本篇的启发仍旧是来自下面这篇文章的学习呢!
零基础入门深度学习(3) - 神经网络和反向传播算法_零基础入门深度学习(三)-优快云博客
传送门:小白学习machine learning的第一天-优快云博客
小白学习machine learning的第二天-优快云博客
小白学习machine learning的第三天-优快云博客
小白学习machine learning的第四天-优快云博客
小白学习machine learning的第五天-优快云博客
小白学习machine learning的第六天-优快云博客
我们首先来认识一下神经网络的计算方式:
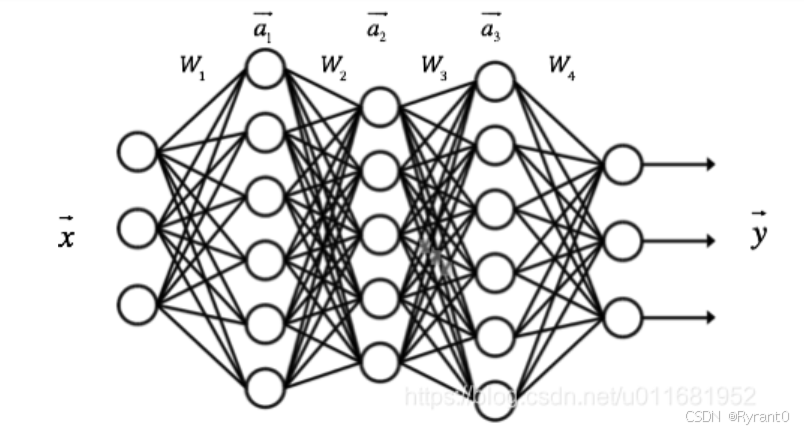
(1)这是神经网络的示意图:
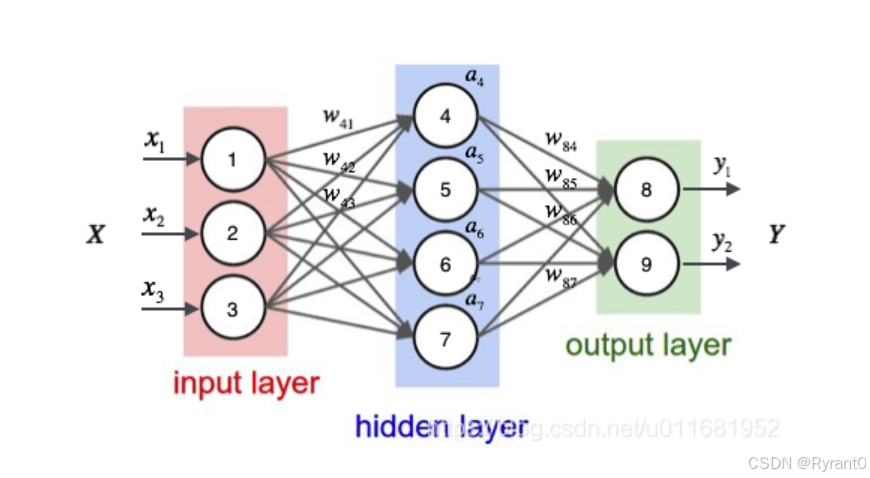
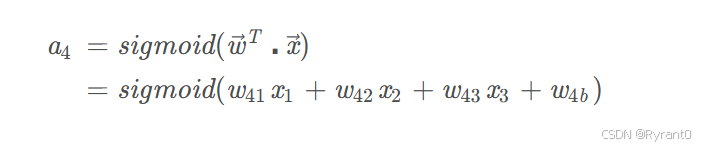
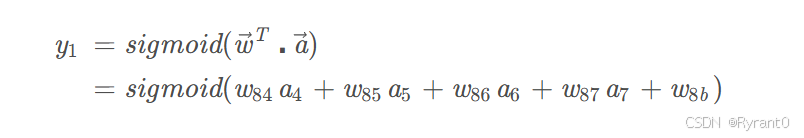
其实,原理就是:
1、每个神经层的所有输出值(eg.a1\a2\a3)(一般不这么写,一般写成多维向量乘上向量)
2、都乘上一个bias(偏差或称权值)后
3、再输给下一个层(eg.4号)
4、然后,再由4号的神经元计算给出输出值:a4 啦!!!
