✅作者简介:热爱科研的Matlab仿真开发者,擅长数据处理、建模仿真、程序设计、完整代码获取、论文复现及科研仿真。
🍎 往期回顾关注个人主页:Matlab科研工作室
🍊个人信条:格物致知,完整Matlab代码及仿真咨询内容私信。
🔥 内容介绍
一、ELM 分类的核心特性与传统训练局限
极限学习机(ELM)作为单隐层前馈神经网络的高效变种,凭借 “输入 - 隐层参数随机初始化、输出层权重解析求解” 的特性,在数据分类领域(如故障诊断、图像识别、风险评估)展现出快速训练的优势。其分类核心是通过隐层将输入特征映射到高维空间,再通过输出层实现对多类别标签的线性划分。然而,传统 ELM 分类模型在复杂数据场景下存在明显局限,难以满足高精度、高鲁棒性的分类需求。







⛳️ 运行结果
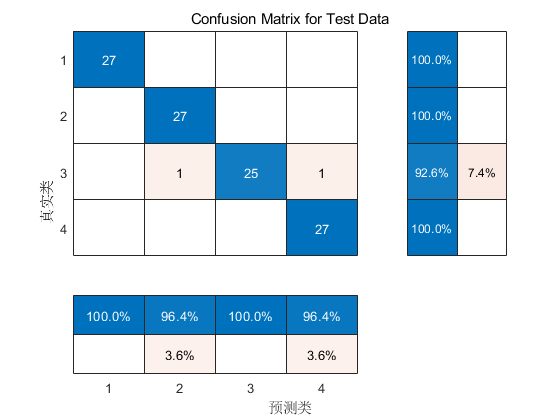
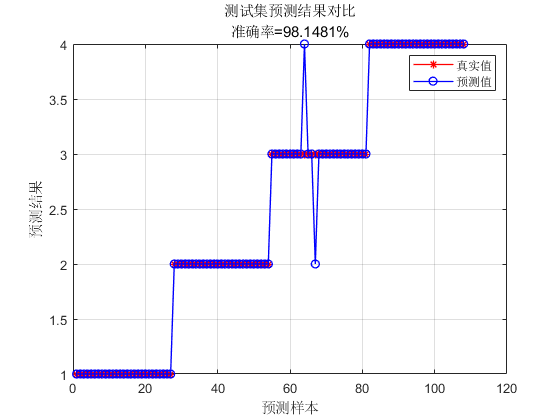
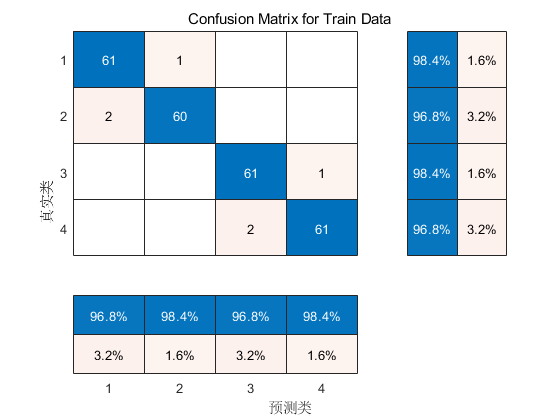
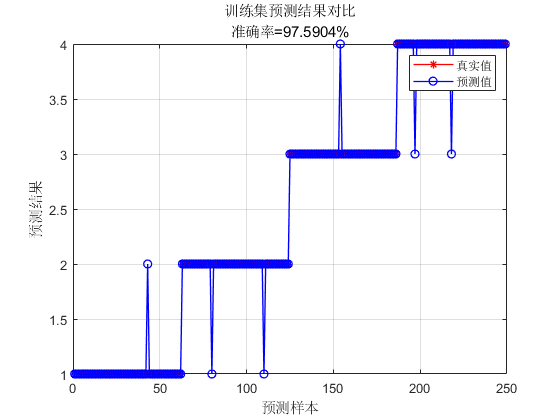
📣 部分代码
function model = changelssvm(model,option, value)
% Change a field of the object oriented representation of the LS-SVM
%
%
% The different options of the fields are given in following table:
%
% 1. General options representing the kind of model:
%
% type: 'classifier' ,'function estimation'
% implementation: 'CMEX' ,'CFILE' ,'MATLAB'
% status: Status of this model ('trained' or 'changed' )
% alpha: Support values of the trained LS-SVM model
% b: Bias term of the trained LS-SVM model
% duration: Number of seconds the training lasts
% latent: Returning latent variables ('no' ,'yes' )
% x_delays: Number of delays of eXogeneous variables (by default 0 )
% y_delays: Number of delays of responses (by default 0 )
% steps: Number of steps to predict (by default 1 )
% gam: Regularisation parameter
% kernel_type: Kernel function
% kernel_pars: Extra parameters of the kernel function
%
%
% 2. Fields used to specify the used training data:
%
% x_dim: Dimension of input space
% y_dim: Dimension of responses
% nb_data: Number of training data
% xtrain: (preprocessed) inputs of training data
% ytrain: (preprocessed,coded) outputs of training data
% selector: Indexes of training data effectively used during training
%
%
% 3. Options used in the Conjugate Gradient (CG) algorithm:
%
% cga_max_itr: Maximum number of iterations in CG
% cga_eps: Stopcriterium of CG, largest allowed error
% cga_fi_bound: Stopcriterium of CG, smallest allowed improvement
% cga_show: Show the results of the CG algorithm (1 or 0)
% cga_startvalues: Starting values of the CG algorithm
%
%
% 4. Fields with the information for pre- and post-processing (only given if appropriate):
%
% preprocess: 'preprocess' or 'original'
% schemed: Status of the preprocessing
% ('coded' ,'original' or 'schemed' )
% pre_xscheme: Scheme used for preprocessing the input data
% pre_yscheme: Scheme used for preprocessing the output data
% pre_xmean: Mean of the input data
% pre_xstd: Standard deviation of the input data
% pre_ymean: Mean of the responses
% pre_ystd: Standard deviation of the reponses
%
%
% 5. The specifications of the used encoding (only given if appropriate):
%
% code: Status of the coding
% ('original' ,'changed' or 'encoded')
% codetype: Used function for constructing the encoding
% for multiclass classification (by default 'none')
% codetype_args: Arguments of the codetype function
