💥💥💞💞欢迎来到本博客❤️❤️💥💥
🏆博主优势:🌞🌞🌞博客内容尽量做到思维缜密,逻辑清晰,为了方便读者。
⛳️座右铭:行百里者,半于九十。
📋📋📋本文目录如下:🎁🎁🎁
目录
💥1 概述
一、引言:
射频(RF)线圈在成像技术中起着至关重要的作用。随着科技的不断发展,对成像质量的要求日益提高,基于成像目标进行 RF 线圈优化成为关键课题。
二、RF 线圈在成像中的重要性: RF 线圈负责发射射频信号以激发成像目标,并接收来自目标的反馈信号。其性能直接影响着成像的分辨率、信噪比和对比度等关键指标。不同的成像目标,如人体组织、工业材料等,对 RF 线圈的要求各不相同。
三、基于成像目标的优化需求: 1. 对于人体成像,需要考虑人体不同部位的形状、大小和组织特性,优化 RF 线圈以实现更均匀的信号激发和接收,减少伪影,提高图像质量,同时确保安全性和舒适性。 2. 在工业成像中,针对不同的材料和检测目标,RF 线圈需进行优化以适应复杂的几何形状和材料特性,提高检测的准确性和可靠性。
四、优化方法: 1. 线圈设计优化:通过调整线圈的几何形状、尺寸、匝数等参数,以实现更好的磁场分布和信号耦合。例如,采用多通道线圈设计、异形线圈等。 2. 材料选择与优化:选择合适的导电材料和绝缘材料,以提高线圈的性能和耐用性。同时,考虑材料的电磁特性对成像的影响。 3. 数值模拟与优化算法:利用有限元分析等数值模拟方法,对不同设计方案进行模拟和评估。结合优化算法,如遗传算法、粒子群优化等,自动搜索最优的线圈设计参数。
五、应用与展望:基于成像目标的 RF 线圈优化在医学成像、工业检测、材料科学等领域具有广泛的应用前景。未来,随着技术的不断进步,RF 线圈优化将更加智能化、精准化,为成像技术的发展提供更强大的支持。
📚2 运行结果
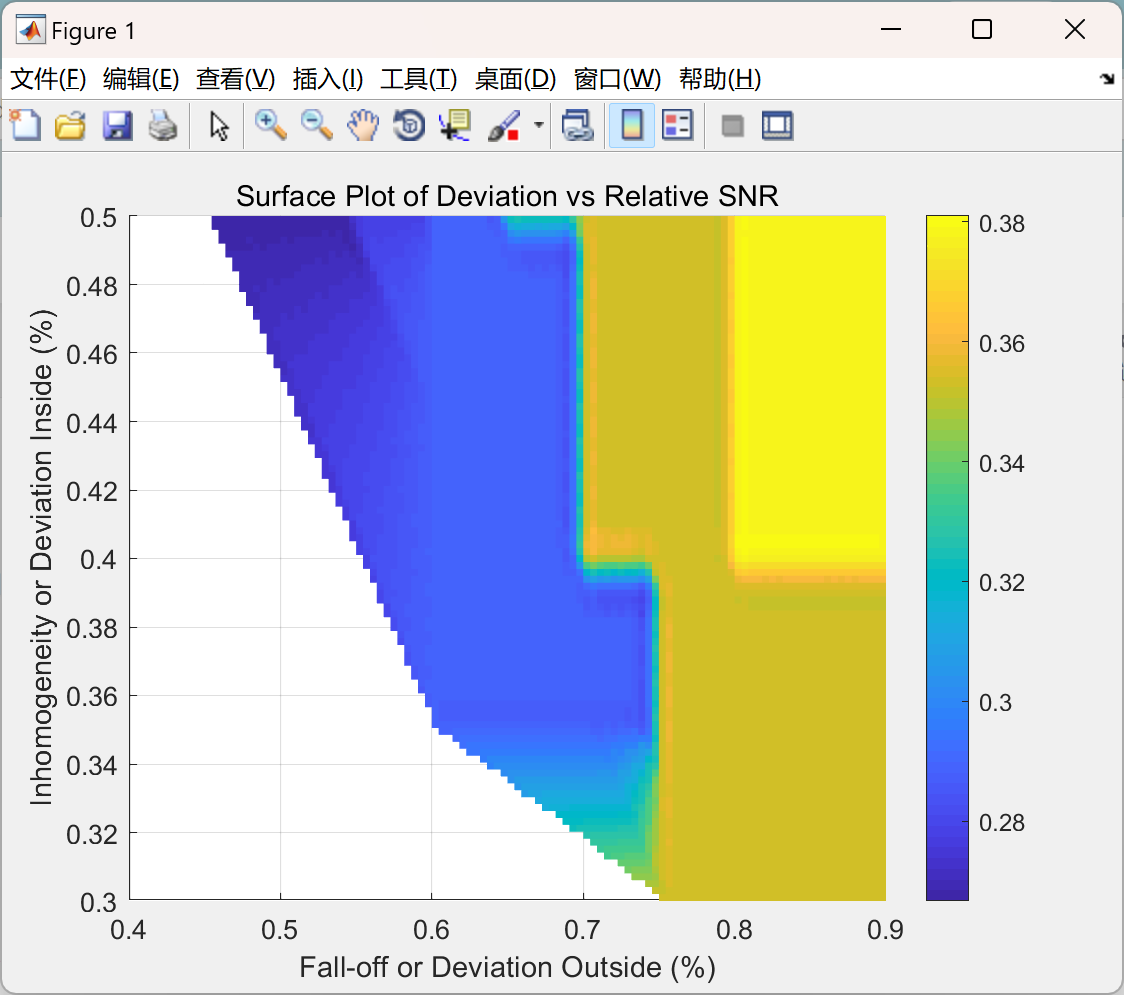
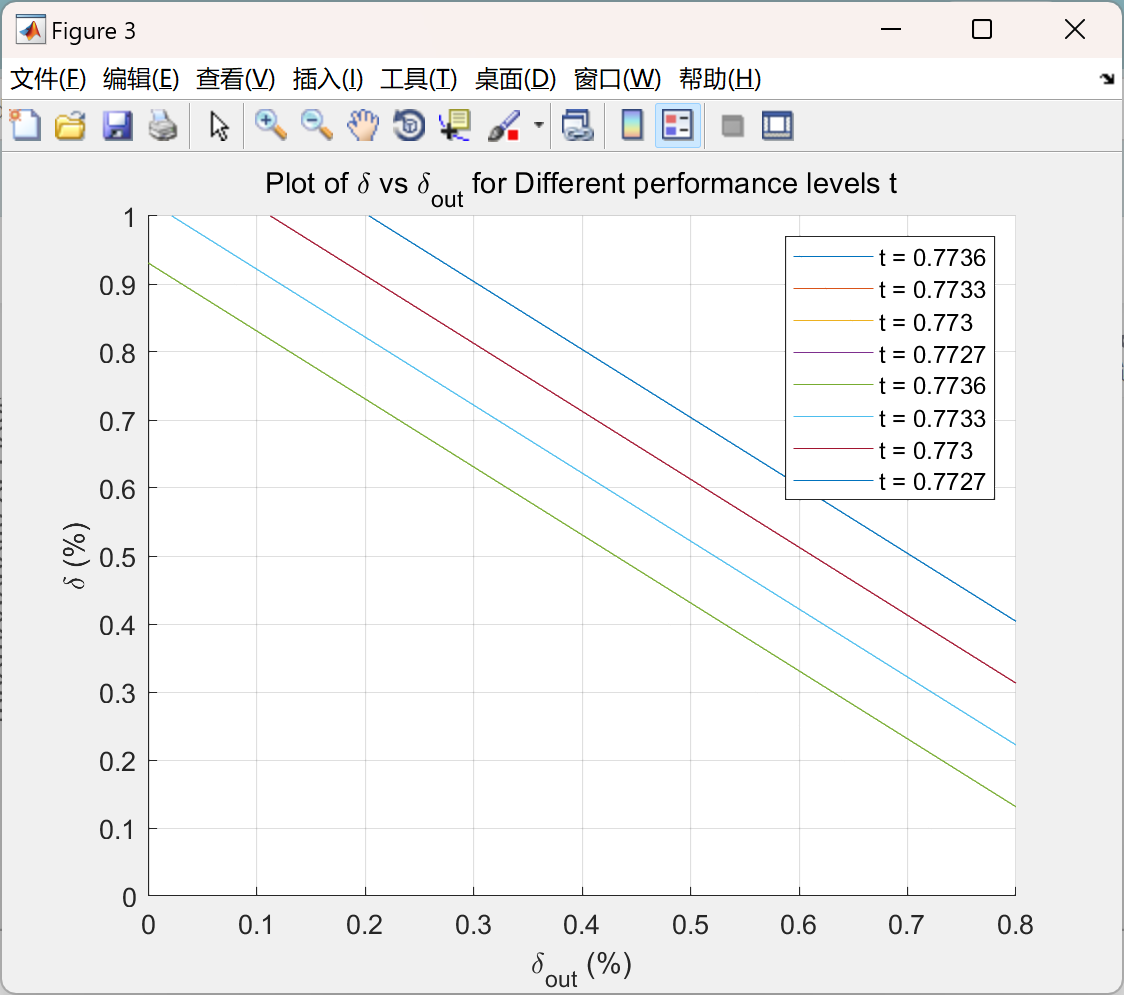
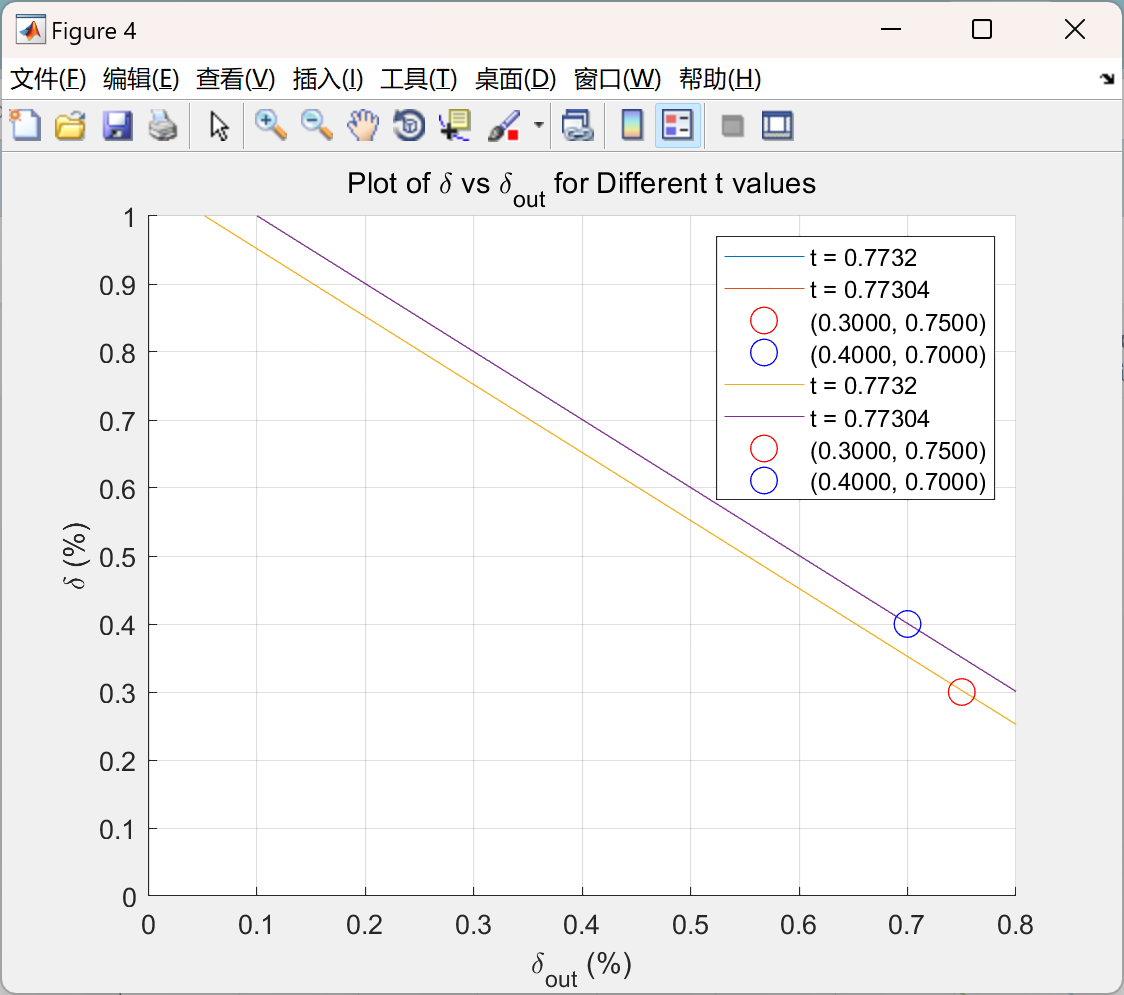
主函数部分代码:
%% Number of grooves and evaluation points
n_grooves = 5; % Number of grooves
