暂无链接
玩串
【问题描述】
艾奇非常喜欢玩串。
艾奇觉得,字符串什么的非常优美。她会有事没事地给一个字符串数它有多
少个好的非空子序列。
一个好的子序列,满足它是SSSSSS的形式。
比如说,abcabcabcabcabcabc就是好的,而233323332333就不是好的。
众所周知,一个字符串的子序列有222的长度次方个,而好的字符串长度一定是偶数。
而一个字符串的权值,就是本质不同的好的子序列的个数。
两个子序列本质不同,当且仅当它们之中任意一个字符所处的位置不同。
(以上大家应该都知道吧)
一天,艾奇数着数累了,她想知道对于一个权值xxx,你能否找到这样一个字符串呢?
当然,本题可能有多个满足条件的解,你只需要输出任何一个即可。
当然我不可能让你随意输出对吧,不然这题还做个球。
任何情况下,字符串的长度不能超过100100100,字符集大小不能超过505050。
就这么简单。
【输入格式】
输入文件名为fkstring.infkstring.infkstring.in。
一行一个整数,表示你输出的串需要包含的权值。
【输出格式】
输出文件名为fkstring.outfkstring.outfkstring.out。
第一行一个数nnn,表示你输出字符串的长度。
第二行nnn个数,表示你输出的满足要求的串。
【输入样例 1】
详见fkstring1.infkstring1.infkstring1.in
【输出样例 1】
详见fkstring1.outfkstring1.outfkstring1.out
【数据范围】
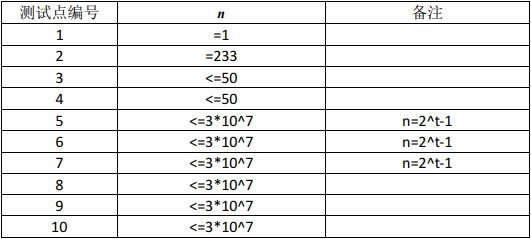
【备注】
下发的样例输出文件,只是供作参考,表示一种合法的字符串。
字符串的输出形式,你需要输出一行不超过100100100个数。每个数的大小不超过 505050。每个
数表示一个对应的字符。不同的数字代表不同的字符。
题解
我们考虑上空串,先让n+1n+1n+1,答案初始为空,价值为111,设整个串由两部分S1,S2S_1,S_2S1,S2构成,其中S1S_1S1为1,2,⋯ ,k1,2,\cdots,k1,2,⋯,k,我们可以由下面两个操作更改整个串的价值:
价值加一:S1,S2→S1,k+1,k+1,S2S_1,S_2 \to S_1,k+1,k+1,S_2S1,S2→S1,k+1,k+1,S2;
价值乘二:S1,S2→S1,k+1,S2,k+1S_1,S_2\to S_1,k+1,S_2,k+1S1,S2→S1,k+1,S2,k+1。
然后就做完了。。。
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
deque<int>dui;
int n,tot,bit[30],top,i;
void in(){scanf("%d",&n);}
void ac()
{
for(++n;n;n>>=1)bit[++top]=n&1;
for(dui.push_front(++tot),i=top-1;i;--i,dui.push_back(++tot))if(bit[i]&1)dui.push_front(++tot);
printf("%d\n",tot-1<<1);for(i=1;i<tot;++i)printf("%d ",i);for(;dui.size()>1;dui.pop_front())printf("%d ",dui.front());
}
int main(){in(),ac();}





 本文探讨了如何根据给定的权值构造满足特定条件的字符串。通过定义字符串的权值为本质不同的好子序列数量,文章提出了一种有效的算法来生成这样的字符串,确保其长度不超过100,字符集大小不超过50。通过对空串进行操作,利用增加和翻倍两种策略,实现了字符串价值的调整。
本文探讨了如何根据给定的权值构造满足特定条件的字符串。通过定义字符串的权值为本质不同的好子序列数量,文章提出了一种有效的算法来生成这样的字符串,确保其长度不超过100,字符集大小不超过50。通过对空串进行操作,利用增加和翻倍两种策略,实现了字符串价值的调整。

















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