% codedist_fct: Function used to calculate to which class a
% coded result belongs
% codedist_args: Arguments of the codedist function
% codebook2: Codebook of the new coding
% codebook1: Codebook of the original coding
%
% Full syntax
%
% >> model = changelssvm(model, field, value)
%
% Outputs
% model(*) : Obtained object oriented representation of the LS-SVM model
% Inputs
% model : Original object oriented representation of the LS-SVM model
% field : Field of the model one wants to change (e.g. 'preprocess')
% value : New value of the field of the model one wants to change
%
% See also:
% trainlssvm, initlssvm, simlssvm, plotlssvm.
% Copyright (c) 2010, KULeuven-ESAT-SCD, License & help @ http://www.esat.kuleuven.ac.be/sista/lssvmlab
%
% alias sigma^2
%
if (strcmpi(option,'sig2')) option = 'kernel_pars'; end
%
% selector -> nb_data
% nb_data -> selector
%
if strcmp(option,'selector'),
model.nb_data = length(value);
end
if strcmp(option,'nb_data'),
model.selector = 1:value;
end
%
% xtrain
%
if strcmp(option,'xtrain'),
[nb,model.x_dim] = size(value);
model.nb_data = nb;%min(nb,model.nb_data);
model.selector = 1:model.nb_data;
if length(model.gam)>model.y_dim & length(model.gam)~=size(value,1),
warning('Discarting different gamma''s...');
model.gam = max(model.gam);
end
eval('value=prelssvm(model,value);',...
'warning(''new trainings inputdata not comform with used preprocessing'');');
end
%
% ytrain
%
if strcmp(option,'ytrain'),
if size(value,2)~=size(model.ytrain,2),
model.y_dim = size(value,2);
end
eval('value = codelssvm(model,[],value);',...
'warning(''new trainings outputdata not comform with used encoding;'');');
eval('[ff,value] = prelssvm(model,[],value);',...
'warning(''new trainings outputdata not comform with used preprocessing;'');');
[nb,model.y_dim] = size(value);
model.nb_data = min(nb,model.nb_data);
model.selector = 1:model.nb_data;
end
%
% switch between preprocessing - original data
% model.prestatus = {'changed','ok'}
%
if (strcmpi(option,'preprocess')) & model.preprocess(1)~=value(1),
model.prestatus = 'changed';
end
%
% change coding
%
if strcmpi(option,'codetype') | strcmpi(option,'codebook2') | ...
strcmpi(option, 'codeargs') | strcmpi(option, 'codedistfct'),
model.code = 'changed';
elseif strcmpi(option,'codebook1'),
warning('change original format of the classifier; the toolbox will be unable to return results in the original format');
end
%
% final change
%
eval(['old_value = model.' lower(option) ';'],'old_value=[];');
eval(['model.' lower(option) '=value;']);
if (isempty(value) | isempty(old_value)),
different = 1;
else
eval('different = any(old_value~=value);','different=1;');
end
if different & ~strcmpi(option,'implementation'),
model.status = 'changed';
end
🔗 参考文献
[1]李杰,李蓝青,曹帅,等.基于改进灰狼算法优化和极限学习机的电网电力负荷预测[J].微型电脑应用, 2024, 40(11):75-77.DOI:10.3969/j.issn.1007-757X.2024.11.018.