那么,借用原稿的话来说,就是我们换种逼格更高的写法——矩阵:
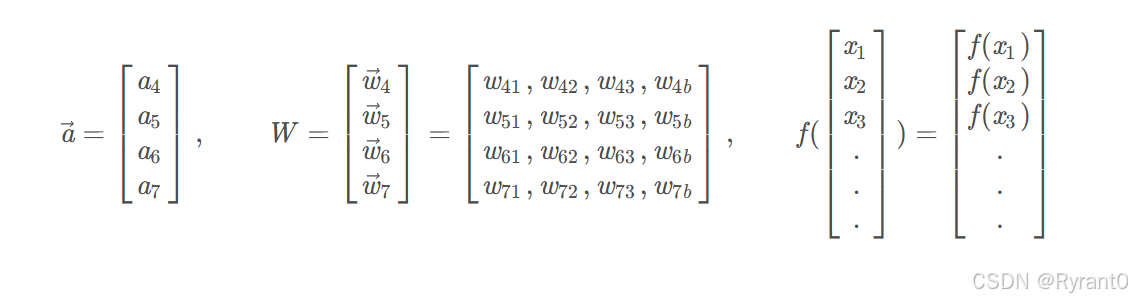
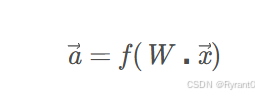
就有如下的计算向量a的式子出来啦!
———————————————————————————————————————————
我们再来个更复杂一点点的神经网络:
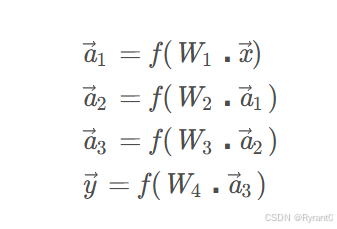
那么,计算结果的表达就是这样啦!其实大差不差的呢。
(2)下面是关于反向传播算法的学习啦
照用上图,我们用4和8两个节点来进行学习,首先需要掌握误差项δ i 的计算公式:
①对于隐藏层节点:
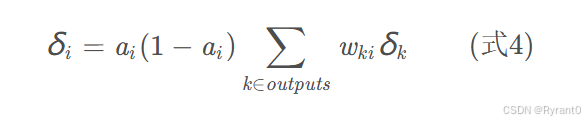
我们来详细看看,ai是节点的输出值,wki是节点i到它的下一层节点k的连接的权重(注意有2个节点可变),δ k 是节点的下一层节点k的误差项(因为有下一个节点决定的变量,所以才是反向传播)。
举个栗子:
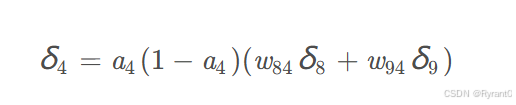
可以看到4与8和9都相连,所以8和9都要加。
②对于输出层节点(别忘了咋们是反向传播哦,所以要从屁股开始耶):
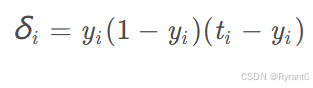
知道了误差项,那么就可以去更新权重wi了啦!
我们来看看:
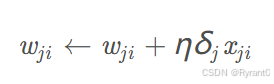
wji是节点i到节点j的权重,η 是学习速率常数,δ j 是节点j的误差项,xji是节点i传递给节点j的输入。
注意的是:原文说到偏置项xji的值一直看作是1。误差项δ j 在有的文献中也叫做敏感度(sensitivity)。它实际上是网络的损失函数Ed对神经元加权输入netj的偏导数。
但是,根据激活函数是sigmoid函数、平方和误差、全连接网络、随机梯度下降优化算法才是上面的公式,而其他的激活函数则需要另外用数学公式链式求导法则得到(♂死我了这数学推导……)
*详见原文有推导过程哦!
