
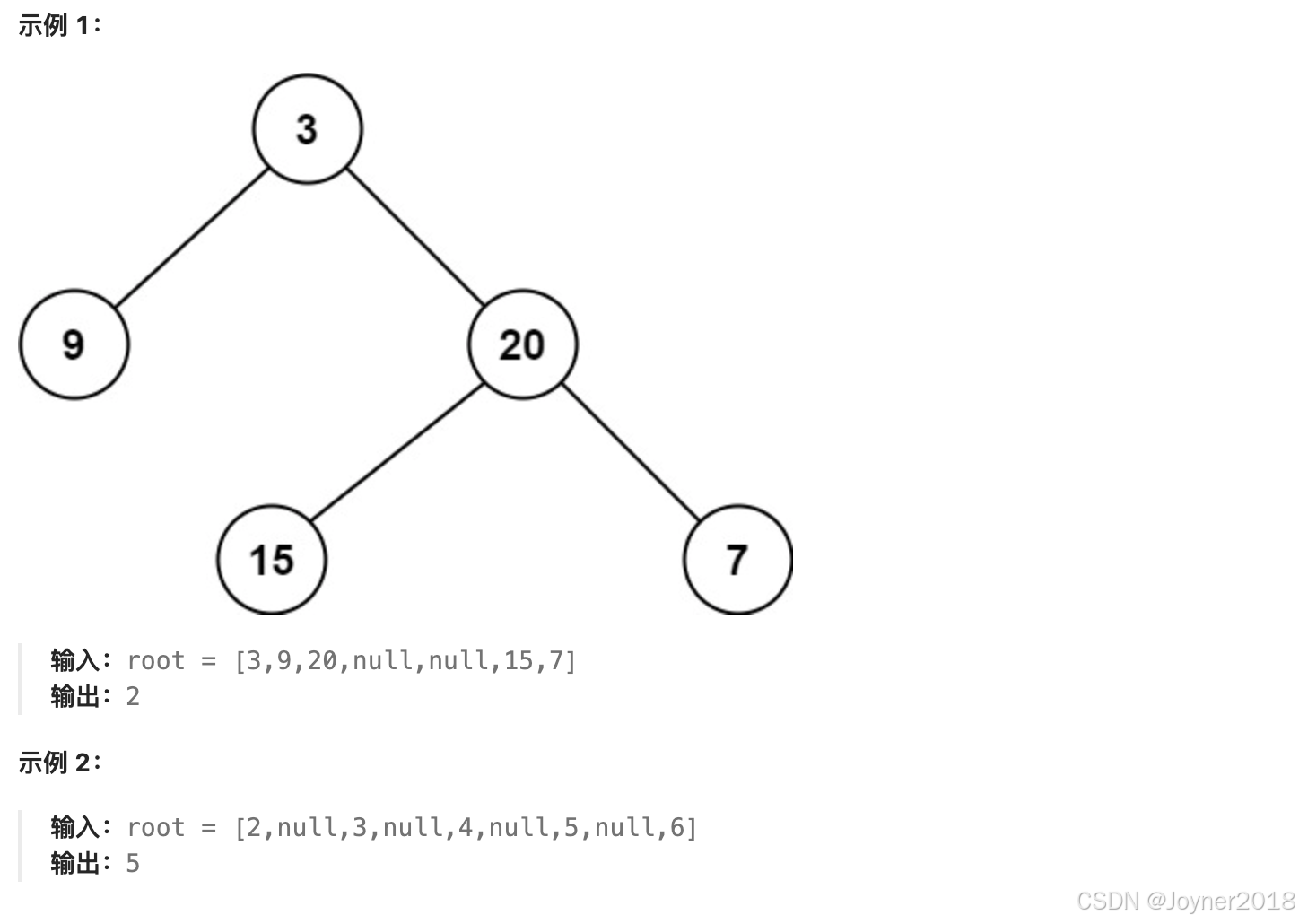

可以使用递归或迭代的方法来求解二叉树的最小深度。以下是递归解法和 BFS(广度优先搜索)解法:
递归解法
如果根节点为空,则最小深度为 0。如果左子树或右子树为空,则返回非空子树的深度,否则返回左右子树深度的较小值加 1。
class TreeNode:
def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
self.val = val
self.left = left
self.right = right
def minDepth(root):
if not root:
return 0
if not root.left:
return minDepth(root.right) + 1
if not root.right:
return minDepth(root.left) + 1
return min(minDepth(root.left), minDepth(root.right)) + 1
BFS 解法(推荐)
使用队列进行层序遍历,遇到第一个叶子节点时返回当前深度。
from collections import deque
def minDepth(root):
if not root:
return 0
queue = deque([(root, 1)]) # (节点, 深度)
while queue:
node, depth = queue.popleft()
if not node.left and not node.right: # 叶子节点
return depth
if node.left:
queue.append((node.left, depth + 1))
if node.right:
queue.append((node.right, depth + 1))
复杂度分析
- 递归解法: 最坏情况下(单链表形式),时间复杂度为 O(N)。
- BFS 解法: 最好情况下(叶子节点靠近根),时间复杂度为 O(logN),最坏情况下 O(N),但在实际应用中更快。
BFS 适用于大规模数据集,因为它在找到第一个叶子节点后立即返回,而 DFS 可能会遍历整个树。





















 1114
1114

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