n_inside = 10; % Evaluation points inside the coil
n_outside = 5; % Evaluation points outside the coil (chest wall)
%% Desired magnetic field strength and allowed deviations
Bav = 1; % Desired magnetic field strength/estimate can be obtained from uniformly wound coil for instance
delta_inside = 0.3 * Bav; % Maximum allowed deviation inside the coil (30%)
delta_outside = 0.9 * Bav; % Maximum allowed deviation outside the coil (90%)/fall off inside the chest-wall
%% Wire lengths for each groove
groove_lengths = [4, 6, 8, 10, 12]; % for instance from tip to bottom of coil
%% Define A matrix based on values obtained from Maxwell-FEM simulations
% Inside matrix (10 rows, 5 columns)
% Each column represents the produced B-fields of one groove
% Each row represents the produced B-fields at one evaluation point inside
% the coil volume (produced by the different grooves)
A_inside = [
0.8, 0.5, 0.3, 0.2, 0.1;
0.75,0.55,0.45, 0.35, 0.15;
0.7, 0.6, 0.4, 0.3, 0.2;
0.6, 0.6, 0.4, 0.3, 0.2;
0.5, 0.7, 0.5, 0.4, 0.3;
0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.5, 0.3;
0.35, 0.45, 0.55, 0.6, 0.4;
0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.7, 0.5;
0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.6, 0.6;
0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.7;
];
% Outside matrix (5 rows, 5 columns)
% Each column represents the produced B-fields of one groove
% Each row represents the produced B-fields at one evaluation point outside
% the coil volume (produced by all grooves)
A_outside = [
0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.6;
0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.5, 0.5;
0.05, 0.15, 0.25, 0.4, 0.4;
0.05, 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.35;
0.0, 0.05, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25
];
% Ensure that A_inside and A_outside have the correct number of rows