(3)接下来,我们来看看原文的全连接神经网络是怎么实现的:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import random
from numpy import *
def sigmoid(inX):
return 1.0 / (1 + exp(-inX))
class Node(object):
def __init__(self, layer_index, node_index):
self.layer_index = layer_index
self.node_index = node_index
self.downstream = []
self.upstream = []
self.output = 0
self.delta = 0
def set_output(self, output):
self.output = output
def append_downstream_connection(self, conn):
self.downstream.append(conn)
def append_upstream_connection(self, conn):
self.upstream.append(conn)
def calc_output(self):
output = reduce(lambda ret, conn: ret + conn.upstream_node.output * conn.weight, self.upstream, 0)
self.output = sigmoid(output)
def calc_hidden_layer_delta(self):
downstream_delta = reduce(
lambda ret, conn: ret + conn.downstream_node.delta * conn.weight,
self.downstream, 0.0)
self.delta = self.output * (1 - self.output) * downstream_delta
def calc_output_layer_delta(self, label):
self.delta = self.output * (1 - self.output) * (label - self.output)
def __str__(self):
node_str = '%u-%u: output: %f delta: %f' % (self.layer_index, self.node_index, self.output, self.delta)
downstream_str = reduce(lambda ret, conn: ret + '\n\t' + str(conn), self.downstream, '')
upstream_str = reduce(lambda ret, conn: ret + '\n\t' + str(conn), self.upstream, '')
return node_str + '\n\tdownstream:' + downstream_str + '\n\tupstream:' + upstream_str
class ConstNode(object):
def __init__(self, layer_index, node_index):
self.layer_index = layer_index
self.node_index = node_index
self.downstream = []
self.output = 1
def append_downstream_connection(self, conn):
self.downstream.append(conn)
def calc_hidden_layer_delta(self):
downstream_delta = reduce(
lambda ret, conn: ret + conn.downstream_node.delta * conn.weight,
self.downstream, 0.0)
self.delta = self.output * (1 - self.output) * downstream_delta
def __str__(self):
node_str = '%u-%u: output: 1' % (self.layer_index, self.node_index)
downstream_str = reduce(lambda ret, conn: ret + '\n\t' + str(conn), self.downstream, '')
return node_str + '\n\tdownstream:' + downstream_str
class Layer(object):
def __init__(self, layer_index, node_count):
self.layer_index = layer_index
self.nodes = []
for i in range(node_count):
self.nodes.append(Node(layer_index, i))
self.nodes.append(ConstNode(layer_index, node_count))
def set_output(self, data):
for i in range(len(data)):
self.nodes[i].set_output(data[i])
def calc_output(self):
for node in self.nodes[:-1]:
node.calc_output()
def dump(self):
for node in self.nodes:
print node
class Connection(object):
def __init__(self, upstream_node, downstream_node):
self.upstream_node = upstream_node
self.downstream_node = downstream_node
self.weight = random.uniform(-0.1, 0.1)
self.gradient = 0.0
def calc_gradient(self):
self.gradient = self.downstream_node.delta * self.upstream_node.output
def update_weight(self, rate):
self.calc_gradient()
self.weight += rate * self.gradient
def get_gradient(self):
return self.gradient
def __str__(self):
return '(%u-%u) -> (%u-%u) = %f' % (
self.upstream_node.layer_index,
self.upstream_node.node_index,
self.downstream_node.layer_index,
self.downstream_node.node_index,
self.weight)
class Connections(object):
def __init__(self):
self.connections = []
def add_connection(self, connection):
self.connections.append(connection)
def dump(self):
for conn in self.connections:
print conn
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, layers):
self.connections = Connections()
self.layers = []
layer_count = len(layers)
node_count = 0;
for i in range(layer_count):
self.layers.append(Layer(i, layers[i]))
for layer in range(layer_count - 1):
connections = [Connection(upstream_node, downstream_node)
for upstream_node in self.layers[layer].nodes
for downstream_node in self.layers[layer + 1].nodes[:-1]]