🎈 部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除
👇 关注我领取海量matlab电子书和数学建模资料
🏆团队擅长辅导定制多种科研领域MATLAB仿真,助力科研梦:
🌟 各类智能优化算法改进及应用
生产调度、经济调度、装配线调度、充电优化、车间调度、发车优化、水库调度、三维装箱、物流选址、货位优化、公交排班优化、充电桩布局优化、车间布局优化、集装箱船配载优化、水泵组合优化、解医疗资源分配优化、设施布局优化、可视域基站和无人机选址优化、背包问题、 风电场布局、时隙分配优化、 最佳分布式发电单元分配、多阶段管道维修、 工厂-中心-需求点三级选址问题、 应急生活物质配送中心选址、 基站选址、 道路灯柱布置、 枢纽节点部署、 输电线路台风监测装置、 集装箱调度、 机组优化、 投资优化组合、云服务器组合优化、 天线线性阵列分布优化、CVRP问题、VRPPD问题、多中心VRP问题、多层网络的VRP问题、多中心多车型的VRP问题、 动态VRP问题、双层车辆路径规划(2E-VRP)、充电车辆路径规划(EVRP)、油电混合车辆路径规划、混合流水车间问题、 订单拆分调度问题、 公交车的调度排班优化问题、航班摆渡车辆调度问题、选址路径规划问题、港口调度、港口岸桥调度、停机位分配、机场航班调度、泄漏源定位、冷链、时间窗、多车场等、选址优化、港口岸桥调度优化、交通阻抗、重分配、停机位分配、机场航班调度、通信上传下载分配优化
🌟 机器学习和深度学习时序、回归、分类、聚类和降维
2.1 bp时序、回归预测和分类
2.2 ENS声神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.3 SVM/CNN-SVM/LSSVM/RVM支持向量机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.4 CNN|TCN|GCN卷积神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.5 ELM/KELM/RELM/DELM极限学习机系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.6 GRU/Bi-GRU/CNN-GRU/CNN-BiGRU门控神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.7 ELMAN递归神经网络时序、回归\预测和分类
2.8 LSTM/BiLSTM/CNN-LSTM/CNN-BiLSTM/长短记忆神经网络系列时序、回归预测和分类
2.9 RBF径向基神经网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.10 DBN深度置信网络时序、回归预测和分类
2.11 FNN模糊神经网络时序、回归预测
2.12 RF随机森林时序、回归预测和分类
2.13 BLS宽度学习时序、回归预测和分类
2.14 PNN脉冲神经网络分类
2.15 模糊小波神经网络预测和分类
2.16 时序、回归预测和分类
2.17 时序、回归预测预测和分类
2.18 XGBOOST集成学习时序、回归预测预测和分类
2.19 Transform各类组合时序、回归预测预测和分类
方向涵盖风电预测、光伏预测、电池寿命预测、辐射源识别、交通流预测、负荷预测、股价预测、PM2.5浓度预测、电池健康状态预测、用电量预测、水体光学参数反演、NLOS信号识别、地铁停车精准预测、变压器故障诊断
🌟图像处理方面
图像识别、图像分割、图像检测、图像隐藏、图像配准、图像拼接、图像融合、图像增强、图像压缩感知
🌟 路径规划方面
旅行商问题(TSP)、车辆路径问题(VRP、MVRP、CVRP、VRPTW等)、无人机三维路径规划、无人机协同、无人机编队、机器人路径规划、栅格地图路径规划、多式联运运输问题、 充电车辆路径规划(EVRP)、 双层车辆路径规划(2E-VRP)、 油电混合车辆路径规划、 船舶航迹规划、 全路径规划规划、 仓储巡逻、公交车时间调度、水库调度优化、多式联运优化
🌟 无人机应用方面
无人机路径规划、无人机控制、无人机编队、无人机协同、无人机任务分配、无人机安全通信轨迹在线优化、车辆协同无人机路径规划、
🌟 通信方面
传感器部署优化、通信协议优化、路由优化、目标定位优化、Dv-Hop定位优化、Leach协议优化、WSN覆盖优化、组播优化、RSSI定位优化、水声通信、通信上传下载分配
🌟 信号处理方面
信号识别、信号加密、信号去噪、信号增强、雷达信号处理、信号水印嵌入提取、肌电信号、脑电信号、信号配时优化、心电信号、DOA估计、编码译码、变分模态分解、管道泄漏、滤波器、数字信号处理+传输+分析+去噪、数字信号调制、误码率、信号估计、DTMF、信号检测
🌟电力系统方面
微电网优化、无功优化、配电网重构、储能配置、有序充电、MPPT优化、家庭用电、电/冷/热负荷预测、电力设备故障诊断、电池管理系统(BMS)SOC/SOH估算(粒子滤波/卡尔曼滤波)、 多目标优化在电力系统调度中的应用、光伏MPPT控制算法改进(扰动观察法/电导增量法)、电动汽车充放电优化、微电网日前日内优化、储能优化、家庭用电优化、供应链优化
🌟 元胞自动机方面
交通流 人群疏散 病毒扩散 晶体生长 金属腐蚀
🌟 雷达方面
卡尔曼滤波跟踪、航迹关联、航迹融合、SOC估计、阵列优化、NLOS识别
🌟 车间调度
零等待流水车间调度问题NWFSP 、 置换流水车间调度问题PFSP、 混合流水车间调度问题HFSP 、零空闲流水车间调度问题NIFSP、分布式置换流水车间调度问题 DPFSP、阻塞流水车间调度问题BFSP
👇




















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








