
①Ablation studies on backbone:
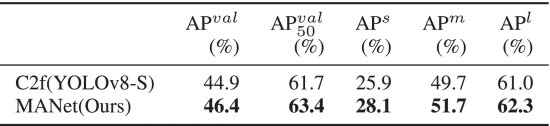
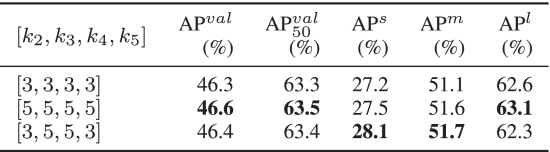
②Ablation studies on kernel size:
2.6.4. Ablation Studies on Neck
①Change hypergraph to traditional GCN:
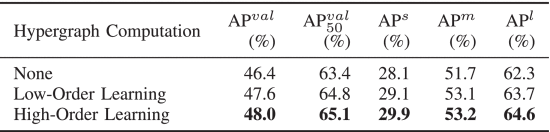
②Ablation on feature map:
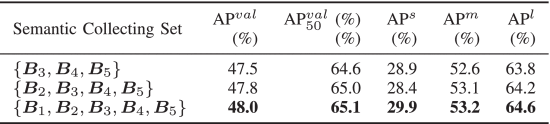
③Ablation on distance threshold:
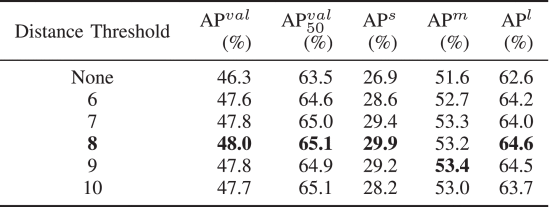
④Ablation on distance:
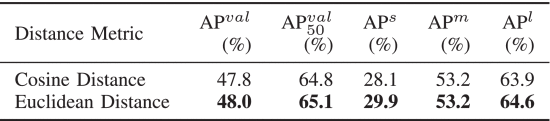
2.6.5. More Ablation Studies
①Model scale ablation:
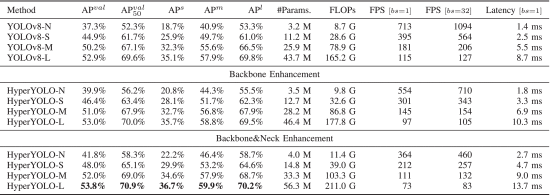
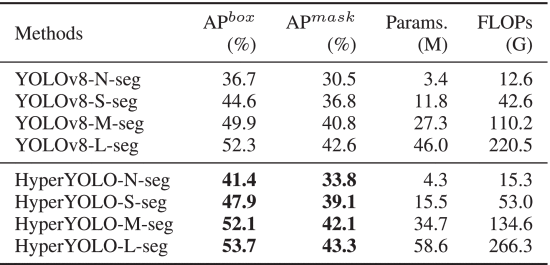
2.6.6. More Evaluation on Instance Segmentation Task
①Performance on instance segmentation:
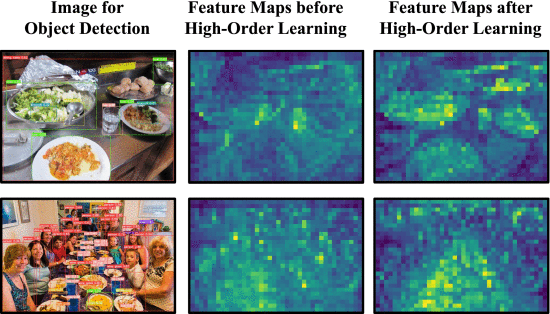
2.6.7. Visualization of High-Order Learning in Object Detection
①Attention changing visualization:
2.7. Conclusion
~






















 700
700

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