for conn in connections:
self.connections.add_connection(conn)
conn.downstream_node.append_upstream_connection(conn)
conn.upstream_node.append_downstream_connection(conn)
def train(self, labels, data_set, rate, epoch):
for i in range(epoch):
for d in range(len(data_set)):
self.train_one_sample(labels[d], data_set[d], rate)
# print 'sample %d training finished' % d
def train_one_sample(self, label, sample, rate):
self.predict(sample)
self.calc_delta(label)
self.update_weight(rate)
def calc_delta(self, label):
output_nodes = self.layers[-1].nodes
for i in range(len(label)):
output_nodes[i].calc_output_layer_delta(label[i])
for layer in self.layers[-2::-1]:
for node in layer.nodes:
node.calc_hidden_layer_delta()
def update_weight(self, rate):
for layer in self.layers[:-1]:
for node in layer.nodes:
for conn in node.downstream:
conn.update_weight(rate)
def calc_gradient(self):
for layer in self.layers[:-1]:
for node in layer.nodes:
for conn in node.downstream:
conn.calc_gradient()
def get_gradient(self, label, sample):
self.predict(sample)
self.calc_delta(label)
self.calc_gradient()
def predict(self, sample):
self.layers[0].set_output(sample)
for i in range(1, len(self.layers)):
self.layers[i].calc_output()
return map(lambda node: node.output, self.layers[-1].nodes[:-1])
def dump(self):
for layer in self.layers:
layer.dump()
class Normalizer(object):
def __init__(self):
self.mask = [
0x1, 0x2, 0x4, 0x8, 0x10, 0x20, 0x40, 0x80
]
def norm(self, number):
return map(lambda m: 0.9 if number & m else 0.1, self.mask)
def denorm(self, vec):
binary = map(lambda i: 1 if i > 0.5 else 0, vec)
for i in range(len(self.mask)):
binary[i] = binary[i] * self.mask[i]
return reduce(lambda x,y: x + y, binary)
def mean_square_error(vec1, vec2):
return 0.5 * reduce(lambda a, b: a + b,
map(lambda v: (v[0] - v[1]) * (v[0] - v[1]),
zip(vec1, vec2)
)
)
def gradient_check(network, sample_feature, sample_label):
'''
梯度检查
network: 神经网络对象
sample_feature: 样本的特征
sample_label: 样本的标签
'''
# 计算网络误差
network_error = lambda vec1, vec2: \
0.5 * reduce(lambda a, b: a + b,
map(lambda v: (v[0] - v[1]) * (v[0] - v[1]),
zip(vec1, vec2)))
# 获取网络在当前样本下每个连接的梯度
network.get_gradient(sample_feature, sample_label)
# 对每个权重做梯度检查
for conn in network.connections.connections:
# 获取指定连接的梯度
actual_gradient = conn.get_gradient()
# 增加一个很小的值,计算网络的误差
epsilon = 0.0001
conn.weight += epsilon
error1 = network_error(network.predict(sample_feature), sample_label)
# 减去一个很小的值,计算网络的误差
conn.weight -= 2 * epsilon # 刚才加过了一次,因此这里需要减去2倍
error2 = network_error(network.predict(sample_feature), sample_label)
# 根据式6计算期望的梯度值
expected_gradient = (error2 - error1) / (2 * epsilon)
# 打印
print 'expected gradient: \t%f\nactual gradient: \t%f' % (
expected_gradient, actual_gradient)
def train_data_set():
normalizer = Normalizer()
data_set = []
labels = []
for i in range(0, 256, 8):
n = normalizer.norm(int(random.uniform(0, 256)))
data_set.append(n)
labels.append(n)
return labels, data_set
def train(network):
labels, data_set = train_data_set()
network.train(labels, data_set, 0.3, 50)
def test(network, data):
normalizer = Normalizer()
norm_data = normalizer.norm(data)
predict_data = network.predict(norm_data)
print '\ttestdata(%u)\tpredict(%u)' % (
data, normalizer.denorm(predict_data))
def correct_ratio(network):
normalizer = Normalizer()
correct = 0.0;
for i in range(256):
if normalizer.denorm(network.predict(normalizer.norm(i))) == i:
correct += 1.0
print 'correct_ratio: %.2f%%' % (correct / 256 * 100)
def gradient_check_test():
net = Network([2, 2, 2])
sample_feature = [0.9, 0.1]
sample_label = [0.9, 0.1]
gradient_check(net, sample_feature, sample_label)
if __name__ == '__main__':
net = Network([8, 3, 8])
train(net)
net.dump()
correct_ratio(net)
(4)那么,会写还不够,还得学会查出错误的地方,梯度检查是一个好办法:
①相当于检查每一个权重了:
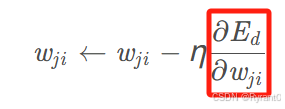
这里检查的是红框里的一定要合适正确!!!