disp(['A_inside size: ', num2str(size(A_inside))]); % Should be [10, 5]
disp(['A_outside size: ', num2str(size(A_outside))]); % Should be [5, 5]
%% Set up the constraints (inside and outside the coil)
rhs_inside_min = (Bav - delta_inside) * ones(n_inside, 1); % Lower bound for inside the coil
rhs_inside_max = (Bav + delta_inside) * ones(n_inside, 1); % Upper bound for inside the coil
rhs_outside_min = (Bav - delta_outside) * ones(n_outside, 1); % Lower bound for outside the coil
rhs_outside_max = (Bav + delta_outside) * ones(n_outside, 1); % Upper bound for outside the coil
%% Combine the constraints (inside and outside)
🎉3 参考文献
文章中一些内容引自网络,会注明出处或引用为参考文献,难免有未尽之处,如有不妥,请随时联系删除。
[1]王兆成,宿博瑜,程雨佳,等.合成孔径激光雷达成像研究进展综述[J].河北工业大学学报,2024,53(05):1-12+86.DOI:10.14081/j.cnki.hgdxb.2024.05.001.
[2]徐锋.激光成像雷达技术下数码印花颜色空间转换方法[J].激光杂志,2024,45(10):209-214.DOI:10.14016/j.cnki.jgzz.2024.10.209.
🌈4 Matlab代码实现





















 2127
2127

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