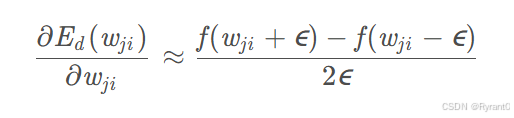
根据原文的推导,我们得到这个式子。
把他右边计算出来跟神经网络代码中计算出来的梯度值进行比较,应该有4位数字相同。
②另外,我们可以检查参数wji的梯度是否正确:
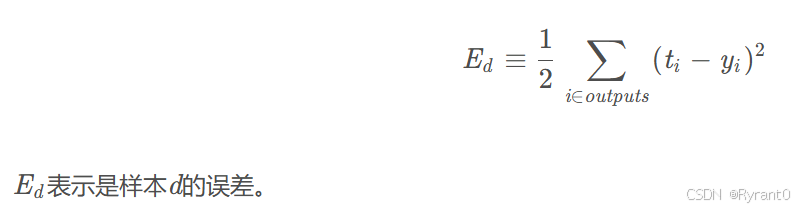
下面引用原文:

(5)那么,用识别手写字母来开启第一个神经网络项目,首先要学习怎么用“好手艺”来设置超参数:
首先来看看“经验学说”怎么看:

代码实现详见原文啦!
(6)从面向对象编程到向量化编程!
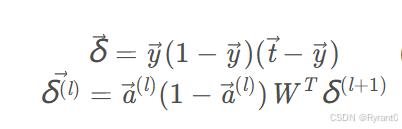
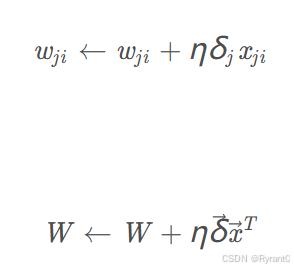
# 全连接层实现类
class FullConnectedLayer(object):
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size,
activator):
'''
构造函数
input_size: 本层输入向量的维度
output_size: 本层输出向量的维度
activator: 激活函数
'''
self.input_size = input_size
self.output_size = output_size
self.activator = activator
# 权重数组W
self.W = np.random.uniform(-0.1, 0.1,
(output_size, input_size))
# 偏置项b
self.b = np.zeros((output_size, 1))
# 输出向量
self.output = np.zeros((output_size, 1))
def forward(self, input_array):
'''
前向计算
input_array: 输入向量,维度必须等于input_size
'''
# 式2
self.input = input_array
self.output = self.activator.forward(
np.dot(self.W, input_array) + self.b)
def backward(self, delta_array):
'''
反向计算W和b的梯度
delta_array: 从上一层传递过来的误差项
'''
# 式8
self.delta = self.activator.backward(self.input) * np.dot(
self.W.T, delta_array)
self.W_grad = np.dot(delta_array, self.input.T)
self.b_grad = delta_array
def update(self, learning_rate):
'''
使用梯度下降算法更新权重
'''
self.W += learning_rate * self.W_grad
self.b += learning_rate * self.b_grad
这个类一举取代了原先的Layer、Node、Connection等类,不但代码更加容易理解,而且运行速度也快了几百倍。
现在,我们对Network类稍作修改,使之用到FullConnectedLayer:
_____________________________________________________________________________
# Sigmoid激活函数类
class SigmoidActivator(object):
def forward(self, weighted_input):
return 1.0 / (1.0 + np.exp(-weighted_input))
def backward(self, output):
return output * (1 - output)
# 神经网络类
class Network(object):
def __init__(self, layers):
'''
构造函数
'''
self.layers = []
for i in range(len(layers) - 1):
self.layers.append(
FullConnectedLayer(
layers[i], layers[i+1],
SigmoidActivator()
)
)
def predict(self, sample):
'''
使用神经网络实现预测
sample: 输入样本
'''
output = sample
for layer in self.layers:
layer.forward(output)
output = layer.output
return output
def train(self, labels, data_set, rate, epoch):
'''
训练函数
labels: 样本标签
data_set: 输入样本
rate: 学习速率
epoch: 训练轮数
'''
for i in range(epoch):
for d in range(len(data_set)):
self.train_one_sample(labels[d],
data_set[d], rate)
def train_one_sample(self, label, sample, rate):
self.predict(sample)
self.calc_gradient(label)
self.update_weight(rate)
def calc_gradient(self, label):
delta = self.layers[-1].activator.backward(
self.layers[-1].output
) * (label - self.layers[-1].output)
for layer in self.layers[::-1]:
layer.backward(delta)
delta = layer.delta
return delta
def update_weight(self, rate):
for layer in self.layers:
layer.update(rate)
到这里就结束啦!!!请等待下一次更新哦哈哈




















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








